Patho Exam 1 PowerPoint
0.0(0)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:45 AM on 10/27/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
1
New cards
Symptoms
Clients describing feeling lightheadedness, dizziness, short of breath,
2
New cards
Homeostasis
state of equilibrium or balance within and organism.
fever is indicative of an alteration in homeostatic control)
fever is indicative of an alteration in homeostatic control)
3
New cards
Eukaryote
any cell or organism that possesses a defined nucleus
4
New cards
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell,
Makes ATP (energy) production
Makes ATP (energy) production
5
New cards
Endoplasmic reticulum
A system of membranes that is found in a cell's cytoplasm
that assists in the production, processing, and transport of proteins and in the production of lipids.
that assists in the production, processing, and transport of proteins and in the production of lipids.
6
New cards
Ribosomes
Makes proteins
7
New cards
Kidneys secrete renin RAAS
when there is a drop in arterial blood pressure to increase peripheral resistance and increase blood pressure.
8
New cards
Aldosterone
Hormone that stimulates the kidney to retain sodium ions and water
9
New cards
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
produced by the hypothalamus.
10
New cards
Fluid Volume Deficit (FVD)
FVD may result from
hemorrhage
excessive loss of GI
fluids
Vomiting
diarrhea
hemorrhage
excessive loss of GI
fluids
Vomiting
diarrhea
11
New cards
Highest loss of daily fluids
the urinary tract
12
New cards
Symptoms of fluid volume deficit (FVD)
thirst
weight loss
tachycardic.
weight loss
tachycardic.
13
New cards
Fluid Volume Excess (FVE) results from
Heart failure
End-stage kidney failure
End-stage kidney failure
14
New cards
Symptoms of fluid volume excess
crackles in the lungs
hypertension (High BP)
bounding pulses.
hypertension (High BP)
bounding pulses.
15
New cards
Osmosis
Movement of water between the interstitial and intracellular compartments).
16
New cards
active transport
Requires energy in the form of ATP
for the movement of solutes from an area of low to high concentration
for the movement of solutes from an area of low to high concentration
17
New cards
Potassium exists
In the intracellular fluid
18
New cards
sodium chloride exists
predominately in extracellular fluid.
19
New cards
Both hypokalemia and hyperkalemia can result in what
cardiac arrhythmias.
20
New cards
Hypocalcemia can result in positive what?
Chvostek's sign
21
New cards
Our bones serves as a reservoir for what?
calcium
22
New cards
Isotonic
fluid volume is increased without a fluid shift
23
New cards
Hypotonic
causes fluid shifts from the extracellular space into the intracellular space
24
New cards
Hypertonic
causes fluid shifts from the intracellular space into the extracellular space
25
New cards
isotonic solution
Fluid stays inside the bloodstream
26
New cards
Hypotonic solution
Draws fluid from vessels and move fluid into the cells
27
New cards
hypertonic solution
Draws fluid out of the cells and into the blood
28
New cards
Initial symptoms the body experiences when under stress is the
"fight-or-flight" response
29
New cards
what happens during the fight or flight stage
Dilated pupils
Increased heart rate
Increased blood pressure
Increased respiratory rate
Increased heart rate
Increased blood pressure
Increased respiratory rate
30
New cards
General Adaptation Syndrome
Seyle's concept that the body responds to stress with alarm, resistance and exhaustion
alarm stage
alarm stage
31
New cards
alarm stage
1. fight or flight
2. Resistance stage
3. Exhaustion
2. Resistance stage
3. Exhaustion
32
New cards
Potential complications of chronic stress
Hypertension
Hyperglycemia
Depression
Hyperglycemia
Depression
33
New cards
intact skin
First line of defense against disease
34
New cards
Neutrophils
First to aid in killing bacteria to prevent infection
35
New cards
inflammatory response
second line of defense that occurs due to tissue damage
such as a break in the skin that introduces microorganisms
such as a break in the skin that introduces microorganisms
36
New cards
Staphylococcus
a common cause of bacterial skin infections
37
New cards
Fever
Indicates an alteration on homeostatic control mechanisms
38
New cards
Sepsis is a severe inflammatory response to a pathogen
is a severe inflammatory response to a pathogen
An overwhelming infection
An overwhelming infection
39
New cards
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP)
Are lab tests than can detect inflammation
40
New cards
Signs of inflammation when injured
Pain
redness
warmth
swelling
heat
loss of function to injured area
Increased blood flow to the area of injury
redness
warmth
swelling
heat
loss of function to injured area
Increased blood flow to the area of injury
41
New cards
Skin and mucous membrane
first line of defense
42
New cards
immune response against foreign antigens
Tears
mucous
saliva
mucous
saliva
43
New cards
Pyrogens
substances that cause fever
44
New cards
Interferons
small protein released by virus-infected cells to stop the replication of a virus
45
New cards
Complement proteins
Plasma proteins enhance antibodies
46
New cards
innate defense
Skin and mucous membranes
47
New cards
Mast cells
Release histamine
48
New cards
Macrophages
Mature monocyte that engulf foreign substances
49
New cards
passive immunity
IgA antibodies transferred to newborn via breast milk
50
New cards
adaptive immunity
Acquired immunity
51
New cards
HIV
Virus invades CD4+ (T helper cells)
52
New cards
Histamine
Causes blood vessels to dilate
53
New cards
active immunity
Immunity associated with vaccines
54
New cards
Artificial active immunity:
polio vaccine to prevent poliomyelitis,
flu vaccine during the flu season
flu vaccine during the flu season
55
New cards
IgA
breast milk, tears, and saliva
56
New cards
IgD
plays a role in B-cell activation
57
New cards
IgE
associated mainly with allergic reactions
found in the lungs skin
mucous membranes.
found in the lungs skin
mucous membranes.
58
New cards
IgG
found in all body fluids and protects against bacterial and viral infections
59
New cards
IgM
initial antibody produced after an infection
60
New cards
Hypersensitivity
an inappropriate or excessive response of the immune system
Four of them
Four of them
61
New cards
Type 1 hypersensitivity
reaction mediated by IgE antibodies involving development of urticaria, or hives
Example: allergic reaction
Example: allergic reaction
62
New cards
Type 2 hypersensitivity
cytotoxic
example: Hemolytic disease of the newborn (erythroblastosis fetalis)
example: Hemolytic disease of the newborn (erythroblastosis fetalis)
63
New cards
Type 3 hypersensitivity
immune complex mediated
Example lupus
Example lupus
64
New cards
Type 4 hypersensitivity
Delayed reaction mediated by cellular response
Example: Poison ivy breaks out on arms after initial exposure 2 days ago
Mantoux tuberculin skin test
Example: Poison ivy breaks out on arms after initial exposure 2 days ago
Mantoux tuberculin skin test
65
New cards
hypertrophy
increase in cell size
Increasing workload increases organelle size and contractility
Example: Body builder
Increasing workload increases organelle size and contractility
Example: Body builder
66
New cards
Hyperplasia
increase in the number of cells in an organ or tissue
67
New cards
metaplasia
a pathologic replacement of normal cells with abnormal cells
68
New cards
Dysplasia
a pathologic mutation of normal cells into atypical cells (different size, shape, and appearance)
69
New cards
Cellulitis
inflammation of subcutaneous connective tissue
mostly in the Low extremities
Affected skin appears swollen, red, and is typically painful and warm to touch.
mostly in the Low extremities
Affected skin appears swollen, red, and is typically painful and warm to touch.
70
New cards
Scleroderma
autoimmune disease affecting the skin and other organs of the body
there are massive deposits of collagen with fibrosis
Hardening and tightening of the skin and connective tissue
The inflammatory response causes edema.
there are massive deposits of collagen with fibrosis
Hardening and tightening of the skin and connective tissue
The inflammatory response causes edema.
71
New cards
Psoriasis
lifelong inflammatory immune disorder
Keratinocytes in the skin undergo rapid proliferation in the development of psoriasis
Keratinocytes in the skin undergo rapid proliferation in the development of psoriasis
72
New cards
Two hallmark characteristics of cancer:
Uncontrolled cell growth
Altered cell differentiation
Altered cell differentiation
73
New cards
Apoptosis
programmed cell death
Cancer cells do not undergo apoptosis
Cancer cells do not undergo apoptosis
74
New cards
Dysplasia
uncontrolled growth in which cells vary in size, shapes, and organization
75
New cards
Neoplasia
abnormal new cell growth
76
New cards
Anaplasia
Loss of differentiation
77
New cards
Most skin cancers occur on areas that have the most sun exposure
arms and hands
78
New cards
ABCDE Rule when monitoring skin lesions/moles for changes
Asymmetry
Borders
Color
Diameter
Evolving
Borders
Color
Diameter
Evolving
79
New cards
Colon Cancer
3rd most common form of cancer in the United States
80
New cards
What should you screen for colon cancer
50
81
New cards
Atrophy
the wasting away or deterioration of muscle
82
New cards
kyphosis
increase in the curvature of the thoracic spine outward
Hunchback
Hunchback
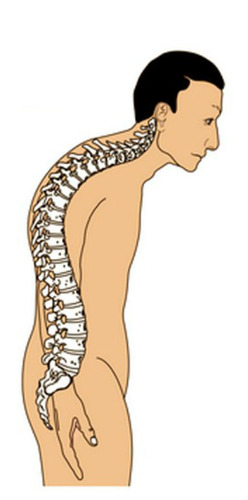
83
New cards
Lordosis
Exaggerated concave curvature of the lumbar spine
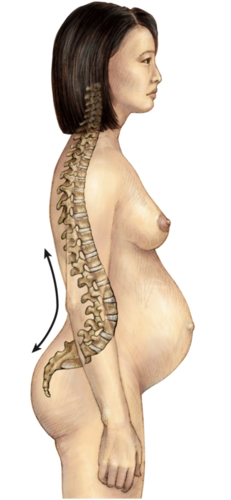
84
New cards
Scoliosis
lateral curvature of the spine
Respiratory difficulties may result
Respiratory difficulties may result
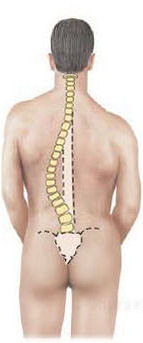
85
New cards
Transverse fracture
occurs straight across the bone
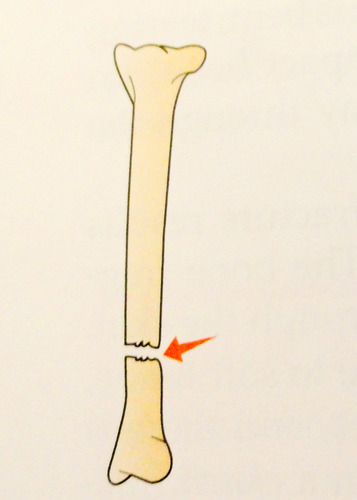
86
New cards
Oblique fracture
occurs at an angle across the bone
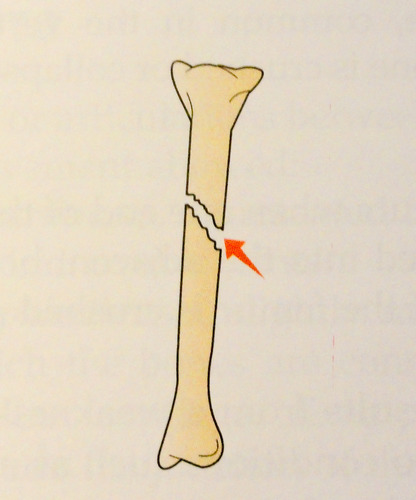
87
New cards
Compression fracture
bone is crushed
88
New cards
Pathologic fracture
occurs when a weakened bone breaks under normal strain
Example: patient with osteoporosis falls and fractures a hip
Example: patient with osteoporosis falls and fractures a hip
89
New cards
Stress or fatigue fracture
occurs from repeated excessive stress
Example: Marathon training
Example: Marathon training
90
New cards
Complications of bone fractures may include
osteomyelitis
fat embolism
compartment syndrome
fat embolism
compartment syndrome
91
New cards
Osteomyelitis
infection of the bone
92
New cards
Fat embolism
fat enters the bloodstream, usually after a long bone fracture
Outcome can be fatal if the emboli travel to vital organs such as the lungs, brain, or heart
Outcome can be fatal if the emboli travel to vital organs such as the lungs, brain, or heart
93
New cards
Dislocation
bone becomes separated from the joint which causes loss of joint function
94
New cards
Sprain
Injury to a ligament that often involves stretching or tearing of the ligament
95
New cards
Herniated intervertebral disk-
Weakness of skeletal muscles resulting from impaired nerve supply
96
New cards
Osteoporosis
progressive loss of bone that leaves the bones brittle
Risk for fractures
Risk for fractures
97
New cards
Rickets
Vitamin D deficiency in children
Bowlegged appearance
Bowlegged appearance
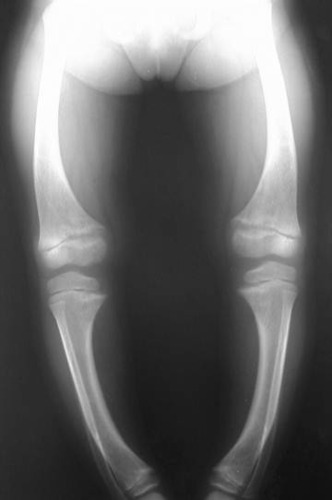
98
New cards
Osteomalacia:
adult form of rickets
vitamin D deficiency can cause this metabolic, soft, weak bone disease
vitamin D deficiency can cause this metabolic, soft, weak bone disease
99
New cards
Paget disease
bone metabolism disorder associated with accelerated bone remodeling resulting in bone that is structurally abnormal
enlarged thick bones with skeletal deformities and increased fracture risk
enlarged thick bones with skeletal deformities and increased fracture risk
100
New cards
Gout
Gout - Inflammatory disease
Excessive uric acid metabolism
Excessive uric acid metabolism