Seedless Vascular plants
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What are the characteristics of seedless Vascular plants?
Possession of the vascular tissue
Exhibit alternation of heteromorphic generations
The sporophyte is large and complex and is nutritionally independent phase
Produce Lignin and vascular tissue
What is the Stele and the three basic arrangements of Stele?
~Primarily vascular tissue and pith make up the central cylinder of the stem and root.
Protestele, Siphonostele , and Eustele
What arrangement is the Protostele?
Solid core of Vascular tissue, Simplest and most ancient type of stele
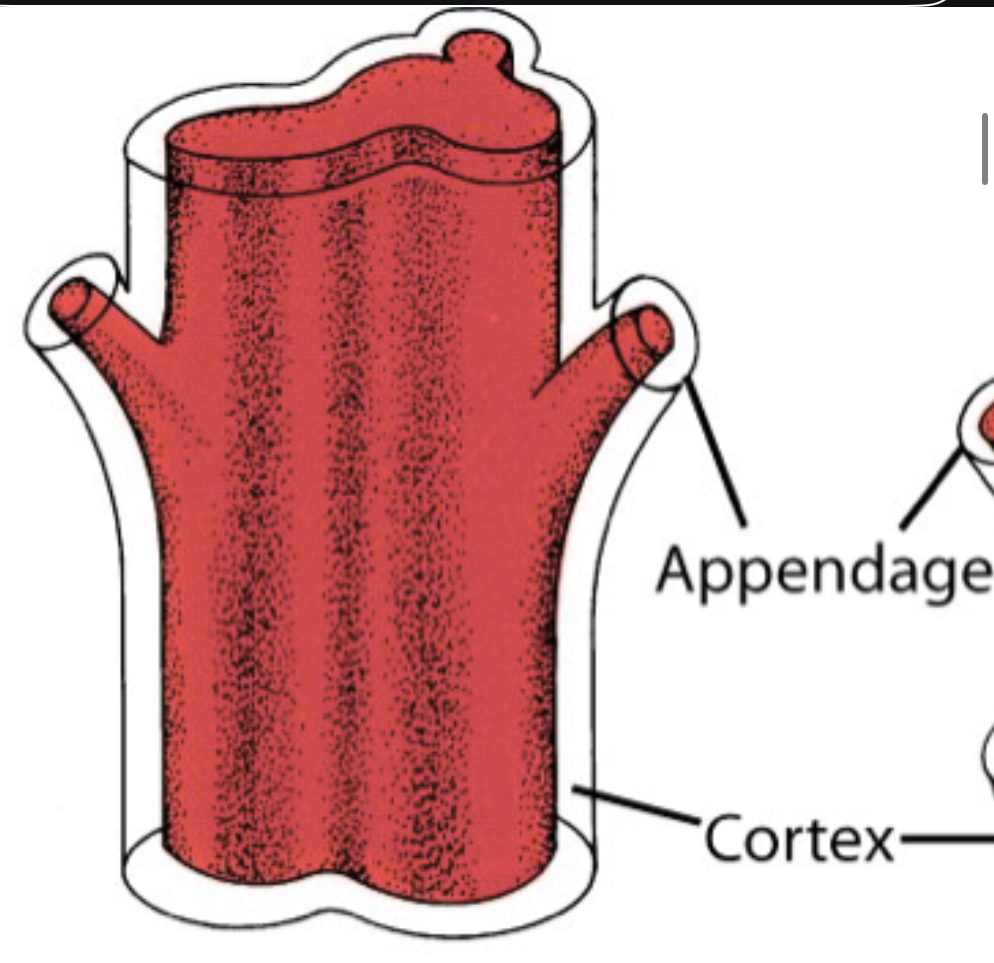
What is the arrangement of the Siphonostele?
Pith surrounded by a vascular tissue that contains leaf gaps or no leaf gaps that show leaf traces (shown in ferns)
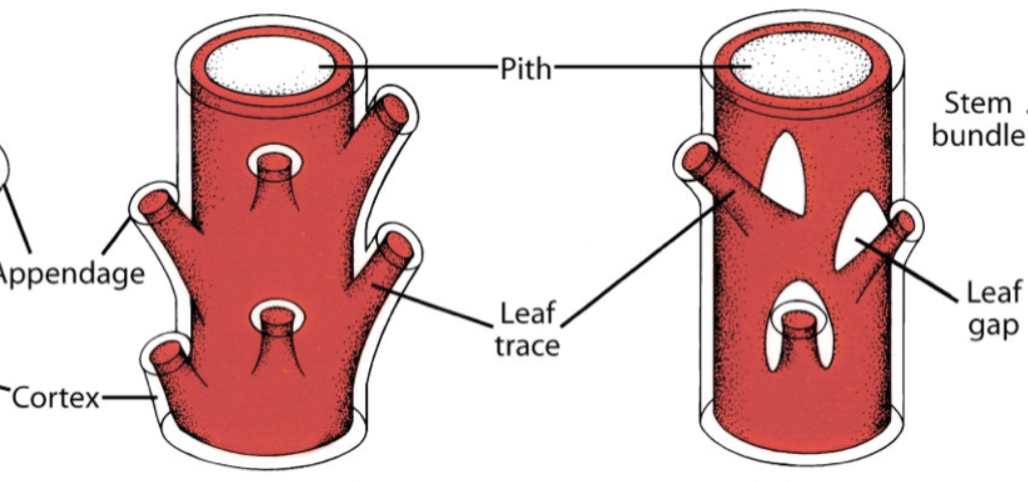
What’s the basic arrangement of the Eustele?
System of strands surrounding a pith: the strands are separated from one another by ground tissue.
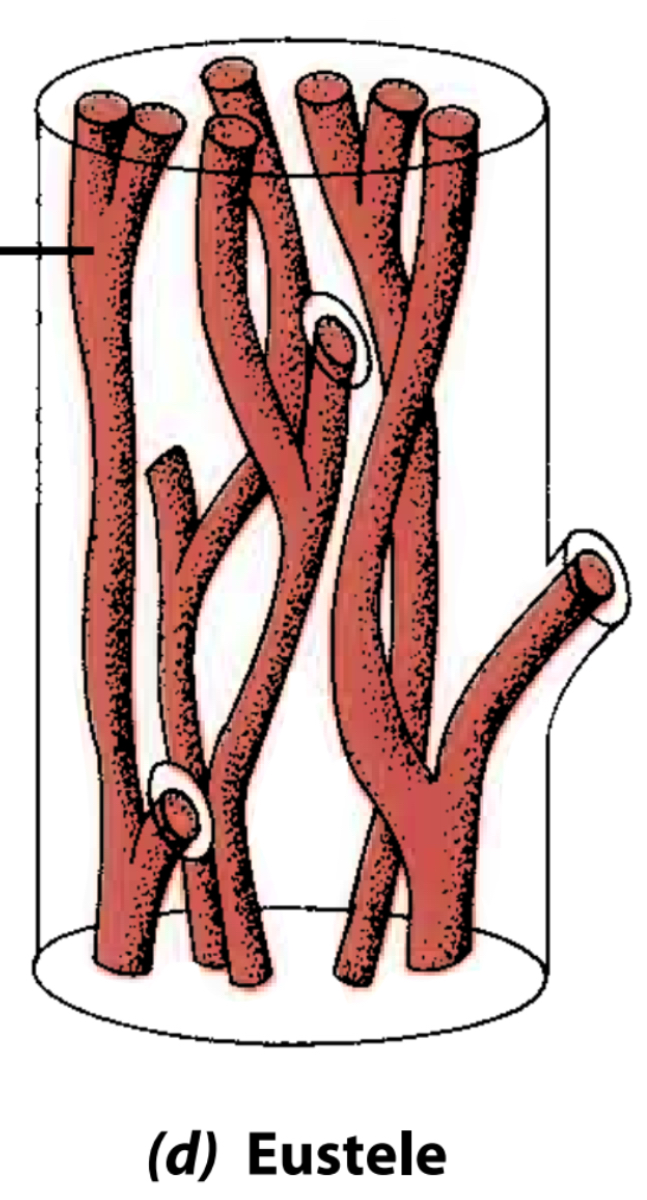
What are Tracheary elements?
The conducting cells of the xylem , they have distinctive, ligininfied wall thicking.
What are sieve elements?
The conducting cells of the phloem, have soft walls and often collapse after they die
What are Tracheids?
The only type of water conducting cell in most vascular plants other than angiosperms
More primitive than the vessel elements.
What are microphylls?
Are relatively small leaves that contain only one single strand of vascular tissue “small leaf”
Associated with protosteles And found in lycophytes: club mosses and the resurrection plant
Have superficial lateral outgrowth of the stem (theory that they were spinelike outgrowths devoid of vascular tissue

What are megaphylls?
They are associated with stems that have either siponosteles or eusteles (leaf gaps or traces
Leaves with complex vexation, enveloped from branched system (branching veins)
What is the reproductive system in vascular plants?
Oogamous, have large nonmotile egg and small sperm that swim to the egg. They also have alternation of Heteromorphic generations
In vascular plants gametophyte is…?
Much reduced in size and less complex than the sporophyte
There are two types of spore produced by meiosis in vascular plants what are they?
Homosporous and Heterosporous
What is a spore that is homosporous?
One type of spore, which gives rise to the bisexual gametophyte. (Produces both male and female gametes
Found in almost all ferns, horsetails
What does it mean when a vascular plant is heterosporous?
Production of two types of spores in two different kinds of sporangia
Found in some of the lycophytes
Produce two types of spores which are micro spores and mega spores that give rise to male and female gamtophytes.
What are the major groups of seedless vascular plants?
Early vascular plants characterized by small stature and simple primitive morphology. Rhyniphytes and zosterophyllophytes and trimerophytes
Monilophytes, lycophytes and progymnosperms, dominat from late Devonian period
Seed plants: late Devonian period, Gymnosperms dominanted
Flowering Plants
What are the Characteristics of Rhyniophyte
425 Mya
Simple dichotomousy branched (lateral branching) axes,lacking roots and leaves. Conducting cells are similar to bryophytes
Branched axis with multiple sporangia
What is the 4 Phyla of Living Seedless Vascular Plants?
Lycophyta-club mosses lycopodium,selgelnilla
Psilotophyta: whisk fern psilotum timesipteris- no leaves or roots
Sphenophyta: horsetails, equisetium
Pterophyta: ferns only phyla with rich species with phylum of seedless vascular plants
What phylum is the club mosses?
Lycopodiophyta, family lycopodiaceae
Which contains a branching rhizomes which aerial branches and roots arise. The mircophylls are spirally arranged
Homosporous- which the sporangia occurs on the upper surface of the microphylls called sporophylls
Characteristic of phylum Zosterophyllophyta?
Dichotomously branched and the Ariel stems were covered with a cuticle but only the upper ones contained stomata
Lower branches produced lateral branches that forked in two axis one up and one down.
What are a few Saglaginella characteristics?
Heterosporous with a unisexual male and female Gametophyte separated into megasporangia and microsporangia
Has a small scale like outgrowth called ligule near the base of the upper surface of the microphyll and sporophyll
Sporophylls arrranged in strobili
In a megagameteophyte of Salaginella, what occurs?
The megaspore wall ruptures and the gametophyte protrudes through the rupture to the outside.
This portion is where the archegonia develop
Quillwarts belong to what family?
Isoetaceae, they are either aquatic or grow in pools that become dry at certain seasons.
Underground stem that bears quill-like microphylls on the upper surface and roots on the lower surface
Heterosporous- which are the microsphorophylls and the megasporophylls

In isoetes each leaf is a what…?
Potential to be a sporophyll
What is the great majority of phylum monilophyta? And the four major lineages?
Ferns and horsetails
1.Psiltopsida 2.marattiosida 3. Polyposida 4.Equisetopsida
What are the two kinds of sporangia within the ferns?
Euporangiate (the parent cells are located at the surface of the tissue from which the sporganium is produced) or Letosopraiate(single superficial cell that produce a part of the sporangial stalk)
What is a Annulus?
Each sporangia contains a special layer of unevenly thick-walled cells
When drying out of the sporangia, this creates a tearing in the middle of the capsule
The classes Psilotopsida contains two orders of homosporous ferns. What are they?
Orppioglossales and Psilotales
Filicales chracteristics
Leptosporangitiate ferns
Has siponostelic rhizomes that produces new sets of leaves each year
The fern embryo produces a true root, but then is replaced by advents roots
The leaves are megaphylls
The Lavinia of Filicales is divided what are the parts?
Into pinnae, which are leaflets attached to rachis, which a re extension of the leaf stalk or petiole
Young fern leaves are coiled and known as fiddleheads and this type development is known as..?
Circinate vernation which the uncoiling results from more rapid growth on the inner than the outer surface
Ophioglossales characteristics
Eusporangngiate ferns
Contain Botrychium and Ophioglossum
Have fertile and sterile segment of leaves
Psilotum characteristics
Whisk ferns
Lacks roots and leaves, with diachotomoously branching sporophyte.
Associated with Protostele and are homosporous
Spore give rise to bisexual gametophyte (some contain symbiotic fungi)
Sperm are mutiflagellate
The sporophyte becomes detached from the foot, which remains in the gametophyte
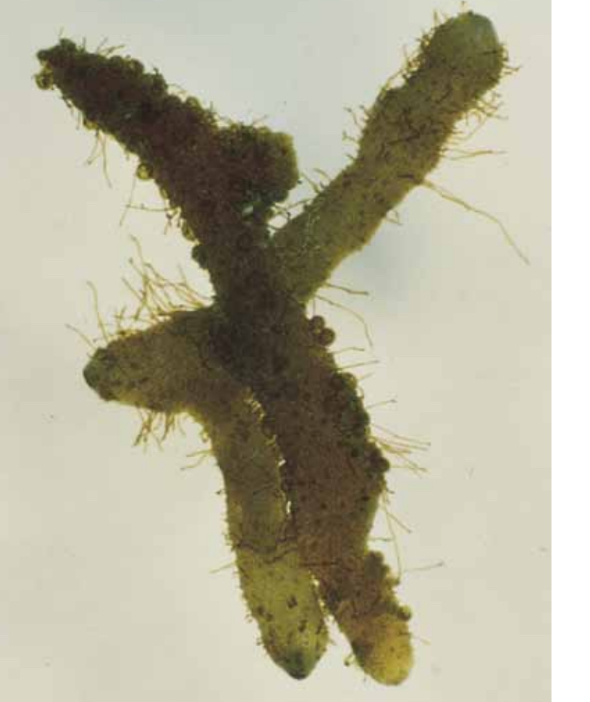

The sporangia of Polypodiopsida occur where,,?
On the margins or lower surfaces of the leaves or on modified stalks. Commonly occur in clusters called sori which many appear as yellow- blackish dots lower surface of the fond.
The young sori are covered by outgrowth of the leafs, the indusia (which shrivel when the sporangia is ready to shed their spores)
In Polypodiopsida the gametophyte typically develops into what..?
A flat hearted shaped membranous structure called the Prothallus, that has numerous rhizomes on its lower surface.
Both Antheridia and archegonia develop on the lower surface of the prothallus.
What does the Class of Polypodiopsida contain?
One order, the Salviniales and two families, Marsileaceae and Salviniaceae. These two families were derived from a common ancestor
All of the water ferns are heterosporous, there are 5 genera of water ferns
What are the two genera of Salviniaceae and the characteristics?
Azolla and Salviniaceae- both small plants that float on water and both produce their sporangia in sporocarps
In Azolla the tiny bigoted leaves are borne on slender stems, which a pouch forms on teh upper photosynthetic lobe of the leaf
Equisetum CHaracteristics
Horsetails that are widespread in moist or damp places by streams along the edge of the woods
Mircophylls are whorled in the nodes and the internodes are ribbed
They rhizomes are perennial, when the plants die the rhizomes stay
Hollow Pith surrounded by smaller canals called cardinal canals each has a strand of xylem and phloem
Homosporous with groups of small umbrella like structures known as sporganiophores which are clustered into stability
What do the spores contain in Equiestum when mature?
The sporangia contract and split along their inner surface releasing numerous spores.
Elators which are thicker bands that arise from the outer layers of the spore wall they play a role in spore dispersal