Week 3: Marketing Information System
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What does the Marketing Information System look like?
when talking about gathering information, it’s in the context of what is happening in the marketing environment.
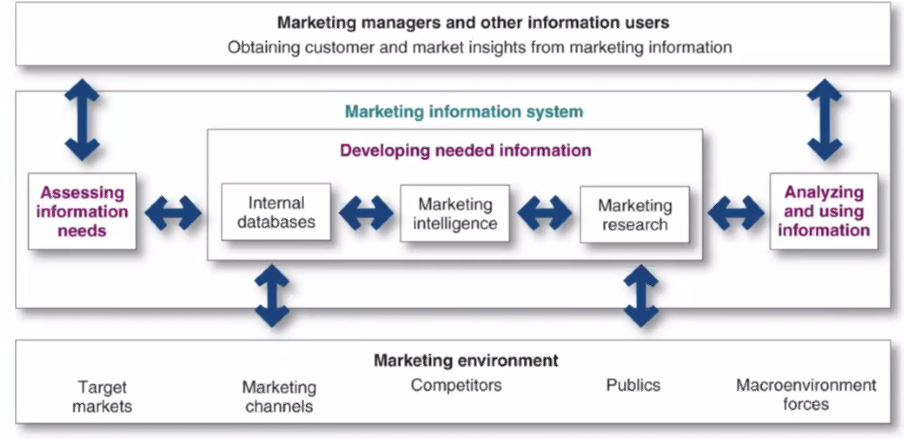
Developing Needed Info: Internal Databases
What information do we have already?
If you go use your shopper's card at a store (Giant, Jersey Mikes, etc.) companies learn a lot of information from tracking your consumption.
They can decide to create new products, remove products, etc.
A grocery store can learn what time of day people shop, how often people shop, brand loyalty, etc.
Developing Needed Info: Marketing Intelligence
What public information is available?
Social media is monitored. What's being posted? What are they tagged in?
This info is public, since the public are the ones saying it.
This enables interaction between the public and the company.
Wendy's Twitter following took off (literally by millions) after they started being witty and sassy in their tweeting.
Shows how much power engaging with your audience holds.
Developing Needed Info: Marketing Research
The systematic design, collection, analysis, and reporting of data relevant to a specific marketing situation facing an organization.
This is necessary for a business so you can gain consumer insights. Understanding their preferences is important.
Typically, Home Depot and Lowes are typically located near each other.
As are fast food, car dealerships, Target and Starbucks, etc.
This is b/c it gives consumers substitute options. This enables convenience. They can capitalize on traffic in one area.
This is also b/c it enables companies to engage in marketing research while looking across at their competitors:
What is being sold out front?
How many cars are in the parking lot?
When are they busy during the day? Are they more busy than us?
What types of cars are in their parking lot?
The Process of Marketing Research
typically, the first step in the marketing research process is the most complicated step.
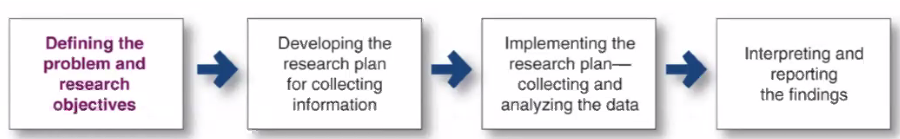
Domino’s example: Marketing Research
Domino's was very popular at one time, but then demographic forces, tech forces, and cultural forces all hit at once.
They had to start over with their product. They had to acknowledge the public's opinion of their product in order to make a better product and increase sales and customer satisfaction again.
Engaging in this process showed a huge increase in their stock.
Philip F's Dominos costumes example illustrates all of the following EXCEPT:
Customer evangelism (customers telling others about the product), true friendship (high on loyalty and profitability), customer generated marketing (he's literally walking around in a domino's storm trooper outfit, generating marketing as a customer), marketing intelligence, promotions (they ran a promotion to show their love for Domino's).
Marketing. This is the weakest answer b/c this is based on online chatter. If these guys went out and were posting this on social media, then this could be considered strong. However, b/c this was mean to be an IRL promotion, this was weaker.
what are the three types of research?
exploratory research, descriptive research, and causal research
Exploratory research:
gathers preliminary info that will help define the problem and suggest hypotheses.
Descriptive research:
describes things (ex: market potential for a product, demographics, attitudes)
Causal research:
tests hypotheses about cause-and-effect relationships.
what are the two types of data?
Primary data: collect specific info, directly applicable, costly
Secondary data: rely on existing info, often not as applicable, less expensive
examples of companies that gather secondary data for other companies to use:
Company examples:
LexisNexis: Database company info
Nielsen: worldwide shopping scanner data
Simmons: surveys on consumer behavior and brand preferences
Television example (source: Experian Simmons)
Collected data on Democrats/Republicans, Millennials/Gen X, states, etc.
This matters b/c companies can assist in running political ads when a certain party is watching tv.
Secondary data collection is important b/c having the funds for primary data gathering is not always possible, but secondary data gathering is very helpful.
Primary Data Collection Process
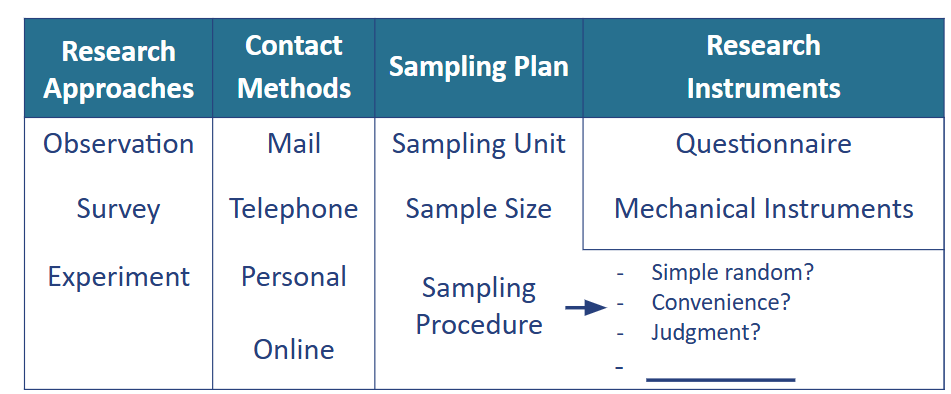
How should the people in the sample be chosen?
sampling procedure.
Under probability samples, each member of the studied population has the same probability of being surveyed.
Limiting costs and saving time are achieved by taking nonprobability samples or convenience samples. These can be easily assembled or reached.
Findings from such surveys may be biased and the sampling error cannot be measured.
The needs of a project should guide the choice of the sampling method.
Quota
what are the three types of research approaches?
observational
survey
experimental
observational research: the gathering of primary data by observing relevant people, actions, and situations.
ethnographic research
mechanical observation
Observational research » ethnographic research
observation in a "natural environment".
What do people buy in the grocery store? How do children act in a classroom?
Ex: Oxo observed how people with arthritis used kitchen tools to see how they should alter their products to be more comfortable when cooking.
Ex: Marriott felt like people weren't using their rather opulent lobbies, so they did research on what people preferred to sit on, etc.
They did an entire remodel that made the lobbies much more comfortable.
Observational research » mechanical observation
On-device meters. This could track software progress.
Nielsen devices that would track who would watch what on the tv in the household.
Checkout scanners. This tracks what people purchase and where.
Eye cameras. These tell what people's eyes are physically drawn to.
Kellogg's brand manager should put Rice Krispies just below eye level b/c we have a slightly downwards gaze.
Research is important b/c whose eye level should it be put at (people being different heights).
Eye tracking: shape, color, area around object. It is hard for consumers to learn what the new packaging looks like.
what do companies do with all of the data they collect?
Big data:
What are they searching for? What do people click on? What websites do they visit What do they watch? What do they share? What do they read?
Others: demographics, psychographics, geolocation, sex, recent purchases, location, etc.
Ex: Netflix often comes to know customer viewing preferences better than customers do. For ex, they know:
What scenes are rewatched.
When/what you watch.
"there are 33mil different versions of Netflix".
75% of views are based on recommendations = 15hours/month
survey research:
most widely used method for primary data collection.
Best for gathering descriptive information. You can gather info about people's knowledge, attitudes, preferences, or buying behavior.
experimental research:
Best for gathering causal info
Process:
Select matched groups of subjects
Give different treatments
Control for unrelated factors
Check differences in responses between groups
Ex: putting a "sale" sign up on Campbell's Soup aisle and stating "12 cans per person limit". This encouraged people to buy a lot more cans than they usually would, due to the fear of scarcity. "limit" signals popularity, urging people to buy more to catch up.
what are the four different types of contact methods when researching?
personal interview
phone
mail
online marketing research
contact methods » personal interview
Used for surveys, experiments, and some observational research
Pros: highly flexible, good control of sample
Cons: high cost per respondent, highly subject to interviewer bias
Beware of conformity and bias (when respondents change their answer/opinion to agree with the rest of the group or to preserve someone's feelings).
contact methods » phone
Used for surveys, some experiments
Pros: gathers info fast and greater flexibility than mail surveys (can make things more understandable easier)
Cons: higher costs than mail (takes much more time than mailing), interviewer effects exist, and quantity of data that can be collected is smaller than in mail surveys
contact methods » mail
Mostly used for surveys using a questionnaire
Pros: can reach a lot of people, inexpensive, can ask for more information, no interviewer effect
Cons: easy to ignore -- low response rate, no flexibility (if someone misunderstands something, etc.)
contact methods » online marketing research
Can do surveys, experiments, and personal (individual and group) interviews
Pros: least expensive way to gather info, flexible, saves time on data processing
Cons: super easy to be dishonest -- invalid data, prevents people from accessing other things
Test Markets: based on how similar the population there is to the US population is as a whole.

Interpreting and Reporting:
What does the data mean?
Transform that data into usable knowledge
Report to management
Presentations
Written reports
What does the Buyer Decision Process look like?
Buyers don't realize they do these things, and if they make the same buying decision processes frequently, they can skip over some steps (for ex: you know where all your fav restaurants are in town).
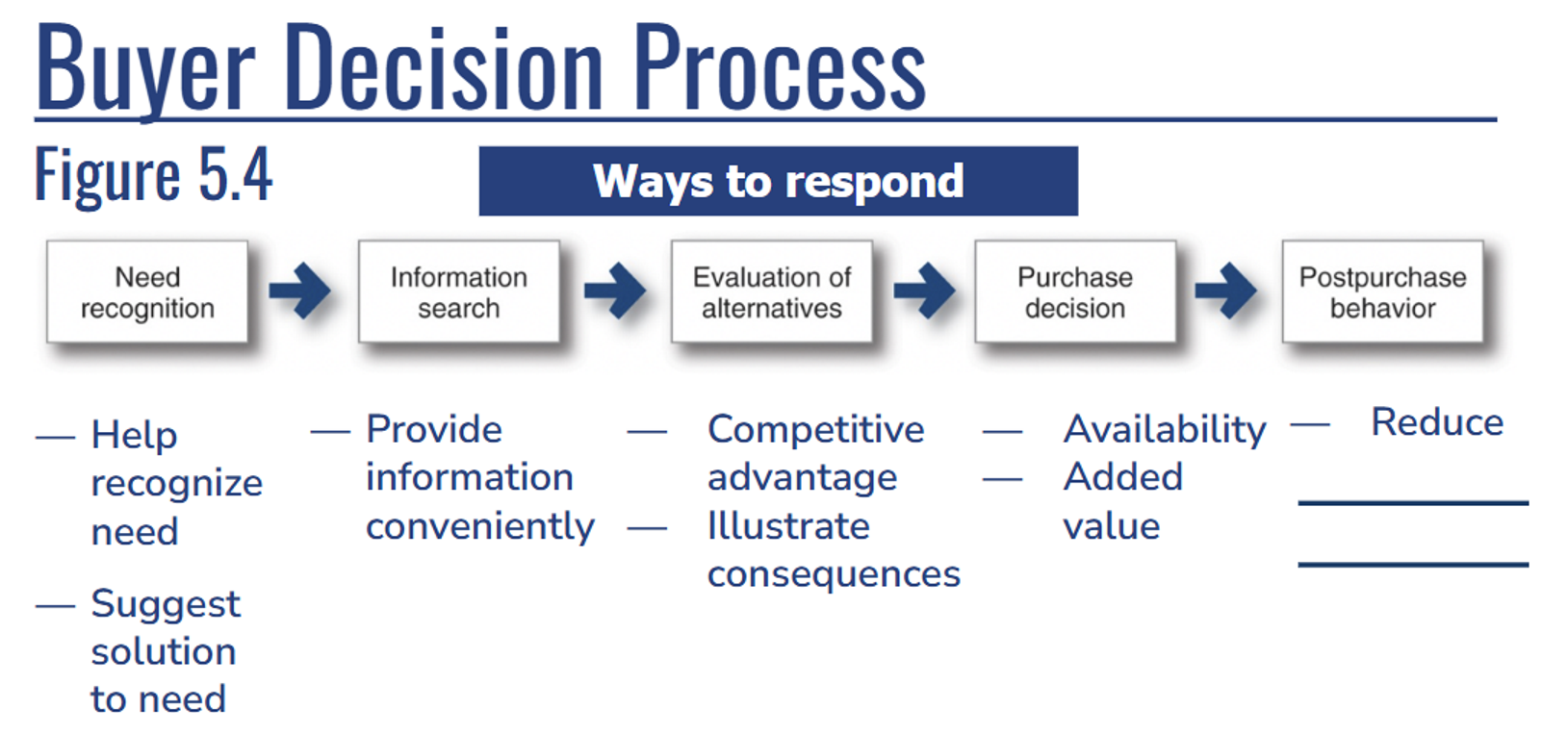
Buyer Decision Process » Need Recognition
Need recognition:
Help recognize a need
Suggest solution to need
Buyer Decision Process » Info Search
Information search:
Ex: hungry? Options for lunch, are they open, etc.
If consumers don't know, that's useless
Buyer Decision Process » Evaluation of Alternatives
Evaluation of alternatives:
Ex: hungry? Have to go home and make food and clean up, pickup food, sit in restaurant, etc.
Weight the competitive advantages and illustrate the consequences
Buyer Decision Process » Purchase Decision
Purchase decision:
You make a choice. It has to be available and have value.
When people buy, it's b/c the value exceeds the money you will pay.
Buyer Decision Process » Post-Purchase Behavior
Post-purchase behavior:
We want to reduce our cognitive dissonance,
We evaluate the purchase. Was it worth it?
We internally question. We want to reduce the tension and completely validate your purchase.