302 unit 2 - mood, pain/comfort
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
crisis
A sudden event in one’s life, during which usual coping mechanisms cannot resolve the problem
3 factors influencing a patient’s crisis response
1. The individual’s perception of the event.
2. The availability of situational supports.
3. The availability of adequate coping mechanisms
types of crises

Dispositional crisis
An acute response to an external situational stressor
Example: extreme stress response from someone struggling with the decision of divorce
Crisis of anticipated life transitions
Normal life-cycle transition that may be anticipated but over which the individual may feel a lack of control
Example: moving to college and being separated from normal support system leading to anxiety
Crisis resulting from traumatic stress
Precipitated by an external stressor over which the individual has little or no control, and from which he or she feels emotionally overwhelmed and defeated
Example: a rape victim developing PTSD
Maturational/developmental crisis
Occurs in response to a situation that triggers emotions related to unresolved conflicts in one’s life
Example: starting a new job, leaving home for college, etc leading to anxiety/depression
Crisis reflecting psychopathology
A crisis that is triggered by a preexisting mental illness
Example: someone with a personality disorder might have trouble coping with a stressful life event
Psychiatric emergency
A crisis situation in which general functioning has been severely impaired and the individual is rendered incompetent or unable to assume personal responsibility
Example: severe emotional situation leading to a suicide attempt
milieu
a person’s social environment
SOLER acronym for active listening
SOLER = sit square, open posture, lean forward, eye contact, relax
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
depressed mood or loss of interest/pleasure in usual activities; impaired social & occupational functioning for >2 weeks; no hx of manic behavior

Persistent Depressive Disorder (Dysthymia)
milder sx than MDD, chronically depressed/irritable mood most days for >2 yrs; describe mood as sad or “down in the dumps”
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder
markedly depressed mood, anxiety, mood swings, decreased interest during week before menstruation
Depression - implications in childhood and adolescence
Adolescence:
• Behavioral change that lasts for several weeks
• Psychosocial intervention & medications
• SSRIs: fluoxetine, escitalopram (age 12-17)
→ Black-box warning

Depression - implications for elderly
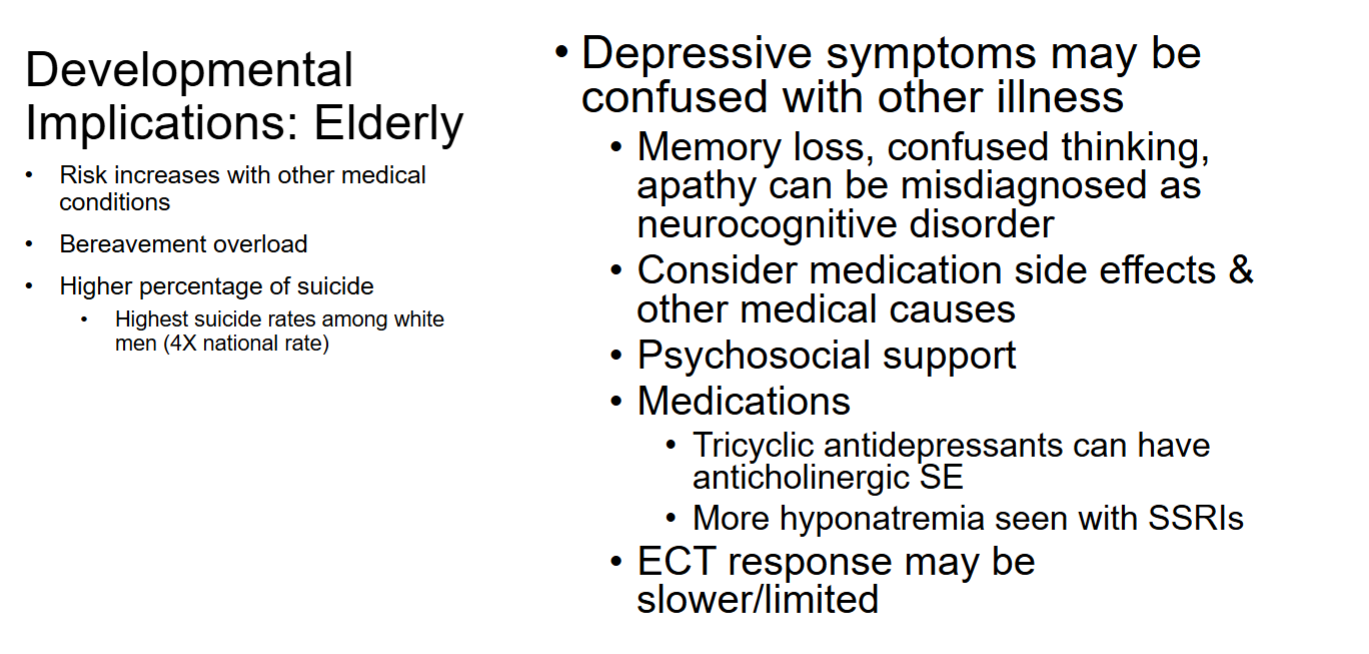
Nursing process - planning/implementation of depression care

Types of talk therapy for depression

ECT - electroconvulsive seizure for depression
*Most common AE’s = memory loss and confusion
*Mortality risk = cardio complications
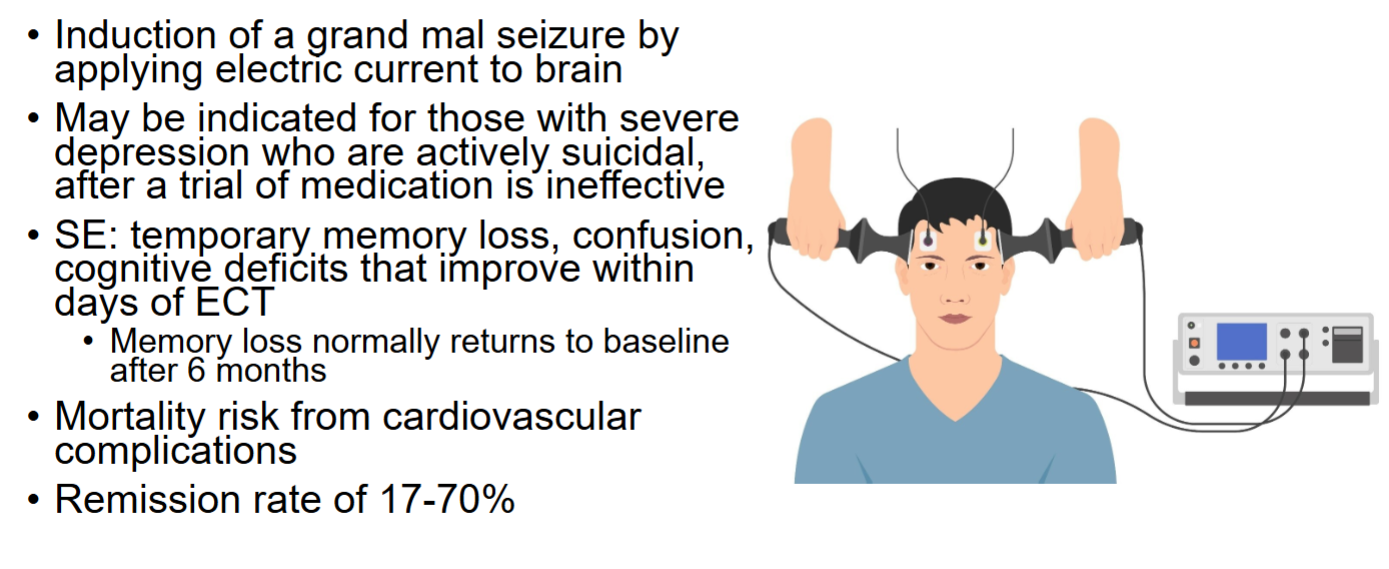
Pre-treatment meds for ECT
Atropine or glycopyrrolate
-30m before IM
-given to decrease secretions (prevent aspiration) and to reduce vagal stimulation from ECT which would lead to bradycardia
In-treatment meds for ECT
Short-acting anesthetic (propofol or etomidate)
Muscle relaxant = succinylcholine chloride
-Given to prevent severe muscle contractions during seizure
**Paralyzes resp muscles → must be on O2
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS)
Stimulates nerve cells in brain by use of short magnetic pulses
• Waves passed through coil placed on scalp
• 40min sessions 3-5X/wk
• SE: tinnitus, headache, facial twitching
• Rarely seizures can occur
• Remission rate of 30%
Mood vs Affect
Mood = a pervasive and sustained emotion that may have major influence on someone’s perception of the world
Affect = an observable emotional rxn that is associated with an experience
Mania vs hypomania vs delirious mania
Mania = feelings of elation, inflated self-esteem, grandiosity, hyperactivity, agitation, and accelerated thinking and speaking. Lasts at least 1 week
Hypomania = manic symptoms that do not meet criteria for mania (not as severe). Lasts at least 4 days
Delirious mania = extreme exacerbation of acute mania. Rare.
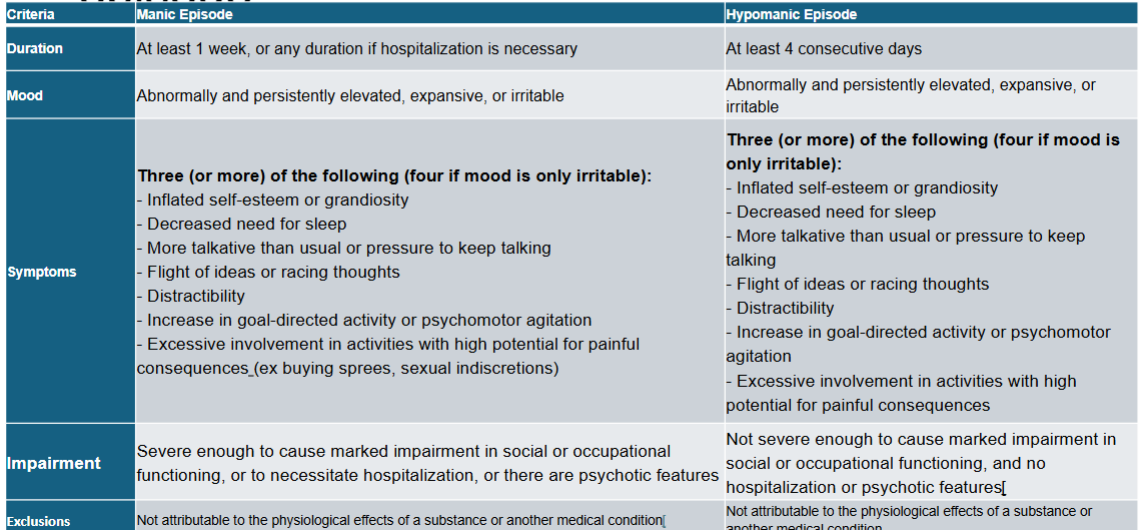
Bipolar I vs Bipolar II
BP I = Pt has at least 1 full manic episode during life, may also have experience depressive episodes
BP II = Pt has major depressive episodes, with episodic occurrence of hypomania. Has never met criteria for full manic episode
Cyclothymic disorder
-Pt cycles between depression and hypomania, but neither episodes are ‘severe’ enough to meet criteria for BPI or BPII
-Experienced for at least 2 years
Bipolar & ADHD
-ADHD is the most common comorbid condition for people w/ bipolar
-ADHD meds may exacerbate mania → only give after bipolar symptoms have been controlled
Lithium therapeutic range
*Narrow therapeutic index, must check serum levels 1-2 months
Acute Mania: 0.5-1.5 mEq/L
Maintenance: 0.6-1.2mEq/L
Lithium and hydration
Hyponatremia can cause lithium toxicity → must drink 2-3L water per day and have lots of salt in diet
Anticonvulsants for Bipolar

Verapamil for Bipolar

Antipsychotics for bipolar

Cluster A personality disorders
Behaviors described as odd or eccentric.
• Paranoid personality disorder
• Schizoid personality disorder
• Schizotypal personality disorder
Cluster B personality disorders
Behaviors described as dramatic, emotional, or erratic.
• Antisocial personality disorder
• Borderline personality disorder
• Histrionic personality disorder
• Narcissistic personality disorder
Cluster C personality disorders
Behaviors described as anxious or fearful.
• Avoidant personality disorder
• Dependent personality disorder
• Obsessive-compulsive
personality disorder
Paranoid PD
• Constantly on guard
• Hypervigilant
• Appear tense and irritable
• Become immune or insensitive to the feelings of others
• Always feel that others are there to take advantage of them

Paranoid PD - predisposing factors
• Possible hereditary link
• Subject to early parental antagonism and harassment
Schizoid & Schizotypal PD
Schizoid = Characterized by a profound defect in the ability to form personal relationships → failure to respond to others in a meaningful way
-Diagnosis occurs more frequently in men than in women
Schizotypal = Less severe version → Aloof and isolated, behaves in a bland and apathetic manner
Antisocial PD
A pattern that is exploitative, socially irresponsive, and w/o remorse - “psychpath”
-more common in men and poverty, very common in prison centers
-Predisposing factors: childhood physical abuse, poverty, inconsistent parental discipline
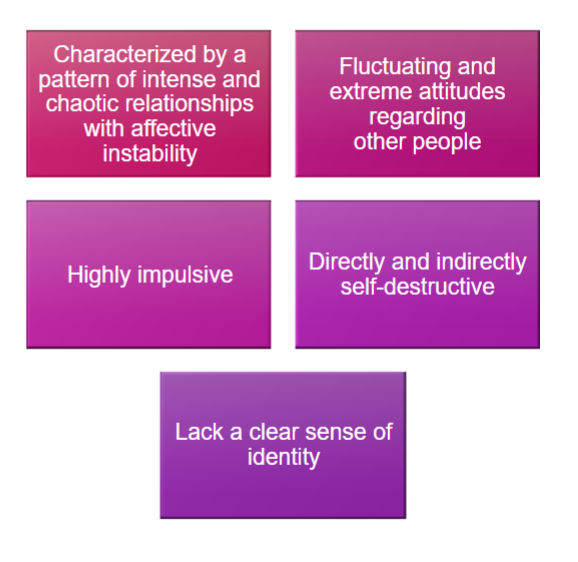
Borderline PD
Common behaviors: depression, manipulation, inability to be alone, splitting, impulsivity, self-destructive behaviors
-More common in women
-Predisposing factors: Childhood trauma/abuse, especially if they fail to find autonomy btwn 16-24months
Histrionic PD
Behavior is excitable, emotional, colorful, dramatic, extroverted
Narcissistic PD
Exaggerated sense of self-worth, lack empathy
-More common in men
Avoidant PD

Dependent PD
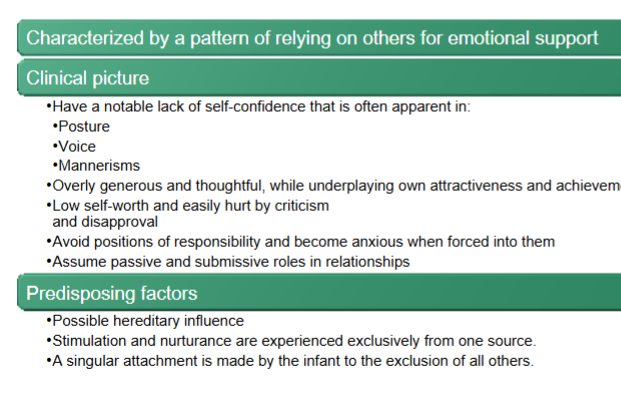
Obsessive-compulsive PD
especially concerned with organization + efficiency
rank-conscious, integrate with authority figures
rigid and unbending

Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD)
In children
Characterized by a persistent pattern of angry mood and defiant behavior that interferes with life activities. Can have low self esteem and low social interaction
-begins no later than adolescence
-May be a precursor to BPD in adulthood

Conduct disoder
In children and adolescents
Persistent physical aggression in the violation of the rights of others
-more common in males
-May be a precursor to APD in adulthood

Palliative care
Comfort and supportive care that is non-curable, NOT specific to end-of-life
-symptom management; an approach that improves quality of life
Palliative vs end-of-life (hospice) care
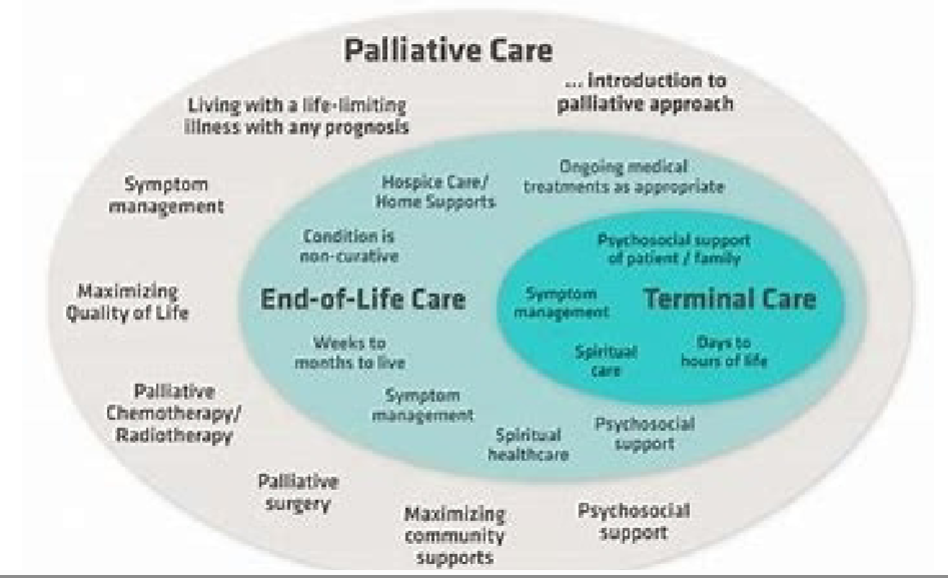
primary goal of EOL care
comfort
SPIKES communication model
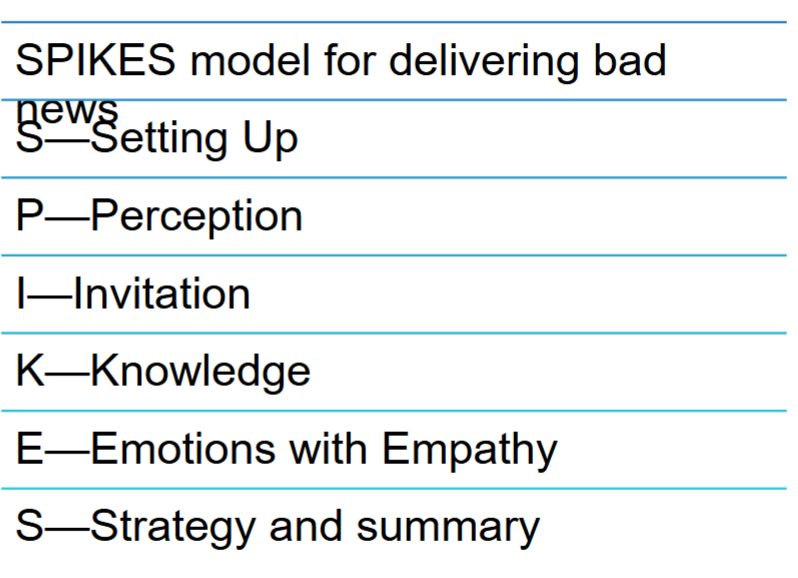
SPIKES - S and P
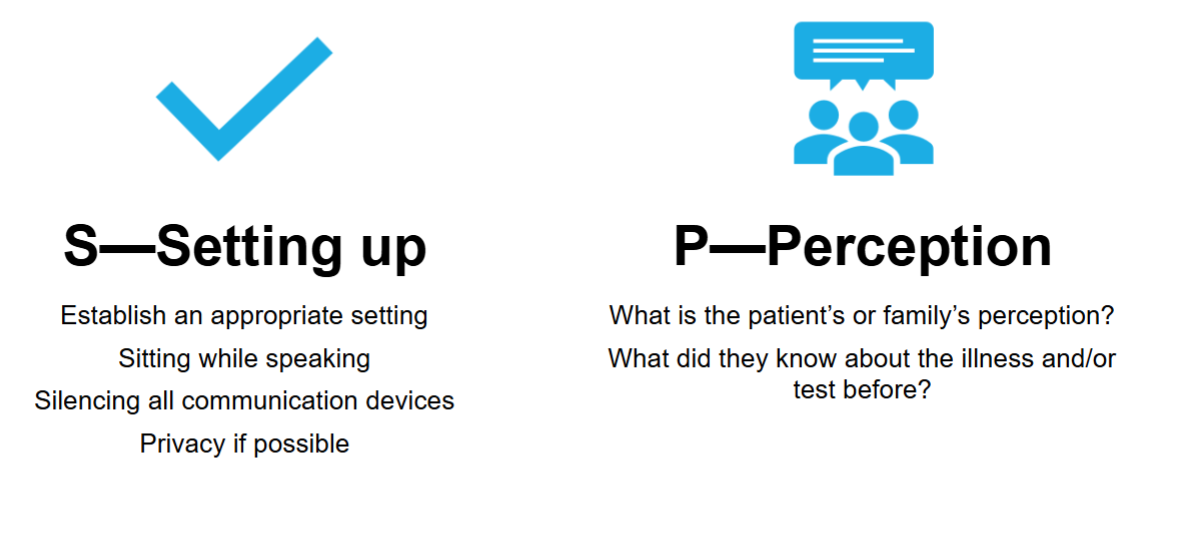
SPIKES - I and K

SPIKES - E and S

Most common EOL medications
-Morphine
-Lorazepam (ativan)
-other opioids/pain meds, nausea meds, GI meds
How is death determined?
-Absence of apical pulse for at least 1 minute
-Brain death (apnea test, reflexes test, no brain activity)