Market Equilibrium
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Market
A market is where goods and services as well as factors of production are exchanged between two parties; buyers and sellers
There are two types of markets
Goods and services market: the market that exchanges goods and services
Factor market: the market that exchanges factors of production such as land, Labour, and capital
Functions of a market
In a market, goods and services are demanded by consumers and supplied by producers
Households demand goods & services while firms demand factors of production. On the other hand, firms supply goods and services for consumption, while households supply factors of production.
Demand for factors of production exists due to the demand for goods and services.Therefore, goods and services have a direct demand while production factors have an indirect demand/derived demand.
Demand for goods and services for consumption depends on their marginal utility while the demand for factors of production depends on their marginal productivity.
Goods and services market and factor services market
Goods and services market | Factor services market |
Exchange of consumer goods and services | Firms demand factors of production |
Firms supply goods and services | Households supply factors or production |
Goods and services have a direct demand | Factor services have an indirect demand |
Market equilibrium
Market equilibrium is the situation where the expectations of purchasers and suppliers at a competitive market equal each other
At that situation, there’s no excess demand or excess supply as quantity demanded equals to quantity supplied,
there’s no excess demand price or excess supply price as purchasers expected price equals to suppliers expected price
Conditions of market equilibrium
Expected demand price should be equal to expected supply price
Expected quantity demanded should be equal to expected quantity supplied
Excess demand and excess supply must be zero
Expected demand price and expected supply price should be zero
Consumer expenditure and producer revenue should be equal to each other
Two outcomes or the product market equilibrium
The equilibrium price (Pd= Ps)
This is called the equilibrium price because the demand price of the product is equal to the supply price of the product.
Demand Price = Supply price
Pd = P
The equilibrium quantity
This is called the equilibrium guantity because the quantity demanded of the product is equal to the quantity supplied.
Quantity demanded = Quantity supplied
Qd = Qs
Excess demand
The amount of quantity demanded which exceeds the amount of quantity supplied at a certain price is called as excess demand
Excess demand = (Quantity demanded-quantity supplied)
ED= Qd-Qs
Excess supply
The amount of quantity supplied which exceeds the amount of quantity demanded at a certain price is called as excess supply
Excess supply= ( Quantity supplied- Quantity demanded)
ES= Qs-Qd
Excess demand price
Excess demand is the amount by which the demand price exceeds supply price at a certain quantity
Excess demand price = demand price- supply price
EDP = Pd-Ps
Excess supply price
Excess supply price is the amount by which supply price exceeds demand price at a certain quantity
Excess supply price= supply price- demand price
ESP= Ps-Pd
consumer surplus
The difference between the price that the consumer is willing to pay and the price that the consumer actually pays for the quantity of the goods exchanged at the market
Market equilibrium price is the price which consumer pays for goods and not the price consumer is willing to pay. The price that the consumer is wiling to pay may be higher than that price.
When consumers expect to pay a higher price, the demand and supply determines a suitable price which remains as an equilibrium price. This creates a beneficial situation for consumers as Consumers get a surplus for what they don’t actually pay
Consumer surplus
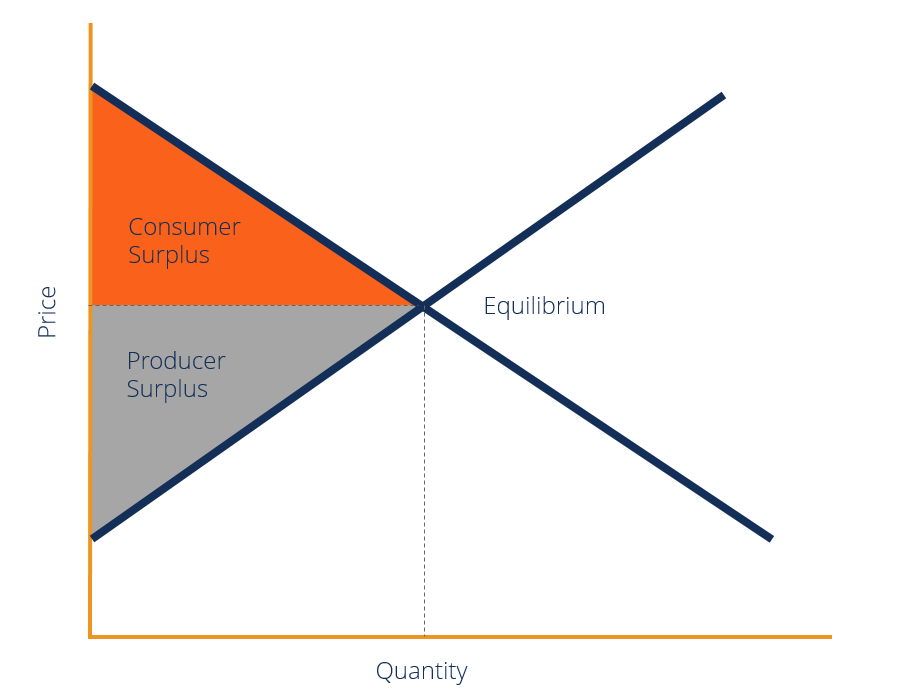
Consumer surplus equilibrium
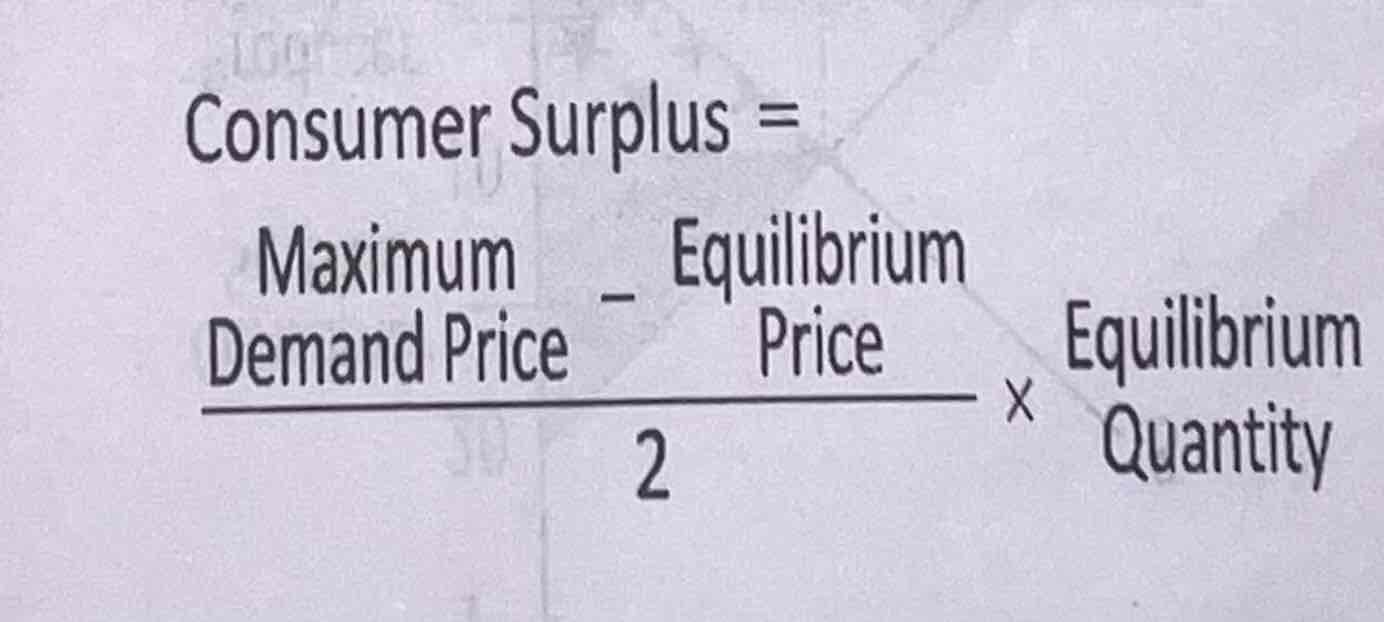
Producer surplus
The difference between minimum price that the suppliers are willing to receive and the price they actually receive
The balance obtained by reducing total variable cost from total revenue is the producer surplus
Producer surplus calculation
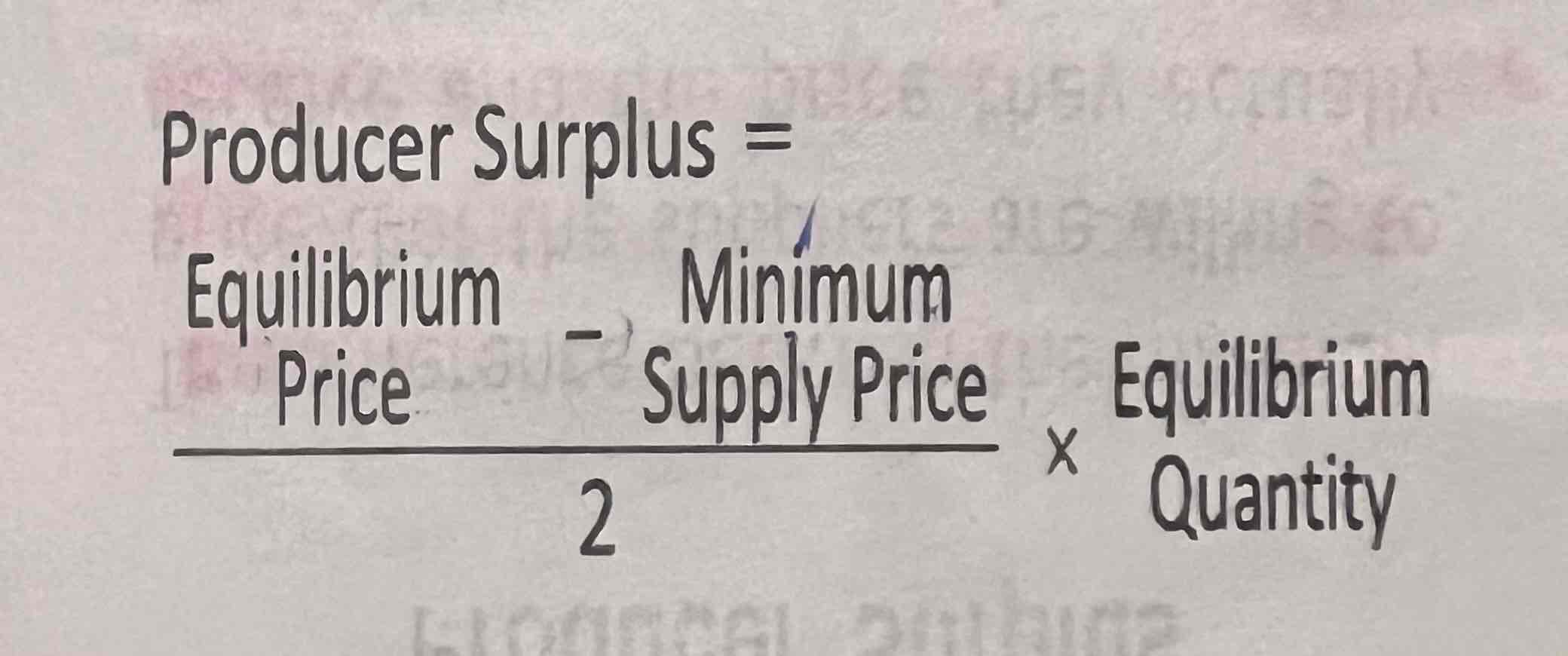
Economic surplus
Buyers and sellers gain profits through the equilibrium exchange, the gain achieved by both parties is called economic surplus.
Economic surplus = consumer surplus + producer surplus
Increase in demand and increase in supply
The impact on equilibrium price is uncertain
The equilibrium quantity definitely increases
Increase in demand and decrease in supply
The equilibrium price increases
Equilibrium quantity is uncertain
Decrease in demand increase in supply
The equilibrium price falls
Equilibrium quantity is uncertain