DENT Fun. I - Tolerance & Autoimmunity
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Immune Tolerance
Unresponsiveness to antigen, particularly self-antigen
What happens when Tolerance breaks down?
Autoimmune Disease
What are the 2 types of Tolerance?
- Central
- Peripheral
Central Tolerance
Cells that bind to "self" antigen are eliminated in Primary Lymphoid Tissue during development
Peripheral Tolerance
Suppression/Deletion of self-reactive cells in tissues outside of the Primary Lymphoid Tissues
How are TCRs regulated by Central Tolerance?
Negative Selection during the Single Positive Phase
What enzyme is used during Negative Selection of TCRs?
AIRE
How are BCRs regulated by Central Tolerance?
BCRs that react to self-antigen undergo apoptosis
BCRs can be altered once they leave the Bone Marrow (T/F)
True; They can undergo Somatic Hypermutation, Affinity Maturation, and Isotype Switching in Germinal Centers
What are 4 methods of Peripheral Tolerance?
- Trafficking of Naive Cells
- Lack of Costimulation (Anergy)
- Downregulation (AICD)
- Suppression via Treg-Cells
Naive T-Cells can only travel to ____.
Secondary Lymphoid Tissue
What molecules regulate Lymphocyte Trafficking?
- Adhesion Molecules
- Chemokine Receptors
A lack of Costimulation will cause ____.
Anergy
What Costimulatory Molecule can suppress T-Cell activity?
CTLA-4
Activation-Induced Cell Death (AICD)
Induced apoptosis of B/T-Cells via...
- Death Receptors (Fas/FasL)
- Loss of survival signals at the end of infection
Treg-Cells
Regulatory T-Cells
- CD4+/CD25+/FoxP3+
What are the 4 functions of Treg-Cells?
- Cytokine Deprivation
- Release of Inhibitory Cytokines
- Inhibit APCs
- Cytotoxicity
What 2 Factors can lead to the breakdown of Tolerance?
- Environmental Factors
- Genetic Factors
Environmental Factors
Infection can lead to activation of B/T-Cells that might cross-react with Host Epitopes
- Molecular Mimicry/Antibody Cross-Reactivity
- Epitope Spreading
Molecular Mimicry
- Close resemblance between foreign and self-antigen that can lead to the Immune System attacking self-antigen
- Can lead to Antibody Cross-Reactivity
Epitope Spreading
Progression of the Immune Response to target more epitopes of an Antigen; Can lead to the Immune Response mistaking a self-antigen for foreign
Cryptic Antigens
- Exposure of antigens that were previously "hidden"
- These antigens were never tested for self-reactivity, therefore, they are recognized as foreign
Acute Rheumatic Fever
Systemic illness of streptococci generates antibodies that cross-react with myocardial proteins, causing autoimmune disease
Genetic Factors
Expression of genes that influence Immune Function (MHC Expression)
Immune Responsiveness depends on ____.
strength of interaction between an MHC allele and the peptide
Expression of certain MHC alleles can cause stronger immune responses that can lead to Autoimmunity
Where do Peptides bind the MHC?
The MHC Binding Groove
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Systemic Inflammatory Arthritis that causes enthesis and the vertebrae to fuse
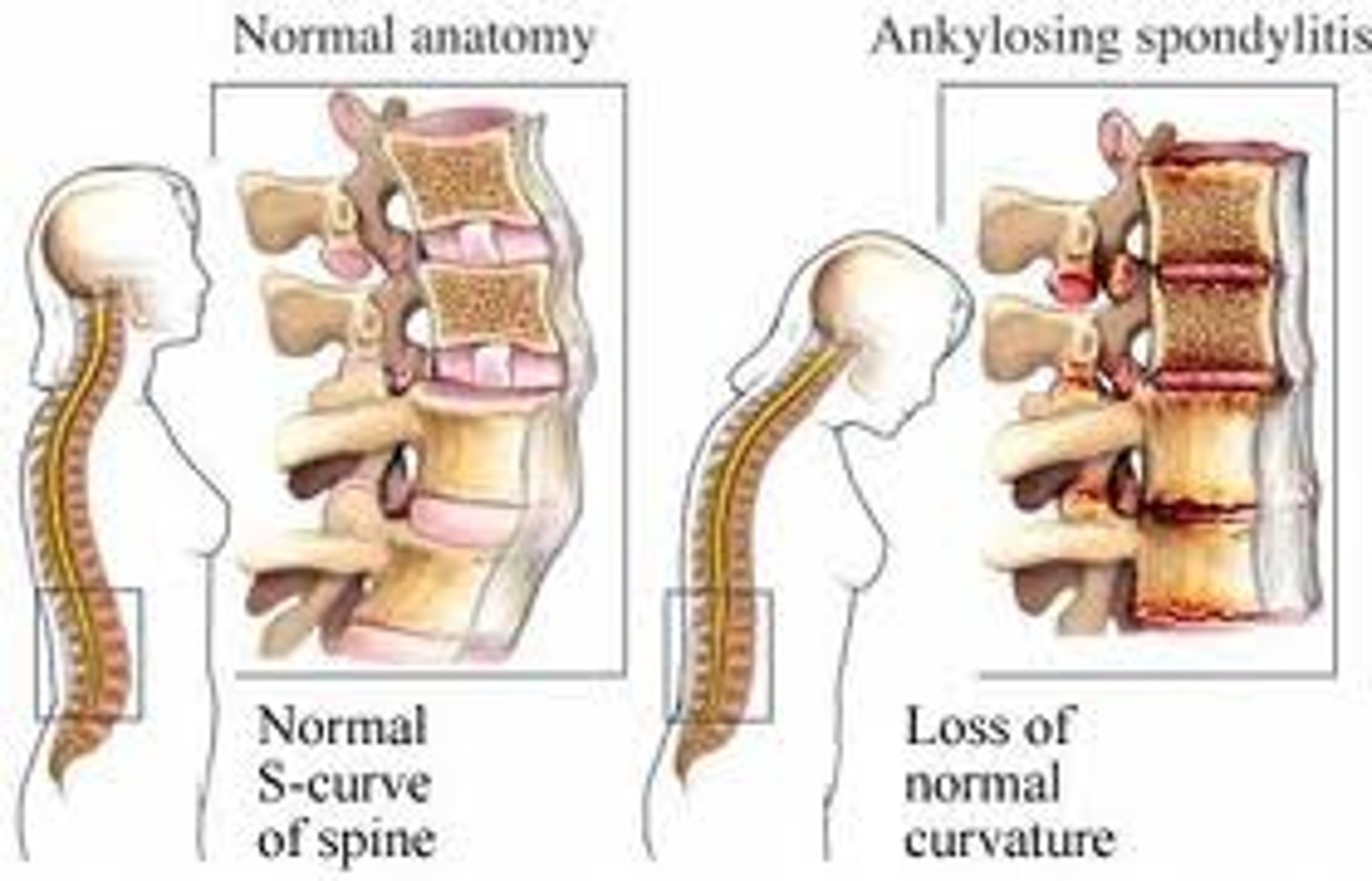
What proteins are most likely presented to T-Cells in cases of Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Proteins of the Entheseal Fibrocartillage
Enthesis
Sites where ligaments, tendons, and the joint capsule are inserted into bone
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- Chronic joint inflammation
- Autoantibodies (RF) that react with altered self-protein are deposited into joints
____ of Peptides causes them to be more readily presented on MHC Molecules.
Citrullination
Citrullination
- Conversion of Arginine to Citrulline via Peptidyl Arginine Deiminases (PADs)
- Normal process during cell death that would cause increased immune response
Citrullination of several molecules within RA Joints have been found (T/F)
True
Immune Privileged Sites
Areas that do not elicit an inflammatory immune response upon antigen presentation because these areas cannot tolerate swelling
- Brain
- Eyes
- Testes
- Uterus
Immune Privilege is a suppression of Immune Responses (T/F)
False; It is more so a selective downregulation of certain responses that would cause harmful effects
What are the 3 Characteristics of Immune Privileged Sites?
- Surrounded by a barrier that excludes Naive Lymphocytes
- High level of Immunosuppressive Cytokines (TGFβ)
- High expression of Fas/FasL
Fas/FasL causes apoptosis of ____.
T-Cells