Meiosis and Inheritance Flashcards
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Asexual Reproduction
Mitosis
Produces exact copies
Single-celled eukaryotes
Simple multicellular eukaryotes
Sexual Reproduction
Reproduction in complex multicellular organisms
Variation in offspring
Reproductive cells are produced by meiosis
Meiosis
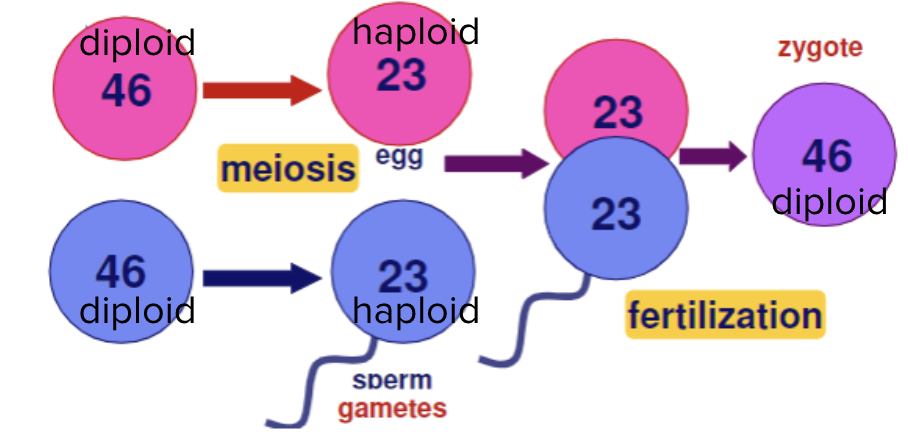
Produces gametes (reproductive cells)
Two cell divisions
Reduces the number of chromosomes by half
Diploid (containing 2 copies of each chromosome) → haploid (containing one copy of each chromosome)
The cells that are produced are different from each other and from the original cell
Interphase
DNA is replicated
The cell prepares for division
Interphase only happens once
Prophase 1
Homologous pairs can exchange segments during crossing over
Metaphase 1
Homologous pairs line up in the middle of the cell
Independent assortment
Independent Assortment
Pairs randomly line up in the middle
during metaphase I of meiosis results in the formation of gametes that are different from each other (223 combinations in gametes
Anaphase 1
Homologous pairs are separated
Telophase 1
Two nuclei form and the cell splits into two (haploid)
Meiosis 2
Sister chromatids are separated
Prophase 2
Crossing over does not occur
Metaphase 2
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase 2
Sister chromatids are separated
Telophase 2
Nuclei form and cells split (haploid)
Crossing Over
Mixes alleles across homologous chromosomes, creating new combinations of traits on each chromosome
Random Fertilization
of an egg cell (any two parents will produce a zygote with 223 x 223 possible diploid combinations)
Autosomes
44 non-sex chromosomes.
Nondisjunction
chromosomes don’t separate properly during meiosis
Results in zygotes with 3 copies of a chromosome (trisomy) or 1 copy (monosomy) instead of 2 copies of each chromosome
Breaking of chromosomes
Deletion
Duplication
Inversion
Translocation
Deletion
A deletion removes a chromosomal segment.
Duplication
A duplication repeats a segment
Inversion
An inversion reverses a segment within a chromosome
Translocation
moves a segment from one chromosome to another, nonhomologous one.
Phenotype
physical appearance of a trait
Genotype
an organism’s genetic makeup
Law of Segregation
During meiosis, alleles segregate (separate)
Homologous chromosomes separate during anaphase I
Each allele for a trait is packaged into a separate gamete
Law of Independent Assortment
Different genes separate into gametes independently
Non-homologous chromosomes align independently during metaphase I
Only true for genes on separate chromosomes or on same chromosome but far apart so that crossing over happens frequently
Incomplete Dominance
Heterozygotes show an intermediate phenotype
red, pink, white
Co-Dominance
2 alleles affect the phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways
Pleiotropy
affect more than one phenotypic character
Epistasis
One gene masks another
Polygenic Inheritance
Some phenotypes are determined by the additive effects of 2 or more genes on a single character
Phenotypic Plasticity
Phenotype is controlled by the environment and genes