Veins
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
calf vessels best seen w posterolateral approach
peroneal
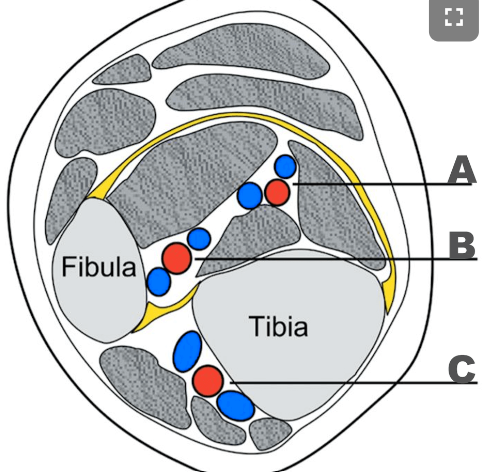
A: PTV
B: Peroneal vein
C: ATV
vein that receives blood from DFV & GSV
CFV
spontaneous flow vs nonspontaneous flow
spontaneous: actively moves w/out external maneuvers
normal vein
nonspontaneous: flow only moves w maneuvers (valsalva)
LE veins w normal nonspontaneous flow
GSV & calf veins
*may need distal augment to see
start & end of GSV
@dorsum, ant to medial malleolus TO FV (3cm below inguinal ligament)
how breathing affects LE venous return
inspiration:
low intrathoracic P
increases P gradient
INCREASE VEIN FLOW TO HEART
expiration:
high intrathoracic P
decreases P gradient
DECREASE VEIN FLOW TO HEART
total blood volume vein vs artery
vein: 70%
artery: 30%
veins w/out valves
IVC, SVC
brachiocephalic
PV
CIV
only vascular structure post to IVC
RRA
vein along posteromedial fibula
pero v
normal venous blood flow goes…
superficial-to-perforator-to-deep
SSV location
from lat dorsal venous arch of foot
ascends post to lat malleolus & along midline of post leg
runs w sural nerve
SSV empties at…
saphenpopliteal junction (SPJ) into pop vein
vein w greatest threat to PE
CFV
*large, closer to heart, in LE
UE PE less common bc no soleal sinuses
venous return from deep vs superficial
deep: 90%
superficial: 10%
only drains skin & subcutaneous tissue
role in thermoregulation
venous return against gravity depends on muscle pumps in the…
foot & calf
prothrombin time (PT)
how long it takes for blood to clot
normal: 10-13s
international normalized ratio (INR)
*asses risk of bleeding or coagulation status
blood’s clotting ability
normal: <1
UE veins w pulsatile flow & spontaneous flow
brachiocephalic
IJV
subclavian
*axillary may or may not
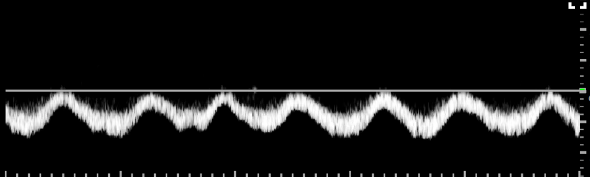
normal CFV
*phasic & lil pulsatile
# of valves below knee
(GSV, SSV, ATV/PTV/PERO)
GSV: 10-12
SSV: 6-12
ATV, PTV, PERO: 9-12 each
# of valves in perforators
# of valves in soleal
1
0
# of valves above knee
(POP/SFV, CFV)
POP V & SFV: 1-3 each
CFV: 1
% of EIV w valves
25%
# of IJV valves
1
peroneal veins
posterior tibial veins
anterior tibial veins
peroneal: empty lateral leg into tibioperoneal trunk
posterior tibial: empty post leg into tibioperoneal trunk
btwn medial malleolus & achilles
anterior tibial: empty ant leg & joins tibioperoneal trunk to form pop v
btwn tib/fib
from dorsalis pedis v
LEV visual
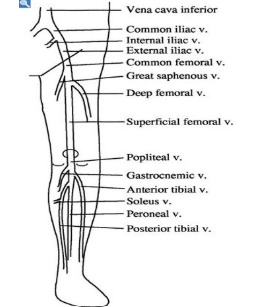
deep veins & superficial veins
deep veins:
muscles surround
push blood back to heart (90%)
superficial:
no muscles around; above fascia
feed into deep veins
slower flow bs NO muscles to squeeze/pump
perforator veins
superficial-to-deep
w valves
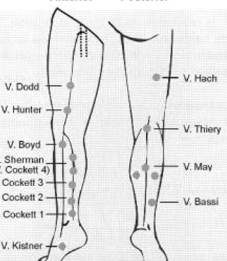
cockett
boyd
hunterian
dodd
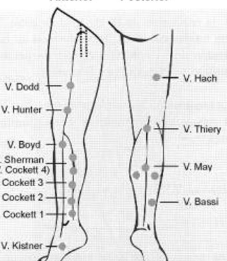
perforator that connects GSV to PTV
boyd perforator
*common site for primary vv
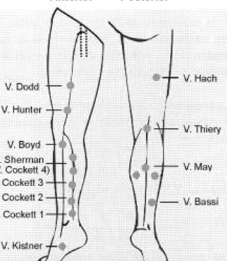
perforator to connect GSV to SFV
hunterian
sinuses
brain
space btwn dura mater & periosteum
receive venous return
LEV (soleal)
dilation superior to valve cusp in calf
accumulates venous blood & drains into PTV/PERO
helps valve close
SSV & Giacomini V
SSV:
back of leg into PopV
<3mm
Giacomini:
continuation of SSV into thigh
drains into GSV
gatier area
posterior arch veins connect w 3 ankle perforators
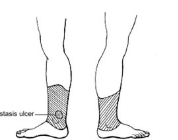
mc for stasis ulcers
gastroc veins & soleal veins
*superficial*
gastroc empties into PopV
soleal empties into PTV/PERO
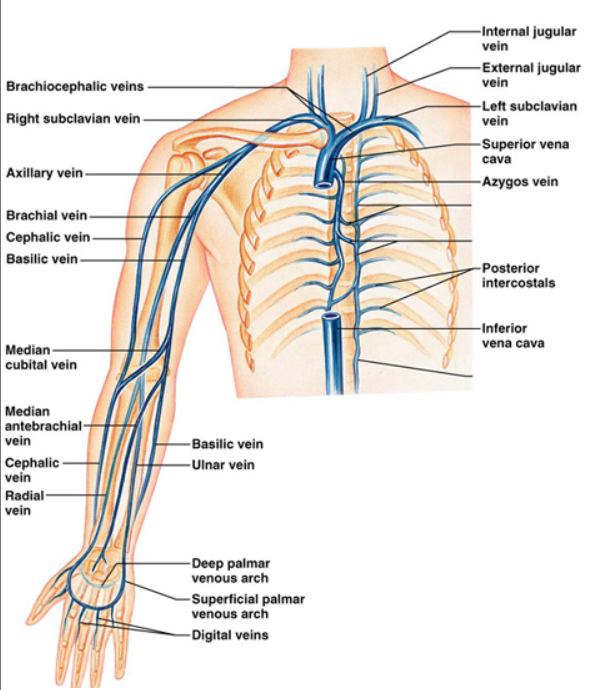
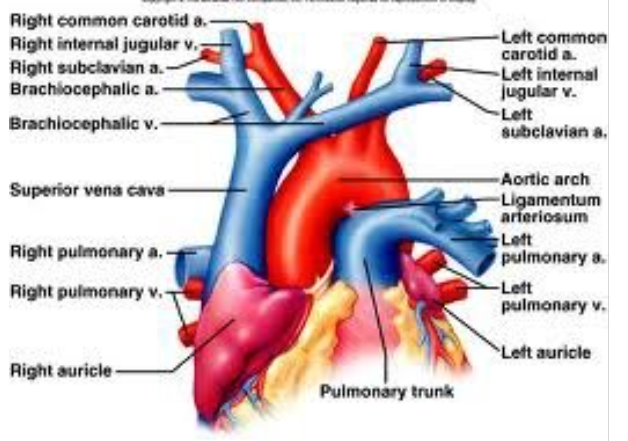
UE veins
IJV+subclavian…brachiocephalic (innominate)
RT innominate +LT innominate…SVC
……
cephalic joins axillary
basilic+brachial…axillary
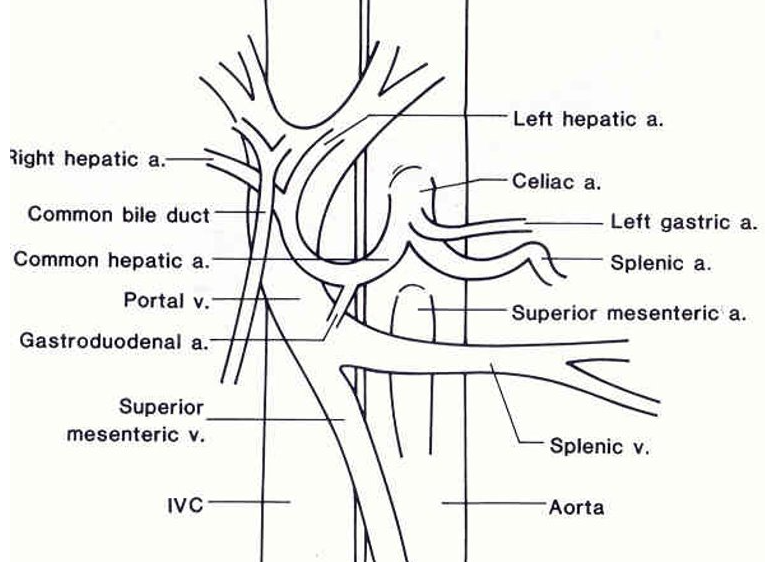
PV facts
MPV<13mm
hepatopetal
intrasegmental (w/in liver)
low V (20-40cm/s)
respiratory phasicity
portal HTN can lead to…
ascites, splenomegaly, GI bleeding, jaundice
cirrhosis (w intrahepatic obstruction) mc
UEV diagram
IVC & AO diagram
what determines cross sectional shape of vessel?
transmural P
difference btwn intraluminal P (inside) & interstitial P (outside)
is venous P high or low?
low
15-20mmHg in venules
0-6mmHg in RA
transmural P in supine
LOW transmural P
dumbbell shape
low volume
venous resistance & vein shape
veins have higher resistance bc not completely full
partially empty: dumbbell shape (more resistance)
intraluminal pressures when…
standing: 80mmHg
walking: 25mmHg
lying: 10mmHg
breathing affects on venous flow
inspiration…decreases thoracic P & increases abdominal P
less flow from LE
expiration…increases thoracic P & decreases abdominal P
less flow from UE
calf veno pump
*gastrocnemius & soleus muscles
w muscle contraction…venous valves open & perforator valves close
w muscle relaxation…venous valves close & perforator valves open
**to reduce P
primary vs secondary venous insufficiency
valves dont work & blood flows back down in muscle relaxation
primary venous insufficiency:
congenital absence of valves
secondary venous insufficiency:
valve damage bc DVT
valsalva maneuver & LE flow
LE flow will cease w competent valves; NO retrograde flow
if damaged valves…retrograde flow
*never do w severe CAD or acute MI
venous stasis/insufficiency S&S and RF
S&S:
recurrent calf & ankle swelling
ankle ulcers
varicose veins
RF:
vessel trauma, post op
MI, CHF, hypotension
stasis
venous stasis/insufficiency
incompetent valves allow back flow deep-to-superficial
high P in veins causes damage
allows blood pooling [stasis]
w discolored skin & ulcers @ medial malleolus
lymphedema
“ant farm” on US
obstruction of lymph vessels
may mimic DVT
edema
sign of high peripheral venous P
bc obstruction & unable to reabsorb fluid bc high capillary P
virchows triad
DVT development based on…
vessel trauma
venous stasis
hypercoagulability
paget-schroetter syndrome
‘stress/effort thrombosis’
thrombosis of subclavian/axillary w intense, repetitive activity
mc place for thrombosis to form
valve cusps
soleal sinuses
what does positive D-dimer indicate?
DVT
DVT pain is usually located…
in posterior or medial calf
**2-3wks of pain or in anterior leg…not DVT
mc cause of UE DVT
PICC line
acute vs chronic DVT
acute:
<4wks
loose thrombus-vein wall attachment
hypoechoic; free floating tail
distended lumen; spongy/non-compressible
chronic:
firm wall attachment
echogenic; no tail; calcs
small lumen; incompressible
w collaterals
recanilization
w chronic DVT
body naturally tries to restore flow
w heparin & vitamin K inhibitors
often produces incompetent valves
primary vs secondary vv
primary vv:
hereditary
bc high venous P…not obstruction
secondary vv:
bc DVT
varicose veins
tortuous & dilated; >4mm
bc venous insufficiency…then damaged, leaky valves
flow is reversed w standing
pressure ulcers are located on…
bony prominence
causes of venous & arterial ulcers
venous: blood pools; cant pump out
arterial: inadequate blood suppled in
mechanisms of ulcers
tissue breakdown bc lack of O2 & nutrients
incompetent perforators that carry blood GSV-to-deep system
**near medial malleolus (where 3 perforators meet)
neuropathic skin ulcers
‘diabetic’
little to no sensation in feet bc DM nerve damage
venous ulcers
medial/lateral malleolus
mild pain
shallow, irregular shape
venous ooze
stasis changes (brawny discoloration, vv)
arterial ulcers
tibial, toes, bony prominences
severe pain
deep, regular shape
little ooze
trophic changes (shiny skin, hair loss, thick toenails)
phlegmasia alba dolens
arterial spasms bc acute iliofemoral DVT
severe LE swelling
pale
absent pulses
pregnancy
phlegmasia cerulea dolens
severely reduced venous & arterial flow
cyanotic
extreme pain
massive iliofemoral DVT bc obstruction
may thurner syndrome
L iliac v compressed by R iliac a
higher risk of DVT in LT LE
-<20yo females
-L leg pain & edema
-oral contraceptives, pregnancy
superior venous thrombophlebitis
“trousseau syndrome”
in UE bc IV/cath
in LE above knee…high DVT risk
vv, pain, warm & red skin
treat w NSAIDS & warm compress or heparin
photoplethysmography PPG
measures capillary blood volume
evaluates venous insufficiency (reflux)
*infrared light
*not w acute DVT
PPG technique
place sensor on medial malleolus (seated patient w feet dangling)…
pt dorsiflexions (move blood to heart)…
record VRT
normal VRT: >20s
if VRT >20s w/out cuff…
normal venous filling
if VRT <20s w/out cuff & then >20s w cuff below knee…
SSV reflux
if VRT <20s w/out cuff & >20s w cuff above knee…
GSV reflux
if VRT <20s w & w/out cuff…
deep & superficial reflux
if VRT <20s w cuff on thigh…
deep reflux
retrograde flow times for reflux
perforator: >0.35s
superficial: >0.5s
deep: >1-1.5s
*>1.5s means superficial & deep reflux
minimum artery & vein diameter to create AV fistula or AV graft
artery: 2mm
vein: 2.5mm
which UE vein is mc taken for CABG?
non-dominate radial v
gold standard for venous exams
contrast venography
NOT used often now
varicose veins
dilated, tortuous, >4mm
mc in calf bc incompetent GSV or SSV
RF:
age, female, pregnant
anticoagulants
help prevent clot formation
by reducing vitamin K in clotting process
mc is coumadin
acute anticoagulation»heparin
chronic anticoagulation»warfin
another name for internal iliac v
hypogastric v
PICC line locations
mc subclavian
lowest clot risk
IJV
FV
highest clot risk
highest arterial injury
most common & least common DVT locations for PE
most common: prox iliofemoral v
least common: calf v
superficial thrombophlebitis
bc IV vessel wall injury
mc w varicose veins & IV therapy
pain, redness, swelling, fever
PE S&S
tachycardia
low PCO2
chest pain
dyspnea
IVC filters
reduce risk of PE
placed below renal v to trap large clots
thru neck or groin
patients not on anticoagulants
extrinsic compression of iliac vein results in…
continuous CFV flow w no DVT
AVF
common after catheter insertion
high V w/in neck
bruit
vv ablation
vein is heated to seal the vein off
vv stripping & ligation
incision in groin area w thin wire inserted into vein
vein is stripped & ligated (tied off) at both ends
hydrostatic P when standing
(below heart) + hydrostatic P
measured P will be higher than true circulatory P
(above heart) - hydrostatic P
measured P will be lower than true circulatory P