Exam 2 Full Set
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
HCl (Hydrochloric Acid)
-6
CH3CO2-H (Acetic Acid)
4.8
H2O (Water)
14
CH3CH2O-H (Ethanol)
16
HC≡CH (Acetylene)
25
H-H (Dihydrogen)
35
H2N-H (Ammonia)
38
CH2=CH2 (Ethylene)
44
CH3-H (methane)
50
Polar dissolves?
Polar
Non-polar dissolves?
Non-polar
F,O,N molecules may be water soluble if?
They have 5 or more carbons per non-carbon element
What is an ionophore?
An organic molecule that disrupts cell membranes.
What is a crown ether?
A synthetic ionophore.
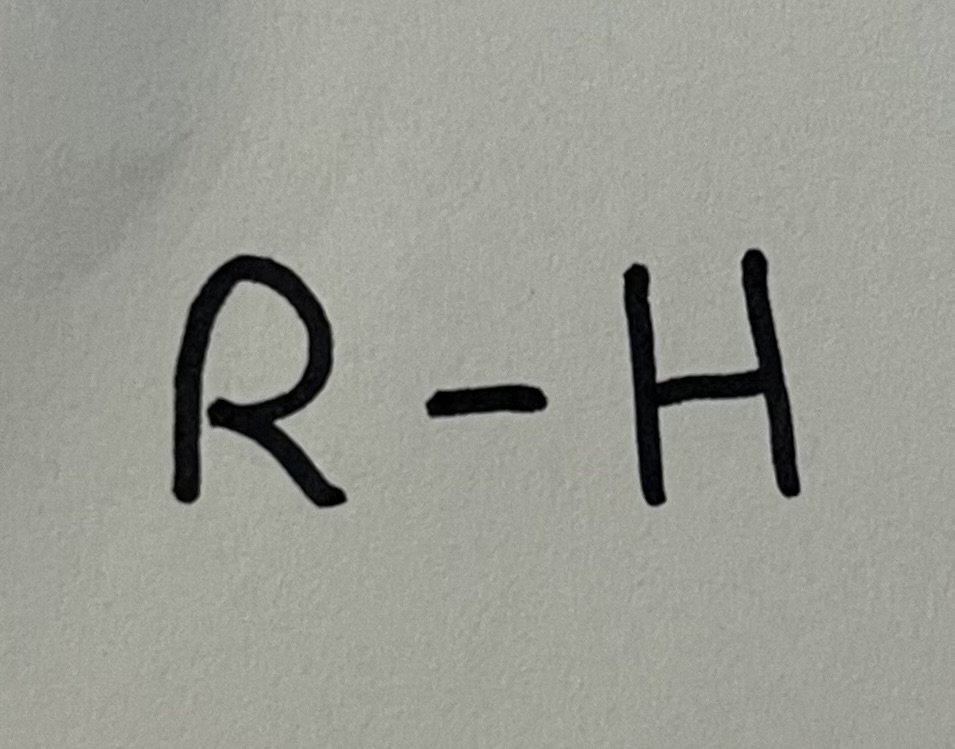
Alkane
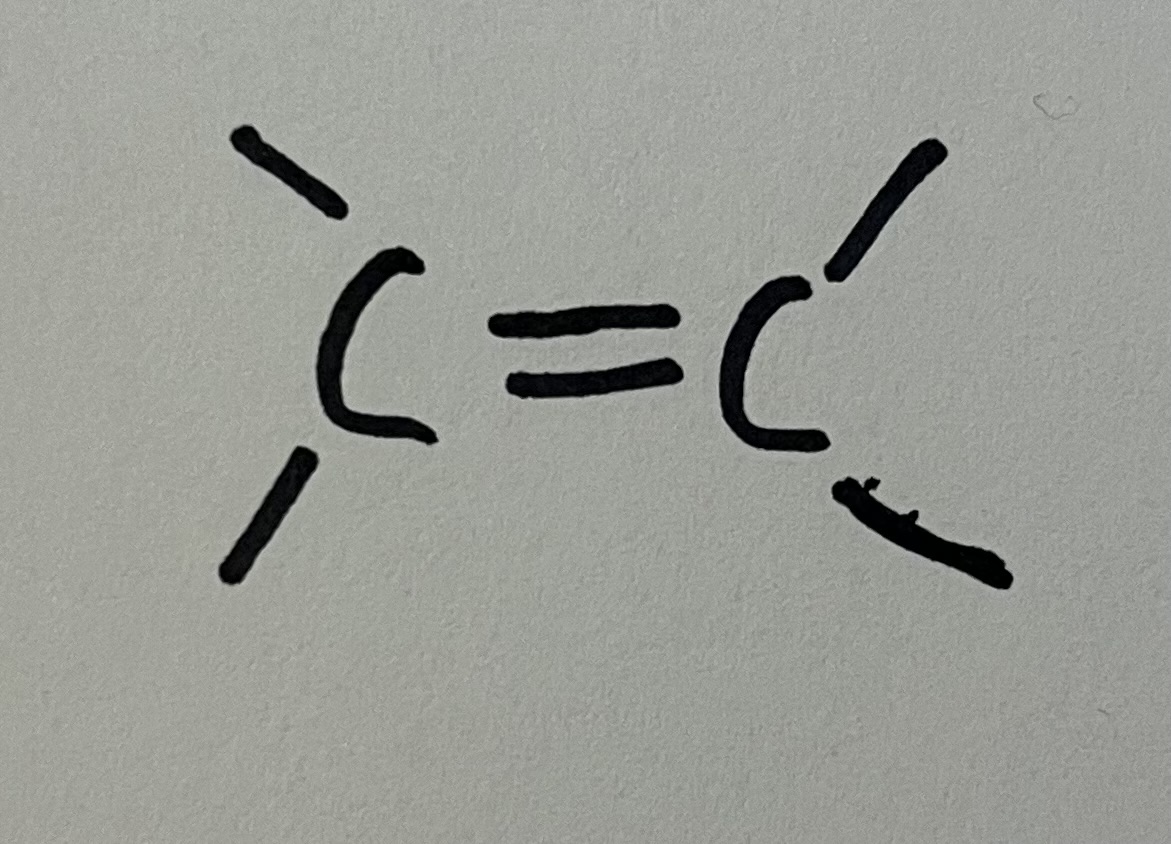
Alkene
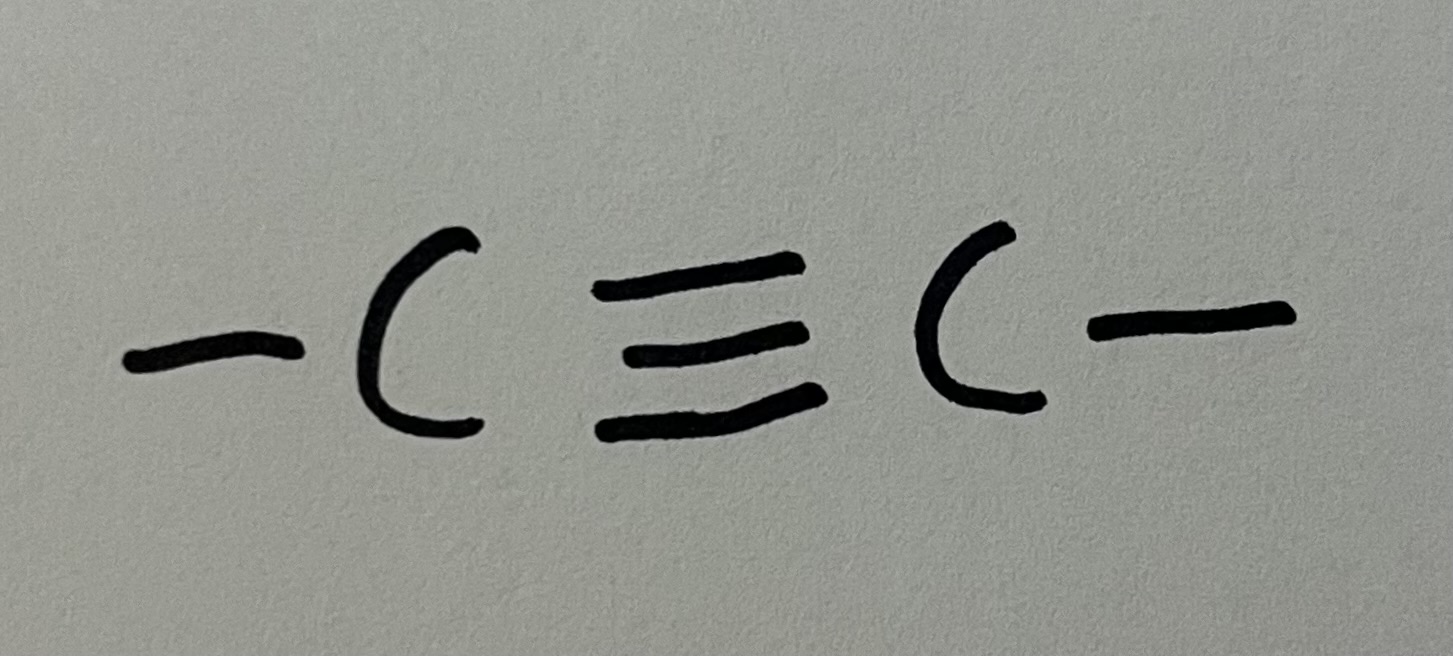
Alkyne
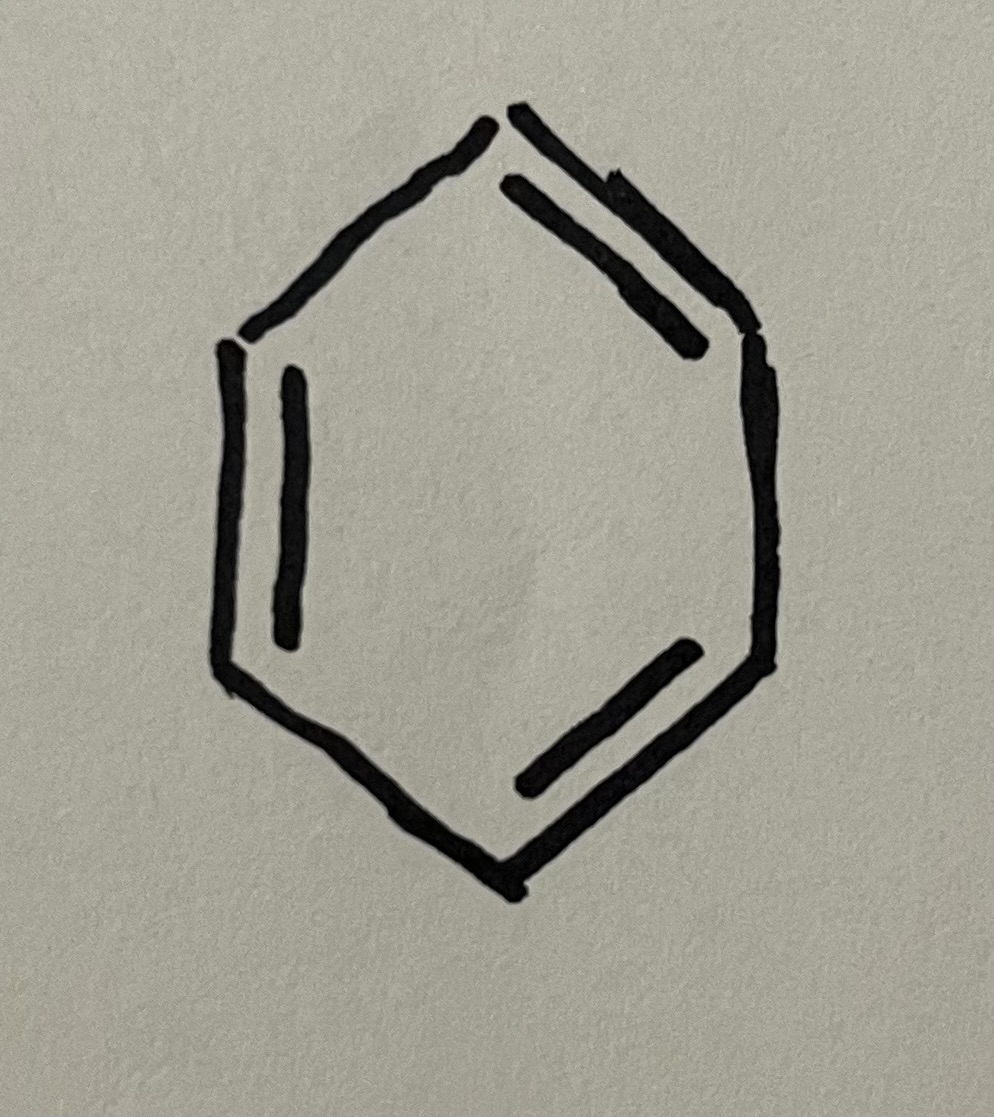
Aromatic/benzene ring
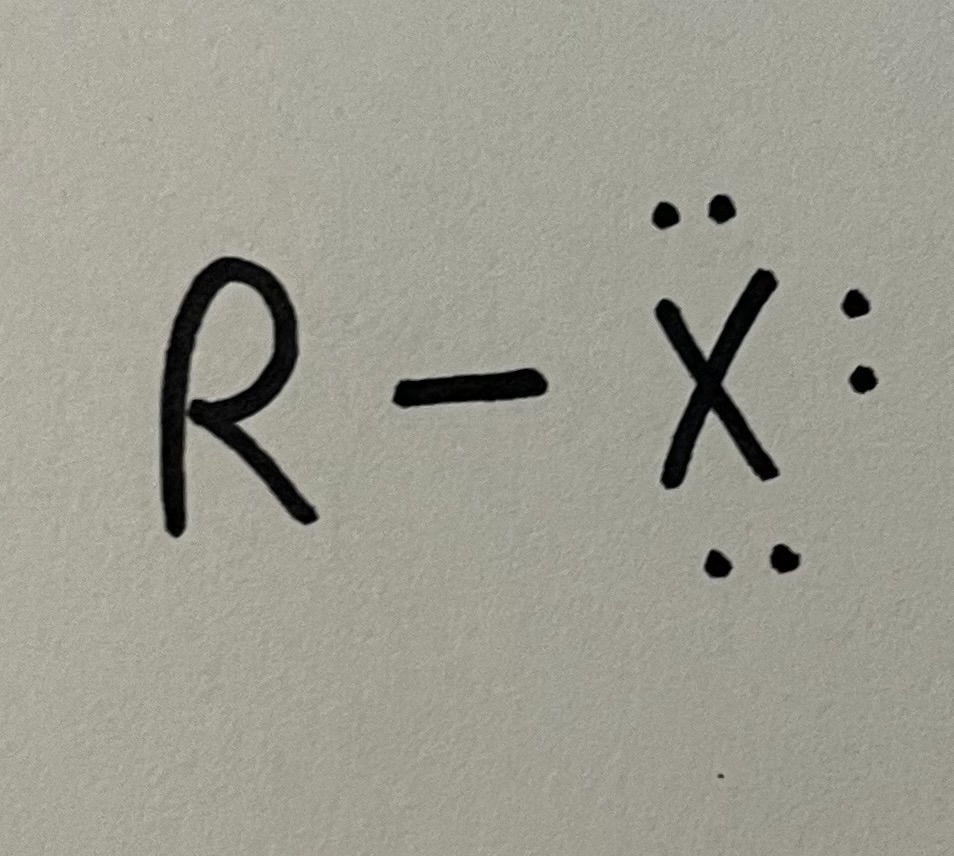
Alkyl halide
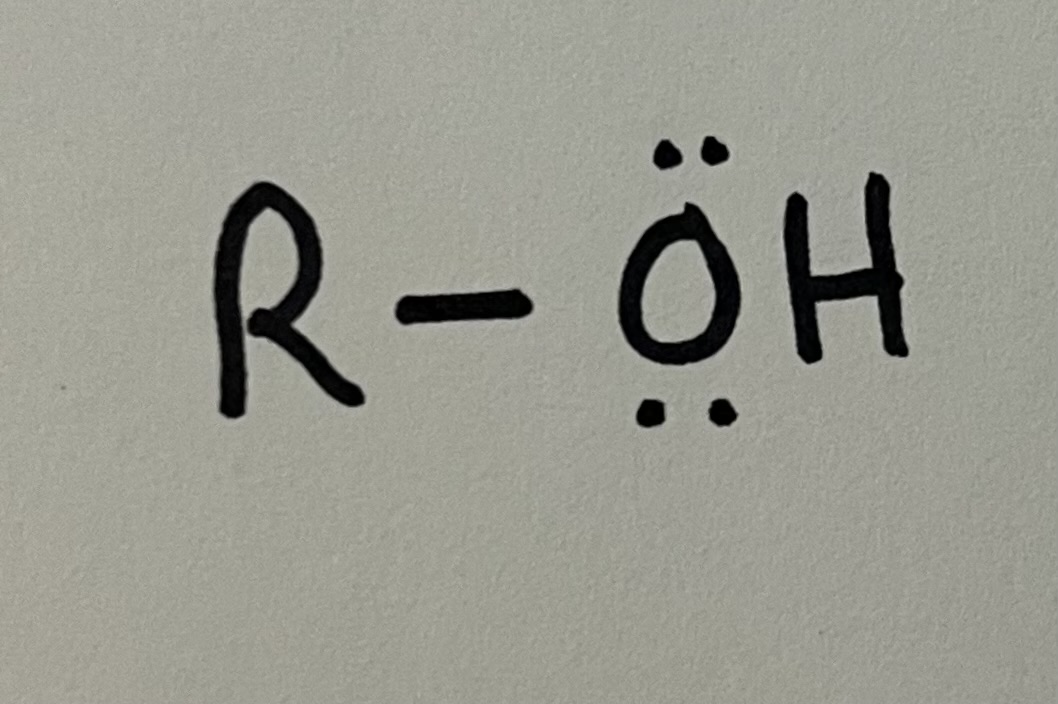
Alcohol
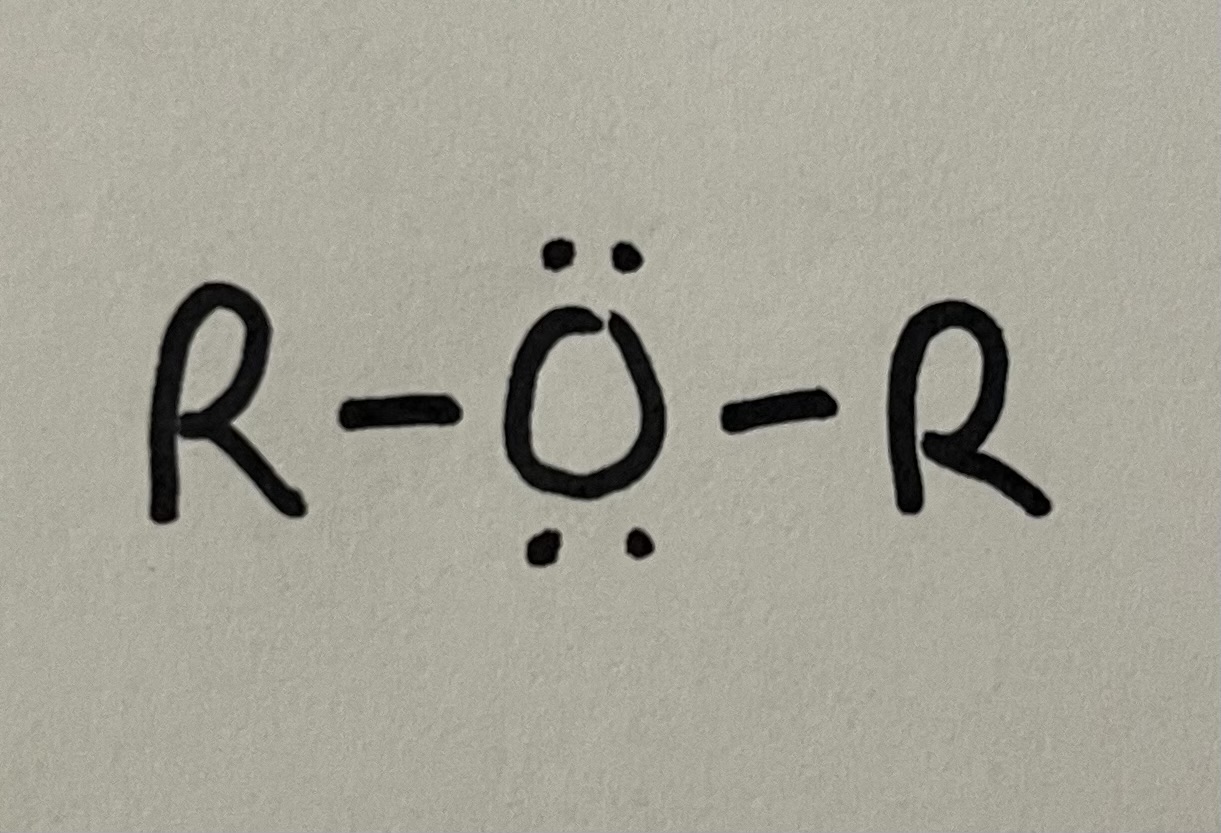
Ether
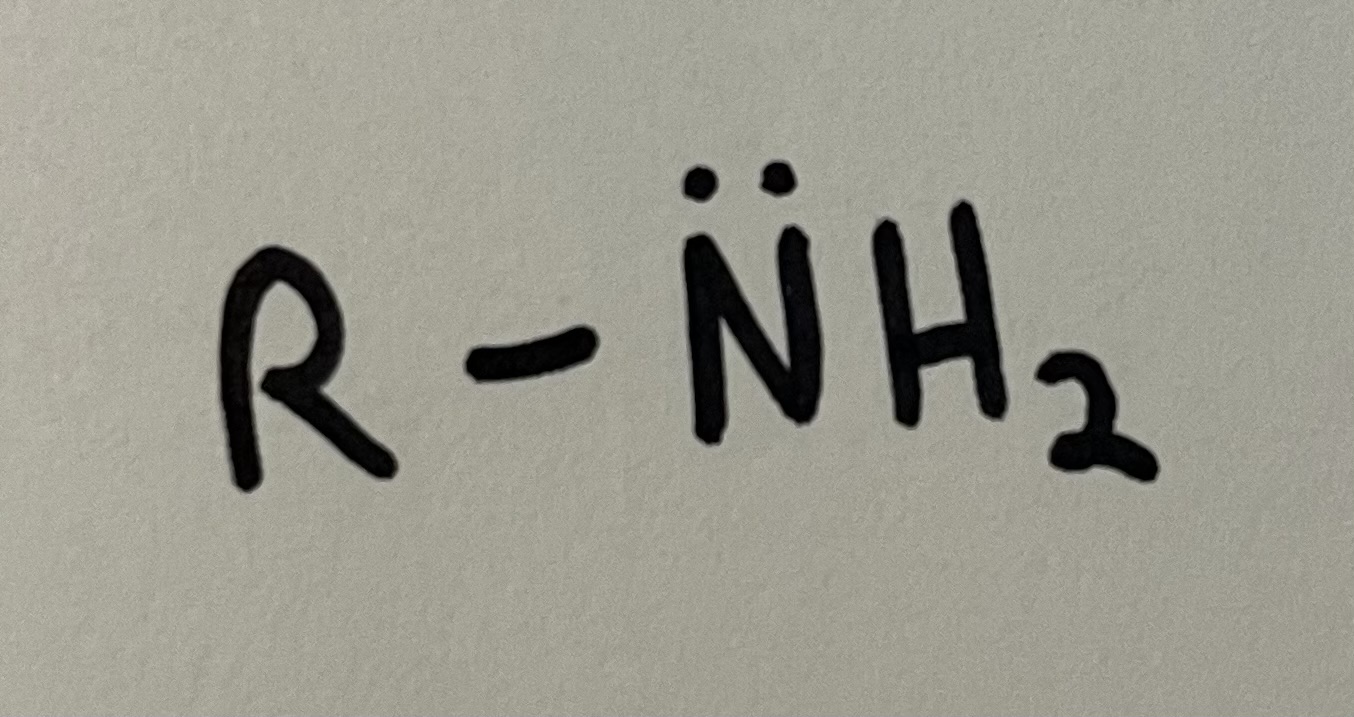
Amine
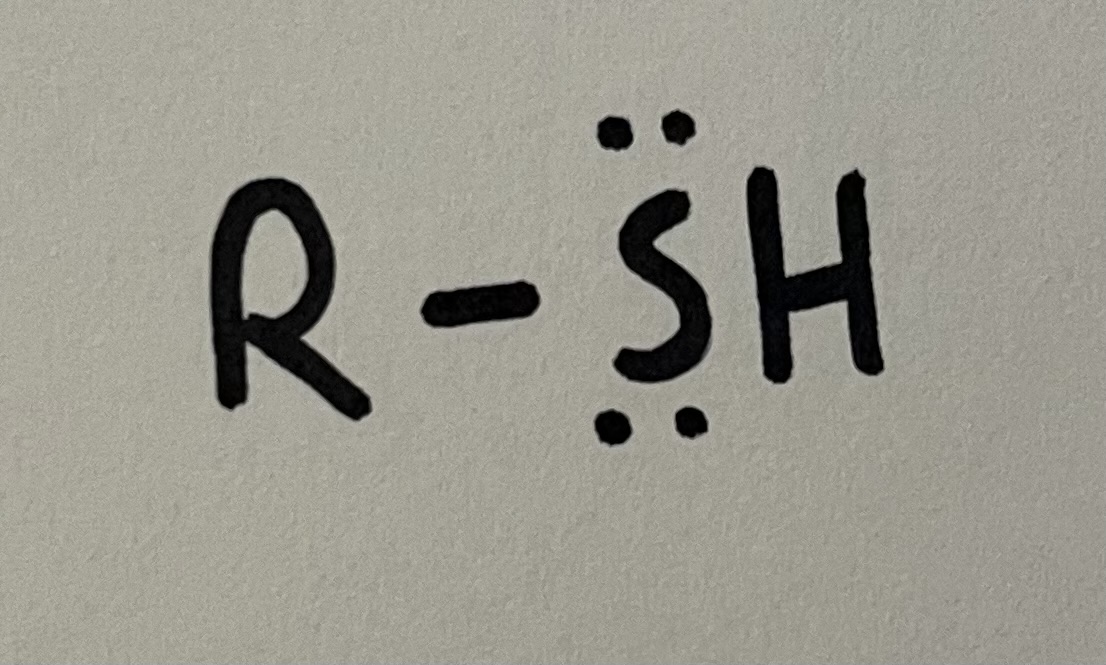
Thiol
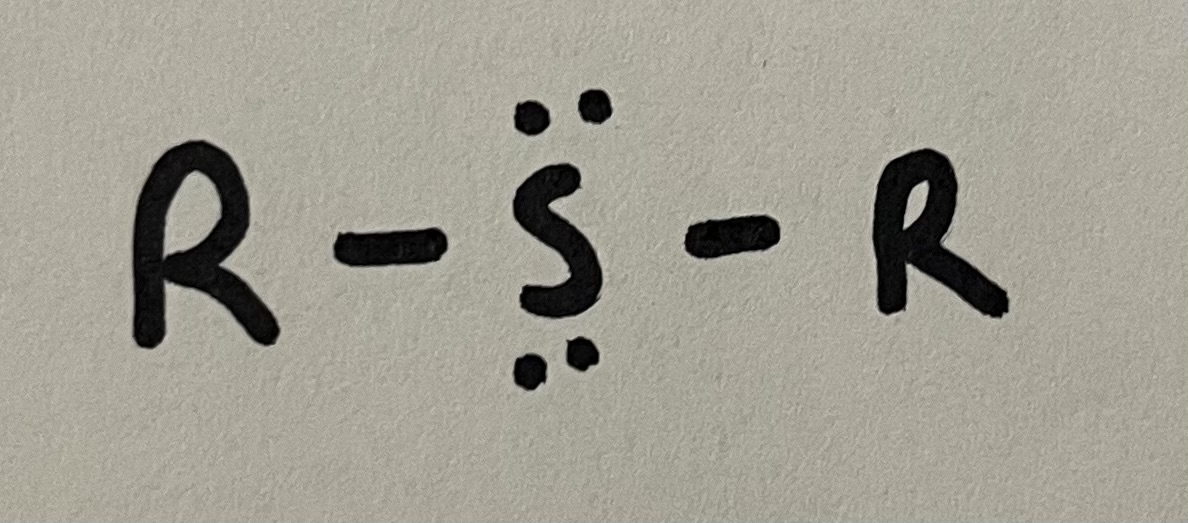
Sulfide
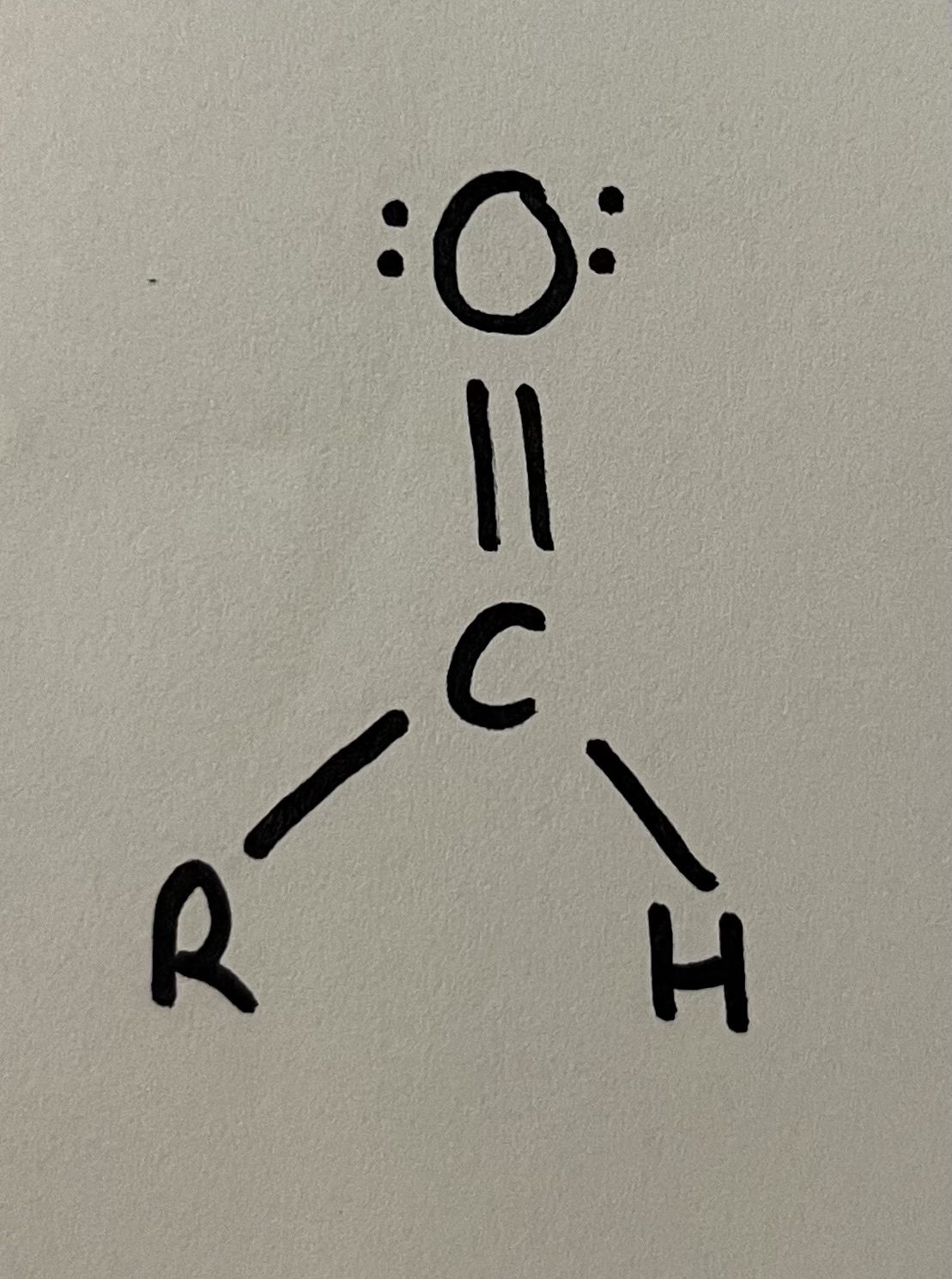
Aldehyde
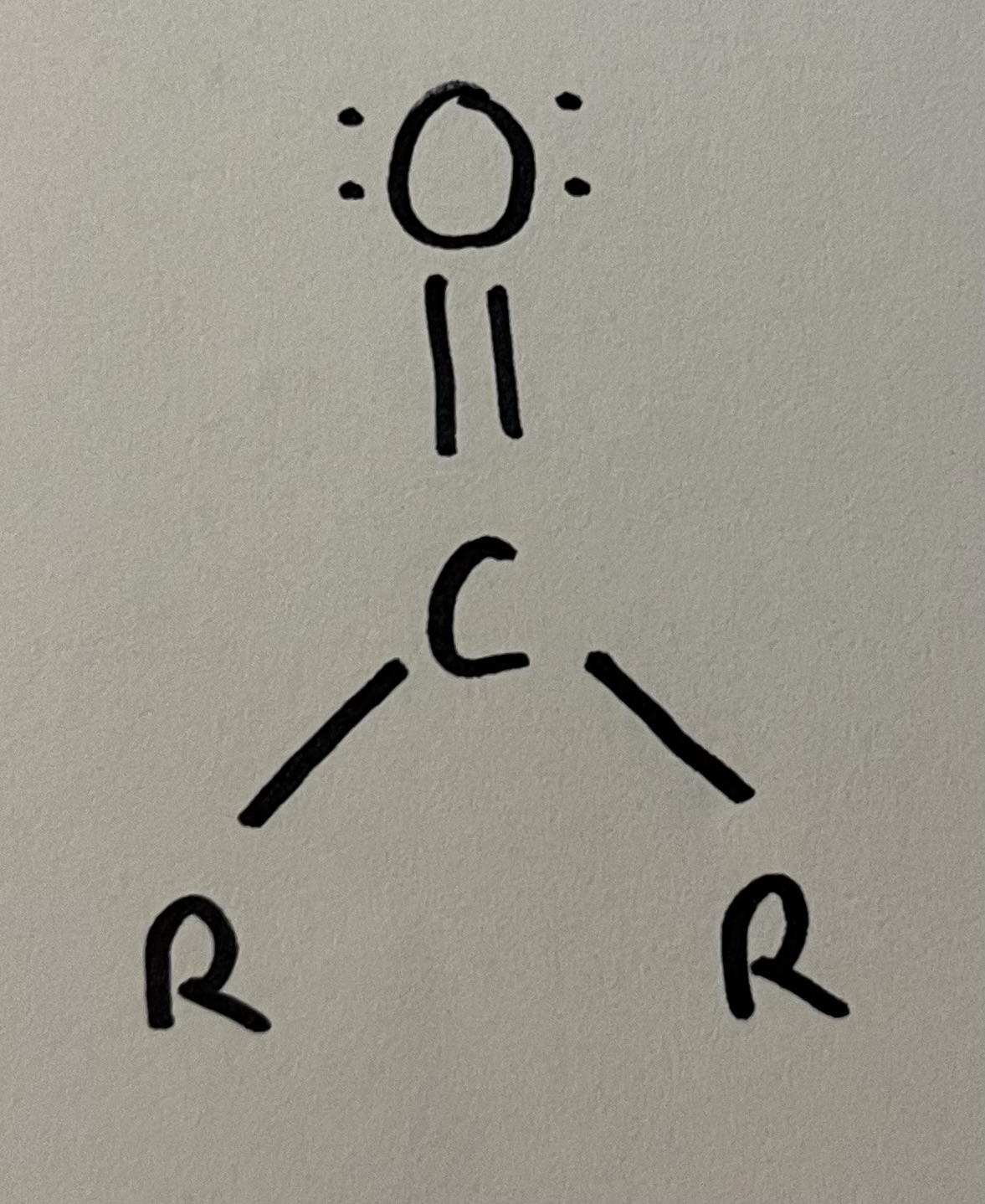
Ketone
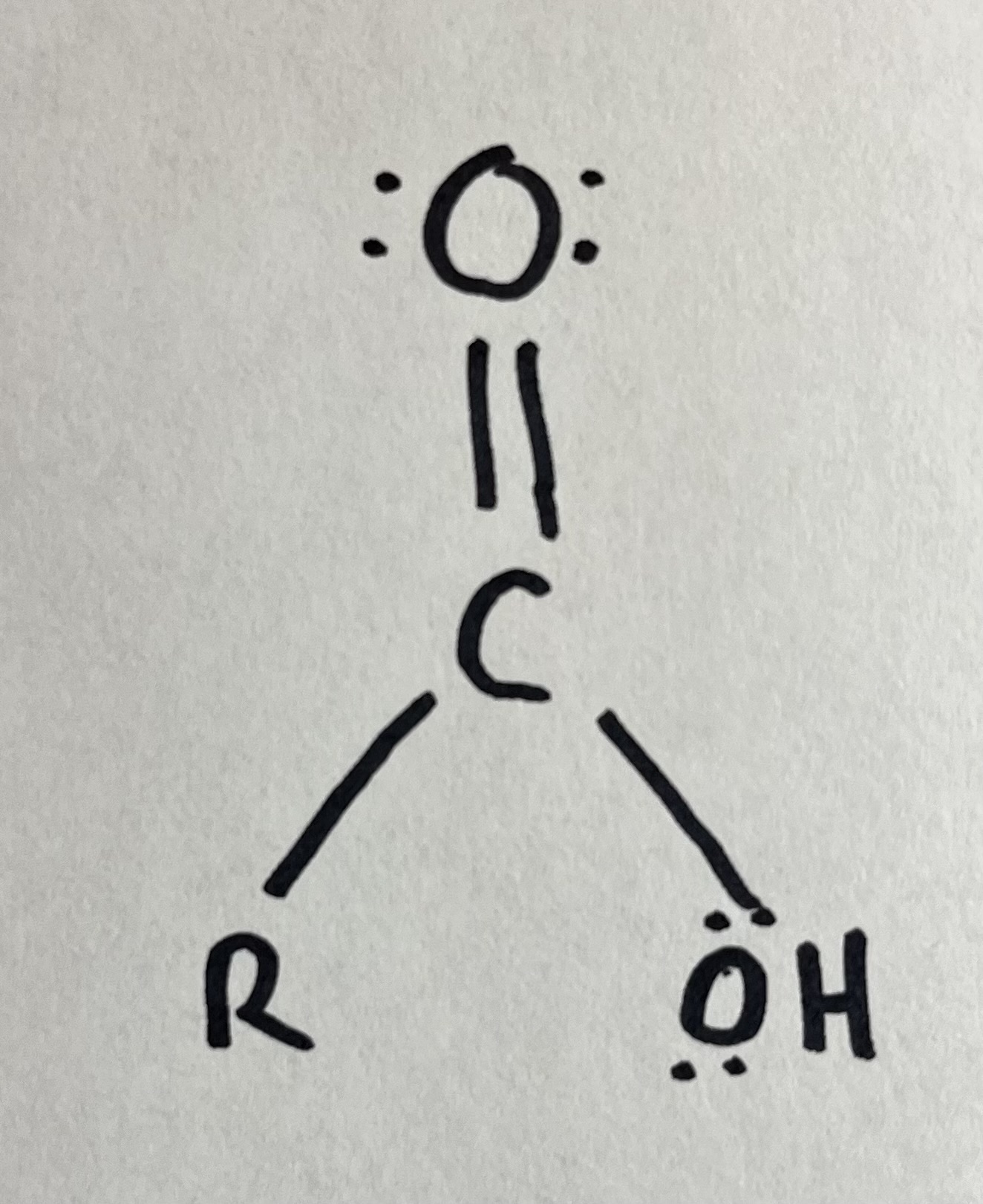
Carboxylic acid
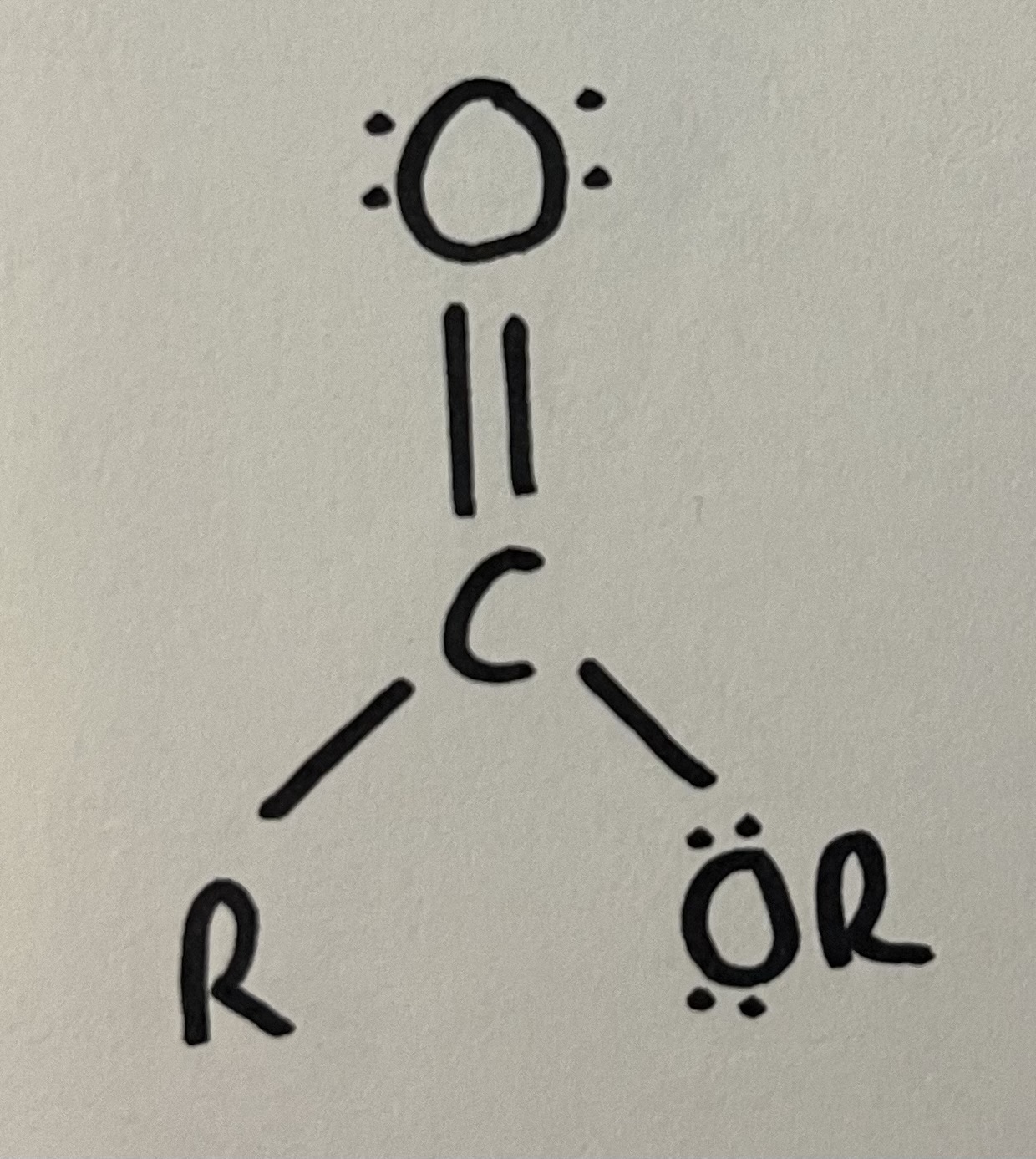
Ester
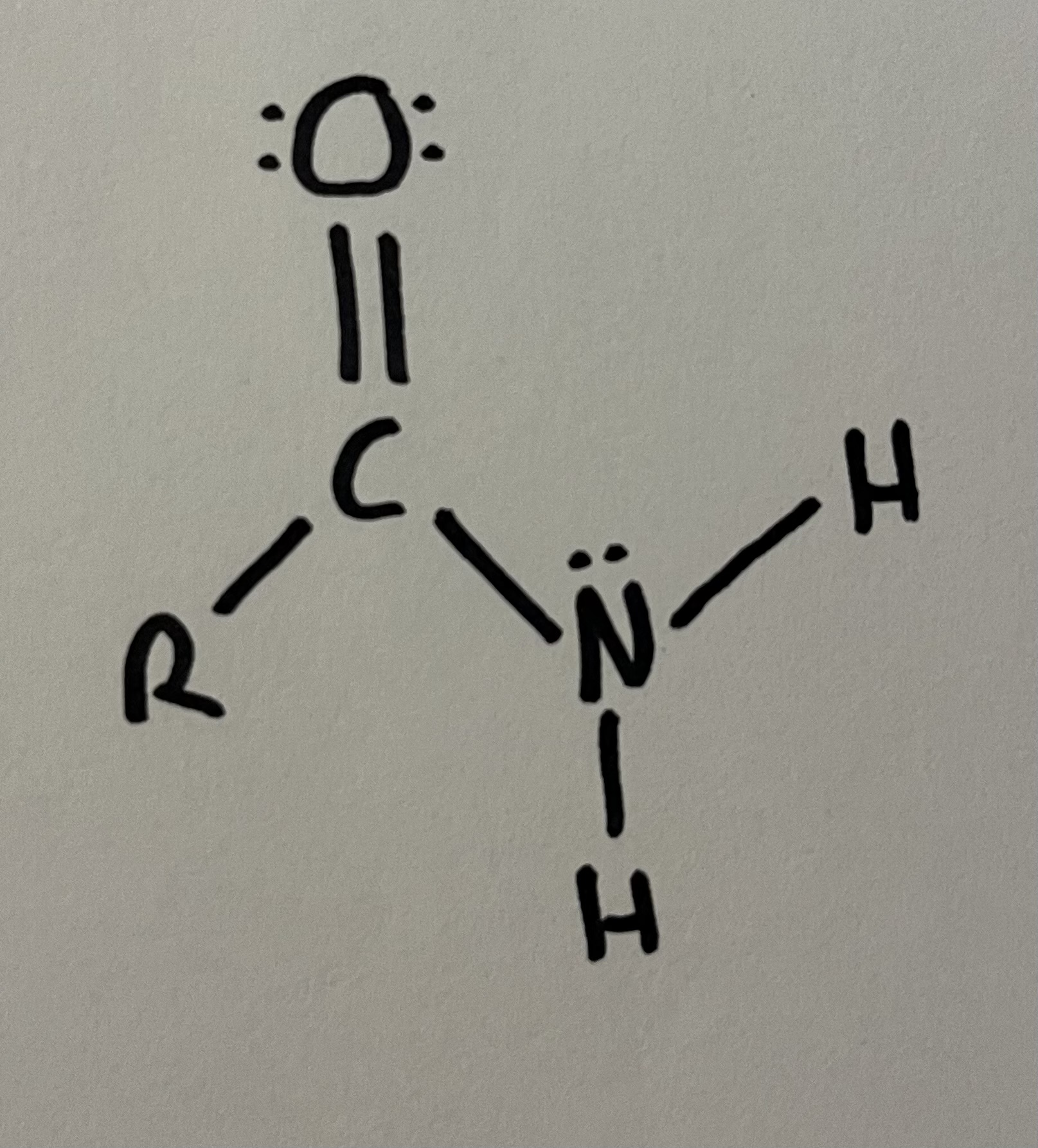
Amide
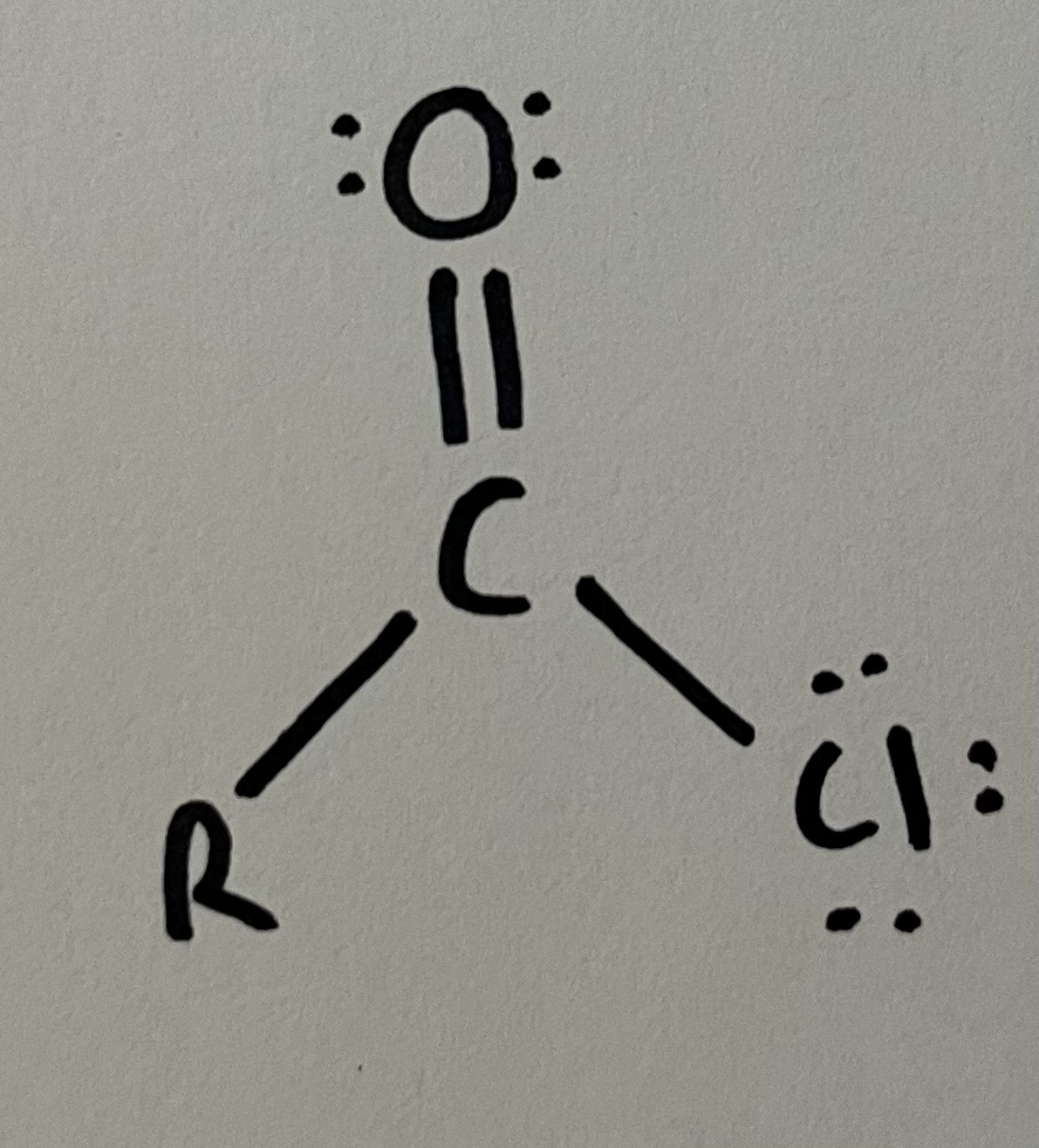
Acid chloride
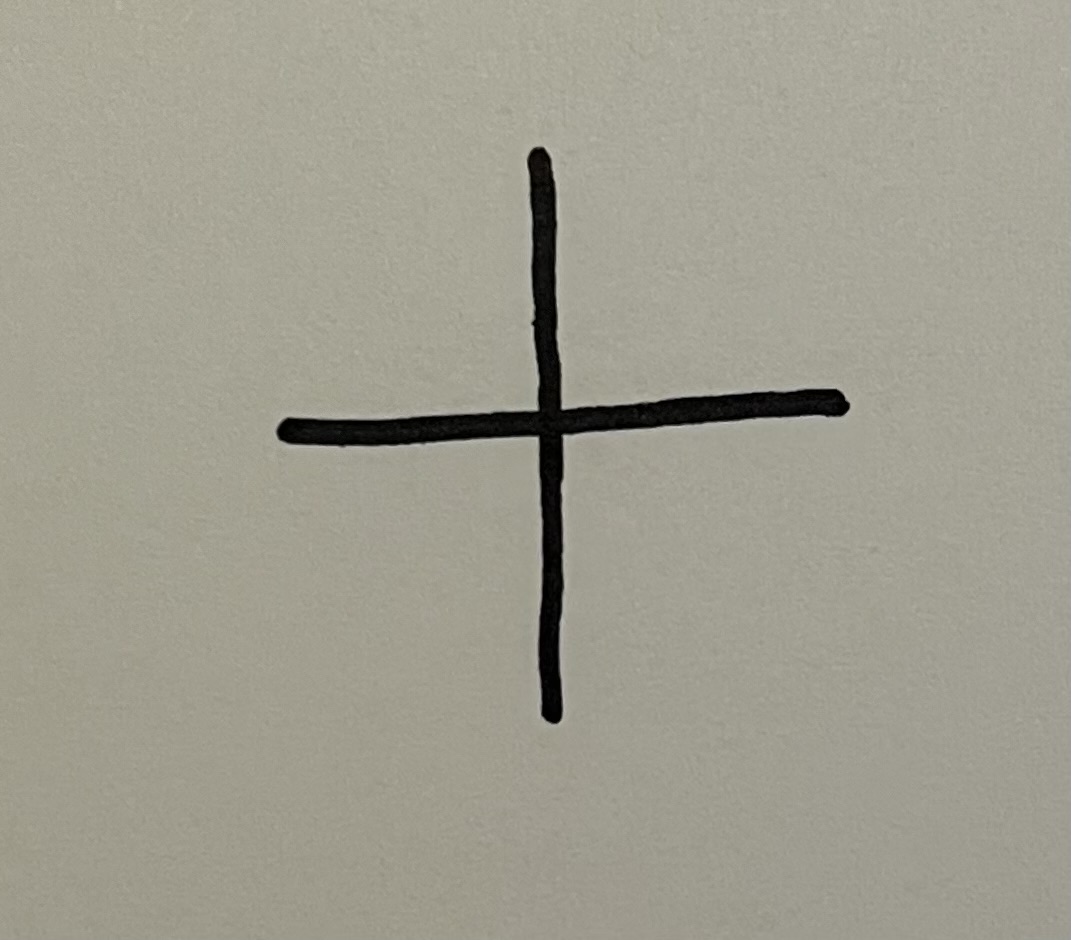
tert-butyl
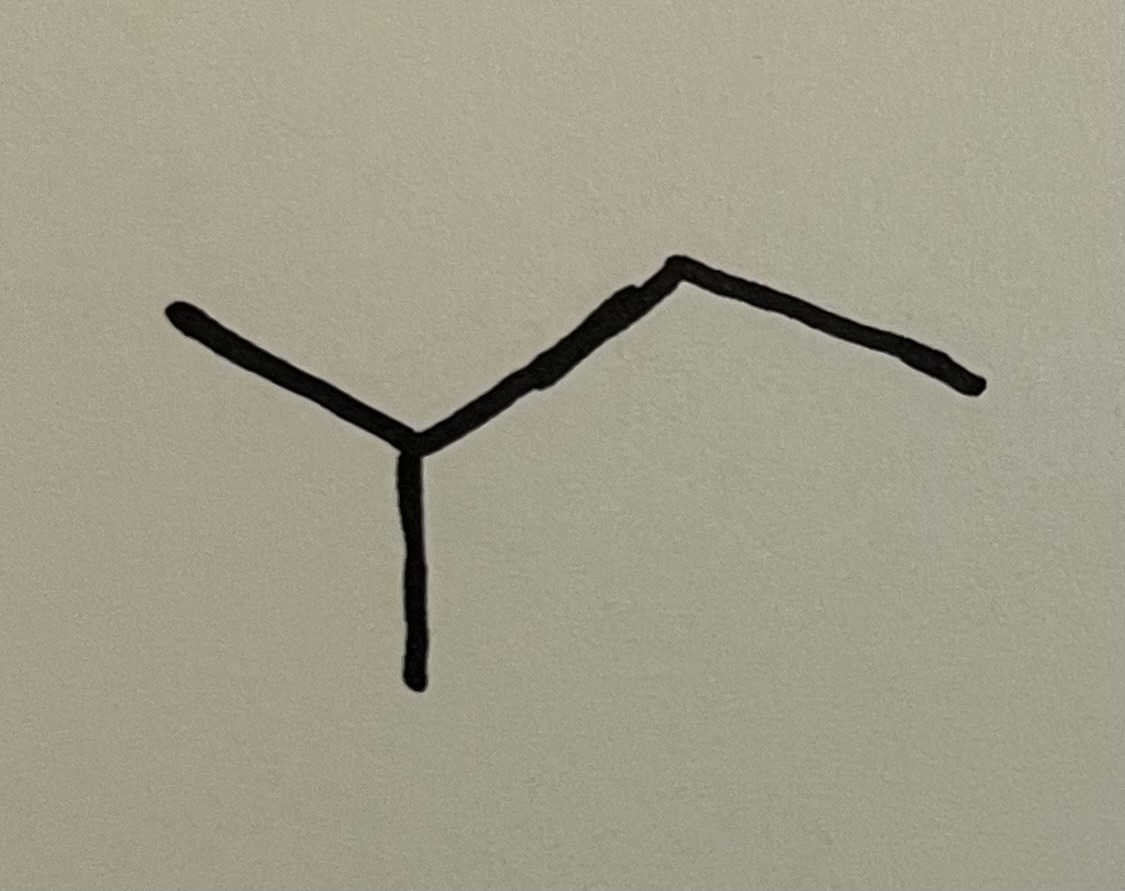
sec-butyl
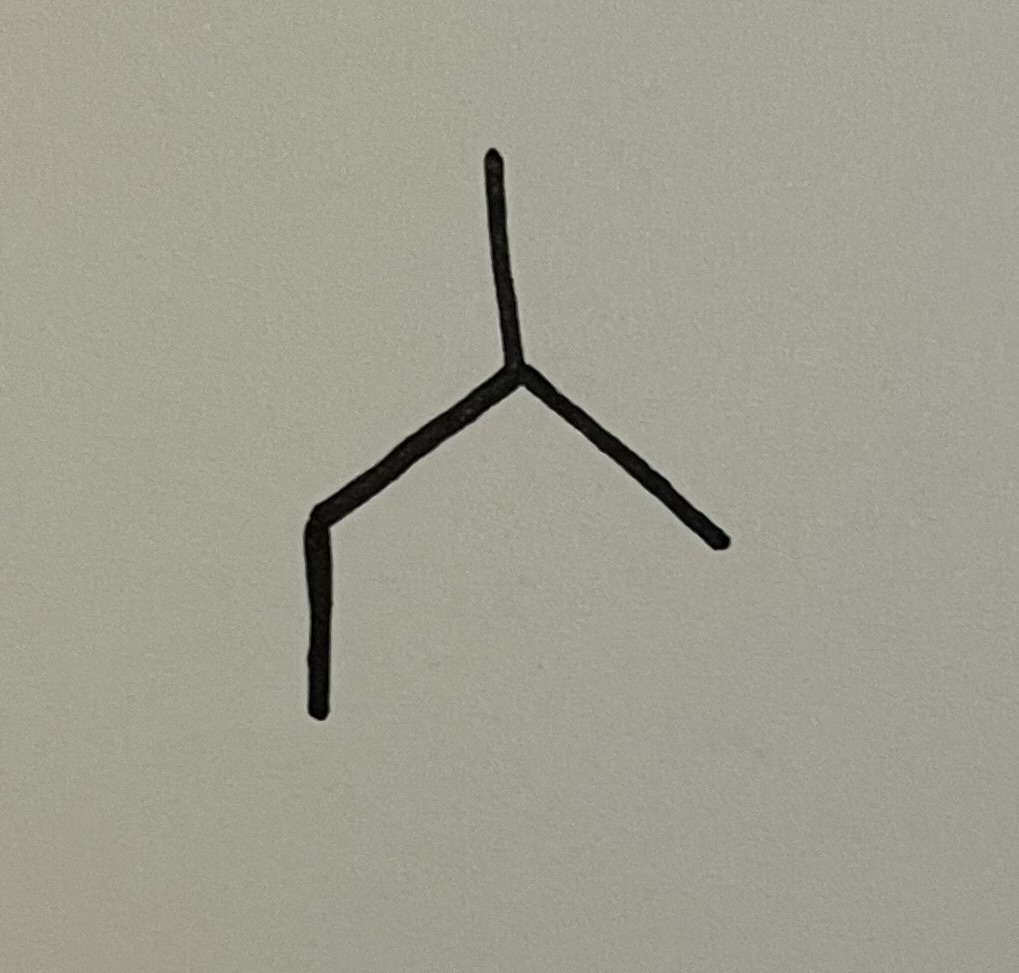
isobutyl
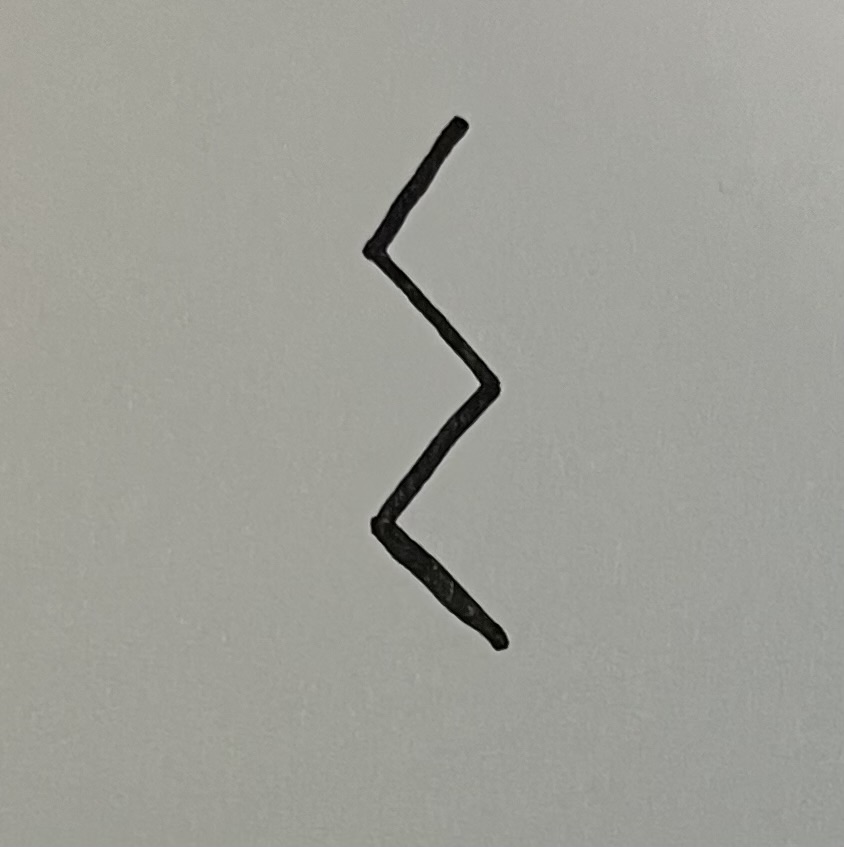

butyl
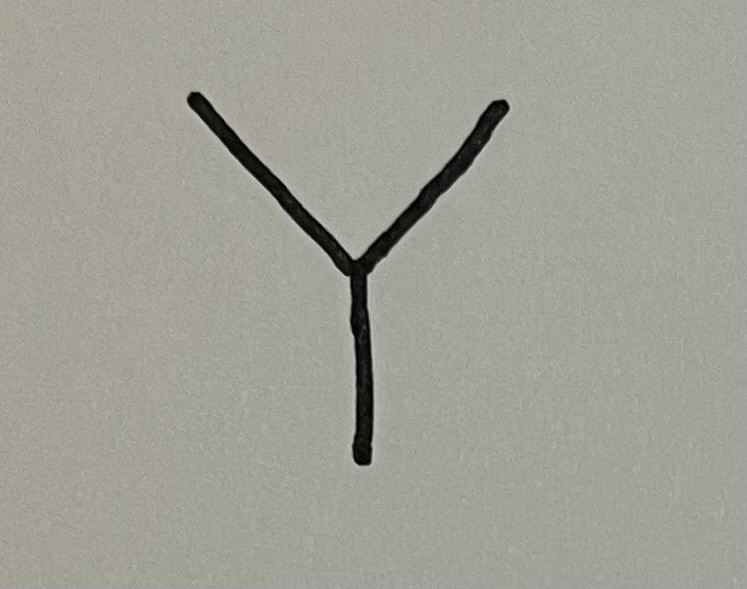

isopropyl
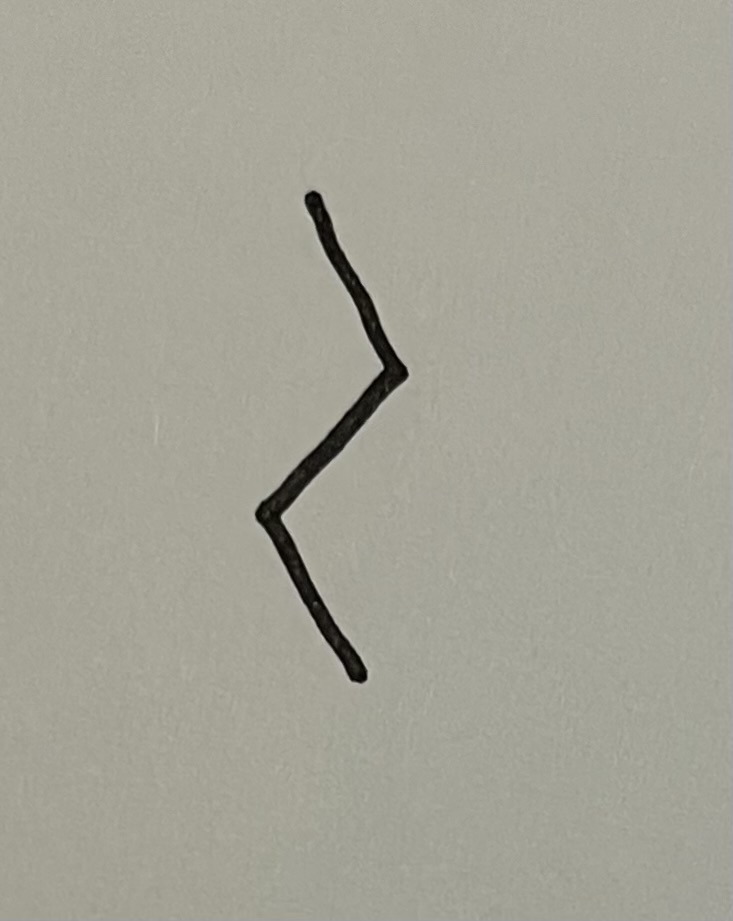

propyl
1 C atom
Methane/methyl
2 C atoms
Ethane/ethyl
3 C atoms
Propane/propyl
4 C atoms
Butane/butyl
5 C atoms
Pentane/pentyl
6 C atoms
Hexane/hexyl
7 C atoms
Heptane/heptyl
8 C atoms
Octane/octyl
9 C atoms
Nonane/nonyl
10 C atoms
Decane/decyl
If two chains of equal length are present pick the one with?
The largest number of branch points
Begin numbering a chain from?
The end closest to the first branch point
If a chain has two branch points an equal distance from both ends then number from the end that?
Is closest to the next branch point. If there is no second branch go in alphabetical order.
What prefix is not ignored when alphabetizing?
iso
Rings have the parent prefix of?
cyclo
If a ring has 1 substituent start numbering
at that substituent
If a ring has multiple substituents that are the same number towards?
The next closest substituent.
If a ring has two different substituents start numbering?
Alphabetically then the shortest way to the next sub.
If a ring has three or more subs then number?
In a way that makes the numbers as low as possible
What is a Lewis acid?
An electron pair acceptor
What is a Lewis base?
Electron pair donor
Acids are known as?
Electrophiles
Bases are known as?
Nucleophiles
What are the intermolecular forces from weakest to strongest?
London dispersion
Dipole-Dipole
Hydrogen bonding
Boiling point increases with?
Intermolecular forces
Melting point is also increased by?
Packing
Polar substances dissolve?
Polar substances
Non-polar substances dissolve?
Non-polar substances
An organic compound is water soluble if?
It contains at least one H-bonded F,O, or N for every five carbons.
How does pka affect reaction equilibrium?
Equilibrium moves towards the side with the higher pka. (Weaker acid)
A BL acid is a?
Proton (H+) donor.
A BL base is a?
Proton (H+) acceptor.
What 4 factors determine the strength of an acid?
-Elemental effects
-Inductive effects
-Resonance effects
--Hybridization effects
What is the elemental effect on acids?
Acid strength increases with the electronegativity of the atom bonded to H. Acidity increases as you move down colums.
What is the inductive effect?
Electronegative atoms pull through bonds.
What is the resonance effect?
Having more stable resonance forms makes a molecule more acidic.
What are hybridization effects?
Higher s character (single>double>triple bonds) makes a molecule more stable and acidic.
What are the types of Newman projections?
Eclipsed (Highest energy)
Staggered gauche
Staggered anti (Lowest energy)
What is torsional strain?
Repulsive forces between two close carbons.
What is steric strain?
Forces between two large groups that are close together.