A&P 1 Ch. 6&8
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/160
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
161 Terms
1
New cards
T/F: The term osteoid refers to the organic part of the matrix of compact bones.
True
2
New cards
Which of the following is **not** a function of the skeletal system?
communication
3
New cards
T/F: Compact bone is replaced more often than spongy bone.
False
4
New cards
Normal bone formation and growth are dependent on the adequate intake of ______
calcium, phosphate, and vitamin D
5
New cards
The structural unit of compact bone is the ______
osteon
6
New cards
What can a deficiency of growth hormone during bone formation cause?
decreased proliferation of the epiphyseal plate cartilage
7
New cards
The Haversian canal is the opening for ________
blood vessels and nerve fibers
8
New cards
The canal that runs through the core of each osteon is the _______
Haversian canal
9
New cards
The terms inversion and eversion pertain only to the ________.
Feet
10
New cards
Pointing the toes is an example of ________.
plantar flexion
11
New cards
Yellow bone marrow contains a large percentage of ________.
fat
12
New cards
Bone forming cells that produce the body matrix in a developing bone are ________.
osteoblast
13
New cards
Articulations permitting only **slight** degrees of movement are ________.
amphiarthroses
14
New cards
The **gliding** **motion** of the wrist uses ________ joints.
Plane
15
New cards
A fracture in the **shaft of a bone** would be a break in the ________.
diaphysis
16
New cards
Fibrous joints are classified as ________.
Sutures, syndesmoses, gomphoses
17
New cards
What kind of **tissue** is the forerunner of **flat bones** in the embryo?
dense fibrous connective tissue
18
New cards
The presence of a synovial cavity, articular cartilage, synovial membrane, and ligaments are characteristics of what type of joint?
hinge joint
19
New cards
Spongy bone is made up of **small, flat pieces of bone** called ______
trabeculae
20
New cards
The process of **bones increasing in width** is known as ________.
appositional growth
21
New cards
In some cases the epiphyseal plate of the long bones of children closes too early. What might be the cause?
elevated levels of sex hormones
22
New cards
The hip joint is a good example of a(n) ________ synovial joint.
diarthrosis
23
New cards
T/F: The trabeculae of spongy bone are oriented toward lines of stress.
True
24
New cards
On the basis of structural classification, which joint is fibrous connective tissue?
syndesmosis
25
New cards
T/F: The only movement allowed between the first two vertebrae is flexion.
False
26
New cards
Which structure allows the bone to increase in length until early childhood?
epiphyseal plate
27
New cards
Wolff's law is concerned with ______
the thickness, shape, and remodeling of a bone being dependent on stresses placed upon it
28
New cards
What is a comminuted fracture?
fracture in which the bone is splintered or crushed
29
New cards
A comminuted fracture fragments into _____ pieces.
3 or more
30
New cards
To whom are comminuted fractures particularly more common in?
the aged, whose bones are more brittle
31
New cards
When the bone is crushed, it is a(n) ______
compression fracture
32
New cards
Where are compression fractures common?
porous bones subjected to extreme trauma, as in a fall
33
New cards
_______ is a **ragged break** that occurs when excessive **twisting** forces are applied to a bone.
spiral fracture
34
New cards
A common sports **fracture found in athletes** is a _______
spinal fracture
35
New cards
When the epiphysis separates from the diaphysis along the epiphyseal plate is a(n) ______
epiphyseal fracture
36
New cards
_______ tends to occur where cartilage cells are dying and calcification of the matrix is occurring.
epiphyseal fracture
37
New cards
When a broken bone portion is pressed inward is a(n) _______
depressed fracture
38
New cards
A ________ is typical of a **skull fracture**
depressed fracture
39
New cards
When the **bone grows incompletely** it is a(n) ________
greenstick fracture
40
New cards
A **fracture that is common in children** that have more of an organic matrix and are more flexible than those of adults.
greenstick fracture
41
New cards
_______ is Red Bone Marrow that has changed to **fat**.
Yellow bone marrow
42
New cards
What does yellow bone marrow do?
stores fat
43
New cards
Where do you find yellow bone marrow?
in the medullary cavity of long bones
44
New cards
What are osteoblast?
Are bone forming cells that secrete the bone matrix.
45
New cards
What does osteoblast do?
Builds new bone
46
New cards
What is the secretion of the osteoblasts composed of?
Collagen and calcium binding proteins
47
New cards
What hormone stimulates the secretion of the osteoblast cells?
Calcitonin
48
New cards
Where does the calcitonin hormone come from?
Thyroid
49
New cards
What are osteoclasts?
Derived from hematopoietic stem cells that become macrophages
50
New cards
What do osteoclasts do?
break down bone
51
New cards
What is the secretion of osteoclasts composed of?
Enzymes & acids
52
New cards
What hormone stimulates the secretion of osteoclasts?
Parathyroid (PTH)
53
New cards
Where does parathyroid hormone come from?
parathyroid gland
54
New cards
What are the 2 types of ossification?
intramembranous and endochondral
55
New cards
What type of tissue makes up endochondral ossification?
hyaline cartilage
56
New cards
What structure makes up the epiphyseal growth plate?
hyaline cartilage
57
New cards
Cartilage bones are referred to as ______
endochondral bone
58
New cards
What bones develop from endochondral ossification?
most of the skeleton
59
New cards
Endochondral ossification forms most of all bones inferior to the base of the skill *EXCEPT* ________
clavicles
60
New cards
What type of tissue makes up intramembranous ossification?
fibrous membrane
61
New cards
intramembranous ossification bones are called _______
membrane bones
62
New cards
What bones develop from intramembranous ossification?
flat bones, clavicles, and cranial bones
63
New cards
Where does intramembranous ossification **begin**?
within fibrous connective tissue membranes formed by mesenchymal cells
64
New cards
What can a deficiency of growth hormone during bone formation cause?
decreased epiphyseal plate activity
65
New cards
What is the **shaft** of the bone called?
diaphysis
66
New cards
What do you call each **end** of the bone?
Epiphysis
67
New cards
What is appositional growth?
Bones grow in width
68
New cards
The process of bones increasing in length is known as _______.
interstitial growth
69
New cards
When does interstitial growth stop?
Female- 18 years old
Male- 21 years old
Male- 21 years old
70
New cards
When does appositional growth occur and end?
It occurs throughout life
71
New cards
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
support, protection, movement, storage, blood cell formation
72
New cards
What is the osteon?
structural unit of compact bone
73
New cards
What are the structures that make up the osteon?
lamellae “rings”
74
New cards
What is the Haversian canal?
Channels in the bone that contain blood vessels and nerves
75
New cards
What is the epiphyseal growth plate?
cartilage junction between ends and shaft
76
New cards
What are the zones of the epiphyseal growth plate in order from top to bottom?
Resting zone
proliferation zone
hypertrophic zone
Calcification zone
ossification zone
proliferation zone
hypertrophic zone
Calcification zone
ossification zone
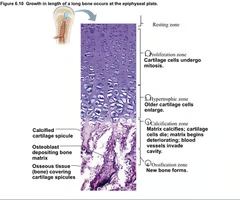
77
New cards
What is trabeculae?
Spongy bone
78
New cards
Where do you find trabeculae?
at the ends of long bones and in short, flat, and irregular bones
79
New cards
What vitamins and minerals are required for normal bone growth?
calcium, protein, magnesium, phosphorus, vitamin D, potassium, and fluoride.
80
New cards
Calcium functions in _______
nerve impulse transmission, muscle contraction, blood coagulation, secretion by glands and nerve cells, and cell division
81
New cards
immovable joints of the skull; Fibrous joint
Sutures
82
New cards
A fibrous joint connected by ligaments is classified as a _______
Syndesmosis
83
New cards
The connecting of the radius and ulna is a _______ joint
Syndesmosis
84
New cards
Peg-in-socket joints of teeth in alveolar sockets fibrous joint are _______
Gomphoses
85
New cards
Cartilaginous joints are classified as ______
Sychondrosis, symphysis
86
New cards
Two bones forming an **immovable joint** found in the vertebra or pubic joined by fibrocartilage is a _______
symphysis
87
New cards
What are the only **freely movable** joints?
Synovial
88
New cards
What are the six distinguishing features of synovial joints?
1. articular cartilage
2. joint cavity
3. articular capsule
4. synovial fluid
5. reinforcing ligaments
6. nerves and blood vessels
89
New cards
What is articular cartilage?
hyaline cartilage
90
New cards
Where is articular cartilage found?
At the ends of long bones where they unite by synovial joints
91
New cards
Which joints are made of fibrous connective tissue?
Sutures, syndesmoses, gomphoses
92
New cards
**fluid-filled, connective tissue sacs** that act as a ball bearing to reduce friction are called ______
bursae
93
New cards
The two main types of joint classification are ______.
structure and function
94
New cards
T/F: Hinge joints permit movement in only two planes.
False
95
New cards
T/F: Supination is the movement of the forearm in which the palm of the hand is turned superiorly.
True
96
New cards
An **immovable** joint, no movement
synarthrosis
97
New cards
A **slightly movable** joint
amphiarthrosis
98
New cards
A **freely movable** joint
diarthrosis
99
New cards
A joint that has **circular motion** flexion and extension.
condyloid joint
100
New cards
A joint that allows **side to side movement** and **up and down movemen**t.
pivot joint