BIO98 LECTURE 12
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Regulation of Glucose Metabolism + Polysaccharides as Storage Molecules
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Understand the difference between feed-forward and feed-back regulation
-Feedback inhibition: “We have enough products, let’s stop”
ex. hexokinase regulation
-Feed-forward activation: “We have enough substrates, let’s go”
ex. Fructose-2,6-bisphophate, Pyruvate Kinase (PK) Regulation
Regulation of Glycolysis
-involve irreversible steps
-Feedback inhibition & feed-forward activation
STEP1 Hexokinase regulation: hexokinase is inhibited by its product, which is?
classic feedback inhibition
STEP1 Hexokinase regulation: What does hexokinase do?
2-Deoxyglucose (2-DG) can be phosphorylated by hexokinase to make 2-DG-phosphate (2-DGp)
-Glucose turns into Glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) bc of hexokinase
STEP 2 Hexokinase regulation: What happens with 2-DGp?
-2-DGp CANNOT be CONVERTED by PHOSPHOGLUCOSE ISOMERASE (competitive inhibitor)
-Excess 2-DG blocks more glucose from being phosphorylated, starving cells
STEP 2 Hexokinase regulation: What happens to G6P?
-G6P turns into F6P (Fructose-6-phosphate) bc of phosphoglucose isomerase
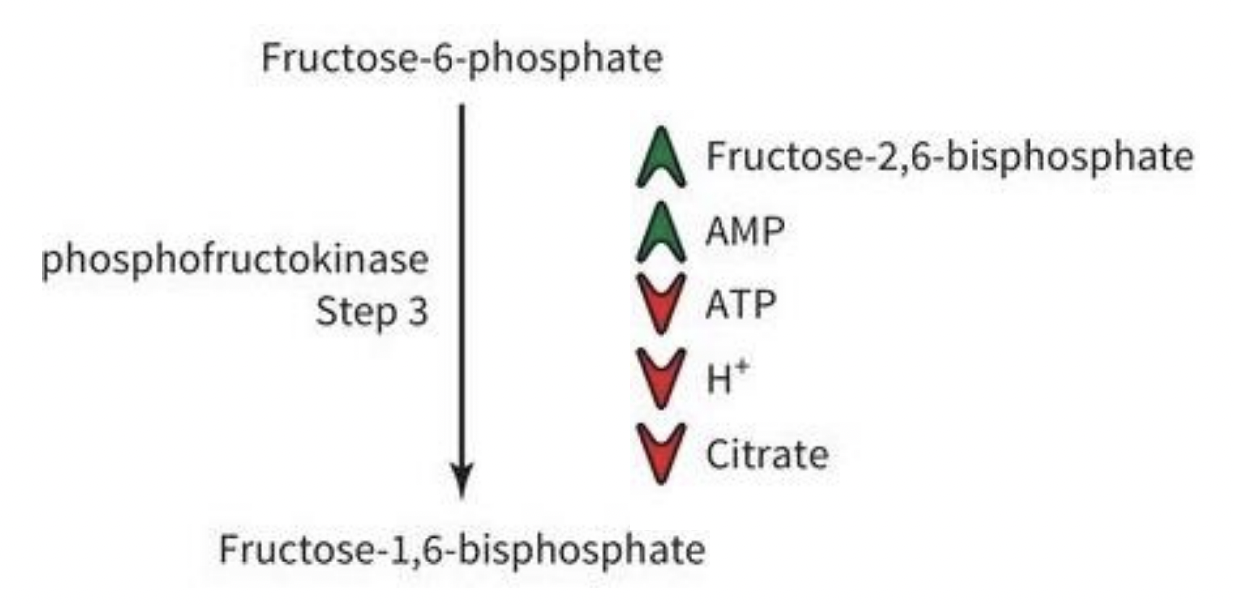
Mechanisms of PFK Regulation
-AMP= adenosine monophosphate
cells are low on ATP, need more energy, so do more glycolysis!
-Super high levels of ATP
don’t need more energy - block glycolysis
-H+ build up = too much lactate
build up of product - shut down
-Citrate: part of aerobic metabolism, also a product, same idea
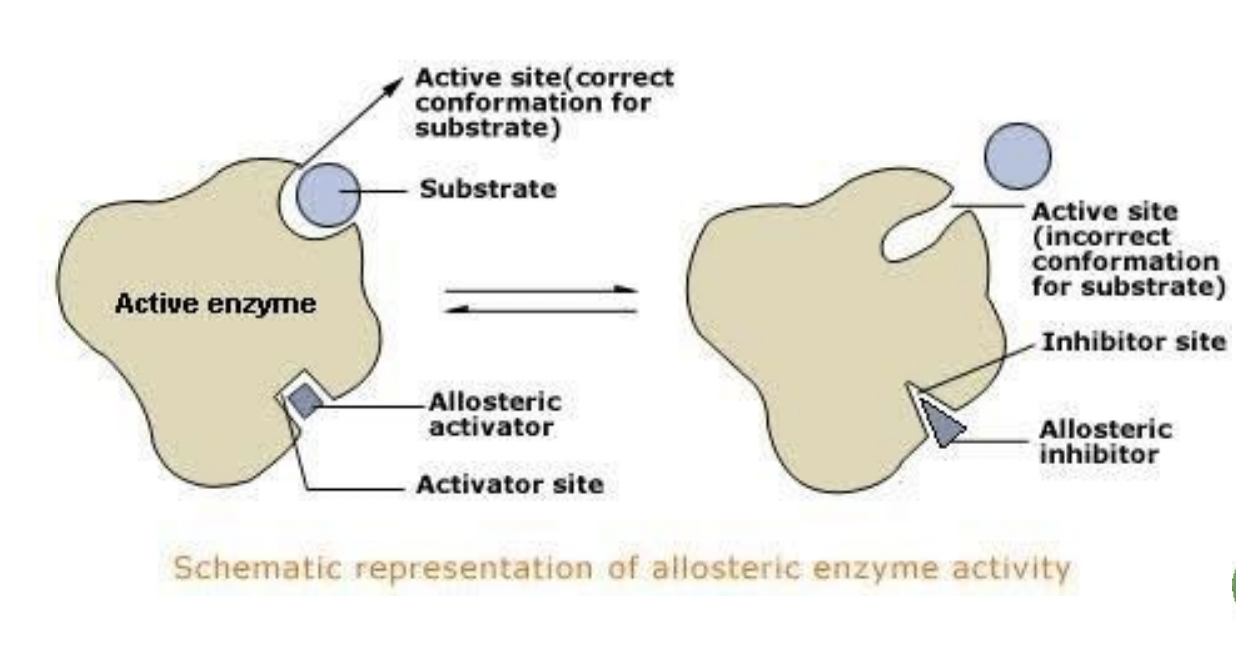
Most PFK regulators work __
allosterically
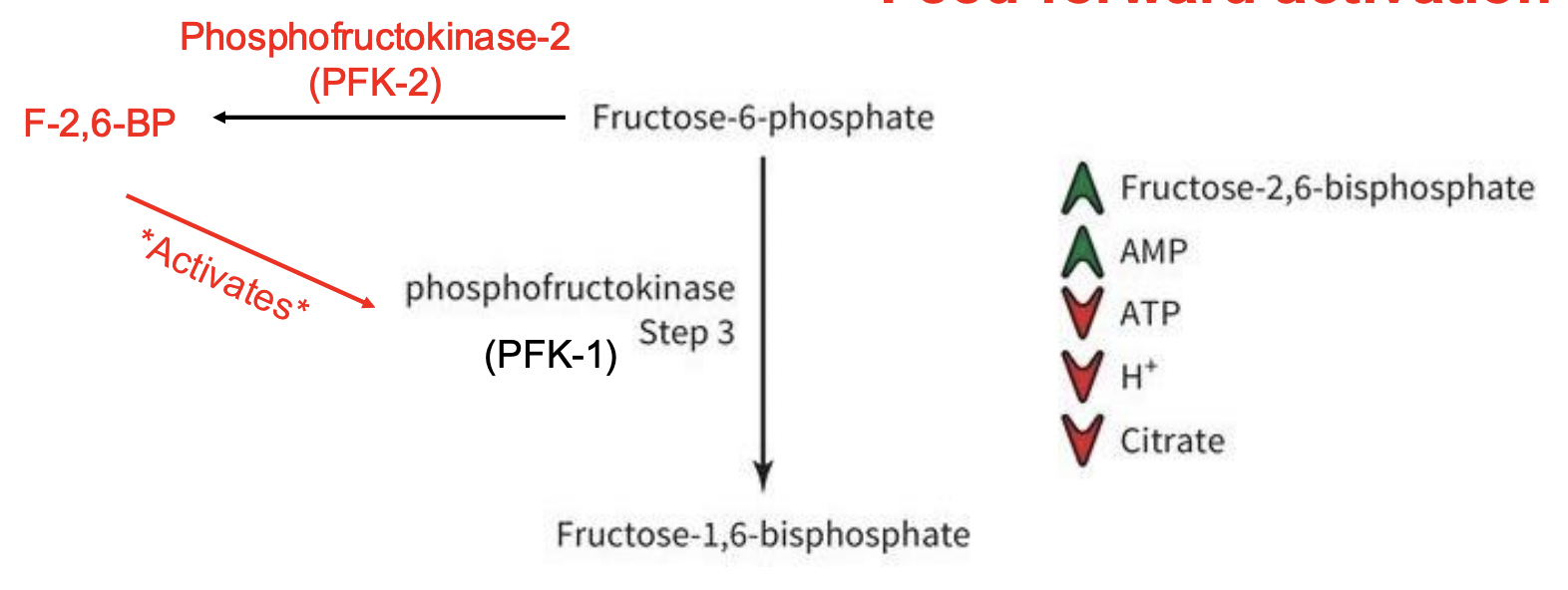
• F-2,6-P • What is it and where does it come from?
Fructose-2,6-bisphophate = F-2,6-bisphosphate
Strong PFK allosteric activator
Produced by another isoform of PFK called PFK-2 (Phosphofructokinase-2)
lots of F-6-P leads to production of F-2,6-BP = activates PFK to increase rate
Feed-forward activation
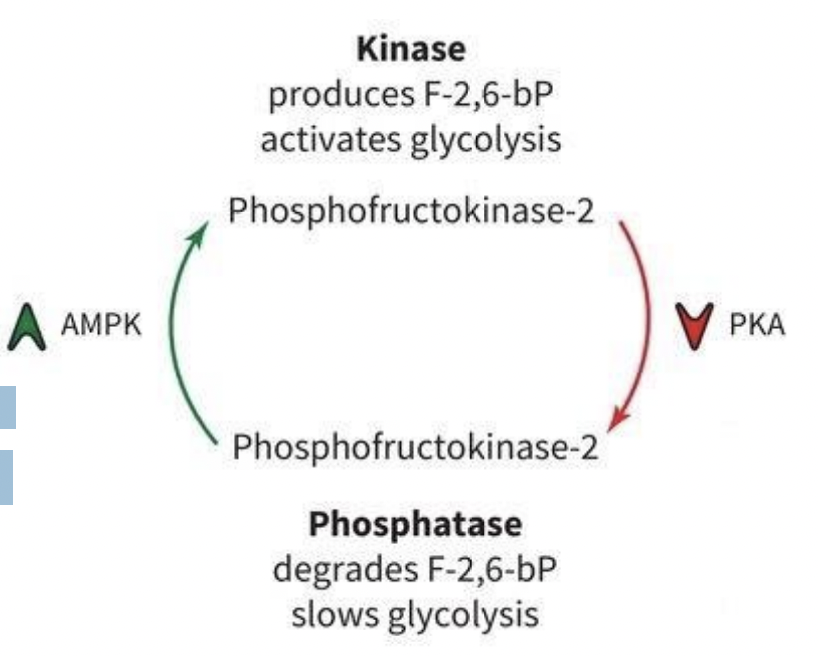
PFK-2 Regulation
• AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) senses high levels of AMP, turns on the kinase activity of PFK-2
• PFK-2 then makes F-2,6-BP from F-6-P
• Ramps up glycolysis!
• Protein kinase A (PKA) inactivates PFK-2 kinase and activates PFK-2 phosphatase function • F-2,6-BP -> F-1,6-bP
• Loss of F-2,6-BP slows glycolysis
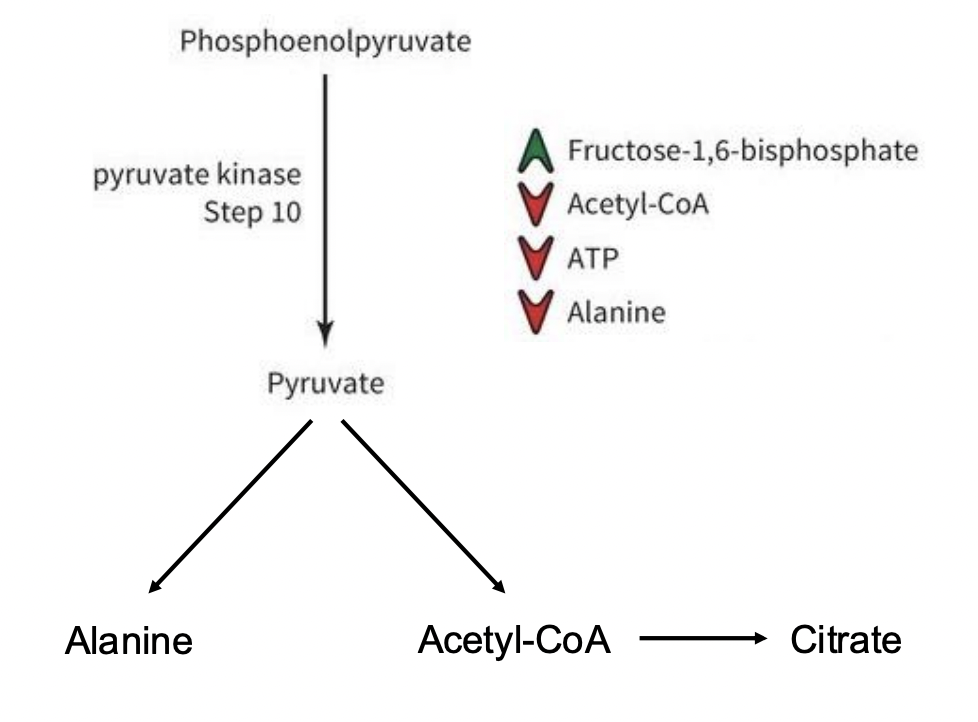
Pyruvate Kinase (PK) Regulation
• F-1,6-BP ; There are more reagents ready to go, Feed forward!
• ATP = high energy state
• We don’t need to keep going- shut down energy production!
• Acetyl-CoA and alanine are downstream products, if they are building up we don’t want to make more
Why regulate multiple enzymes?
-Glucose is primary point of entry for carbon at most cells
-this carbon is used in almost everything!
-glycolysis is common to practically all life on earth (evolving early on), lots of chances to build in regulatory elements
Glucose Storage
-Glucose: simple sugar that’s easily broken down
-Plants & animals store glucose in more stable polymers
-Glycose & other sugars on their own = monosaccharides
-Sugars are stored as polysaccharides
• Know the different types of glucose-derived polysaccharides
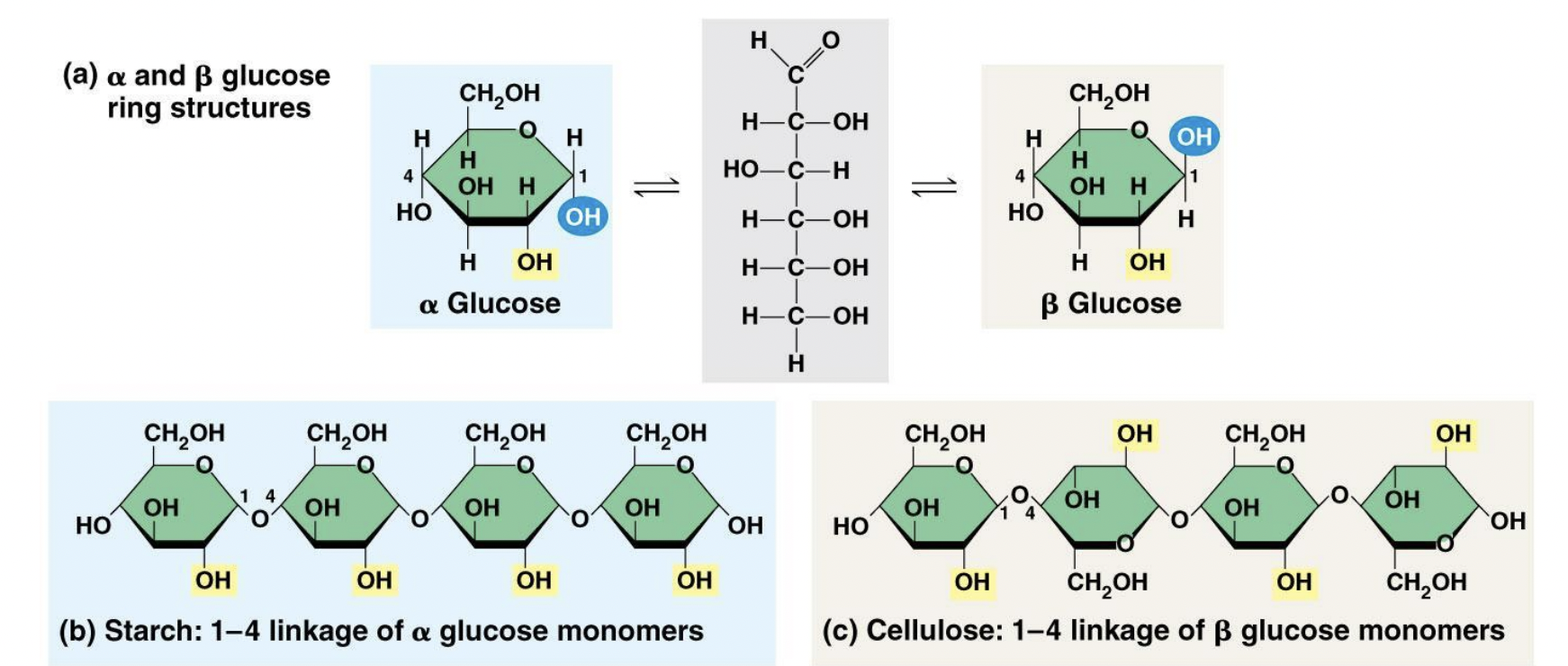
1) Plants: make starch and cellulose
2) Animals: glycogen
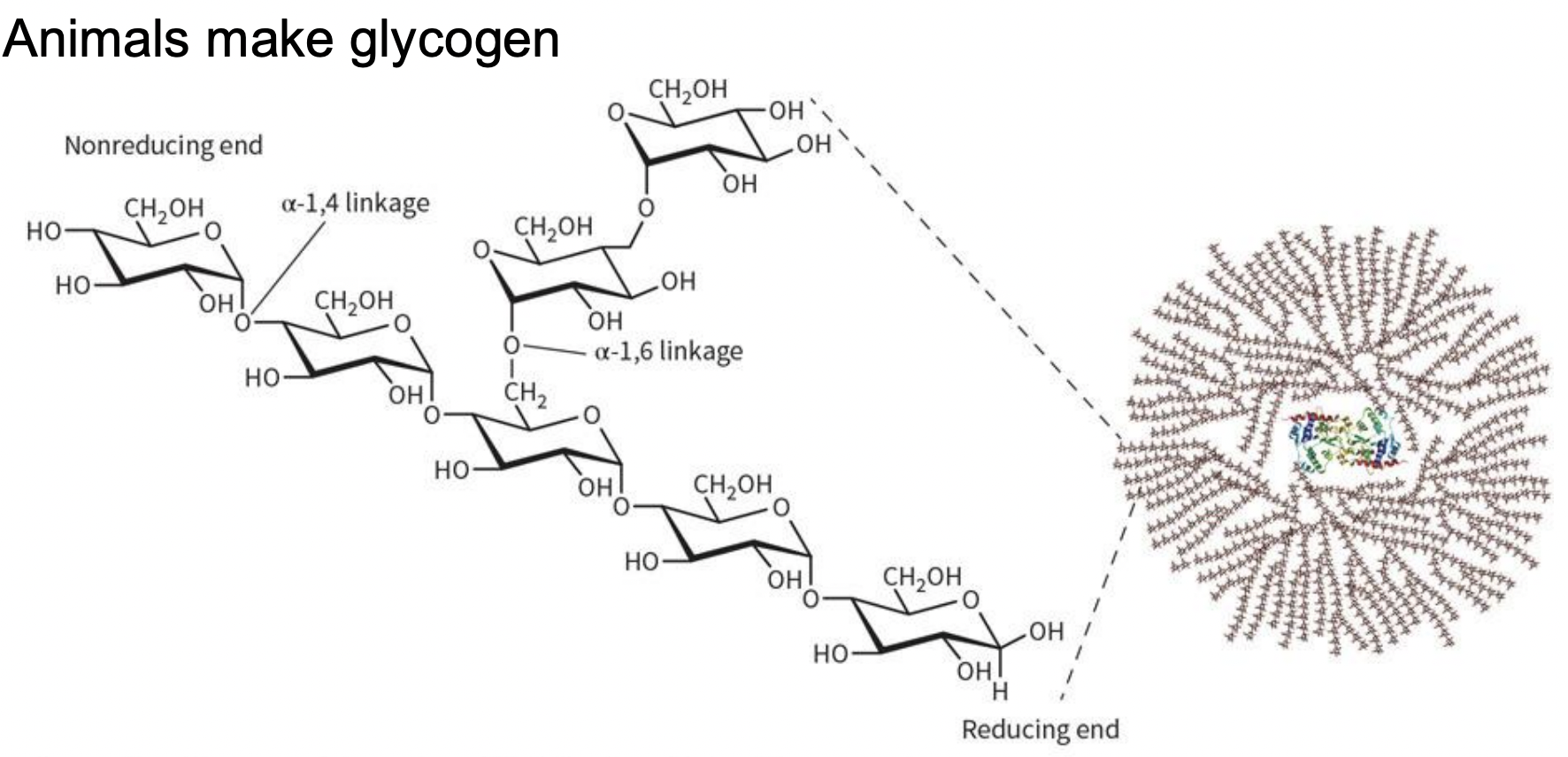
Glycogen (basic facts)
-a branching polymer
~75% found in muscle tissues
25% in liver
MOST tissues cannot create glycogen
glycogen can’t be transported (must be metabolized)
muscle never shares liberated glucose, but the liver does !
Glycogen Synthesis Pathway
• Glucose-6-P (G6P) is converted to Glucose-1-P (G1P) by phosphoglucomutase (not phosphoglucose isomerase from glycolysis)
• G1P is attached to a UDP to facilitate addition to growing chain
• UDP is lost during chain addition
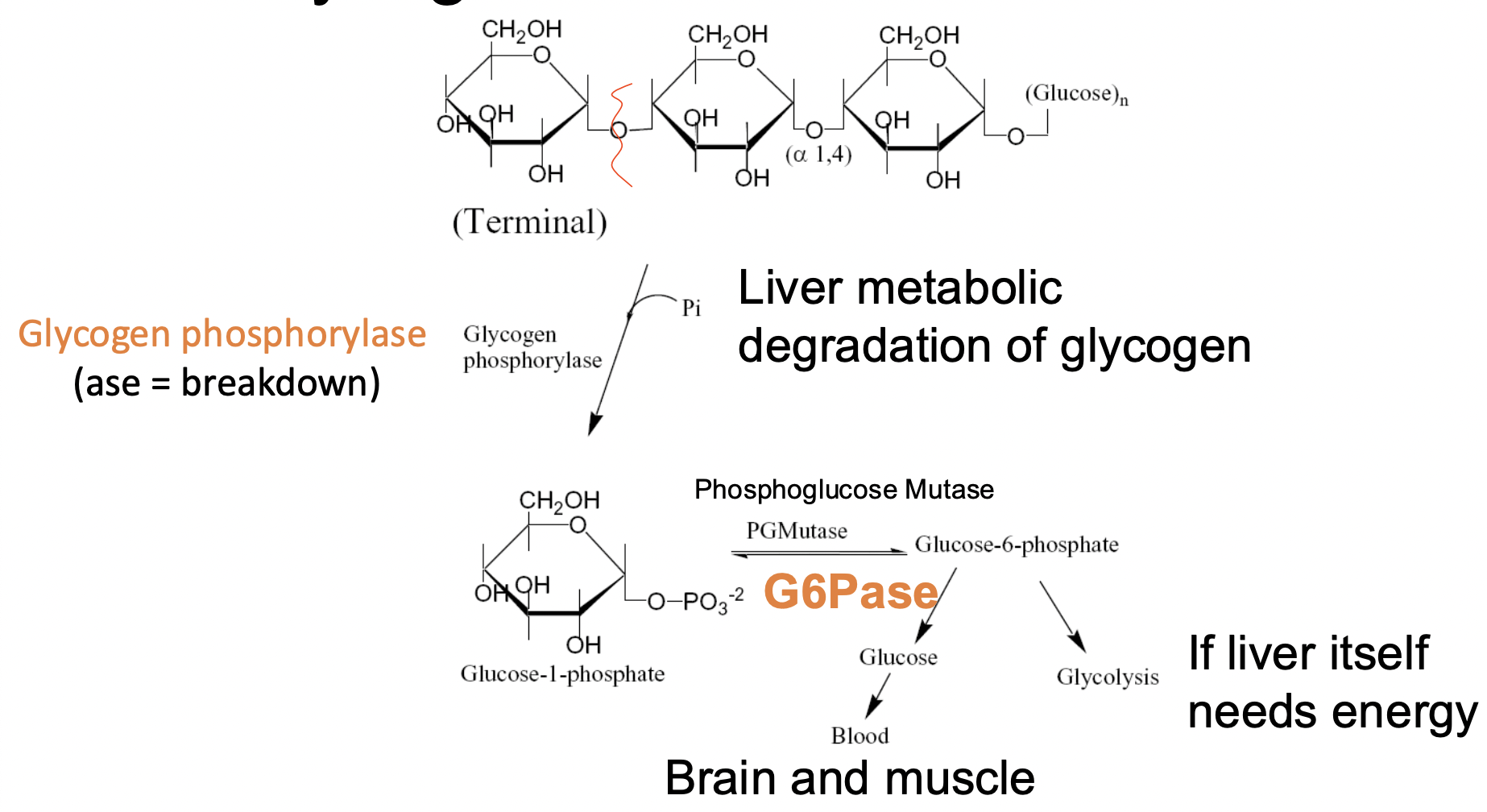
Glycogen Metabolism: Breakdown
1) Glycogen phosphorylase (enzyme; ase= breakdown): breaks down glycogen ; liver metabolic degradation of glycogen→ generates Glucose-1-phosphate
2) G-1-P is converted back to Glucose-6-phosphate by phosphoglucose mutase (PGM) ; usable form for glycolysis in liver.
it can also be for muscles; the G6P is converted back into glucose, which will circulate back into blood. by glucose-6-phosphatease (G6Pase)
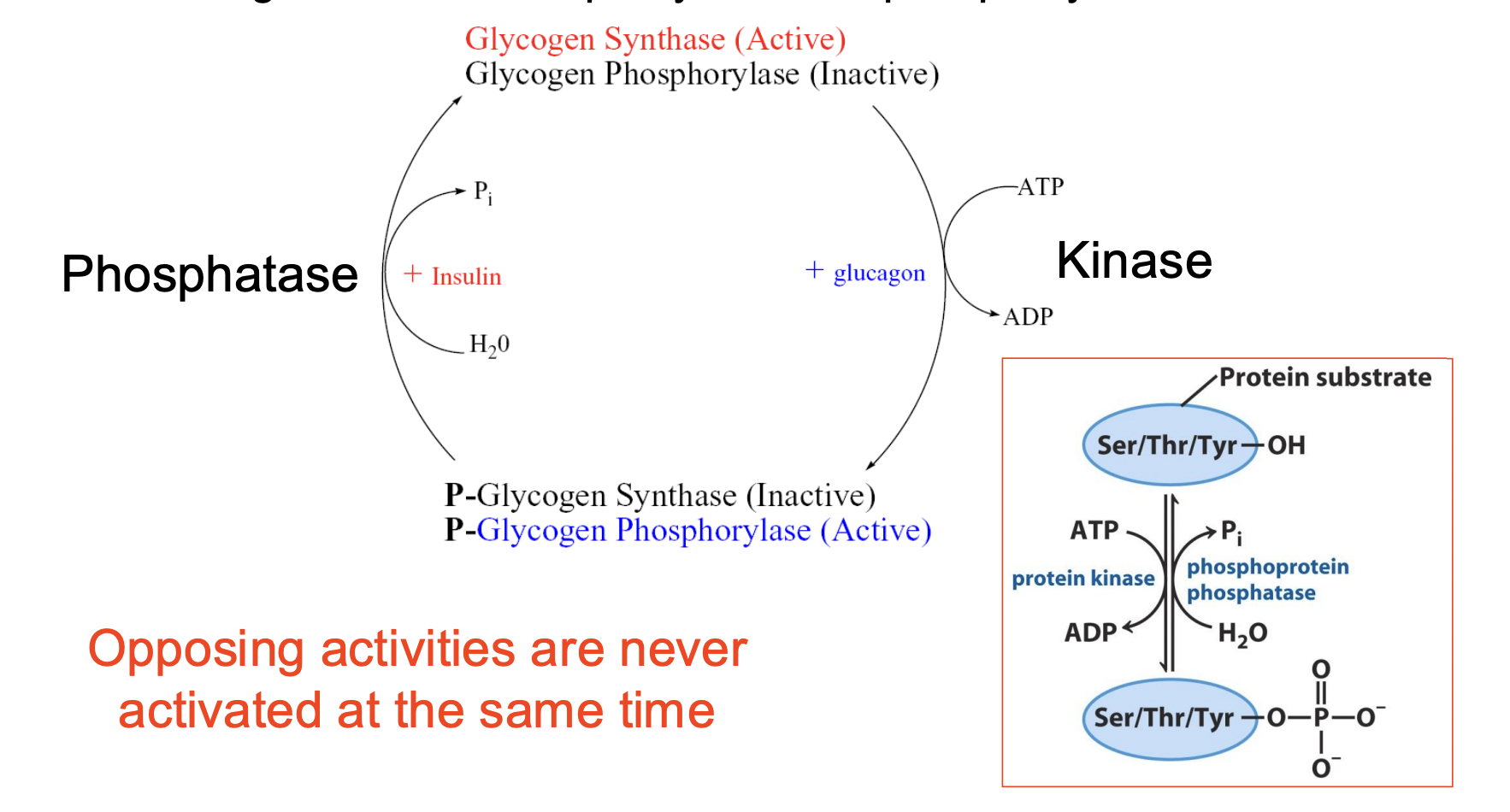
Glycogen Metabolism: Reciprocal Control
Glycogen Storage & Breakdown Regulation via Phosphorylation/De-phosphorylation
coordinated effort of kinases and phosphatases that are activated or inactivated by hormones
opposing activities are never activated at the same time
1) Glucagon stimulates kinase (uses ATP)→ Both glycogen synthase and glycogen phosphorylase get phosphorylated; glycogen phosphorylase activates while glycogen synthase inactivates. (BREAKDOWN OF GLYCOGEN)
2) Insulin triggers inactivation of glycogen phosphorylase (stops glycogen breakdown) & activation of glycogen synthase → Phosphatase activity = dephosphorylation of the enzymes/kinases (STORAGE)
Protein Phosphorylation
Proteins are phosphorylated primarily at serine, threonine, or tyrosine residues, but other amino acids can also be phosphorylated or dephosphorylated.
-It's just a hydroxyl going into a phosphate.Water is involved.
Glycogen Synthesis & Metabolism: the organs that store/consume?
liver & pancreas
-Hormone Signaling regulates glucose
-Dysregulation drives disease
Type 1 diabetes: lack of insulin production drives elevated blood glucose
The influence of insulin
Move glucose from blood to cell: blood glucose level goes down.
-Insulin receptors recognize insulin and trigger the following:
-Protein phosphorylation:
1) Active transport
2) Glycolysis
3) Glycogen synthesis
4) Lipid synthesis (turn sugar into fat)
5) Lipid breakdown (turn sugar into protein) X (don’t wanna do this, we’d rather store sugar)
6) protein synthesis
7) Gluconeogenesis X (we don’t wanna make more glucose; we have too much)
-Insulin: “I want to get rid of blood glucose”
All of the following is true about glucose EXCEPT:
-The blood glucose level is maintained to keep glucose from precipitating in blood
-Decreased [Glucose] in blood can lead to coma
-Hormones like insulin and glucagon can regulate blood glucose levels
-The main source of energy for the brain is glucose
-Blood glucose levels are typically ~4-5mM
-The blood glucose level is maintained to keep glucose from precipitating in blood
The main reason why [AMP] is a key regulator of many metabolic reactions (rather than [ATP]) is:
-DeltaG of ATP -> AMP hydrolysis is higher than DeltaG of ATP -> ADP hydrolysis
-The relative change in [AMP] is usually much greater than the relative change in [ATP]
-[ATP] is typically greater than [AMP], ATP is the form present in nucleic acids
-AMP is less charged than ATP
-The relative change in [AMP] is usually much greater than the relative change in [ATP]
PFK-1 is regulated by all of the metabolites below EXCEPT:
-Activation by ADP or AMP
-Inhibition by ATP
-Inhibition by citrate
-Activation by glucose
-Activation by F-2,6-BP
-Activation by glucose
Glycogen formation. What is true?
-Glycogen synthesis requires CDP
-Glycogen synthesis is catalyzed by glycogen synthase
-Glycogen breakdown is catalyzed by glycogen synthase
-Glycogen breakdown is catalyzed by hexokinase
-Glycogen synthesis is catalyzed by glycogen synthase
Which statement is FALSE? When blood glucose level is high,
-Insulin goes up
-Glycogen breakdown goes up
-Glycogen synthesis goes up
-Glycolysis goes up
-Glycogen breakdown goes up