MCBL Lab Lecture 5
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What can UV light do?
260-265nm can be lethal since it’s the maximal absorption for DNA.
UV causes the formation of pyrimidine (C or T) dimers, leading to DNA replication errors. (Overexposure to sun)
What does Heat do?
Heat & water disrupts hydrogen bonds, denaturing macromolecules such as DNA & proteins.
Strategies to reduce heat damage
Heat shock esponse
Heat stability can be conferred by structural changes in macromolecules
Specific compounds can stabilize proteins.
What is Disc Diffusion Test (Antibiotic Efficacy)
Disks with specific drugs/antibiotics are placed on agar plates inoculated w/test microbes.
Traditional methods of identification.
Gram status, morphology, and physiological properties.
Bacterial Growth Curve
Four Phases
Lag Phase
Exponential Phase
Stationary Phase
Death Phase
Lag Phase
Period after inoculation & before exponential growth where cells do not immediately divide
Factors affecting Lag phase
Age of Culture
Growth Substrates
Environmental Changes
Log/exponential phase
Period characterizied by cell doubling across the cell population.
Equation for Log phase
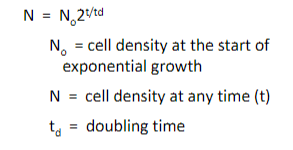
Stationary Phase
Cells are live but death rate > production rate
Many cells stop growing
Subsrate limitation & waste accumulation
Cells are smaller
Death Phase
Loss of viable cells due to accumulation of toxins & byproducts of metabolism & absence of new nutrients.
Decline in cell #s highly variable & not predictable by any relationships
Accompanied by cell lysis.