Physpharm week 8&9
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:46 PM on 12/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
1
New cards
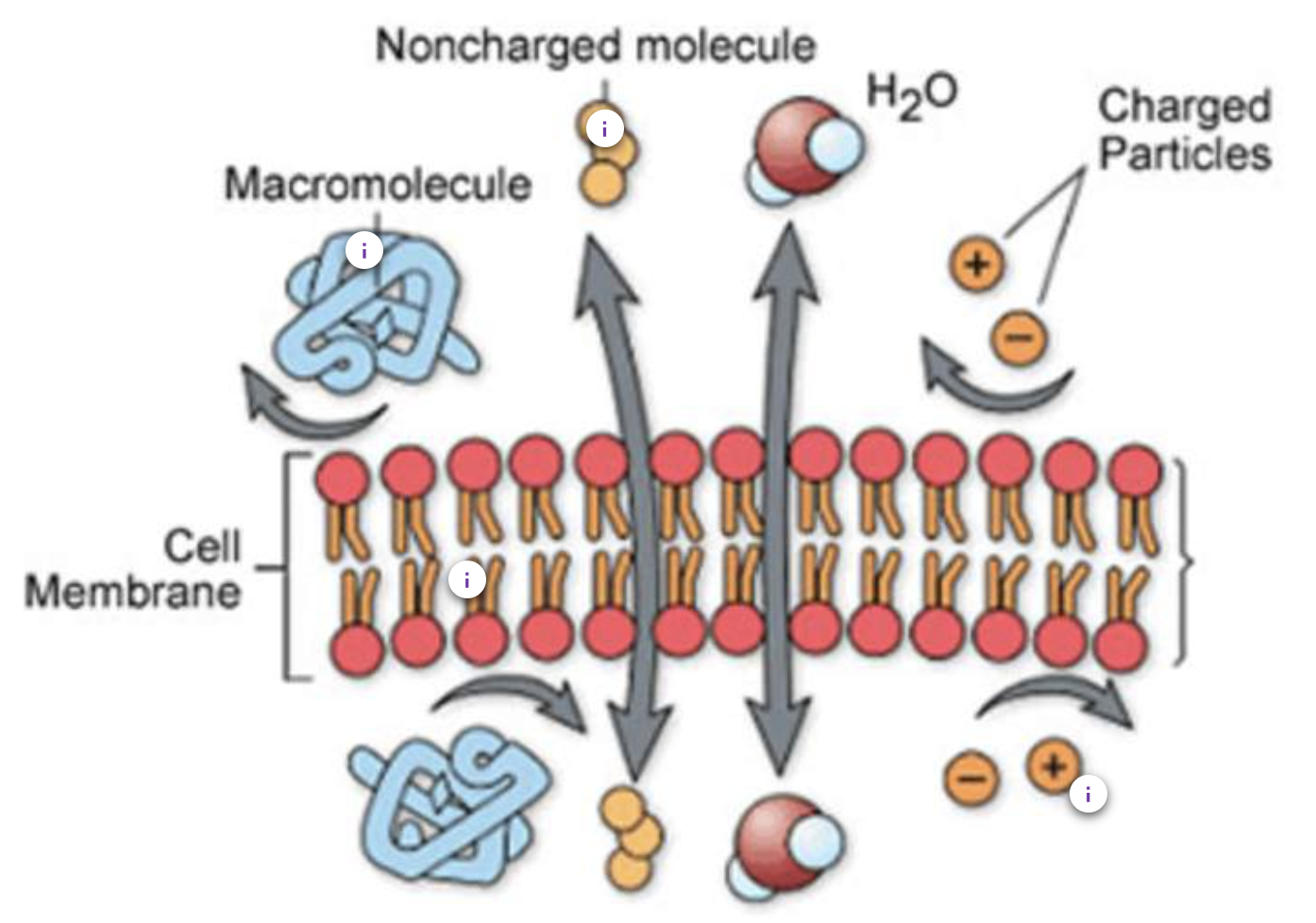
cell membrane
made of phospholipid bilayer, with proteins embedded into membrane
lipid soluble molecules can pass through
lipid soluble molecules can pass through
2
New cards
non charged molecule example
steroid hormones, pass through the lipid bilayer to interact with specific receptors
(steroid cases the receptor is located in cell, either in cytoplasm or nucleus)
(steroid cases the receptor is located in cell, either in cytoplasm or nucleus)
3
New cards
macromolecules example
peptide hormones
cannot go through lipid bilayer, must interact with specific receptor to transmit messages to cell
cannot go through lipid bilayer, must interact with specific receptor to transmit messages to cell
4
New cards
ions
carry a charge, cannot pass through lipid bilayer and have to rely on protein channels in membrane to move across
5
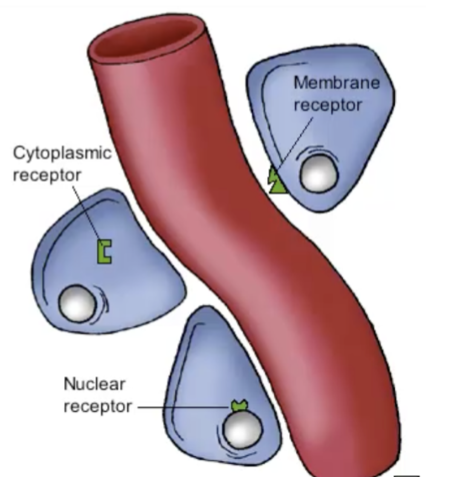
New cards
image of molecules that can pass through and can not
6
New cards
hormones
chemical molecules that have different properties
there are lipophilic steroid hormones, hydrophilic peptide hormones (bind to membrane-bound receptor)
there are lipophilic steroid hormones, hydrophilic peptide hormones (bind to membrane-bound receptor)
7
New cards
how does the endocrine system help maintain homeostasis
hormone expression can regulate many body functions, primarily controlled by negative feedback loops
the endocrine system acts as the negative feedback loop
hormones can be effectors and controlled variables
communication is key to maintain homeostasis
the endocrine system acts as the negative feedback loop
hormones can be effectors and controlled variables
communication is key to maintain homeostasis
8
New cards
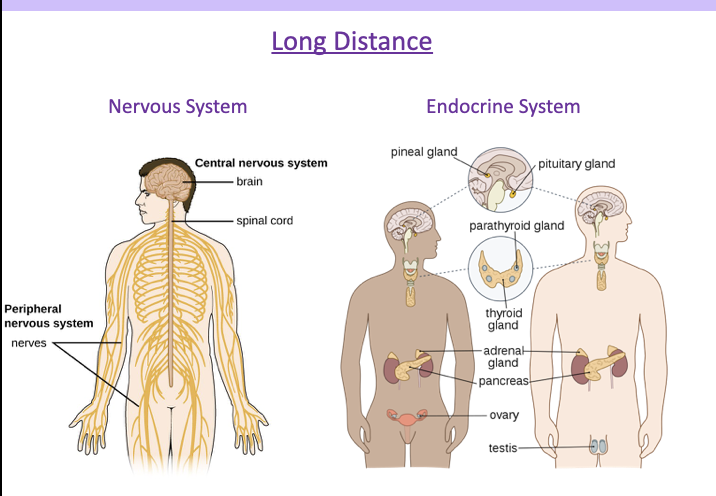
kind of communication in body: long distance communication
nervous system and endocrine system
9
New cards
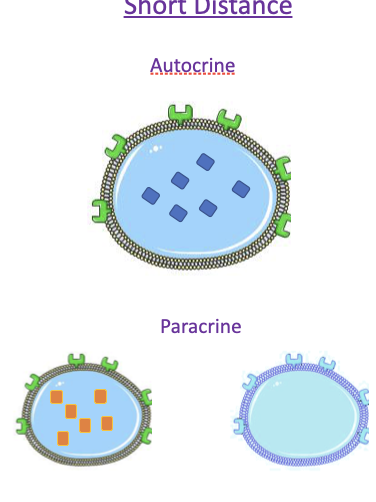
kind of communication in the body: short distance
autocrine and paracrine
10
New cards
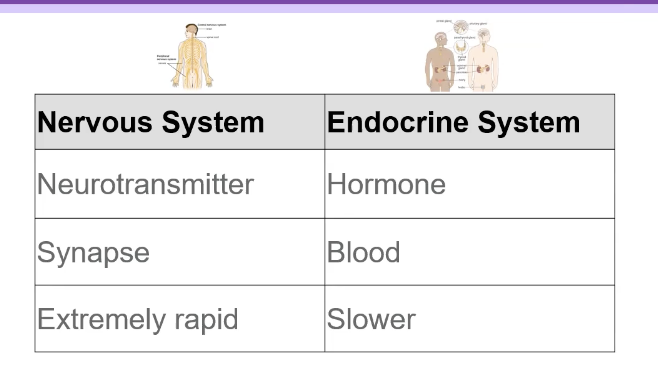
how does a neurotransmitter differ from a hormone and neurohormone
short distance vs long distance
11
New cards
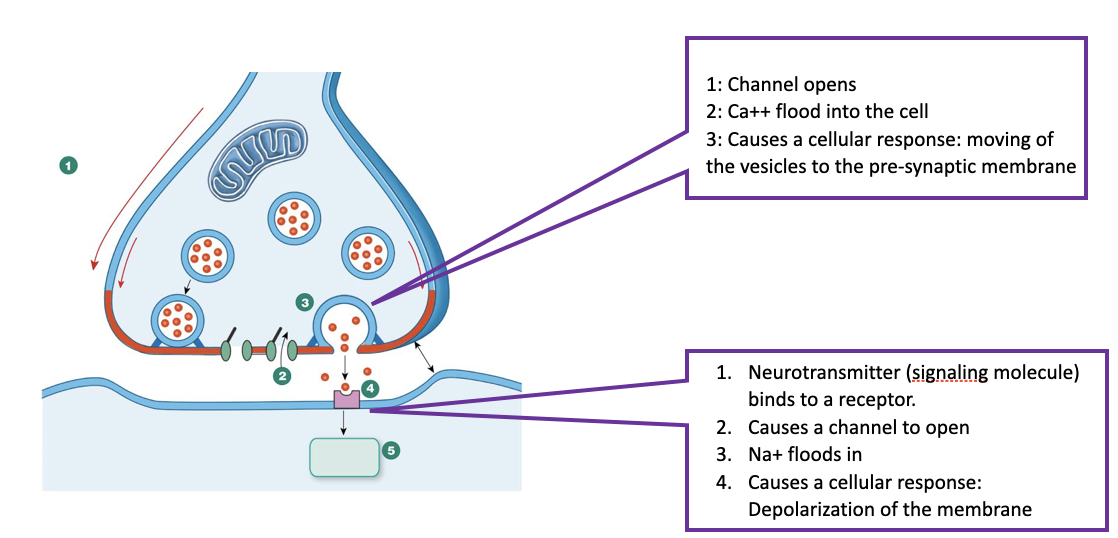
neurohormone
a chemical signal secreted into the blood from a neuron to act on a distant tissue
the brain releases all sorts of hormones, some hormones are released by glands, while others by neuronal tissue
ex. ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
the brain releases all sorts of hormones, some hormones are released by glands, while others by neuronal tissue
ex. ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
12
New cards
how does hormone signalling work?
receptor-ligand specificity
13
New cards
hormones are released to entire body, how are their effects controlled?
1. hormones are released into the blood stream
2. hormones circulate throughout the body
3. hormones will only bind to their specific receptors
4. only target cells will express that receptor
2. hormones circulate throughout the body
3. hormones will only bind to their specific receptors
4. only target cells will express that receptor
14
New cards
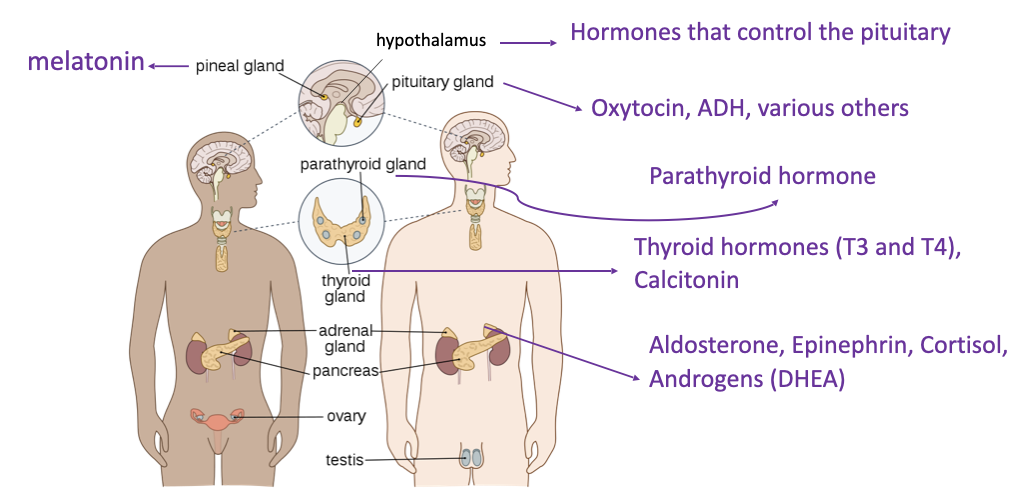
examples of endocrine glands and associated hormones
pineal gland - melatonin
hypothalamus - hormones that control the pituitary
pituitary gland - oxytocin, ADH
parathyroid gland - parathyroid hormone
thyroid gland - thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), calcitonin
adrenal gland - aldosterone, epinephrine, cortisol, androgens (DHEA)
hypothalamus - hormones that control the pituitary
pituitary gland - oxytocin, ADH
parathyroid gland - parathyroid hormone
thyroid gland - thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), calcitonin
adrenal gland - aldosterone, epinephrine, cortisol, androgens (DHEA)
15
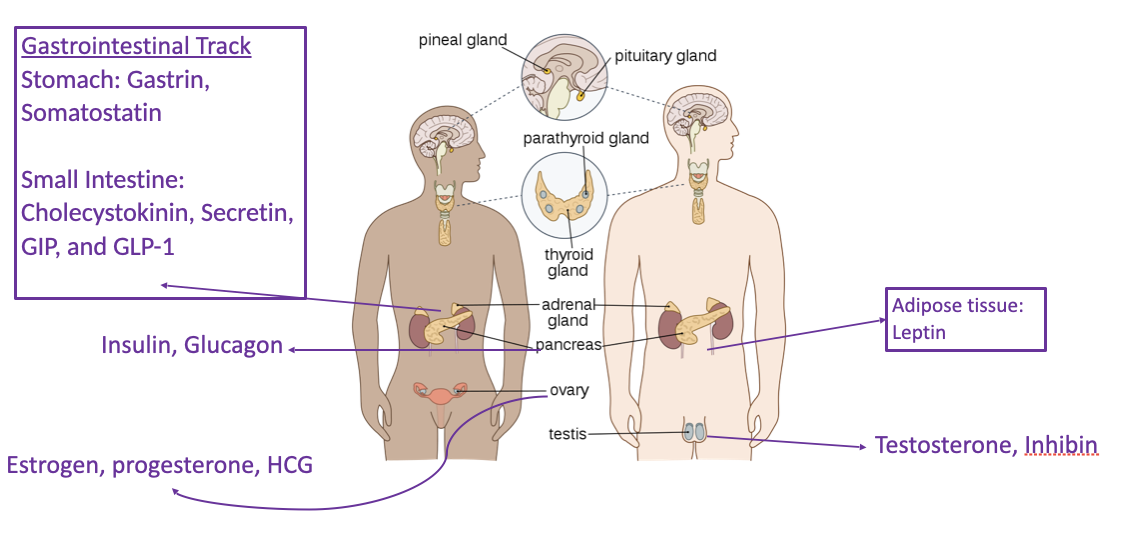
New cards
endocrine glands
16
New cards
protein hormones and how properties differ from other hormones
hormone example: hormones from the hypothalamus and the pituitary, pancreas
precursor: amino acids
location of receptor: membrane bound
time before onset of action: fast acting, short lived
precursor: amino acids
location of receptor: membrane bound
time before onset of action: fast acting, short lived
17
New cards
steroid hormones and how their properties differ from one another
hormone example: estrogen, testosterone, cortisol
precursor: cholesterol
solubility: lipophilic, bound to a protein
location of receptor: intracellular
time before onset of action: slow acting long lived
precursor: cholesterol
solubility: lipophilic, bound to a protein
location of receptor: intracellular
time before onset of action: slow acting long lived
18
New cards
amine hormones and how their properties differ from one another
hormone example: thyroid hormone, epinephrine
precursor: tyrosine
solubility: some are lipophilic and bound to protein, some are hydrophilic and circulate freely
location of receptor: lipophilic = intracellular, hydrophilic = membrane bound receptor
time before onset of action: lipophilic - slow acting, hydrophilic - fast acting
precursor: tyrosine
solubility: some are lipophilic and bound to protein, some are hydrophilic and circulate freely
location of receptor: lipophilic = intracellular, hydrophilic = membrane bound receptor
time before onset of action: lipophilic - slow acting, hydrophilic - fast acting
19
New cards
how do hormones exert their activity on the target cell
membrane receptors: the cell will respond by activating or changing pre-exisiting proteins in the cytoplasm
cytoplasmic or nuclear receptors: the cell will respond by transcribing the DNA to make new mRNA and build proteins
Protein hormones: through secondary messengers
steroid hormones: through new gene transcription and protein production
cytoplasmic or nuclear receptors: the cell will respond by transcribing the DNA to make new mRNA and build proteins
Protein hormones: through secondary messengers
steroid hormones: through new gene transcription and protein production
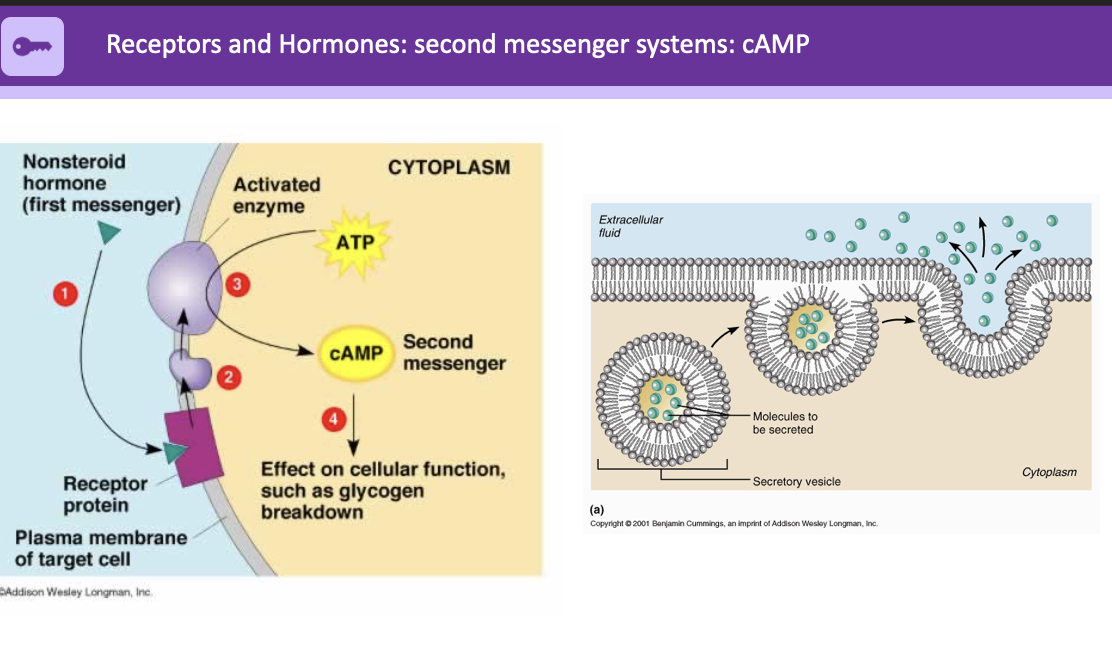
20
New cards
receptors and hormones: second messenger systems: cAMP
1. non-steroid hormone (First messenger)
2. receptor protein attaches to activated enzyme
3. ATP cycles through to cAMP which is second messenger
4. effect on cellular function, such as glycogen breakdown
2. receptor protein attaches to activated enzyme
3. ATP cycles through to cAMP which is second messenger
4. effect on cellular function, such as glycogen breakdown
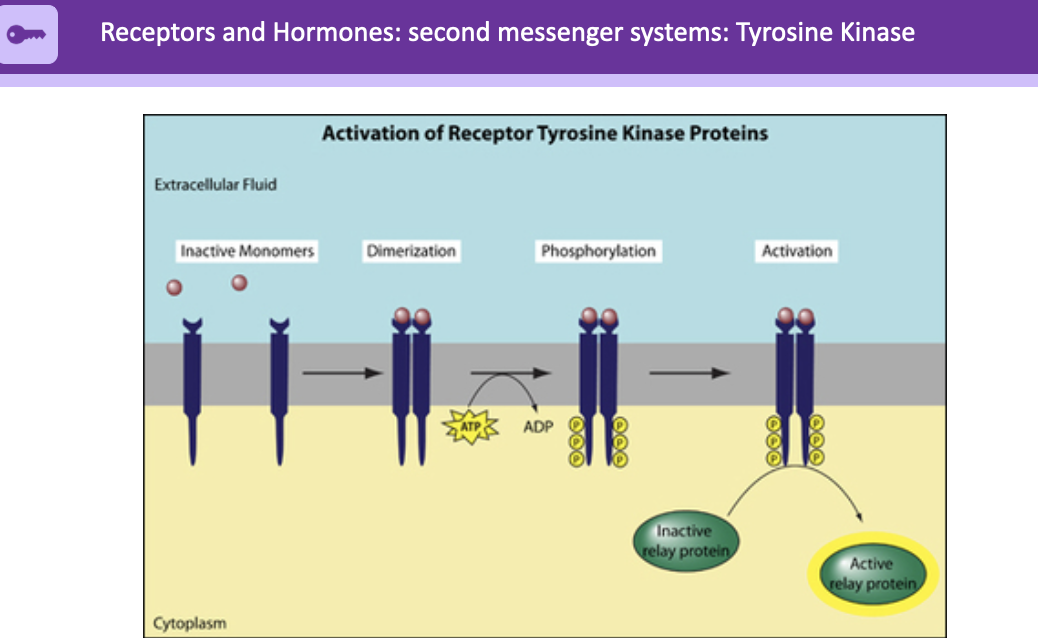
21
New cards
receptors and hormones: second messenger systems: tyrosine kinase
inactive monomers in extracellular fluid
goes through dimerization
ATP turned into ADP; leads to phosphorylation ADP on the bottom ends of proteins in cytoplasm
activation after, leads to active relay protein
goes through dimerization
ATP turned into ADP; leads to phosphorylation ADP on the bottom ends of proteins in cytoplasm
activation after, leads to active relay protein
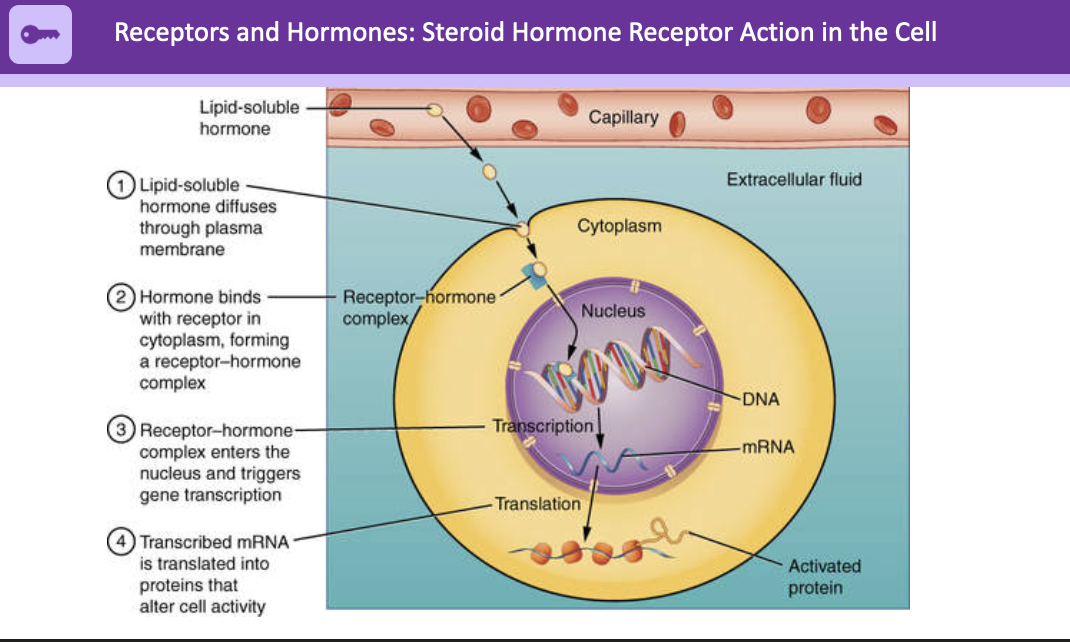
22
New cards
receptors and hormones: steroid hormone receptor action in the cell
1. lipid-soluble hormone diffuses through plasma membrane
2. hormone binds with receptor in cytoplasm, forming a receptor-hormone complex
3. receptor-hormone complex enters the nucleus and triggers gene transcription
4. transcribed mRNA is translated into proteins after cell activity
2. hormone binds with receptor in cytoplasm, forming a receptor-hormone complex
3. receptor-hormone complex enters the nucleus and triggers gene transcription
4. transcribed mRNA is translated into proteins after cell activity
23
New cards
receptor and hormones: Second messenger systems: GPCR and ion channels
ion channel and g-protein and receptor next to each other
receptor binds to hormone
when bound ion channel opens from g-protein moving bottom part
ions flow throughwh
receptor binds to hormone
when bound ion channel opens from g-protein moving bottom part
ions flow throughwh
24
New cards
what does hypothalamus regulate
body temperature
water balance
energy production
thirst
hunger
sexual behaviour
water balance
energy production
thirst
hunger
sexual behaviour
25
New cards
hormone properties and how they affect receptor interactions
hormone binds to specific receptor, receptor goes to target cell which elicits a cellular response
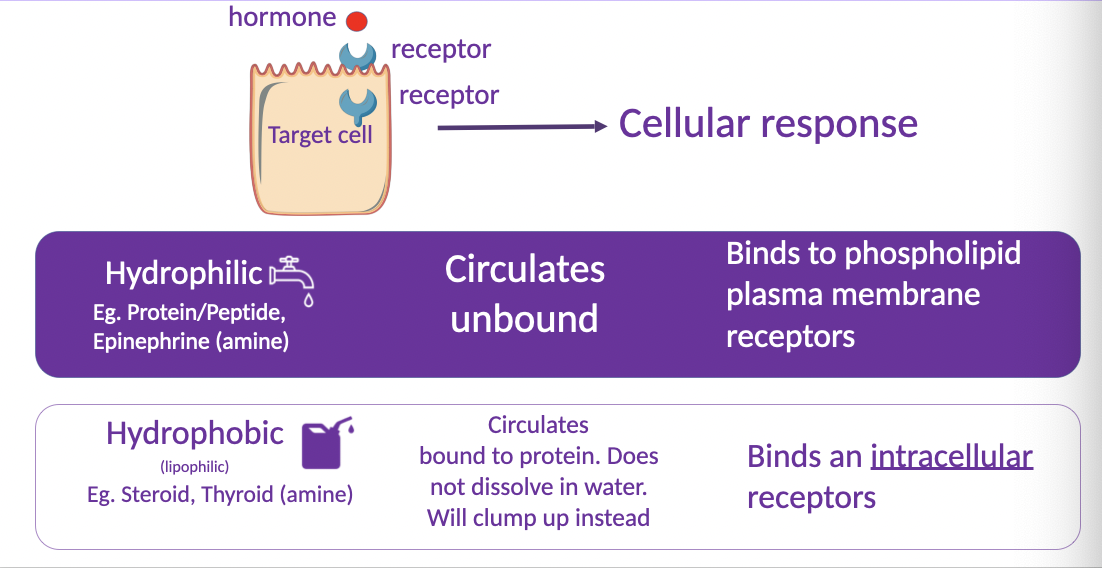
26
New cards
how does the hypothalamus regulate hormone release in the posterior pituitary
a. neuronal tissue
b. regulates kidney, breast tissue, uterus, human behaviour
c. hypothalamus to the posterior pituitary
d. hypothalamic hypophyseal tract
b. regulates kidney, breast tissue, uterus, human behaviour
c. hypothalamus to the posterior pituitary
d. hypothalamic hypophyseal tract
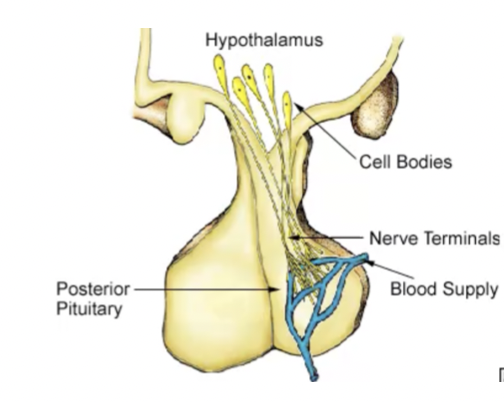
27
New cards
how does the hypothalamus regulate hormone release in the anterior pituitary
a. epithelial cells
b. affects breast tissue, thyroid, adrenal, gonad, various tissues
c. hypothalamus to anterior pituitary
d. hypothalamic hypophyseal portal system
b. affects breast tissue, thyroid, adrenal, gonad, various tissues
c. hypothalamus to anterior pituitary
d. hypothalamic hypophyseal portal system
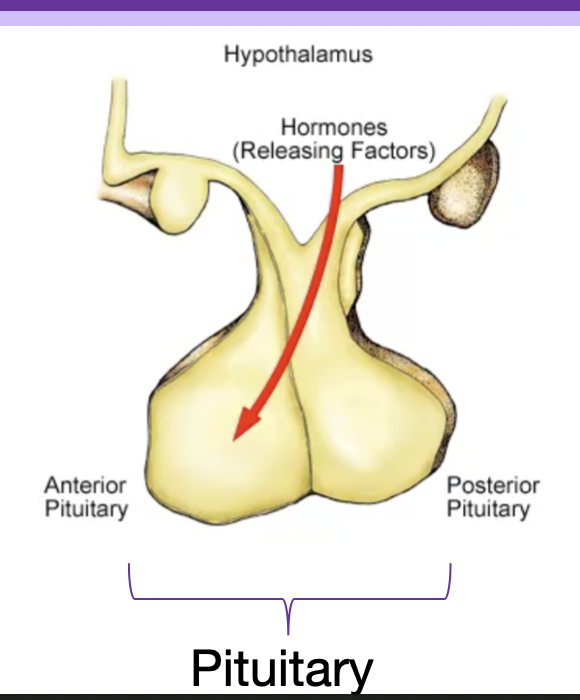
28
New cards
relationship between hypothalamus, anterior pituitary and posterior pituitary gland
hypothalamus to anterior pituitary
hypothalamic hypophyseal portal system
hypothalamus to the posterior pituitary
hypothalamic hypophyseal tract
hypothalamic hypophyseal portal system
hypothalamus to the posterior pituitary
hypothalamic hypophyseal tract
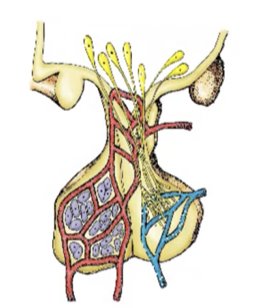
29
New cards
what hormones are released from the posterior pitutary and what effects do they have on the body?
the hypothalamus is connected to the posterior via the hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract
hormones:
a. antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
- peptide neurohormone
function: promotes water reabsorption in kidneys
b. oxytocin
- peptide neurohormone
function: promotes uterine contractions and milk excretion, makes you feel happy/comforted
hormones:
a. antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
- peptide neurohormone
function: promotes water reabsorption in kidneys
b. oxytocin
- peptide neurohormone
function: promotes uterine contractions and milk excretion, makes you feel happy/comforted
30
New cards
hypothalamus and the posterior pituitary
release of ADH
- dehydration
- hyperosmolarity: increased osmolarity in extracellular fluid
inhibition of ADH:
- over hydration
- hyposmoloarity: decreased osmolarity in the extracellular fluid
- alcohol
- high blood pressure
- dehydration
- hyperosmolarity: increased osmolarity in extracellular fluid
inhibition of ADH:
- over hydration
- hyposmoloarity: decreased osmolarity in the extracellular fluid
- alcohol
- high blood pressure
31
New cards
what is diabetes insipidus
insufficent ADH, or ADH activation in the kidney
32
New cards
what causes diabetes insipidus
brain tumour
brain surgery
brain injury
brain surgery
brain injury
33
New cards
what are symptoms of diabetes insipidus
producing lots of urine
urine is very dilute
dehydration
sensations of thirst
urine is very dilute
dehydration
sensations of thirst
34
New cards
hormone replacement theory for diabetes insipidus
replace the hormone ADH
drug is called desmopressin
its a small peptide molecule and acts on the kidneys
can be administered through a pill, injection or a nasal spray
drug is called desmopressin
its a small peptide molecule and acts on the kidneys
can be administered through a pill, injection or a nasal spray
35
New cards
oxytocin and positive feedback loop
oxytocin causes the uterine muscles to contract
this pushes baby down harder to be delivered
nerve impulses sent back to brain that causes more oxytocin released
this pushes baby down harder to be delivered
nerve impulses sent back to brain that causes more oxytocin released
36
New cards
what are parts of anterior pituitary
hypothalamus
hypothalamic-hypopseal portal system
endocrine cells of the anterior pituitary
hypothalamic-hypopseal portal system
endocrine cells of the anterior pituitary
37
New cards
hormones of the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary
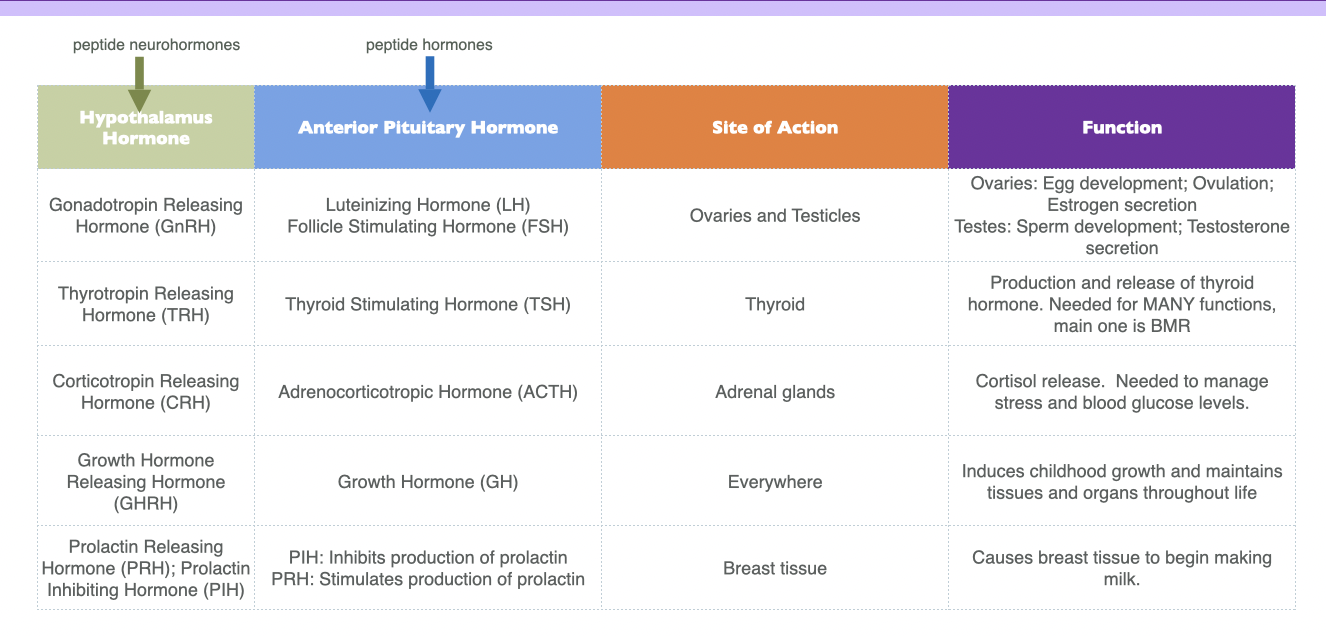
38
New cards
chart 2 hormones of hypothalamus and anterior with target tissues
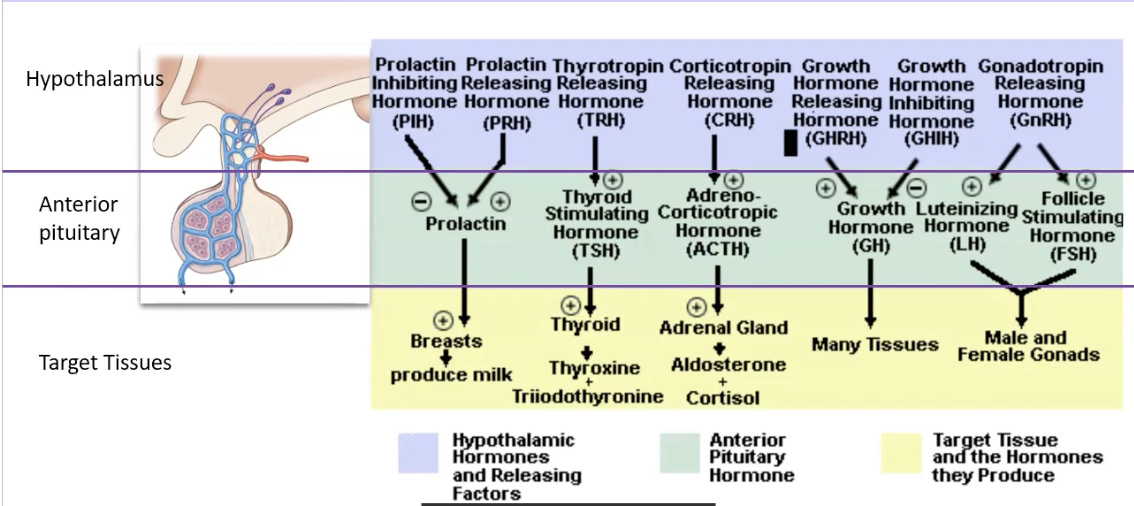
39
New cards
role of hypothalamus
links the nervous system to the endocrine system, regulates the pituitary gland
40
New cards
how does the hypothalamus regulate hormone release in the posterior pituitary
hypothalamic-hypopseal tract
41
New cards
how does the hypothalamus regulate hormone release in the anterior pituitary
hypothalamic-hypopseal portal system
42
New cards
What hormones are released from the posterior pituitary and what effects do they have on the body?
ADH (water balance) and Oxytocin (happy hormones, and reproduction)
43
New cards
What is an example of a pharmacological therapeutic for hormone deficiency?
hormone replacement therapy
44
New cards
reproductive endocrinology
ultimate purpose is to produce a cell (gamete) that can be combined with another cell to create a new organism
45
New cards
chromosomes
made up of long strands of DNA and contain genetic material that makes up an organism
they form an X shape, one half is the paternal (sperm) contribution and other is maternal (oocyte) contribution
they form an X shape, one half is the paternal (sperm) contribution and other is maternal (oocyte) contribution
46
New cards
sister chromatids
half of the chromosome is replicated and it is connected with its own copy to make sister chromatids
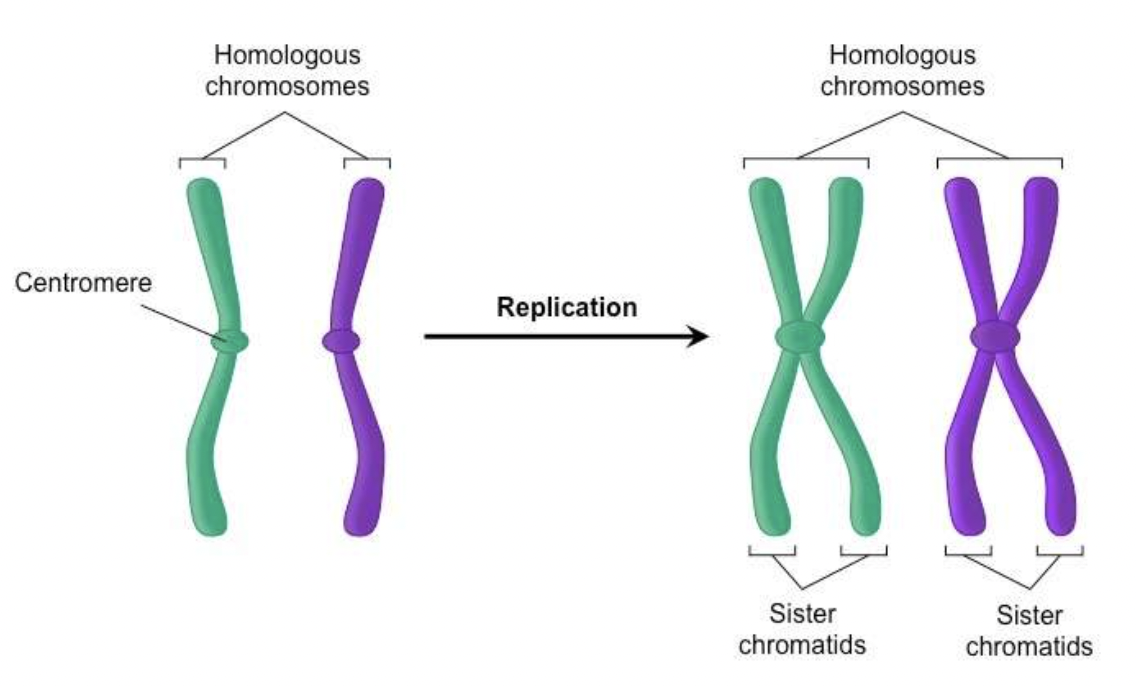
47
New cards
diploid
refers to the number of distinct chromosomes, 23 chromosomes come from sperm and other 23 come from oocyte, together forms a diploid cell with 46 chromosomes
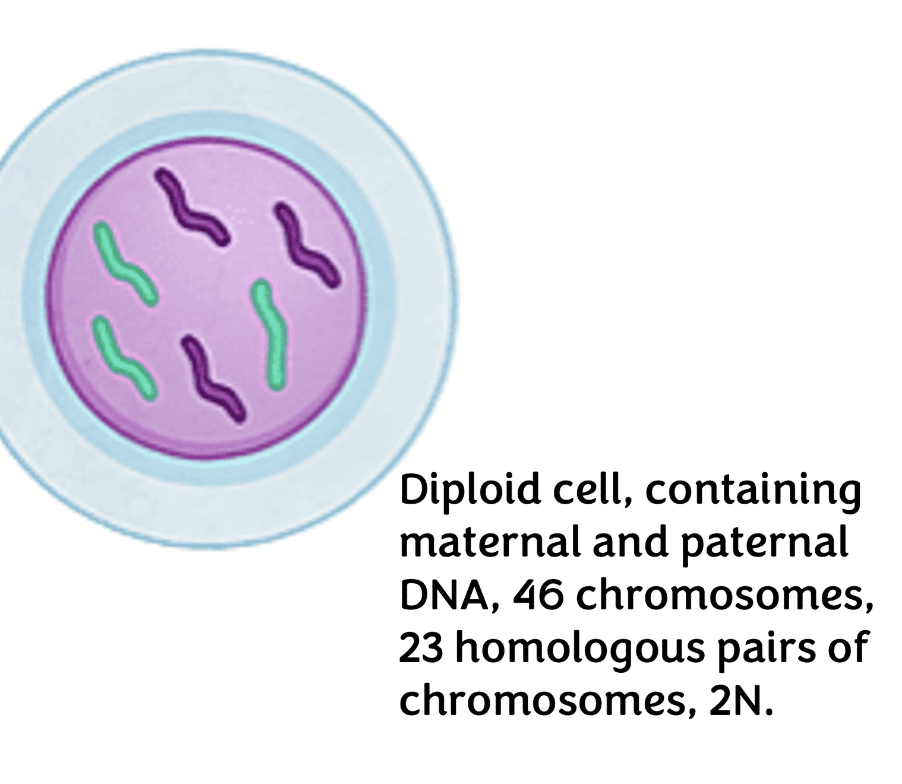
48
New cards
haploid
refers to the number of distinct chromosomes but only half are present gives half of DNA to daughter cell and other half to different daughter cell
49
New cards
gametes
haploid cells involved in fertilization
they are made in the gonads of the parent organism
they are made in the gonads of the parent organism
50
New cards
germ line cells
cells that give rise to the gametes
these cells will eventually become gametes through the process of meiosis
they reside in the testes or the ovaries
these cells will eventually become gametes through the process of meiosis
they reside in the testes or the ovaries
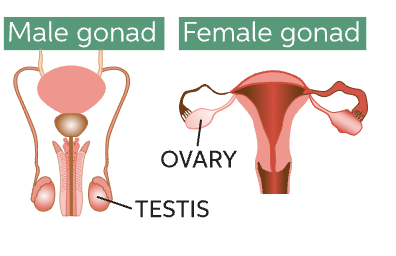
51
New cards
meiosis
the process through which a diploid cell becomes a haploid gamete to be used in fertilization and create a new organism
the phases happen twice in meiosis
the phases happen twice in meiosis
52
New cards
interphase
cell replicates DNA, 46 distinct chromosomes, now has 2 copies of each chromosomes and each chromosome has a sister chromatid
53
New cards
prophase I
homologous pairs of sister chromatids for a tetrad and exchange DNA in a crossing over event
swap certain sections of DNA
swap certain sections of DNA
54
New cards
metaphase I
sister chromatids form a line in the middle of the cell and spindle fibres connect them
homologous pairs are now separated from each other, the resulting daughter cells will have 23 distinct chromosomes that each have sister chromatid and go from 2N to N
homologous pairs are now separated from each other, the resulting daughter cells will have 23 distinct chromosomes that each have sister chromatid and go from 2N to N
55
New cards
anaphase I
sister chromatids are pulled away from their homologous pairs to opposite sides of the cell
56
New cards
telophase I and cytokinesis
cell membrane pinches in the middle to create 2 daughter cells
one that has one set of sister chromatids and the other has other set
these 2 daughter cells have a DNA compliment of N
each chromosome has a sister, it still has 46 chromosomes but only 23 distinct
2 daughter cells need to undergo meiosis II
one that has one set of sister chromatids and the other has other set
these 2 daughter cells have a DNA compliment of N
each chromosome has a sister, it still has 46 chromosomes but only 23 distinct
2 daughter cells need to undergo meiosis II
57
New cards
prophase II
chromatin clumping
these chromosomes condense in each daughter cell and a new set of spindle fibers form
the chromatids move to line up in centre of cell
these chromosomes condense in each daughter cell and a new set of spindle fibers form
the chromatids move to line up in centre of cell
58
New cards
metaphase II
spindle fibers attach to each of the sister chromatids to prepare to seperate them apart
59
New cards
anaphase II
sister chromatids are seperated into opposite sides of the cell
60
New cards
telephase II
creates 4 different sex cells
each daughter cell now splits into 2 new daughter cells, forming 4 genetically distinct cells
these cells have 23 chromosomes, or a DNA compliment of N
each daughter cell now splits into 2 new daughter cells, forming 4 genetically distinct cells
these cells have 23 chromosomes, or a DNA compliment of N
61
New cards
uterer
connects kidney to bladder
62
New cards
bladder
stores urine and is connected to the uterer through a tube that runs through the prostate
63
New cards
seminal vesicle
contributes a large amount of fluid to the semen during ejaculation
64
New cards
prostate
the gland secretes enzymes and fluid to help neutralize the acidic environment of the urethra, and the vagina
without fluids the prostate gland to neutralize acidic environment of vagina, sperm would die
without fluids the prostate gland to neutralize acidic environment of vagina, sperm would die
65
New cards
vans deferens
tube connecting testes to uterer that conducts sperm during ejaculation
66
New cards
ejaculatory duct
drains into the urethra
67
New cards
Bulbourethral gland
releases a neutralizing and lubricating fluid into the uterer prior to ejaculation
the fluid is alkaline and is necessary to neutralize the acidic environment of the urethra that occurs after urination
prior to ejaculation
the fluid is alkaline and is necessary to neutralize the acidic environment of the urethra that occurs after urination
prior to ejaculation
68
New cards
urethra
conducts both urine and sperm to the penis and out of body
69
New cards
penis
largely of erectile tissue and acts as the conduit for sperm transfer during copulation, conduit for urination
70
New cards
testes
site of sperm production
produce and secrete 2 hormones, testosterone and inhibin in response to gonadotropins from the anterior pituitary
produce and secrete 2 hormones, testosterone and inhibin in response to gonadotropins from the anterior pituitary
71
New cards
epididymis
site of sperm maturation and storage
72
New cards
fimbrea
capture the oocyte after its released by the ovary at ovulation
the fimbrea are finger like projections that sweep the oocyte into the fallopian tube
the fimbrea are finger like projections that sweep the oocyte into the fallopian tube
73
New cards
uterine (fallopian) tube
where sperm and oocyte will meet and fertilization will occur
uterine tube contains cilia that help move the oocyte or embryo along the uterine tube of the uterus
movement of the uterine tube is regulated in part by progesterone
uterine tube contains cilia that help move the oocyte or embryo along the uterine tube of the uterus
movement of the uterine tube is regulated in part by progesterone
74
New cards
ovary
site of developing female gamete
responsive to FSH and LH and it secretes estrogen and progesterone
the ovary will release the oocyte during ovulation
responsive to FSH and LH and it secretes estrogen and progesterone
the ovary will release the oocyte during ovulation
75
New cards
uterus
muscular organ that accommodate and maintains a pregnancy
site of normal embryo implantation into the endometrium
development of the endometrium is regulated by estrogen, while the maturation of the endometrium is regulated by progesterone
site of normal embryo implantation into the endometrium
development of the endometrium is regulated by estrogen, while the maturation of the endometrium is regulated by progesterone
76
New cards
cervix
forms the connection between the vaginal canal and the uterus
secretes mucus that varies during the menstrual cycle from thin (facilitate sperm entry) to thick (prevent sperm entry)
higher estrogen levels causes cervical mucus to be thinner, while higher progesterone levels cause the cervical mucus to be thicker
secretes mucus that varies during the menstrual cycle from thin (facilitate sperm entry) to thick (prevent sperm entry)
higher estrogen levels causes cervical mucus to be thinner, while higher progesterone levels cause the cervical mucus to be thicker
77
New cards
vagina
receives the penis and sperm during copulation
allows for the discharge of fluid during menstruation, and the birth of the baby
allows for the discharge of fluid during menstruation, and the birth of the baby
78
New cards
spermatocytes
adult stem cell
developing sperm cells
developing sperm cells
79
New cards
sertoli cells
support and regulate spermatogenesis
blood testes barrier
produce inhibin
blood testes barrier
produce inhibin
80
New cards
leydig cells
produce testosterone
located in the space between seminiferous tubules
located in the space between seminiferous tubules
81
New cards
how is sperm developed (spermatogenesis)
Meiosis occurs in the testes to produce haploid gametes
a. Spermatozoa
b. Spermatids
c. 2 degree spermatocytes
d. 1 degree spermatocytes
e. Spermatogonia
a. Spermatozoa
b. Spermatids
c. 2 degree spermatocytes
d. 1 degree spermatocytes
e. Spermatogonia
82
New cards
features of mature sperm
head
- nucleus
- acrosome
tail
- neck
- middle piece
- principal piece
- end piece
- nucleus
- acrosome
tail
- neck
- middle piece
- principal piece
- end piece
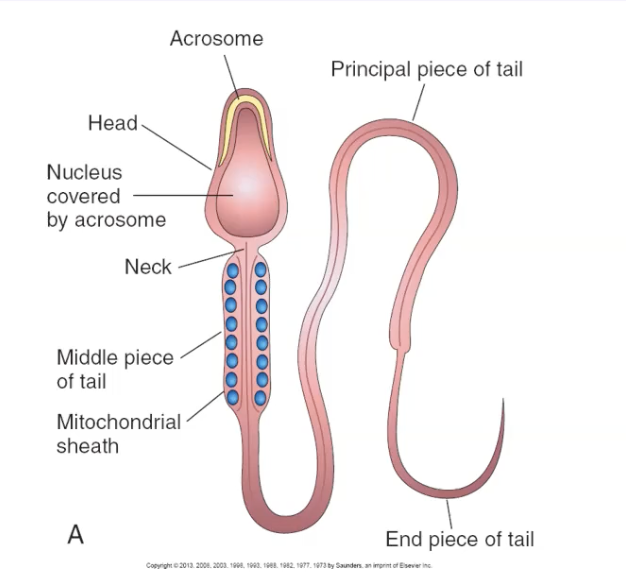
83
New cards
how is sperm development regulated by hormones and negative feedback loops
FSH - inhibin
LH - testosterone
class of hormone - steroid, comes from cholesterol
hydrophobic
intracellular is where receptors located
transported into blood by albumin
LH - testosterone
class of hormone - steroid, comes from cholesterol
hydrophobic
intracellular is where receptors located
transported into blood by albumin
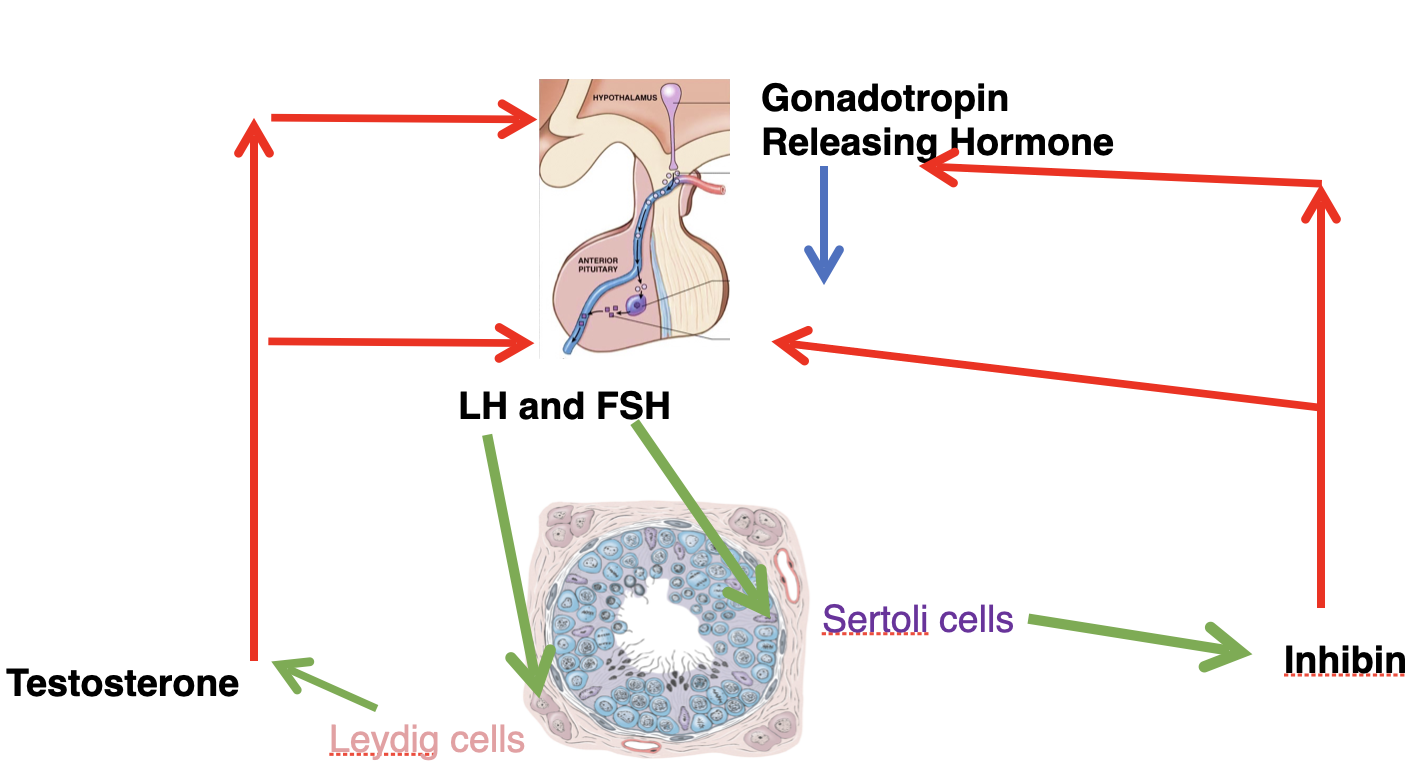
84
New cards
what are the effects of testosterone on the body
muscle mass, lower voice, secondary hair growth, blood cell count
- growth of prostate
- secondary sex characteristics
- vocal changes
- red blood cell count
- anabolic reactions (muscle mass)
- growth of prostate
- secondary sex characteristics
- vocal changes
- red blood cell count
- anabolic reactions (muscle mass)
85
New cards
anti-GnRH - treatment for prostate cancer
- prevents the secretion of LH and FSH
- prevents secretion of testosterone from the testes
- prevents the growth of prostate
- prevents secretion of testosterone from the testes
- prevents the growth of prostate
86
New cards
how are oocytes made (oogenesis)
oogonia - diploid stem cells of ovaries
begin meiosis I, stops at prophase
remains inactive in cortex of immature ovary until puberty
small number activated each month - recruited by FSH
only one continues through meiosis
begin meiosis I, stops at prophase
remains inactive in cortex of immature ovary until puberty
small number activated each month - recruited by FSH
only one continues through meiosis
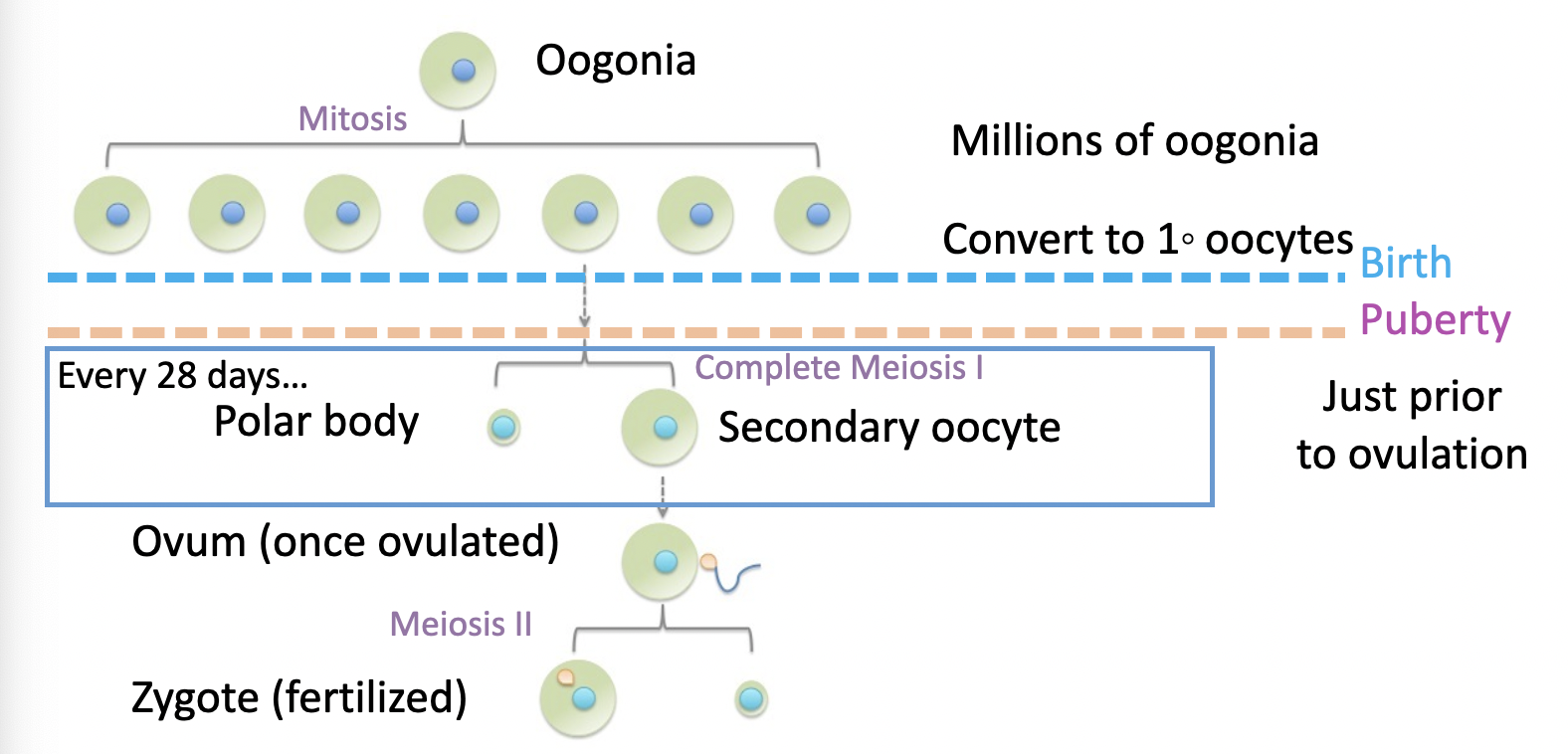
87
New cards
how does gamete development differ between sperm and oocyte
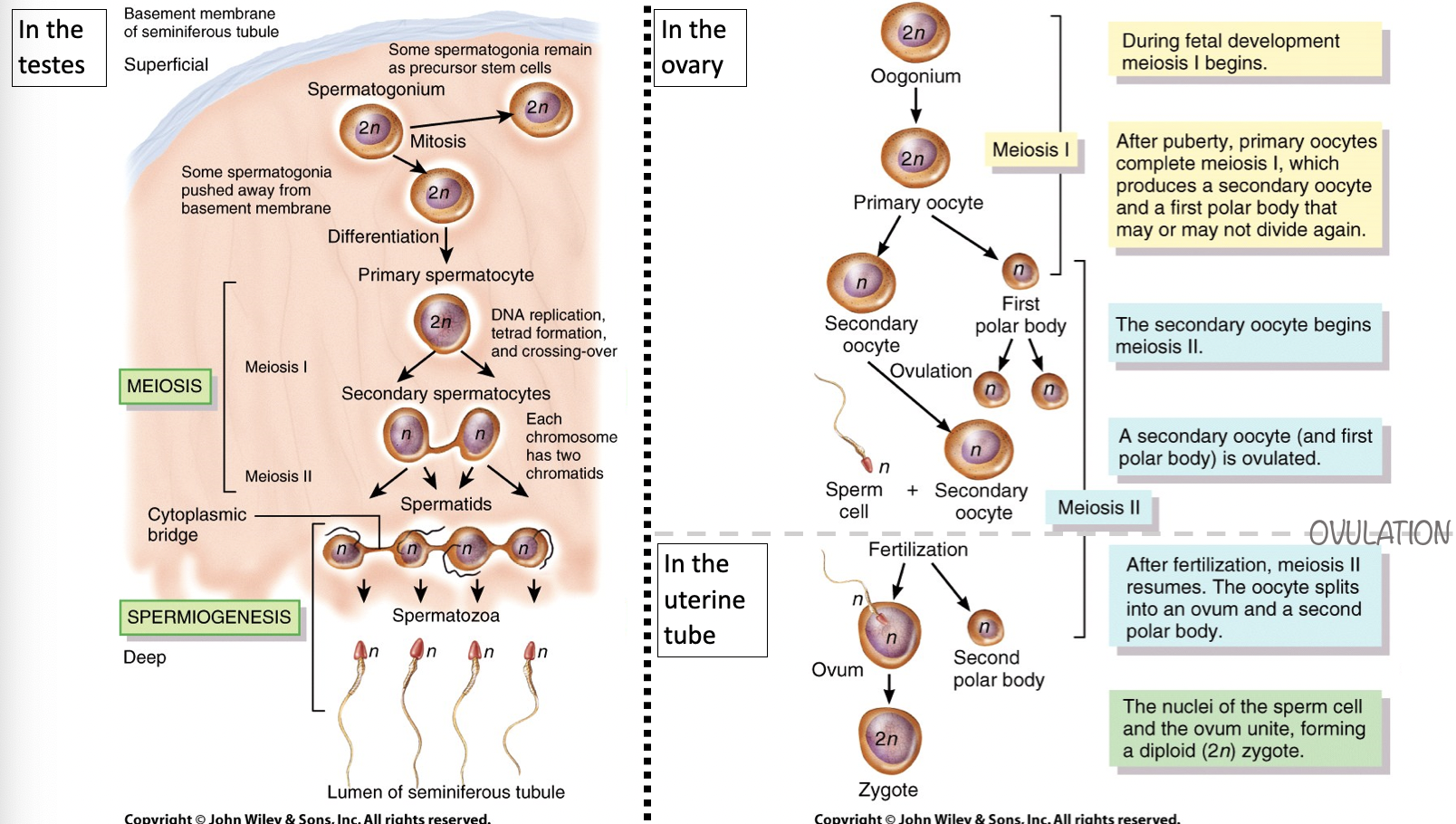
88
New cards
what is folliculogeneis and how does it occur
folliculogenesis of the maturing oocyte
male: the cells that help sperm develop are part of the testes, they include Sertoli and Leydig cells
female: the cells that help the oocyte develop make up the follicle that surrounds the oocyte, they are called Theca and Granulosa cells
*look at week 9 lecture 1 slide 21*
male: the cells that help sperm develop are part of the testes, they include Sertoli and Leydig cells
female: the cells that help the oocyte develop make up the follicle that surrounds the oocyte, they are called Theca and Granulosa cells
*look at week 9 lecture 1 slide 21*
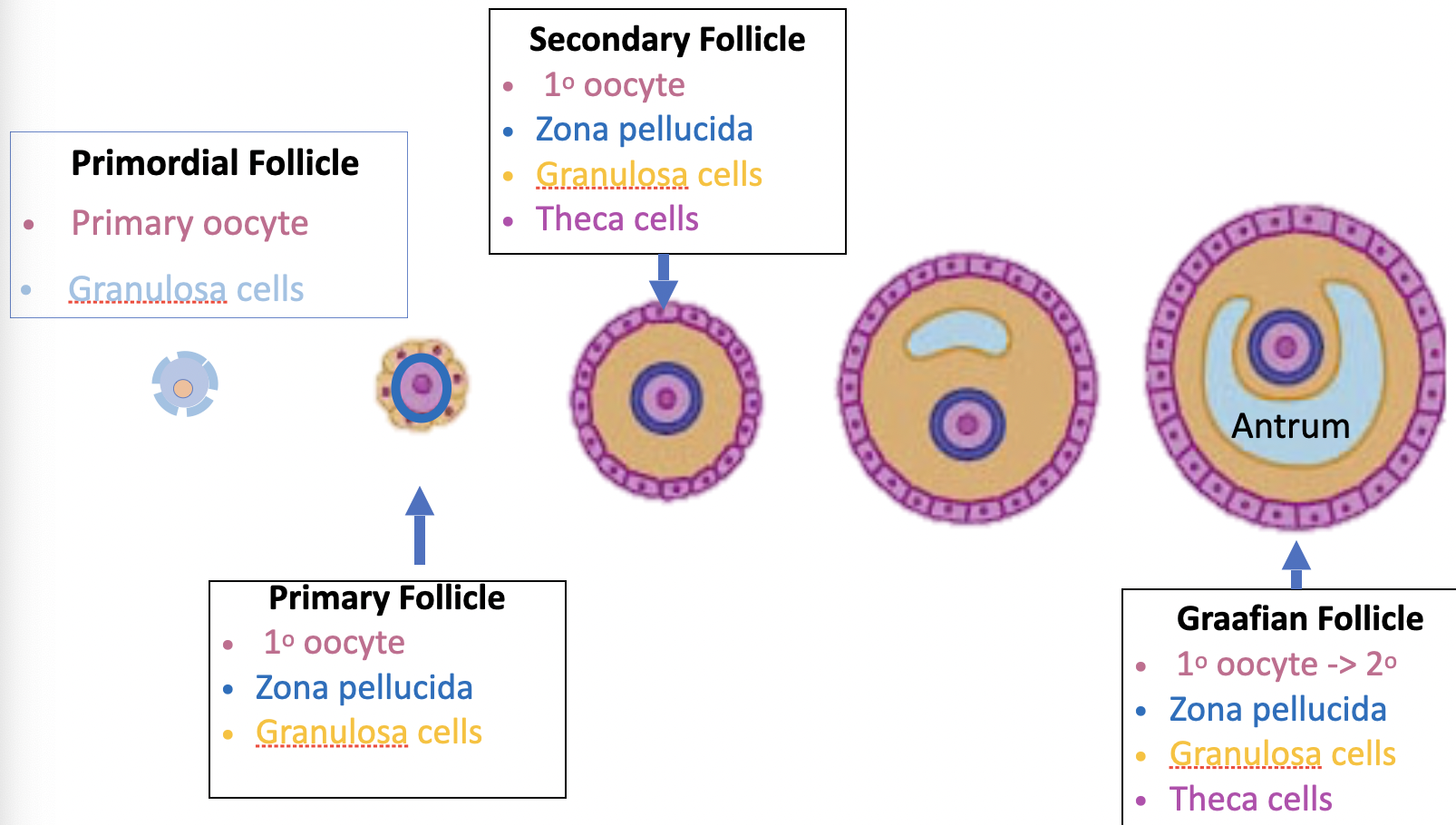
89
New cards
what is the viability of gametes
oocytes
- usually fertilized within 12 hours of ovulation
- cannot be fertilized after 24 hours
spermatozoa
- viable for approximately 48 hours in female reproductive tract
- usually fertilized within 12 hours of ovulation
- cannot be fertilized after 24 hours
spermatozoa
- viable for approximately 48 hours in female reproductive tract
90
New cards
what are the support cells in folliculogensis
Theca cells and Granulosa cells
91
New cards
what are the stages of the female reproductive cycle and how are they regulated by hormone
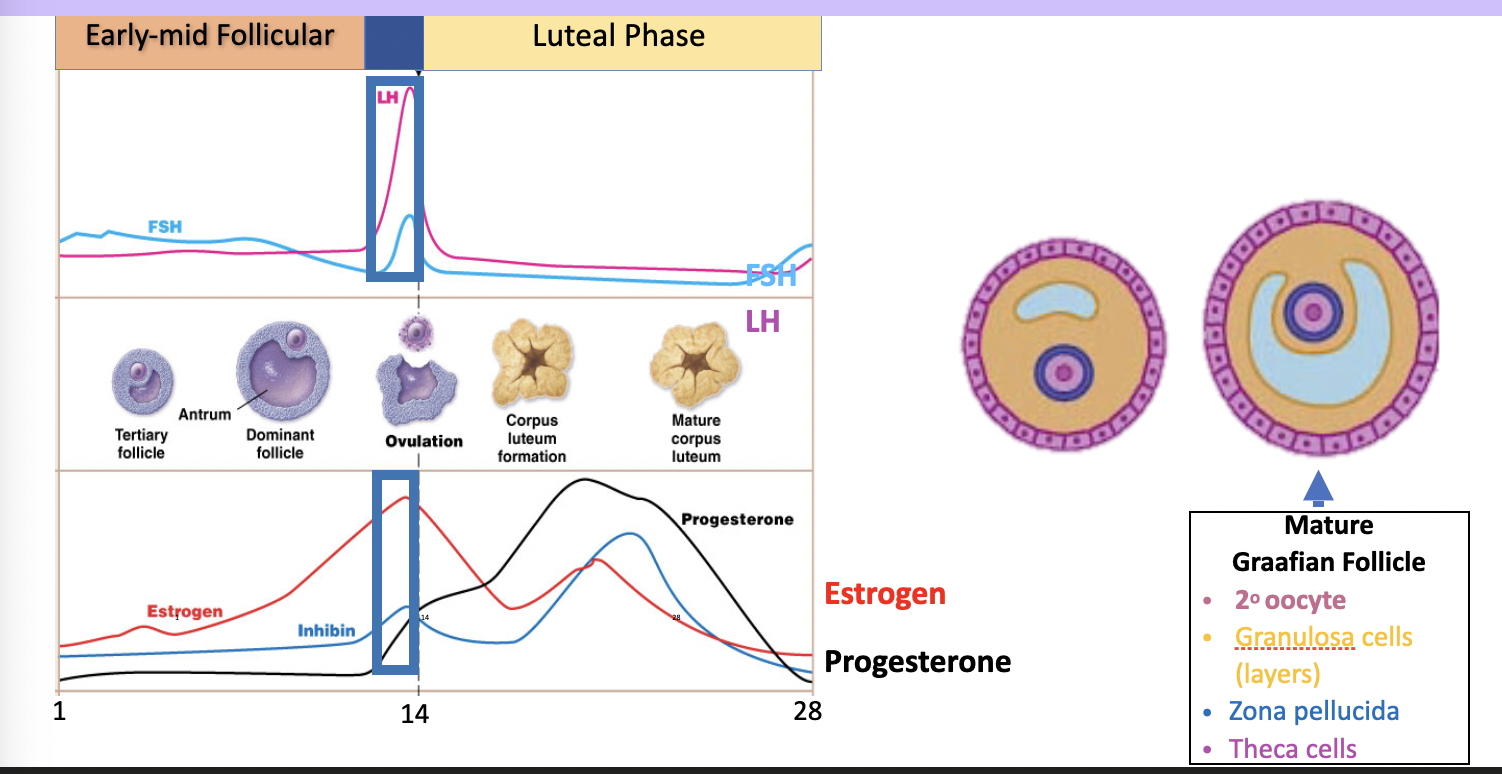
92
New cards
how are female hormones regulated
theca and granulose cells: produce sex steroids
93
New cards
how hormones are regulated using negative and positive feedback loops
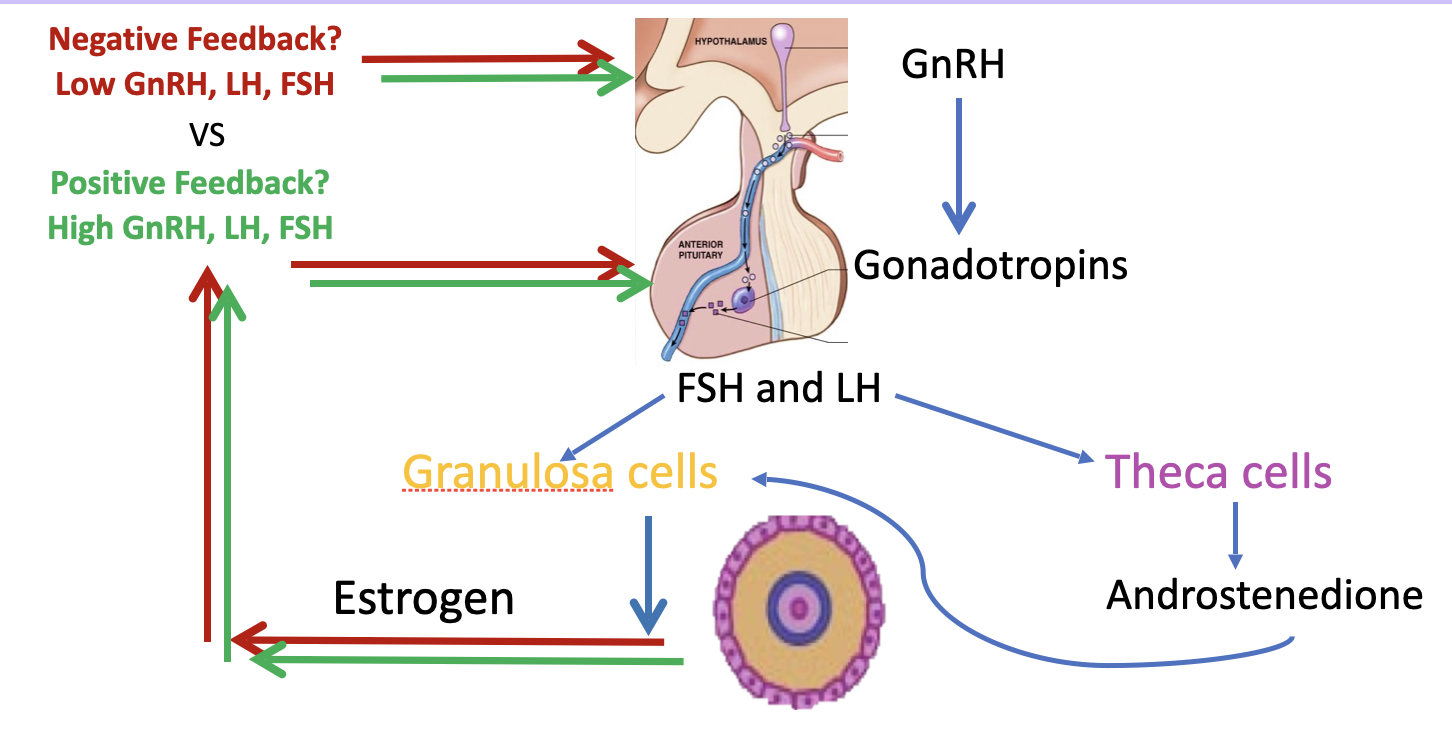
94
New cards
what are the events that occur in the uterus during the reproductive cycle
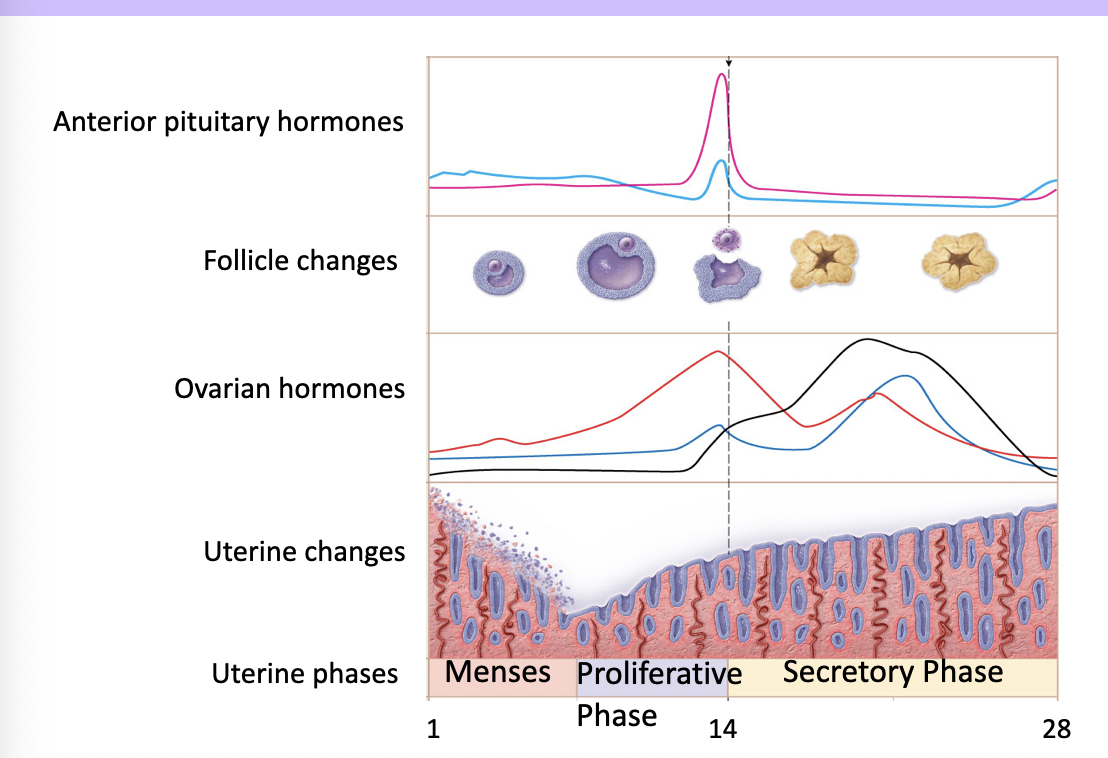
95
New cards
how menopause occurs
loss of primary follicles means less estrogen
less estrogen mens levels are so low that we lose the negative feedback effect
FSH and LH levels rise dramatically, causing strange fluctuations in primary follicle recruitment, and estrogen levels
pituitary becomes exhausted, LH and FSH levels drop
cycle ends, and menopause is reached
begins to happen between 45-55
less estrogen mens levels are so low that we lose the negative feedback effect
FSH and LH levels rise dramatically, causing strange fluctuations in primary follicle recruitment, and estrogen levels
pituitary becomes exhausted, LH and FSH levels drop
cycle ends, and menopause is reached
begins to happen between 45-55
96
New cards
symptoms of menopause
hot flashes
loss of fertility
change in bone health
metabolic changes
loss of fertility
change in bone health
metabolic changes
97
New cards
what does sperm require to successfully locate the oocyte
armour/protection
food
a map
help from other sperm h
food
a map
help from other sperm h
98
New cards
how much sperm is needed
ejaculate: 15 million/ml - 200 million/ml
reach the ovum: 50-100
fertilization: 1
reach the ovum: 50-100
fertilization: 1
99
New cards
what are the stages of early embryo development
zygote
4 cell stage
morula
blastocyst (day 5 post-fertilizatior)
4 cell stage
morula
blastocyst (day 5 post-fertilizatior)
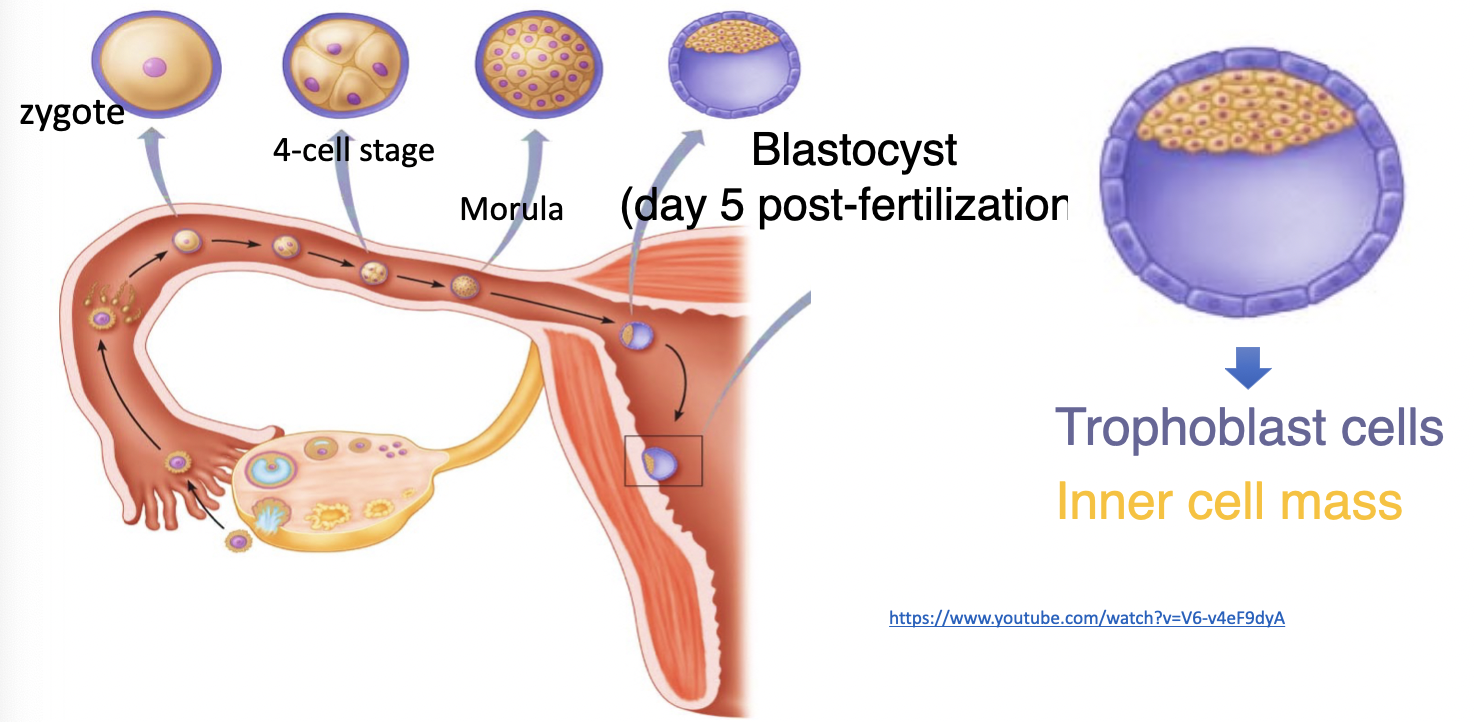
100
New cards
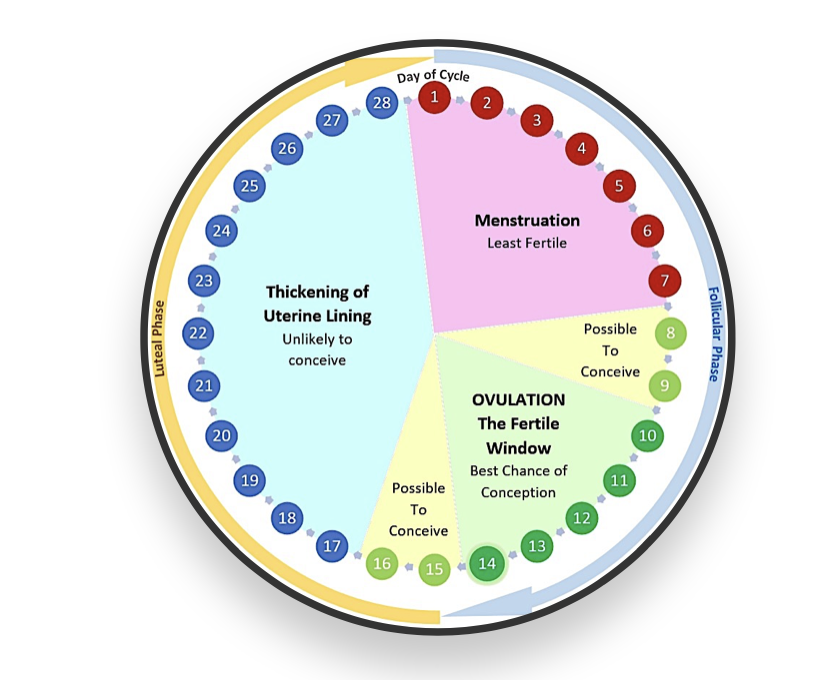
overview of menstrual cycle