CSI FINAL
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
183 Terms
Your goal as a CSI is to prevent the 3 main types of scene integrity issues…
1. Addition of material to scene
2. Destruction of material on scene
3. Movement of material on scene
The six crime scene activities and their basic order are…
Assessing, Observing, Documenting, Searching, Collecting, and Analyzing
Which of the six crime scene activities does this describe? “Assessment of the scene assists the investigator in deciding on what to do, when to do it, and what resources may be required. Assessment must be accomplished before taking any action, but assessment is an on-going activity as well. The investigator is constantly assessing the scene throughout processing.”
Assessing
1. Scope and complexity of the scene
2. Scene integrity and contamination control
3. Team approach and composition
4. Search methods to be used
5. Personal protective measures & safety hazards
Five Issues of Assessment
Assessment by the crime scene team always involves a debriefing of the ____ ______.
Initial responders
What involves two barriers which creates three areas of access? …
◦ Inner Scene: This is the actual crime scene, where only authorized investigators and crime scene technicians operate.
◦ Working Area: This is an area surrounding the inner scene, where other support police may enter,
equipment is staged and evidence is brought to.
◦ Outer Area: This is everything on the outside of the second barrier, where on-lookers, media and others may gather.
Multi-level containment
Photography teams work best with how many individuals?
Two
Sketch teams work best with how many individuals?
Three
Evidence Collection teams work best with how many individuals?
Two
Search teams are a matter of circumstance, but always require a minimum of how many individuals?
Two
What is the area that any given searcher is viewing at any given moment in the
search?
How tight or how broad this _______ will be is a product of several considerations:
◦ Nature of the ground being searched.
◦ Lighting considerations.
◦ On-scene environmental conditions.
◦ Size of the item being searched for.
Swathe size
List all of the basic crime scene search patterns…
Circle search, Wheel/Ray, Strip or line search, Grid search, Zone search, Point to point search
Excellent pattern in most interior or confined exterior scenes. Not effective in large exterior scenes or cluttered areas that impact on the circular movement.
Searcher moves inward or outward from a starting point.
Circle or spiral search
Searching begins in the middle, then searcher work their way out in a straight path.
May add in more searchers as the area becomes wider. May be coupled with additional searches like line searches.
Wheel/ray search
Best performed with 1-2 searchers. Excellent in exterior scenes where a large area
must be examined. Visual alignment to the strip is good for most situations, but as the area to be searched grows, it becomes more difficult to maintain a visual reference of the lanes. Physically laying out the strips with string or tape can help maintain the order.
Strip search
This search is another variation on the strip search. Searchers follows strips in one direction, then cuts across the scene in another set of strips, oriented 90 degrees to the first. Provides for multiple views of the same ground by the same searcher from different perspectives.
Grid search
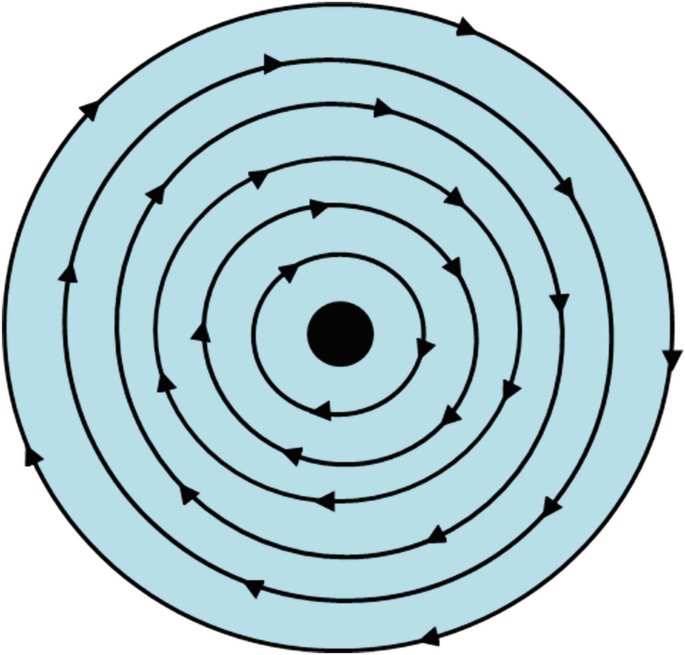
What is this search method?
Circle/spiral search
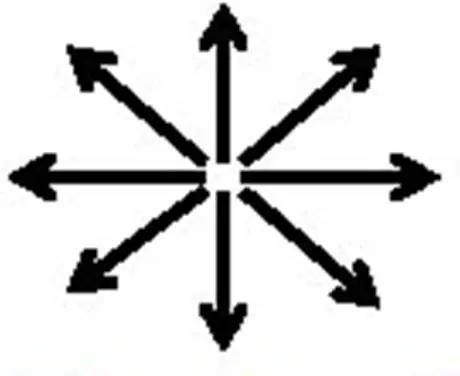
What is this search method?
Wheel/ray search
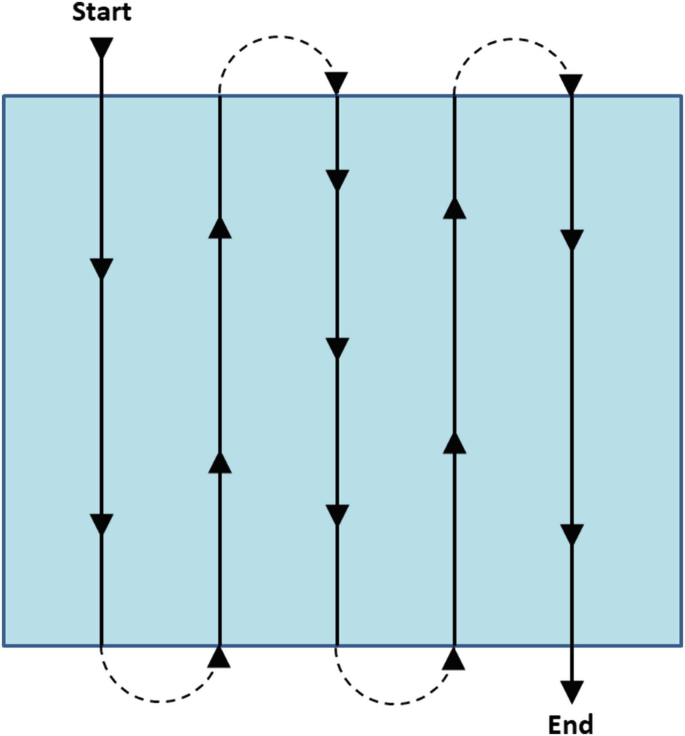
What is this search method?
Strip search
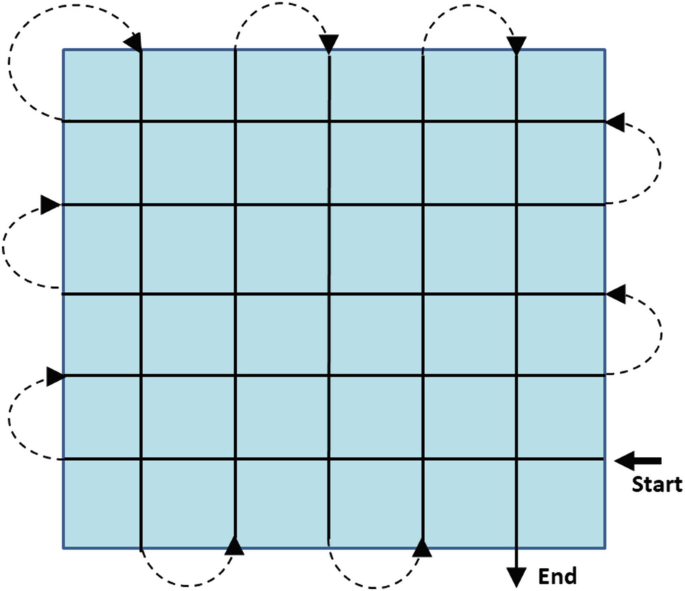
What is this search method?
Grid search
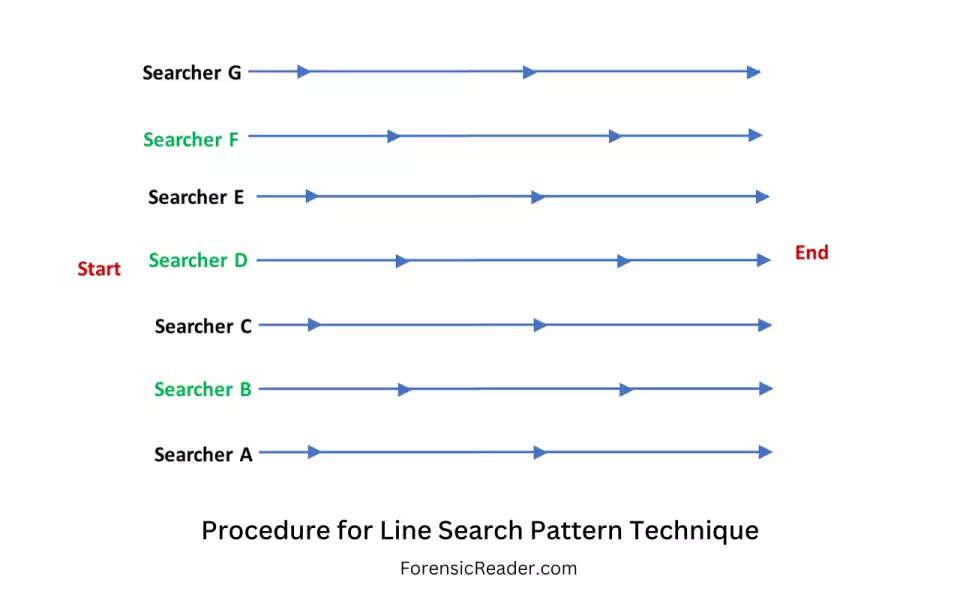
What is this search method?
Line search
This method is a variation of the strip search, where multiple searchers follow a single strip in one direction, while on-line with each other. Excellent for exterior scenes over rough terrain. Usually requires supervisor(s) to maintain the
direction and alignment of the involved searchers.
Line search
This search method is used in several variations: To deal with small confined spaces where no patterned search will work. To break a larger scene up into functional areas, that are then searched using some other patterned technique.
Zone search
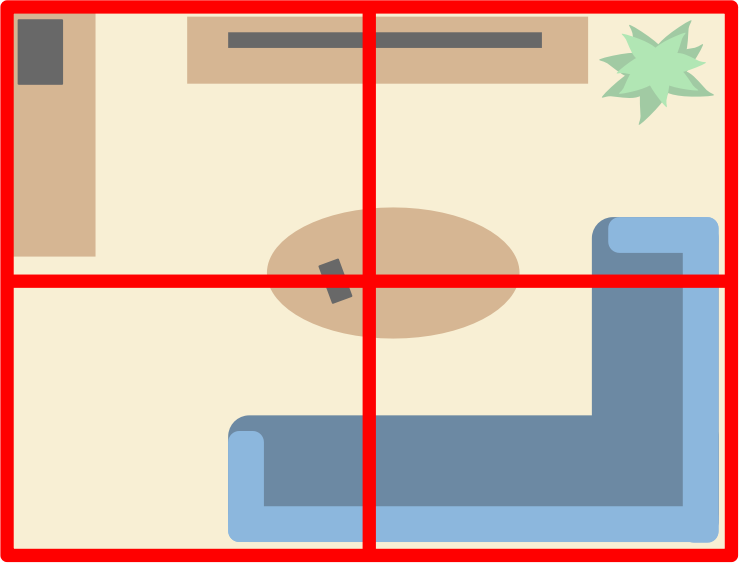
What is this search method?
Zone search
This search method is not widely used in the United States. Searchers move from one focal point to the next, creating cleared pathways to and from each. They do not stray from these pathways. Each focal point is dealt with before moving on to the next.
Point to point search
What are the different parts of the documenting stage for CSI?
Notes, photos/videos, sketches/laser scans, and reports
◦ Clearly show the layout of a crime scene – 2D
◦ Illustrate the relationship in space of all significant items and features
◦ Clarify objects and features already described in notes or shown in photographs
◦ Show measurements over long distances and topography of outdoor scenes
◦ Depict possible paths of entry, exit, and movement through the scene
Sketches
The standard crime scene sketch is drawn as a “_____” view
Birds-eye
What are the five essential elements of a sketch?
Heading, diagram area, legend, title block, and scale/direction notations
What type of sketch is an overhead view from above. Easily demonstrates items in a horizontal plane (e.g. floors, beds). Most common type of sketch.
Overview/birds-eye
What type of sketch portrays a vertical plane rather than horizontal plane (walls). Used to show details for bullet holes, bloodstains, etc. Drawn in a “side” view.
Elevation
What type of sketch shows walls/ceiling flat as if “exploded”. Used to show details/spatial relationship on walls/ceiling
Exploded/Cross-Projection
_______ are used for items that you are going to COLLECT. Make sure the numbers correspond with the photographs, notes, reports.
_______ are used to indicate something important but you are NOT going to collect
◦ Bullet holes
◦ Damage to areas
◦ Burn marks
Numbers, letters
Best utilized in exterior scenes with limited landmarks, but can be used indoors
This mapping technique is extended from a datum point in a cardinal direction. A single measurement is made from the evidence to the baseline at a right angle. Can use a tape measure between two “fixed points”.
How-To:
◦ Baseline created from a datum point.
◦ Evidence measured at right angles to the baseline.
◦ Two measurements required
◦ Distance 90 from tape to item
◦ Distance from 0”
Baseline mapping
◦ Take a GPS reading
◦ Drive a metal stake
◦ Place zero end of tape measure above metal stake
◦ Run tape measure along magnetic north using a compass
What to do if there are no fixed points for baseline mapping
This mapping technique is best utilized in interior scenes with clear, rectangular boundaries. Two measurements are made from the evidence to the surrounding walls and surfaces, at right angles. Best used to document items on a VERTICAL surface – walls/windows/doors
How-To:
◦ Evidence measured from center of mass
◦ To surrounding walls at right angles
◦ Two measurements required
Rectangular mapping
This mapping method is the most common used measurement tool. Best utilized in scenes with evident landmarks (indoors and outdoors). The most precise mapping method as it fixes regular shaped objects in a specific position. It is time intensive due to the measurements required. The number of measurements is based on whether the objects shape is regular or irregular.
How-To:
◦ Measure from 1st fixed point to item then;
◦ Measure from 2nd fixed point to item
◦ Measure distance BETWEEN TWO FIXED POINTS (Reference points)
Triangulation mapping
Irregular shaped objects require ____ straight line measurements from two distinct landmarks in the room to the center of mass on the item.
Two
Regular shaped objects require a total of ____ straight line measurements from two distinct landmarks in the room to two distinct points on the item.
Four
Best utilized in exterior scenes where evidence is scattered over a relatively open area. Requires a surveying instrument (e.g. compass, laser or sighting transit).
Angle from datum point to the evidence is determined with the device (horizontal angle). Distance from datum to the evidence is measured.
How-To:
◦ Angle to the evidence measured from a datum.
◦ Horizontal distance to the evidence measured.
◦ One measurement, one angle per item.
Polar coordinate mapping
Both _____ coordinates and _____ can be used on a grid.
Rectangular, triangulation
What does CAD stand for? —> Helps create final sketches
Computer-aided drafting
Crime scene photography has four recurring problems that detract from its value. These are…
Identification, orientation, confusion, and incomplete documentation Issues
In crime scene photography, ______ issues involve creating photographs where the viewer is lost in the scene. Photographs are taken of items and the photo fails to illustrate what it is in the picture or the photo documentation fails to illustrate why the photograph was taken in the first place.
Identification
In crime scene photography, ______ issues involve creating photographs where the viewer is lost in the scene or has no orientation. Photographs are taken of an object with no scene reference (e.g. Where is it in the scene). Photographs are taken in which orientation is not clear (e.g Which way is up?)
Orientation
In crime scene photography, ______ issues occur when the crime scene team fails to capture pertinent scene details. Too few photographs are exposed. Critical areas of the scene are forgotten. Methodical scene processing techniques help eliminate this issue.
Incomplete documentation
In crime scene photography, ______ issues involve creating photographs where the viewer is unclear of which item is being photographed or which photo came first. Photographs show the scene in altered states. Photographs show multiple similar items with no way to distinguish one from the other. This is particularly true when photographing small objects like shell casings and bloodstains.
Confusion
What are the three cardinal rules of photography?
Fill the frame 2. Maximize depth of field 3. Keep the film plane parallel
What are the unofficial other two rules of crime scene photography?
NEVER delete photographs off of the camera and NEVER have people in your photographs
These types of photographs document the general conditions of the scene. Shows how the scene relates to the surrounding area. Used to establish more detailed photos
Interior & Exterior
◦ “As is” (without evidence markers)
◦ With evidence markers
Taken from a “Natural Perspective”
◦ Eye level
Overall
These types of photos are functioned to frame the item of evidence with an easily recognized landmark (Fixed Point). This visually establishes the position of the evidence in the scene. They are the most overlooked photograph in crime scene work. The evidence establishing photograph is not intended to show details, simply to frame the item with a known landmark in the scene. The close-up and the evidence establishing photograph go hand in hand.
Midrange
These types of photos are functioned to allow the viewer to see all evident detail on the item of evidence. Not concerned about the context or relationship, only the subject, with and without scale. You must get close and fill the frame with the evidence ONLY. They are taken with and without a scale. Very important when taking photos of small items, whose detail may affect another analysis. Ensure a good focus, make the picture sharp.
Non-porous surfaces at crime scenes can be processed for fingerprints with all except...
A. Black powder
B. Magnetic powder
C. Ninhydrin
D. Superglue
C. Ninhydrin
A discipline in forensic science which is primarily concerned with determining if a bullet, cartridge case, or other ammunition component was fired by a particular firearm is called...
Firearms identification
True or false: In stoke’s shift, the energy re-emitted by the sample is a higher energy than the excitation light
False
What reacts with the iron in hemoglobin and produces a bright blue chemiluminescent glow when the area is darkened? Used to detect latent bloodstains at a crime scene. You can tell if it is a false positive by comparing the glow to known blood stains to the unknown stain.
Bluestar
In general, _______ is the best packaging medium.
Paper
True or false: Cardboard counts as paper
True
The package that the actual item is inside
Primary packaging
A container that primary packaging is placed in as appropriate; usually used when
the evidence item is small and will get lost if packaged normally
Secondary packaging
What does “MSIDD” stand for in evidence packaging?
Marking, seal, initials, date/time, describe
A systematic and scientific approach to thoroughly document and process a crime
scene
Crime scene investigation
Reconstruct actions of suspects/victims; establish motive; identify, document, collect and preserve all physical evidence – and do it legally
Goals of crime scene investigation
Strong morals, integrity, patience, calmness under pressure, open mind, thoroughness, efficiency, attention to detail, strong observational skills, interpersonal skills, critical thinking, and personal awareness
Requirements for crime scene investigation
Unconscious errors in thinking that influence how we interpret information and make decisions. In crime scene investigations, these biases can shape observations, evidence handling, and overall case outcomes—often without the investigator realizing it.
Cognitive bias
Favoring evidence that supports a pre-existing theory while discounting
contradictory facts.
Confirmation Bias
Judging evidence differently based on external influences (e.g., suspect
background, location).
Contextual Bias
Relying too heavily on initial information or assumptions when forming
conclusions.
Anchoring Bias
Seeing what one expects to see rather than what is actually present.
Expectation Bias
Altering judgment based on consensus or pressure from colleagues.
Group Think
The principles for forensic medicine (1844)
William Augustus Guy
Police Code and Manual of Criminal Law (1881)
Sir Howard Vincent
Criminal Investigation: A Practical Handbook (1906)
Hans Gross
Anything that tends to prove or disprove a fact in contention
Evidence
True or false: Not all physical evidence is circumstantial evidence
False
What is one of the most concrete ways to complete the linkage triangle?
Biological evidence
True or false: Biological evidence is circumstantial evidence.
True
Type of fluid/tissue
Class characteristics for biological evidence
Who the fluid belongs to via DNA analysis (always done at the lab)
Individual characteristics for biological evidence
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
What DNA is housed in the nuclei of each cell?
Nuclear DNA
Everyone’s DNA is unique with ONE exception…
Identical twins
Who made the discovery of DNA fingerprinting in 1984?
Sir Alec Jeffery
What type of DNA is found outside the nucleus of the cell and is inherited solely from the mother?
Mitochondrial DNA
What are various ways to detect biological evidence?
Oblique lighting, odors, ALS, and chemical enhancement
The ______ the level of energy, the shorter the wavelength. The ______ the wavelength, the greater the ability to penetrate objects.
Higher, shorter
What effects can an object with light have?
Absorb, reflect, transmit, and convert
This is the mechanism of fluorescence. Light of a particular wavelength is projected onto a material. The material absorbs the light. The material emits light at a higher wavelength, not previously contained in the original light. The stimulating light is more intense and overwhelms the fainter fluorescence being emitted. The physical loss of energy (through absorption) and change of color results in a longer wavelength.
Stokes Shift
Short wavelengths
200-300nm
Long wavelengths
300-400nm
_____-wave UV light is very dangerous – please be cautious if using these wavelengths.
Short
General protein stain
◦ React with proteins found in blood, but is not
specific for blood.
Typically used in pattern enhancements
◦ Latents
◦ Blood patterns
◦ Impressions
Amido Black
Chemiluminescent reaction that detects trace blood amounts (not specific to human blood) by reacting with the hemoglobin molecule. May use to look for blood in scenes that may have been cleaned or for trace amounts not visible with naked eye.
Luminol and Bluestar
Luminol based presumptive test that produces a more intense and longer lasting
chemical luminescence. Allows the detection of blood traces with the naked eye up to dilutions of 1 / 100 000. Reacts with iron found in hemoglobin.
◦ NOT 100% Specific to human blood = Presumptive Positive Test
◦ Will chemiluminescent (glow) blue without any light source present.
◦ Must view in darkened setting.
◦ Can photograph with tripod to show patterns
Generally safe for DNA analysis but be careful not to over spray
Bluestar
Limitation:
- Fibrous foods such as apples, turnips, radish, leeks, carrots
- Bleaches
- Some paints and varnishes
- Fecal matter
- Chemicals containing metallic ions
Limitations for BlueStar
Limitations:
- Fibrous foods such as apples, turnips, radish, leeks, carrots, horseradish
- Some detergents
- Bleaches
- Heavy Metals – iron and copper
- Fecal matter
Limitations for Luminol
Rapid qualitative test in a device for PSA detection from traditional biological samples
(serum, plasma, or blood). Sperm samples collected with a swab either on the clothes or on the body of the presumed victim of a sexual assault. Suitable for use in forensic medicine. Highly sensitive: detects PSA levels higher than or equal to 4 ng/ml. Reliable.
Fast: reacts within 10 minutes
Identi-PSA
The strips detect the peroxide-like activity of hemoglobin in a substance. Rub the strip on a moistened stain or across a swab that has a suspected dried blood sample on it. The reagent-coated tip will turn a shade of green if hemoglobin is detected. NOT specific to human blood.
Hemastix
Produces a blue-green or pink response when blood is detected. NOT specific to human blood. Only use when there is enough sample left over for subsequent DNA testing.
TMB or Kastle-Meyer
Presumptive Positive Human blood test. Displays positive reactions for human, primate, ferret, and skunk blood. One bar indicates the test strip and reagent are functioning properly. Two bars appearing confirm that the bloodstain is HUMAN
blood.
Bluestar Identi-HEM