Kime Law of Demand Quiz
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
what is demand?
the desire, ability, and willingness to buy a product at a range of prices at a particular period of time.
represents the consumers pov
law of demand
the quantity demanded varies inversely with the price of the product
income effect
phenomenon that consumers feel richer when prices decreases, tends to purchase more
substitution effect
if a price gets too high, the consumer will buy the substitution instead
law of diminishing marginal utility
as we consume additional units of something, the satisfaction or utility from each additional unit will decrease.
Changes in Quantity Demanded
a change in the number of products because of a change in price.
represented by movement along demand curve
change in price change in quantity demanded
changes in demand
a change in quantity demanded at each & every possible price
represented by entire curve shiftsleft or right - no up or down
non price determinants of demand
consumer income
normal goods vs. inferior goods
consumer tastes, needs and fads
consumer expectations
number of consumers, demographics
prices of related products
Prices of related goods
substitutes or compliments
price elasticity of demand
the extent to which changes in price causes changes in quantity demanded
price elastic
change in price causes a large change in quantity demanded
price inelastic
a change in price causes a small change in quantity demanded
determinants of price elasticity of demand
SPLAT
substitute avaliability
no subs:elastic - many subs: inelastic
proportion of income
high proportion:elastic - low proportion:inelastic
luxury or necessity
luxury:elastic - necessity:inelastic
addictiveness
addictive:inelastic - regular:elastic
time to respond/need
more time:elastic - less time:inelastic
Elasticity Coefficiant
mathematical way to determine elasticity or inelasticity
PED = (%ΔQD) / (%ΔP)
Elasticity Coefficient Relations
if PED < 1 = elastic
if PED < 1 = inelastic
if PED == 1 = unit elastic
if PED == 0 = perfectly inelastic
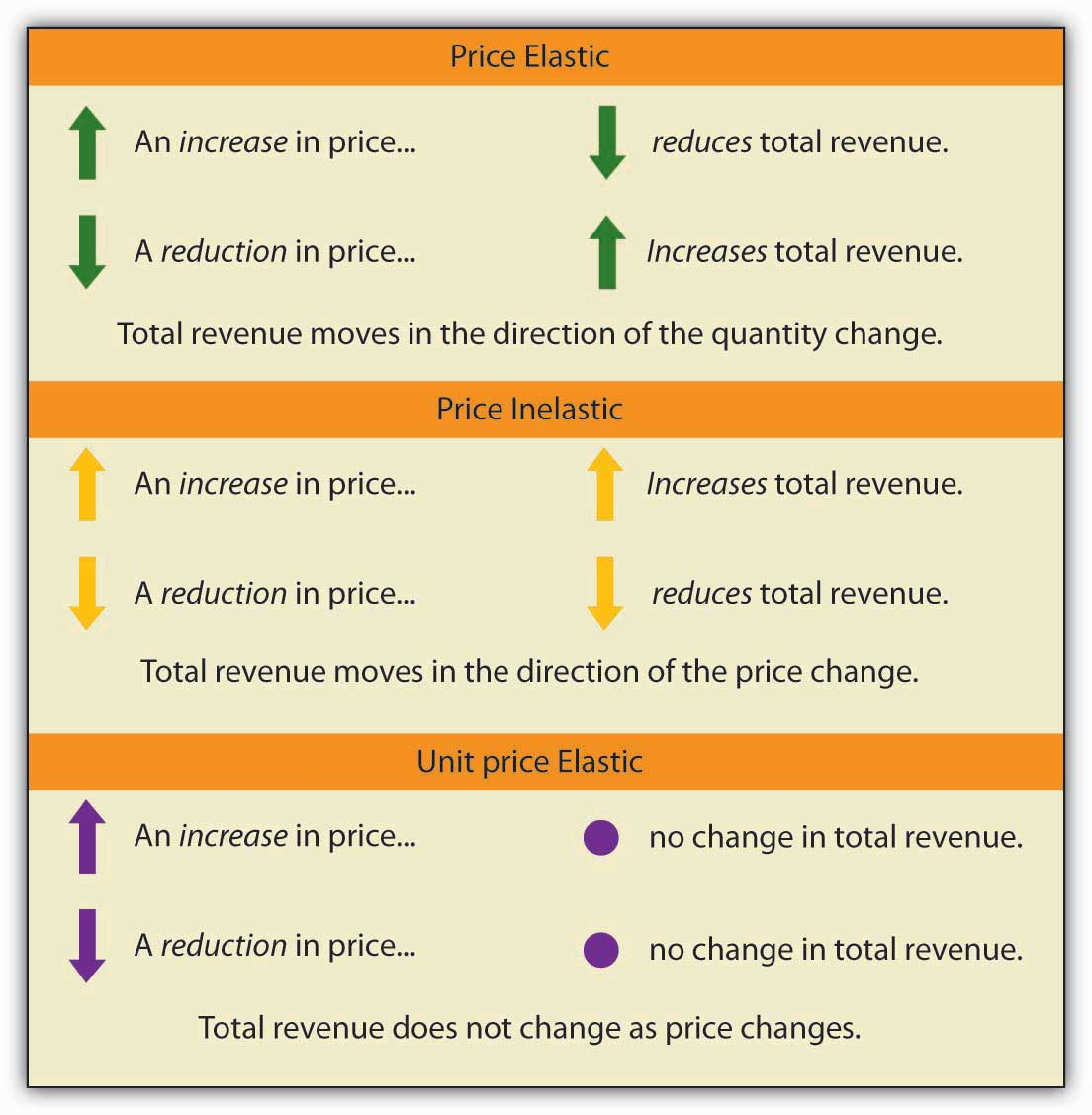
Price Elasticity to Total Revenue
Cross Price Elasticity of Demand
XED = (%ΔQD) / (%ΔP)
With Good A & Price B
Cross Price Elasticity of Demand Relations
if XED is negative = compliments
if XED is positive = substitutes
Income Elasticity of Demand
XED = (%ΔQD) / (%Δincome)
Income Elasticity of Demand Relations
if YED positive = normal good
if YED negative = inferior good
if YED > 1 elastic
if YED < 1 inelastic