NUCLEOTIDES AND NUCLEIC ACIDS
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
FOUNDATIONS IN BIO
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What type of bond is a phosphodiester bond?
A covalent bond
What are some differences between a molecule of DNA and RNA?
The pentose sugar in DNA is deoxyribose and in RNA is ribose. ‘
RNA contains uracil instead of thymine
DNA is double-stranded whereas RNA is single-stranded
DNA has hydrogen bonds between the two complementary strands
What elements do all nucleotides contain?
CHONP
What is the structure of a nucleotide?
Pentose sugar
Phosphate group
Nitrogenous base
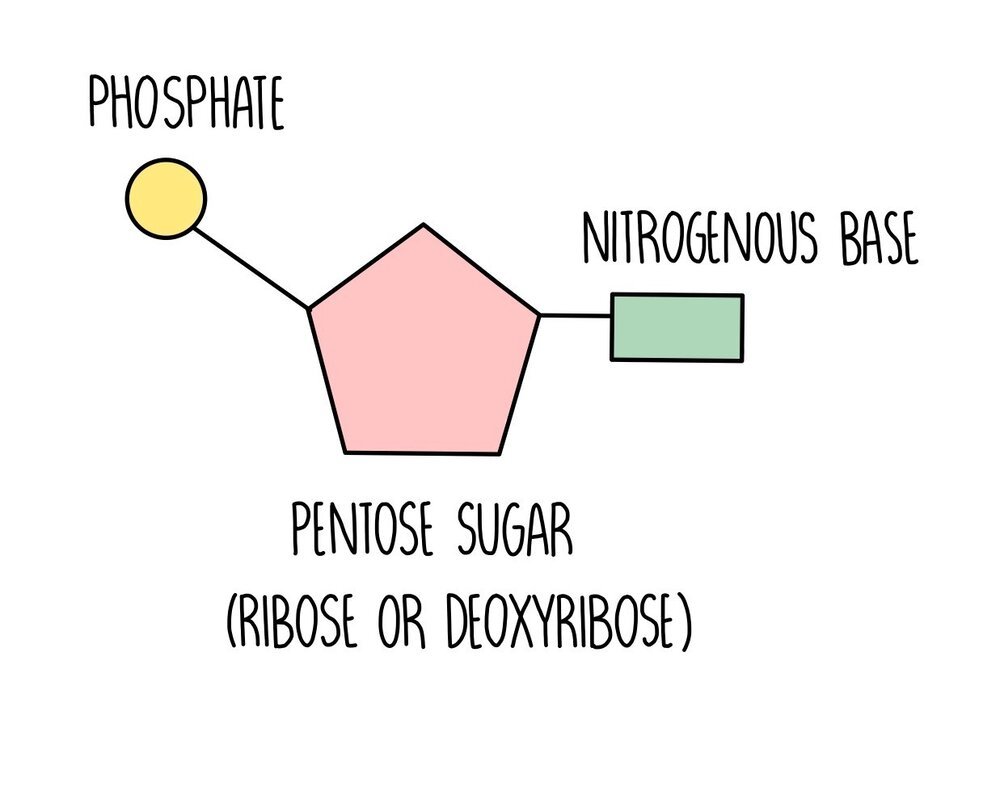
RNA: ribose
Describe how polynucleotide strands are formed and broken down.
Condensation reactions form strong phosphodiester bonds between a sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate group of another (sugar-phosphate backbone).
Hydrolysis reactions use a molecule of water to break these bonds.
Enzymes catalyse these reactions
Describe the structure of DNA.
A double helix of 2 deoxyribose polynucleotide strands (so there are 2 sugar-phosphate backbones).
H-bonds form between complementary base pairs (AT & GC) on the strands
The strands are anti parallel - They have the same sequence running in opposite directions
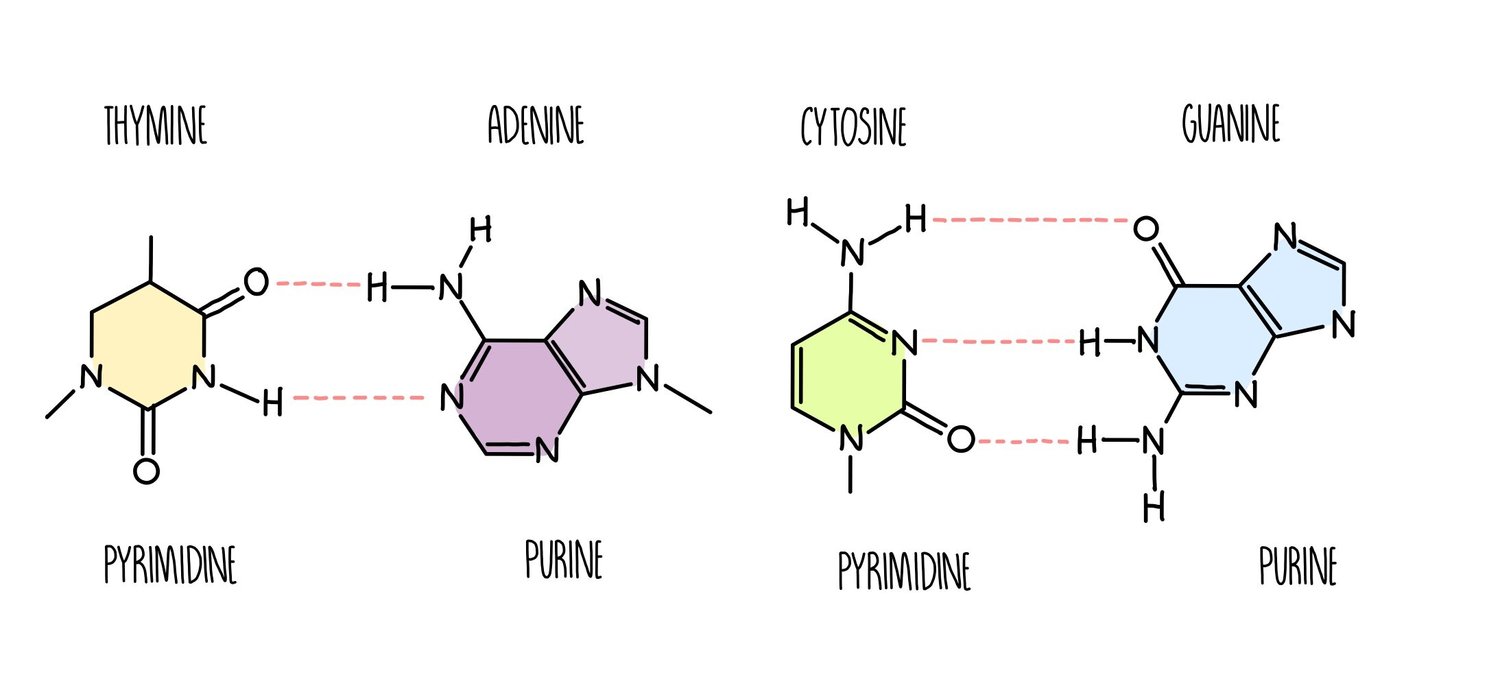
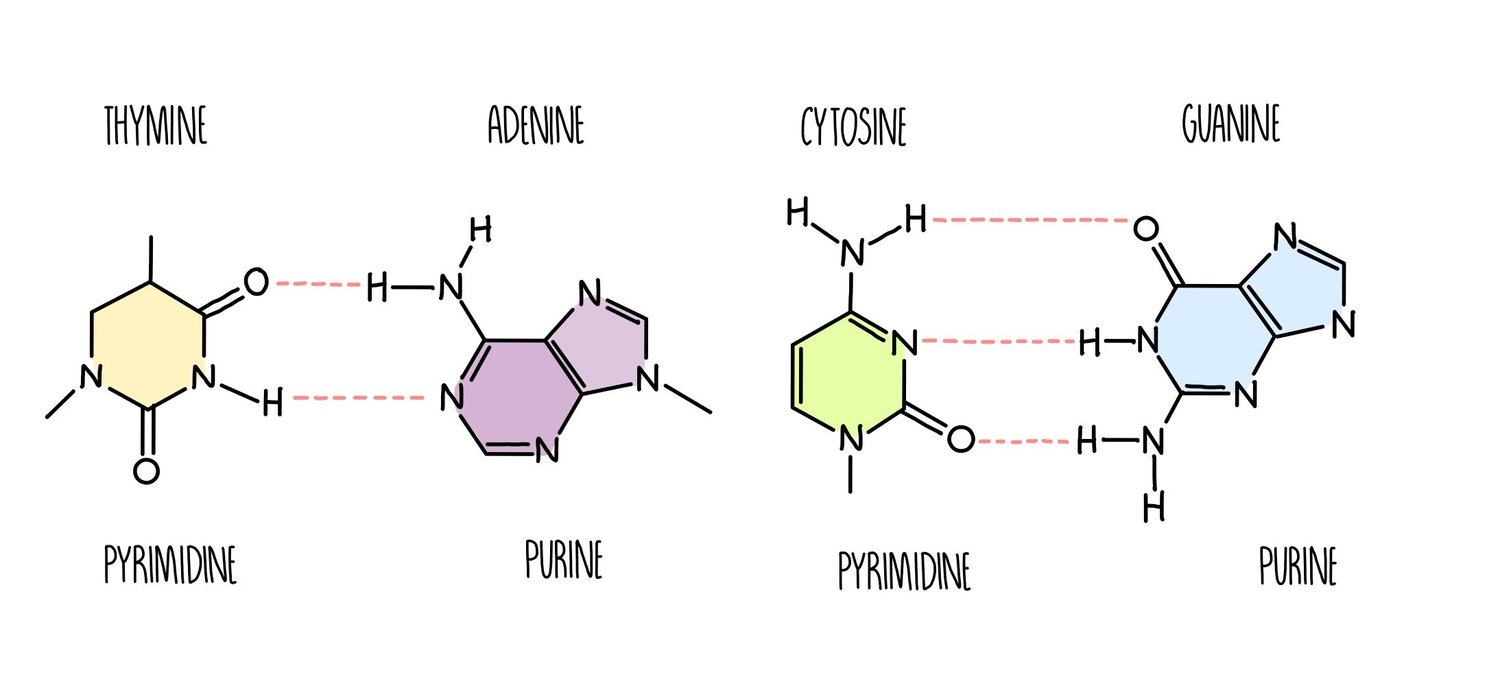
Name the purine bases
Adenine
Guanine
two-ring molecules
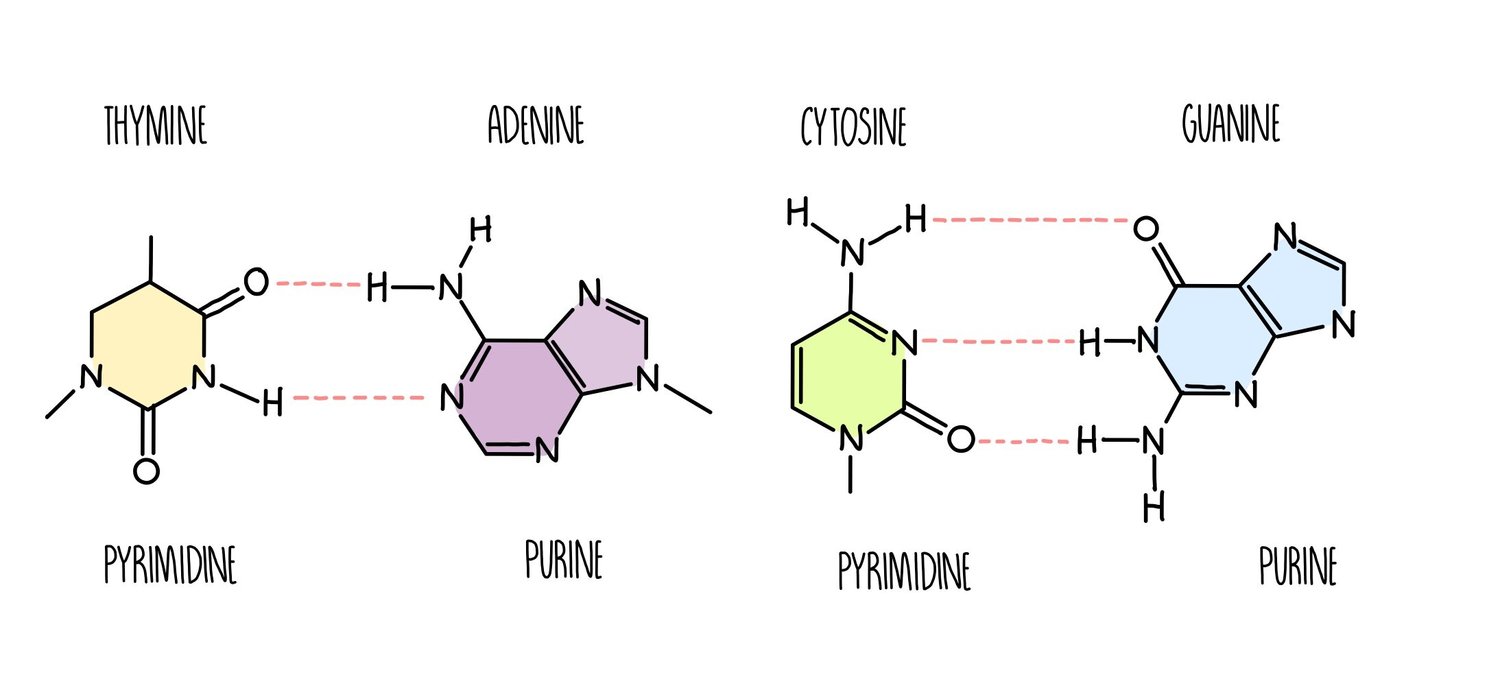
Name the pyrimidine bases
Cytosine
Thymine or Uracil (in RNA)
\
* 3 H-bonds between guanine (G) + cytosine (C)
\
* 3 H-bonds between guanine (G) + cytosine (C)
\
* New DNA molecule contains 1 old strand & 1 new strand
How is a new strand formed during semiconservative replication?
DNA helicase breaks the H bonds between the 2 polynucleotide DNA strands
This causes the helix to unzip and form 2 single strands
Each original strand now acts as a template for a new strand
Free nucleotides attach to exposed bases by complementary base pairing.
DNA polymerase joins adjacent nucleotides on new strand in a 5' → 3' direction via condensation reactions to form phosphodiester bonds.
H-bonds form between the bases on the original and new strand
This causes it to twist into a double helix
\
* Degenerate= more than one triplet codes for the same amino acid (64 possible triplets for 20 amino acids).
\
* Universal= same bases and sequences used by all species.
What does transcription produce and where does it occur?
Produces mRNA
Occurs in nucleus
What happens after a strand of mRNA is transcribed?
RNA polymerase detaches at terminator region.
H-bonds reform & DNA rewinds
Splicing removes introns from pre-mRNA in eukaryotic cells.
mRNA moves out of nucleus via nuclear pore & attaches to ribosome
What does translation produce and where does it occur?
Produces proteins
Occurs in cytoplasm on ribosomes (which are made of protein + rRNA)
Describe the structure of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Has a pentose sugar Ribose
Has a nitrogenous base Adenine
Has 3 inorganic phosphate groups
\
\- has a pentose sugar (Ribose)
\- has a nitrogenous base ( adenine)
\- has 2 inorganic phosphate groups
\
* Mutations often arise spontaneously during DNA replication
What bond is formed between nucleotides?
Phosphodiester bond
What is mRNA?
Messenger RNA
Produced during transcription – RNA polymerase uses DNA as a template to provide mRNA strand
It carries the genetic code from the nucleus to the cytoplasm – provides the instructions for making a protein on the ribosome in translation
What is tRNA?
Transfer RNA
Its found in the cytoplasm
It has an amino acid binding site at one end and an anticodon at the other
It carries amino acids to ribosomes
What is rRNA?
ribosomal RNA
Its found in the ribosome
It helps catalyse the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids during translation
What is RNA?
A single-stranded nucleic acid that passes along genetic messages.
What are Purines?
Nitrogenous bases that have a double ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms
- adenine and guanine.
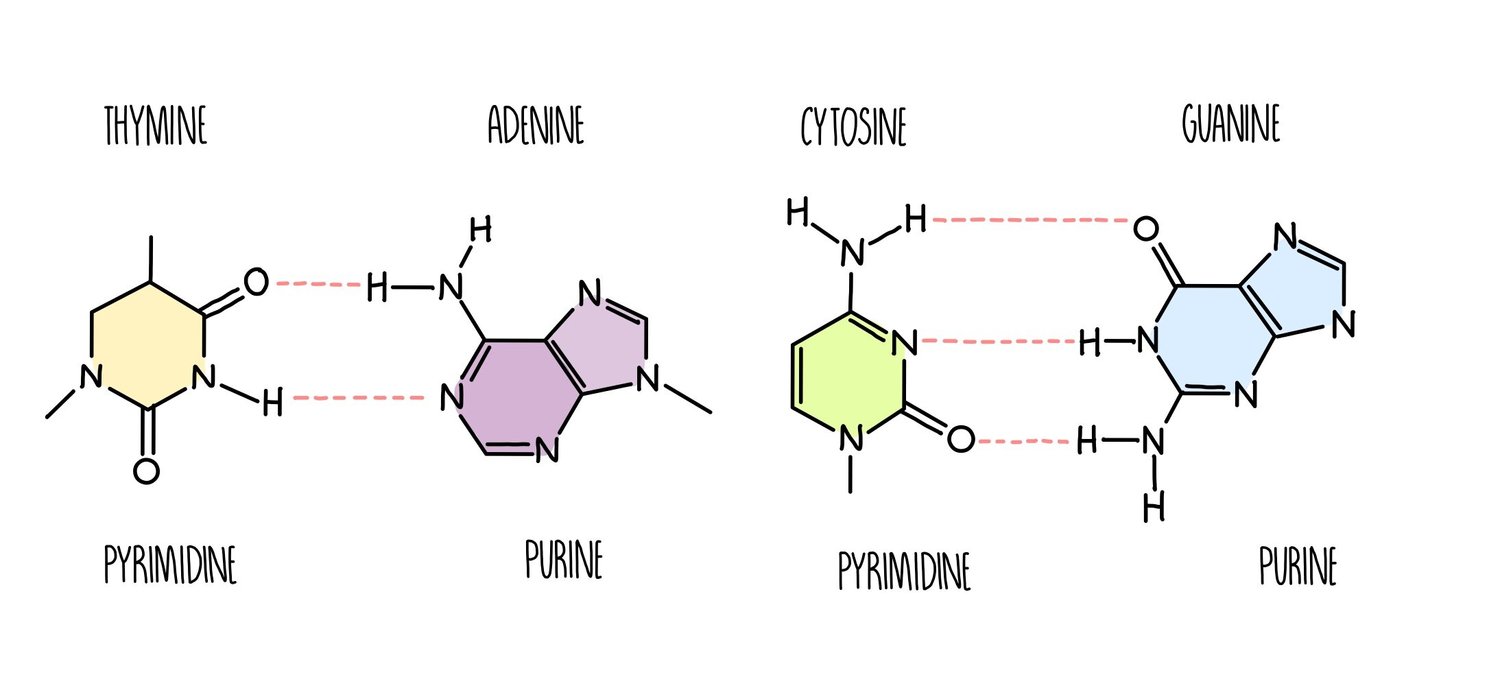
Pyrimidines
Nitrogenous bases that have a single ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms
- cytosine and thymine (Uracil)
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
Provides energy for chemical reactions in the cell
What is a Polynucleotide?
A polymer consisting of many nucleotide monomers in a chain; nucleotides can be those of DNA or RNA.
What is a Phosphodiester bond?
The type of bond that links the nucleotides in DNA or RNA.
It joins the phosphate group of one nucleotide to the hydroxyl group on the sugar of another nucleotide
\
\- Unzips the double helix to form 2 single strands during DNA replication
Gene
A sequence of DNA nucleotides that codes for a polypeptide
What is a Codon?
A specific sequence of three adjacent bases on a strand of DNA or RNA that provides genetic code information for a particular amino acid
What is an anticodon?
A group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
What is DNA polymerase?
An enzyme that catalyses the formation of phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides during the synthesis of a new DNA strand.
What is RNA polymerase?
An enzyme that catalyses the formation of phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides during the synthesis of a new RNA strand.
DNA helicase
DNA primase
DNA polymerase
DNA ligase
What enzymes are needed for transcription?
Helicase
RNA polymerase