SCH4U - Organic Chemistry
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
includes ONLY properties, functional groups, common names and polymerization
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What are the EIGHT functional groups?
alcohols
ethers
ketones
aldehydes
carboxylic acids
esters
amines
amides
What group does alcohol include? + ending
hydroxyl group (-OH) + ol
What group does ethers include? + middle
single bonded oxygen (-O-) + oxy
What group does ketones include?
double bonded oxygen (=O) - in the middle + one
What group does aldehydes include?
double bonded oxygen (=O) - at the end + anal
What group(s) does carboxylic acids include?
double bonded oxygen (=O) & hydroxyl group (-OH) + oic acid
What group(s) does esters include?
double bonded oxygen (=O) & single bonded oxygen (-O-) + oate
What groups does amines include?
ammonia (NH3) (alkyl group replaces a H) + amine
What groups does amides include?
carbonyl group (C=O) attached to Nitrogen atom (N) w/ an alkyl group + amide
— common names —
header
Alcohols (IUPAC name)
Methanol =
Ethanol =
2-proponol =
Alcohols (COMMON names)
Methyl alcohol
Graim alcohol/spirit of wine
Rubbing alcohol
Ethers (IUPAC naming):
Methoxymethane =
Ethoxyethane =
Methoxyethane =
Ethers (COMMON naming):
dimethyl ether
diethyl ether
ethyl methyl ether
Ketones (IUPAC naming):
Propanone =
2-Pentanone =
Ketones (COMMON naming):
Acetone
Methyl propyl ketone
Aldehydes (IUPAC naming):
Formaldehyde =
Acetaldehyde =
Aldehydes (COMMON naming):
Methanal
Ethanal
Carboxylic Acids (IUPAC naming):
Methanoic acid =
Ethanoic acid =
Propanoic acid =
Carboxylic Acids (COMMON naming):
Formic acid
Acetic acid
Propionic acid
Esters (IUPAC naming):
Methyl methanoate =
Methyl ethanoate =
Esters (COMMON naming):
Methyl formate
Methyl acetate
Amines (IUPAC naming):
Methanamine =
Ethanamine =
n-Propylamine =
Amines (COMMON naming):
Methylamine
Methylamine
n-Propylamine
Amides (IUPAC naming):
Methanamide (derived from Formic Acid)
Ethanamide (derived from Acetic acid)
Propanamide (derived from propanoic acid)
Amides (COMMON naming):
Formamide
Acetamide
Propionamide
— properties —
header
Alcohols
Neutral, the -OH does not dissociate
Flammable
Polar molecules (due to -OH group)
Soluble in water, decreases with increasing carbons
Higher boiling points than hydrocarbons
strong smell
Ethers
liquids, sweet smell
lower b.p (no hydrogen bonding b/n other molecules)
slightly soluble
moderately polar
Aldehydes
lower chains are gases or liquids
smell pungent or fruity
b.p is higher than alkanes due to dipole-dipole interactions but lower than alcohols
solubility decreases with chain length
polar due to C=O bond
Ketones
lower chains are liquids
sweet smell
b.p is higher than alkanes due to dipole-dipole but lower than alcohols
solubility decreases with chain length
polar due to C=O bond
Carboxylic acids
lower chains are liquid
lower acids have pungent, sour odour
high b.p due to hydrogen bonding
lower acids are soluble in water and decreases as chain gets longer
polar due to -COOH group
weak acids
Esters
lower esters are volatile liquids
smell often pleasant and fruity odour
b.p is lower than acids and alcohols (no H-bonding)
less soluble in water in water due to H-bonding w/ water; solubility decreases as chain length increases
Polar due to C=O and C-O bonds
Amines
lowr amines are gases or liquids
smell fishy, unpleasant odour
b.p higher than alkanes but lowert than alcohols
lower amines are soluble in water; solubility decreases as akyl chain length increases
Polar due to -NH2 or -NH group
Amides
lower amides are liquid
usually odourless
HIGH b.p due to strong hydrogen bonding between molecules
soluble in water (H-bonding), solubility decreases with larger alkyl groups
Polar due to C=O and -NH groups
Rank the functional groups from lowest to highest b.p
Van der Waals only: Alkanes → lowest BP
Dipole-dipole: Ethers, aldehydes, ketones, esters → moderate BP
H-bonding: Amines < Alcohols < Carboxylic acids < Amides → highest BP
— reactions —
header
What are the reactions to form alcohols?
Hydration of Alkenes (addition)
Substitution (alkyl halides)
What are the reactions to form ketones?
Oxidation of Secondary Alcohols (oxidation)
Hydration of Alkenes (addition)
What are the reactions to form ethers?
Dehydration of Alcohols (condensation)
What are the reactions to form aldehydes?
Oxidation of Primary Alcohols (oxidation)
What are the reactions to form carboxylic acids?
Oxidation of Primary Alcohols (oxidation) → oxidation of an aldehyde (oxidation)
Hydrolysis of Esters (hydrolysis) - add water (excess is water)
What are the reactions to form esters?
Esterfication (condensation) of carboxylic acid + alcohol
What are the reactions to form amines?
Primary: halogenated alkane + ammonia
Secondary & Tertiary: alkane + amine
What are the reactions to form amides?
Primary, secondary, tertiary: Carboxylic acid + amines
— polymerization —
header
Polymer
→ a large, usually chain-like molecule that Is built from small molecules
monomer
→ one of the repeating small molecules that MAKE UP polymers
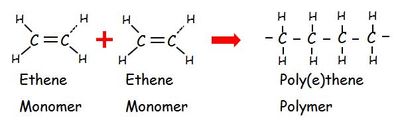
homopolymer
→ a polymer of a single type of monomer
copolymer
a polymer made of two or more different types of monomers combined
What are the two types of polymerization?
Addition polymerization
Condensation polymerization
Addition polymers (+ give example)
→ when monomers link during addition reactions (ex. polyethylene -plastic, PVC)
Condensation polymers (+ give example)
→ formed when monomers join during condensation reactions.
Polyesters are formed by the condensation reactions b/n carboxylic acids and alcohols - ester linkages (ex. nylon)
KEY points for addition polymerization
1. Monomers must be unsaturated
Monomers have C=C
Double bond opens up so monomers can link together
2. No By-products are Formed
KEY points for condensation polymerization
1. Monomers have TWO functional gourds (ex. Alcohol & carboxylic acid)
Ex. Diol + dicarboxylic acid → polyester
2. By-product (H20 usually released)
3. Alternating repeating units in polyester