WBC 4: MDS; Acute Leukemias
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
what is the differentiating factor between SAA and VSAA?
<0.2 × 109/L neutrophils
the following characteristics are characteristic of _____
BM: hypocellular
Neutrophils (x 109/L): 0.5-1.5
PLTs (x 109/L): 20-50
Other:
hemoglobin <10 g/dL
reticulocytes <30 × 109/L
MAA
the following characteristics are characteristic of _____
BM: hypocellular (<25%)
Neutrophils (x 109/L): 0.2-0.5
PLTs (x 109/L): <20
Other:
reticulocytes <20 × 109/L
SAA
the following characteristics are characteristic of _____
BM: hypocellular (<25%)
Neutrophils (x 109/L): <0.2
PLTs (x 109/L): <20
Other:
reticulocytes <20 × 109/L
VSAA
acquired clonal hematopoietic disorders:
MDS
somatic gene mutation at the HSC level:
MDS
characterized by progressive cytopenias in the peripheral blood (reflecting defective maturation in erythroid, myeloid, megakaryocytic lines) and dyspoiesis in each line:
MDS
the following is associated with ____
risk of development into AML
median age of 76
MDS
the following are risk factors for ____
old age (above 65)
inherited BM failure syndromes such as Fanconi anemia, Diamond-Blackfan anemia, and Shwachman-Diamond syndrome
MDS
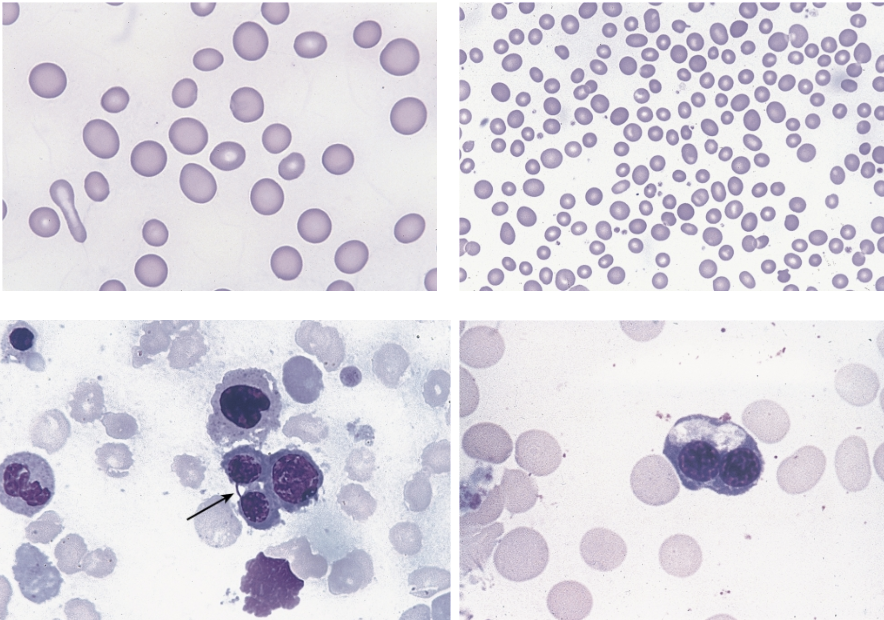
these morphological abnormalities of the peripheral blood (top 2 images) and BM (bottom 2 images) are characteristic of ____.
dyserythropoiesis
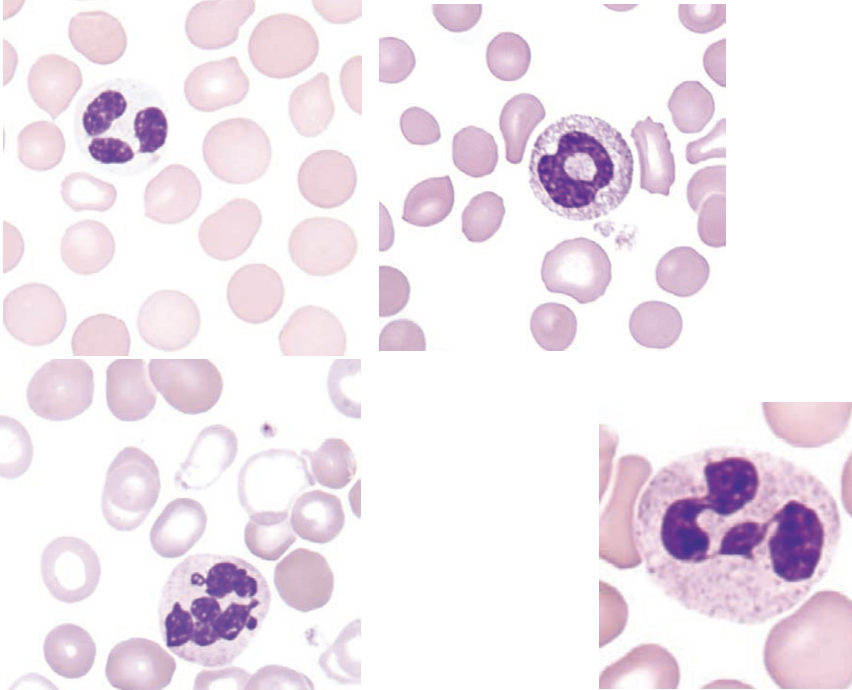
these morphological abnormalities of the peripheral blood are characteristic of ____.
dysmyelopoiesis
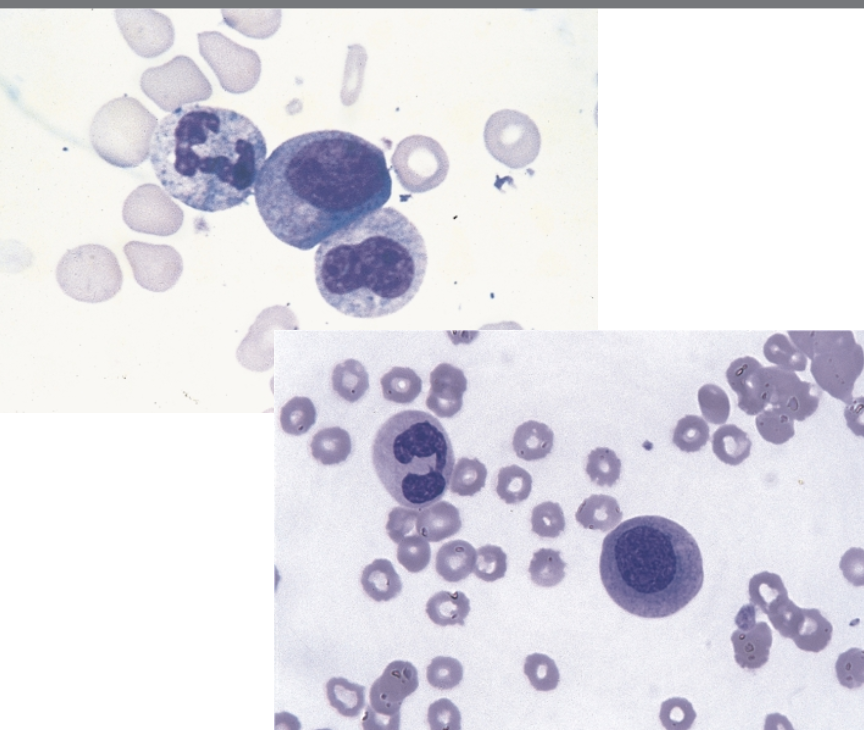
these morphological abnormalities of the BM are characteristic of ____.
dysmyelopoiesis
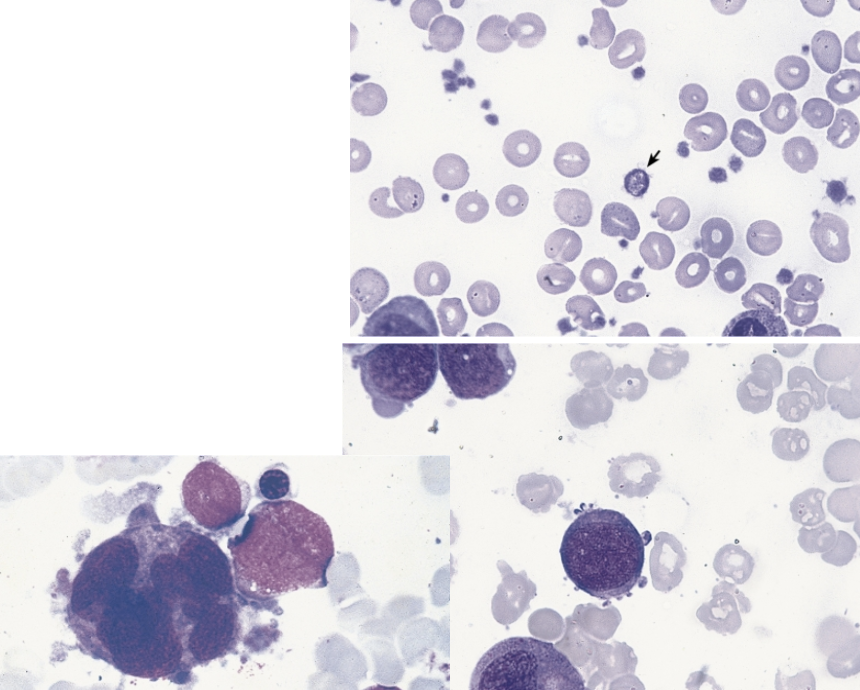
these morphological abnormalities of the peripheral blood (top image) and BM (bottom 2 images) are characteristic of ____.
dysmegakaryopoiesis
immature myeloid/monocyte antigen marker:
CD64
the following are peripheral blood lab features of _____
anemia in >85% cases
high MCV
poikilocytosis (oval, elliptical, teardrop, spheres, fragmented cells)
neutropenia
neutrophil hypogranularity
acquired pelger huet
ring-shaped nuclei in neutrophils
mild to moderate thrombocytopenia
large PLTs with poor granulation
MDS
the following are blood plasma lab features of _____
serum iron, transferrin, ferritin, LDH, and uric acid are elevated
MDS
the following are BM lab features of _____
hypercellular in one or more lines with dysplasia
MDS
which MDS WHO classification is consistent with the following characteristics:
anemia
infection
petechiae (depending on the lineage involved)
<1% blasts in peripheral blood
<5% blasts in BM
MDS-SLD
MDS-SLD refers to MDS with _____ dysplasia.
single lineage
MDS-MLD refers to MDS with _____ dysplasia.
multilineage
which MDS WHO classification is consistent with the following characteristics:
more than one lineage is dyspoietic
<1% blasts in peripheral blood
<5% blasts in BM
MDS-MLD
which MDS WHO classification is consistent with the following characteristics:
SF3B1 (spliceosome) mutation
at least 5% ring sideroblasts
dimorphic RBC picture on PBS (combination of hypochromic and normochromic cells)
MDS-RS
what gene is associated with the spliceosome mutation in MDS-RS?
SF3B1
which MDS WHO classification is consistent with the following characteristics:
trilineage cytopenia
MDS-EB
which type of MDS-EB is consistent with the following characteristics:
5-9% blasts in BM
2-4% blasts in peripheral blood
MDS-EB1
which type of MDS-EB is consistent with the following characteristics:
10-19% blasts in BM
5-19% blasts in peripheral blood
MDS-EB2
which MDS WHO classification is consistent with the following characteristics:
affects predominantly women
occurs at a median age of 70
patients have anemia without other cytopenias
MDS with isolated del(5q)
MDS with isolated del(5q) is also referred to as:
5q syndrome
if there are not enough specific characteristics that align with WHO classifications of we can classify the MDS as ____.
MDS, unclassifiable
what is a major indication of MDS in peripheral blood and BM?
a. dyspoiesis
b. leukocytosis with left shift
c. normal BM with abnormal peripheral blood features
d. thrombocytosis
dyspoiesis
an alert hematologist should recognize all the following peripheral blood abnormalities as diagnostic clues in MDS EXCEPT:
a. oval macrocytes
b. target cells
c. agranular neutrophils
d. circulating micromegakaryocytes
target cells
a patient has anemia, oval macrocytes, and hypersegmented neutrophils. which of the following tests would be most efficient in differential diagnosis of this disorder?
a. serum iron and ferritin levels
b. erythropoietin level
c. vitamin B12 and folate levels
d. chromosome analysis
vitamin B12 and folate levels
FAB mostly considered _____ while WHO is more informative, and considers clinical features, morphology, immunophenotyping, cytogenetics, and molecular genetics.
morphology
what B-ALL translocation is associated with the gene BCR-ABL1?
t(9;22)
what B-ALL translocation is associated with the gene KMTA2 (MLL) rearranged?
t(v;11q23.3)
what B-ALL translocation is associated with the gene TEL-AML1 (ETV6-RUNX1)?
t(12;21)
which gene is associated with t(9;22)?
BCR-ABL1
which gene is associated with t(v;11q23.3)?
KMT2A (MLL) rearranged
which gene is associated with t(12;21)?
TEL-AML1 (ETV6-RUNX1)
in ____, the cytogenetic alterations show less specificity and less correlation with the prognosis and treatment outcome than in B-ALL.
T-ALL
which B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma is associated with the following:
worst prognosis
philadelphia chromosome (+)
more common in adults
responds to imatinib (Gleevec)
a. t(9;22)(q34.1;q11.2);BCR-ABL1
b. t(v;11q23.3); KMT2A (MLL) rearranged
c. t(12;21)(p13.2;q22.1); TEL-AML1 (ETV6-RUNX1)
d. with hyperdiploidy
e. with hypodiploidy
a
which B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma is associated with the following:
more common in very young adults
translocation may occur in utero
very poor prognosis
a. t(9;22)(q34.1;q11.2);BCR-ABL1
b. t(v;11q23.3); KMT2A (MLL) rearranged
c. t(12;21)(p13.2;q22.1); TEL-AML1 (ETV6-RUNX1)
d. with hyperdiploidy
e. with hypodiploidy
b
which B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma is associated with the following:
rare in adults
excellent prognosis in children
cure rate of over 90%
a. t(9;22)(q34.1;q11.2);BCR-ABL1
b. t(v;11q23.3); KMT2A (MLL) rearranged
c. t(12;21)(p13.2;q22.1); TEL-AML1 (ETV6-RUNX1)
d. with hyperdiploidy
e. with hypodiploidy
c
which B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma is associated with the following:
less common in adults
favorable prognosis in children
a. t(9;22)(q34.1;q11.2);BCR-ABL1
b. t(v;11q23.3); KMT2A (MLL) rearranged
c. t(12;21)(p13.2;q22.1); TEL-AML1 (ETV6-RUNX1)
d. with hyperdiploidy
e. with hypodiploidy
d
which B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma is associated with the following:
poor prognosis in both children and adults
a. t(9;22)(q34.1;q11.2);BCR-ABL1
b. t(v;11q23.3); KMT2A (MLL) rearranged
c. t(12;21)(p13.2;q22.1); TEL-AML1 (ETV6-RUNX1)
d. with hyperdiploidy
e. with hypodiploidy
e
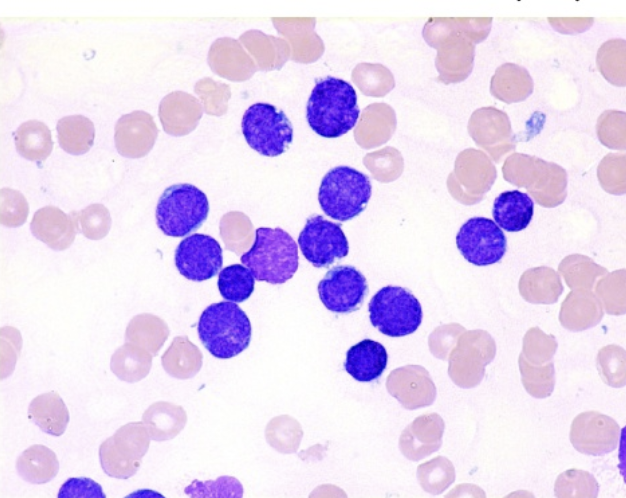
FAB classification that refers to small blasts with a thin rim of cytoplasm:
pre B ALL (L1)
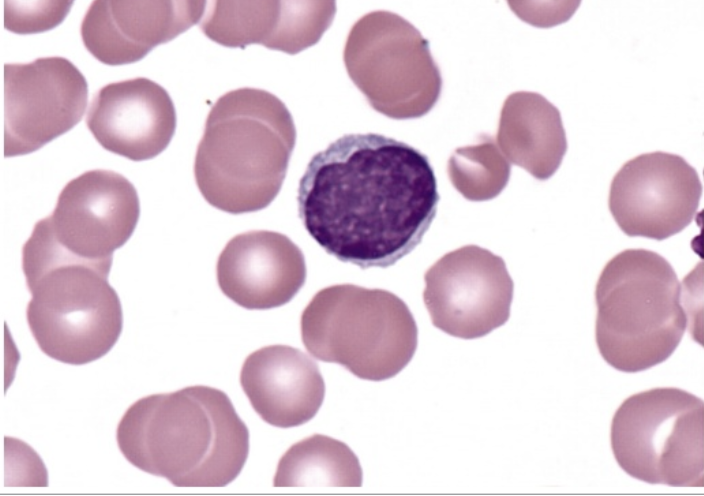
FAB classification that refers to irregular clefts of the nucleus
T cell ALL (L2)
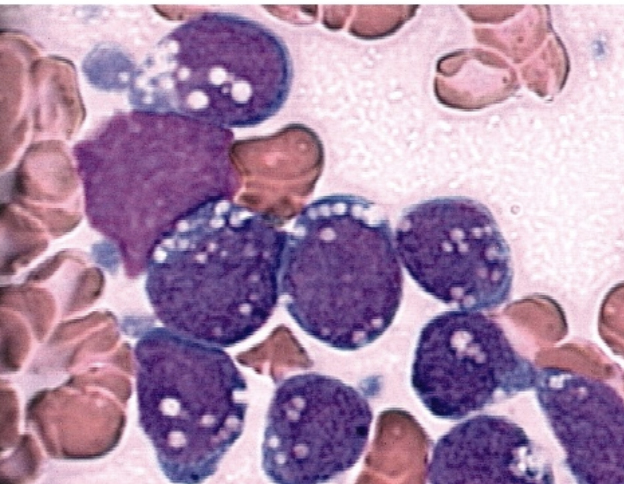
FAB classification that refers to burkitt leukemia with vacuolations:
mature B cell ALL (L3)
the following immunophenotype refers to which ALL subtype:
CD34 +
CD19 +
cytoplasmic CD22 +
TdT +
early (pro/pro-pre) B-ALL
the following immunophenotype refers to which ALL subtype:
CD34 +
CD19 +
CD10 +
cytoplasmic CD22 +
TdT +
intermediate (common) B-ALL
the following immunophenotype refers to which ALL subtype:
CD34 -
CD19 +
cytoplasmic CD22 +
cytoplasmic µ +
TdT +
pre B ALL
the following immunophenotype refers to which ALL subtype:
CD2 +
CD3 +
CD4 +
CD5 +
CD7 +
CD8 +
TdT +
T ALL
_____ is seen most often in teenage males with
mediastinal mass
elevated peripheral blast counts
meningeal involvement
infiltration of extra marrow sites
T ALL
most common type of leukemia in adults, less common in children:
AML
the following lab findings are consistent with ____
>90% show blasts in peripheral blood
WBC between 5-30 × 103/uL
anemia
thrombocytopenia
neutropenia (WBC could be normal but anemia and thrombocytopenia are always present)
AML
the following lab findings are consistent with ____
BM hypercellular with >20% blasts (not enough without specific genetic abnormalities)
serum chemical analysis
hyperuricemia
hyperphosphatemia
hypocalcemia
risk of acute renal failure
tumor lysis syndrome (in case of very high WBC)
AML
the most significant different between FAB and WHO classifications of AML is that FAB requires _____% blasts while WHO requires >20% blasts.
>30%
for AML, which translocation is associated with the gene RUNX1-RUNX1T1?
t(8;21)
for AML, which translocation is associated with the gene CBFB-MYH11?
t(16;16) OR inv(16)
for AML, which translocation is associated with the gene PML-RARA?
t(15;17)
for AML, which translocation is associated with the gene KMT2A (MLL)-MLLT3?
t(9;11)
which gene is associated with the following AML translocation: t(8;21)?
RUNX1-RUNX1T1
which gene is associated with the following AML translocation: t(16;16) aka inv(16)?
CBFB-MYH11
which gene is associated with the following AML translocation: t(15;17)?
PML-RARA
which gene is associated with the following AML translocation: t(9;11)?
KMT2A (MLL)-MLLT3
AML with mutated NPM1 is mostly in ____ leukemias with good prognosis?
monocytic
AML with biallelic mutation of CEBPA has a poor prognosis. true or false?
false
AML with mutated RUNX1 has the worst overall survival. true or false?
true
which FAB classification of AML refers to acute myeloid leukemia with minimal differentiation (*BLASTS! no maturity)?
M0
which FAB classification of AML refers to acute myeloid leukemia without maturation?
M1
which FAB classification of AML refers to acute myeloid leukemia with maturation?
M2
which FAB classification of AML refers to acute promyelocytic leukemia?
M3
which FAB classification of AML refers to acute myelomonocytic leukemia?
M4
which FAB classification of AML refers to acute myelomonocytic leukemia with eosinophilia?
M4eo
which FAB classification of AML refers to acute monocytic leukemia with poor differentiation?
M5a
which FAB classification of AML refers to acute monocytic leukemia that are well differentiated?
M5b
which FAB classification of AML refers to acute erythroleukemia?
M6
which FAB classification of AML refers to acute megakaryocytic leukemia?
M7
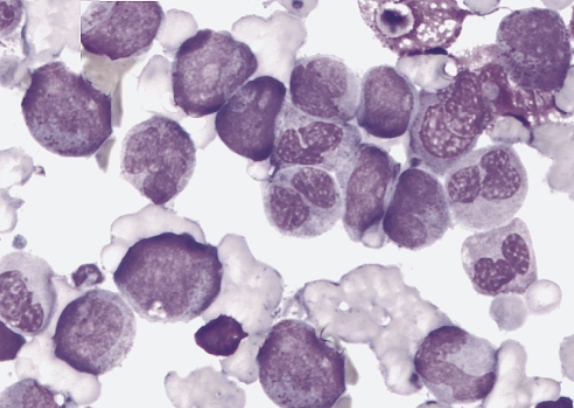
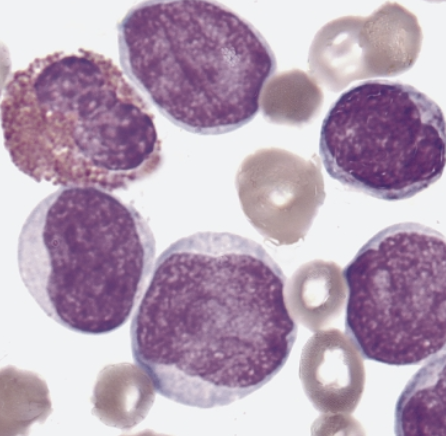
which AML translocation is associated with the following information:
5% of AML cases
predominantly in children and young children
myeloblasts with dysplatic granular cytoplasm, auer rods, and some maturation (similar to FAB M2 phenotype)
pseudo-pelger-huet cells and hypogranulation
eosinophilia may be seen
this diagnosis of the subtype is based on the genetic abnormality, regardless of blast count
t(8;21)
which AML translocation is associated with the following information:
5-8% of AML cases
myeloblasts, monoblasts, and promyelocytes in peripheral blood and BM
eosinophilia with dysplastic changes may be seen in BM
CNS involvement (relapse)
the genetic aberration is sufficient for diagnosis regardless of blast count
t(16;16) OR inv(16)
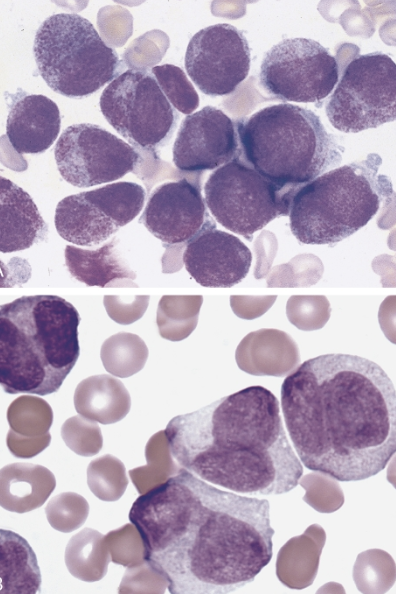
which AML translocation is associated with the following information:
5-10% of AML cases
differentiation block at pro stage
abnormal hypergranular promyelocytes, some with auer rods (sometimes bundle of auer rods, aka faggot cells)
risk of DIC (release of procoagulant from promyelocytes)
a microgranular variant (30-40% of APL cases), may be confused with other AML types (figure B)
unique treatment: all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) and arsenic trioxide
ATRA induces differentiation of promyelocytes
the genetic aberration is sufficient for diagnosis regardless of blast count
t(15;17)
which condition has the unique treatment of all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) and arsenic trioxide?
APL
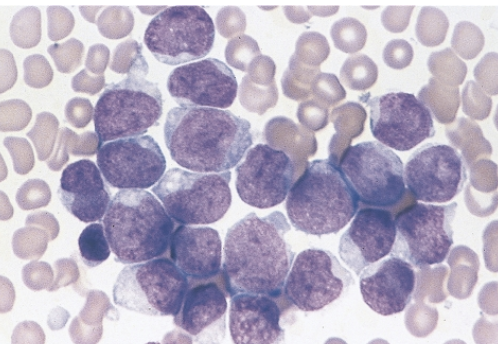
which AML translocation is associated with the following information:
6% of AML cases
increase in monoblasts and immature monocytes
blasts are large with abundant cytoplasm and fine nuclear chromatin
blasts may have pseudopodia, granules and vacuoles
typically in children
skin and gum involvement may occur
t(9;11)
which FAB classification is associated with the following information?
CD13 +
CD33 +
CD34 +
CD117 +
M0; M1
which FAB classification is associated with the following information?
MPO negative
SBB negative
M0
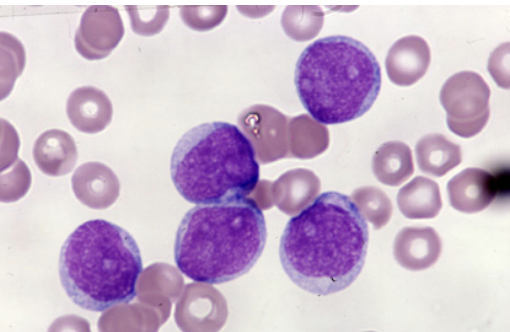
which FAB classification is associated with the following information?
<5% of cases
infants or older patients
M0
which FAB classification is associated with the following information?
MPO and SBB positive in 3% of blasts
M1
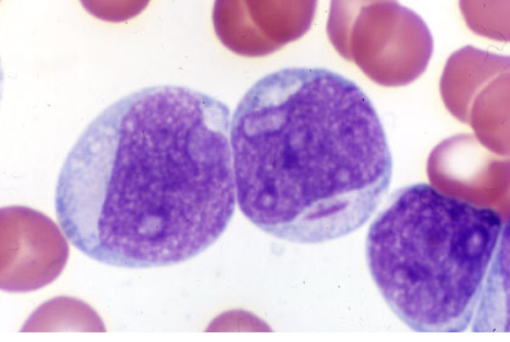
which FAB classification is associated with the following information?
blasts 90% of non-erythroid cells in BM
<10% of cells show maturation up to myeloctes
M1
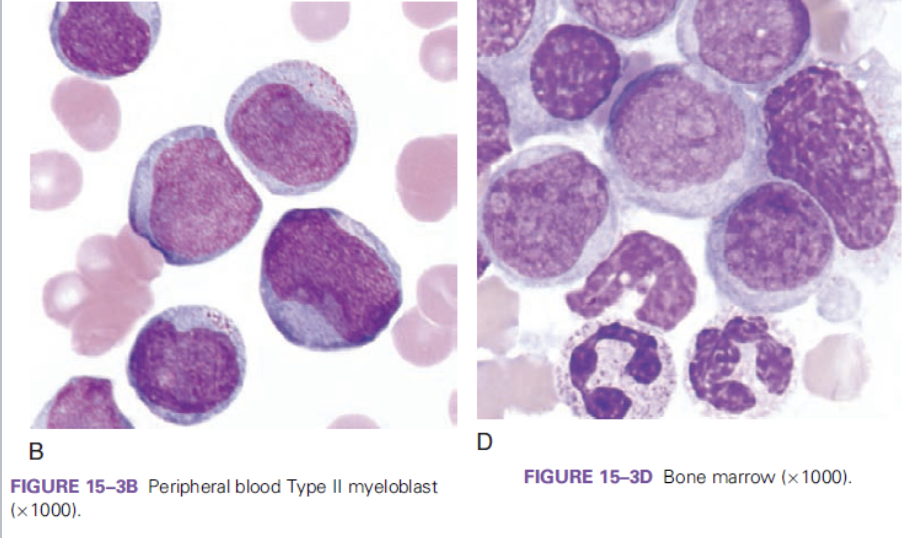
which FAB classification is associated with the following information?
blasts >20% in the BM
>10% maturing neutrophil lineage cells
<10% of blasts of the monocytic lineage
M2
which FAB classification is associated with the following information?
CD34 +
CD13 +
CD15 +
CD11b +
HLA-DR +
negative for monocytic markers: CD36, CD14, CD64
M2
CD36, CD14, CD64 refer to ____ markers.
monocytic
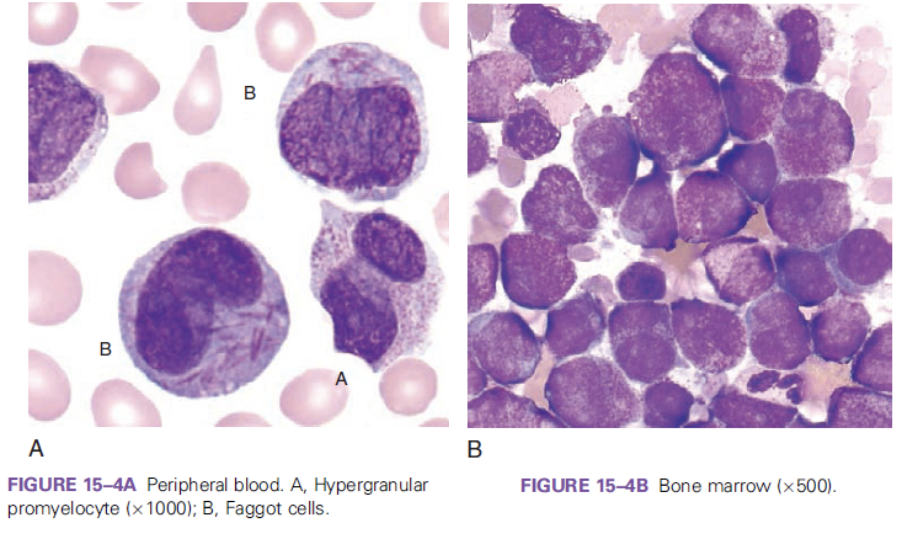
which FAB classification is associated with the following information?
differentiation block at the promyelocyte stage
risk of DIC
M3
which FAB classification is associated with the following information?
CD34 -
CD13 +
CD33 +
CD64 +
CD11b -
HLA-DR -
M3
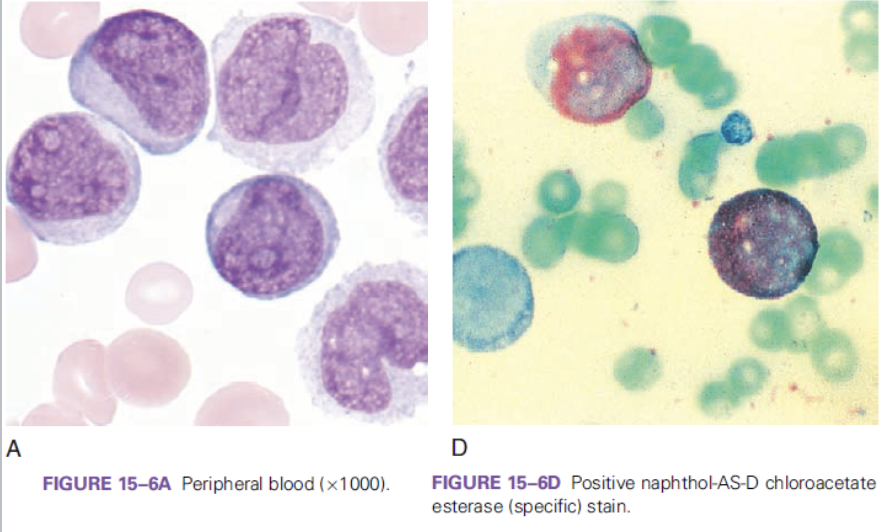
which FAB classification is associated with the following information?
very high WBC count
presence of monocytic cells (monoblasts and promonocytes)
positive naphthol-AS-D chloroacetate esterase (specific stain)
M4
which FAB classification is associated with the following information?
CD13 +
CD33 +
CD64 +
CD14 +
CD4 +
CD11c +
M4
which FAB classification is associated with the following information?
CD14 +
CD4 +
CD64 +
CD11c +
CD11b +
M5
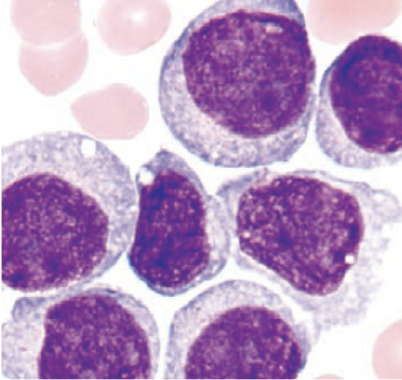
what cell predominates in M5a?
monoblasts
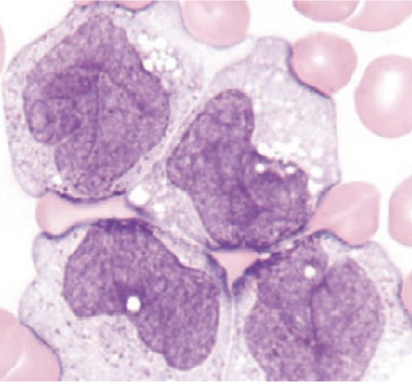
what cell predominates in M5b?
promonocytes
which FAB classification is associated with the following information?
positive alpha-naphthyl butyrate esterase (nonspecific) esterase stain
M5
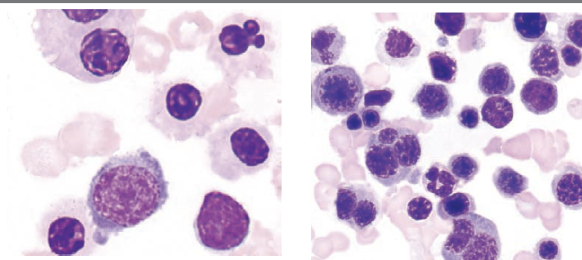
which FAB classification is associated with the following information?
>80% of cells are of erythroid origin
>30% are pro-normoblasts
dysplastic changes in erythroid precursors such as multinucleation (N:C asynchrony, vacuolization)
>50% nRBCs on PBS
ringed sideroblasts, HJ bodies
aggressive and rapid clinical course
M6