Biol 12: How do we analyze cells?
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Non-covalent interactions
Ionic bonds
H-bonds
Hydrophobic interactions
Transient interactions
_______________ between molecules depend on non-covalent bonds, critical aspect of protein-protein interactions and also enzyme-substrate interactions
Methyl
-CH3
Hydroxyl
-OH
Carboxyl
-COOH
Amino
NH2
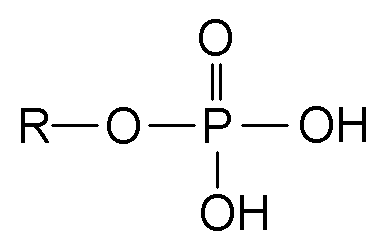
Phosphate
-PO4, a functional group in organic molecules that contributes to energy transfer, such as ATP.
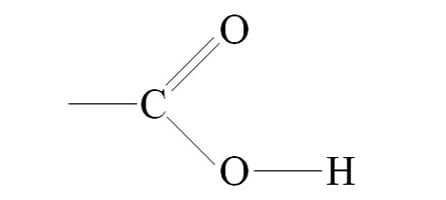
Carbonyl
C=O
Sulfhydryl
-SH, a functional group that can form disulfide bonds, playing a key role in protein structure.
pH
-log[H+]
Low pH
________ will push the equilbrium toward the protonated state
High pH
________ will push the equilbrium toward the deprotonated state
Non-polar R-groups
Alanine
Valine
Leucine
Isoleucine
Methionine
Phenylalanine
Tryptophan
Polar non-charged R-groups
Serine
Threonine
Glutamine
Asparagine
Tyrosine
Polar charged R-groups
Aspartic acid
Glutamic acid
Lysine
Arginine
Histidine
R-groups with unique properties
Glycine
Cysteine
Proline
Flexibility in environment
Special property of glycine
Disulfide link
A covalent bond formed between the sulfur atoms of two cysteine residues, contributing to protein stability and structure.
Helix breaker
Proline creates kinks in polypeptide chains because of its R-group binding to the N of the amino group as well as the alpha carbon, making it regularly a __________
Primary structure
Linear sequence of AA
Secondary secondary
Local regions of structure, beta sheets and alpha helices
Tertiary structure
Overall 3D shape of a polypeptide
Quaternary structure
Assembly of subunits of 2 or more proteins together
C=O and N-H
Alpha helix is stabilized by H-bonds between _______ of different peptide bonds
protrude out
R groups ________ from helix, they are not part of the backbone
C=O and N-H
Beta sheets is stabilized by H-bonds between _______ of different peptide bonds
Parallel or anti-parallel
Beta sheets may be _________ in structure
Motifs
Regular combinations of secondary structures
Non-covalent forces
Tertiary structure is often maintained by _____________
Domains
Structural modules within a protein, usually have distinct functinos and are often conserved and exist in multiple proteins
Ions or covalent modification
Association with __________ can change protein 3D shape and regulate it
Protein phosphatase
Protein that removes phosphate group
Protein kinase
Protein adds phosphate group
Post-traditional modification
____________ can affect:
Interactions
Conformation
Localization
Intrinsic activity
Coiled-coil motif
is a structural motif in proteins that consists of two or more alpha-helices coiled around each other, often involved in protein dimerization and stability.
EF hand motif
is a helix-loop-helix structural motif found in a variety of proteins, primarily involved in calcium binding. It facilitates protein-protein interactions and signal transduction.
Immunogold TEM
combines the specificity of immunolabeling with the high resolution of electron microscopy, secondary antibody is conjugated with gold nanoparticles
Primary cell culture
is the process of isolating and maintaining cells from a living organism (usually animals), most divide for limited period of time
Cell line
is a culture of cells that can divide indefinitely in vitro, derived from a primary cell culture
Cell lysis techniques
Sonification
Force cells through small hole
Use detergent to make holes in the membrane
Tissue homogenizer (leaves organelles intact)
Density gradient equilibrium centrifugation
Technique where components will sediment in a density gradient until they reach their own buoyant density
Separating organelles from each other
Separating membranes from each other
Sodium dodecylsulfate
Less gentle detergent that solubilizes protein but also unfolds it (ionic)
Triton x-100
More gentle detergent that solubilizes protein while retaining secondary and tertiary structureand is often used in cell lysis without denaturing proteins. (non-ionic)
Detergents
Integral membrane proteins can be solubilized by using _______
amphipathic
Non-ionic detergents are ________
Types of chromatography
Ion-exchange
Gel-filtration
Affinity
Gel filtration chromatography
technique where smaller proteins that can fit in the pores of the gel beads spend more time in the pores and come out in later fractions than bigger proteins
Affinity chromatography
A technique that separates proteins based on their specific binding interactions with ligands attached to a stationary phase, allowing for the purification of target proteins from complex mixtures.
Co-immunoprecipiation
Affinity chromatography technique that can be used to purify protein complexes. Antibodies are on the beads and any proteins still interacting with the antigens will be purified
Aliquot
A portion of a sample that is taken for analysis or experimentation, ensuring consistency in testing and measurement.
SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
Proteins treated with:
Beta-mercaptoethanol which reduces disulfide bonds
Heat helps unfold and denature
SDS denatures and coats proteins with negative charge stochiometrically
Reduces disulfide bonds
What does beta-mercaptoethanol do in SDS-PAGE?
Western blotting
technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample after separation by SDS-PAGE, involving transfer to a membrane and use of antibodies for visualization (immunoblotting)
Chemiluminescent detection for immunoblots
Immunoblotting technique where the secondary antibody is conjugated to an enzyme. when the substrate is incubated with membrane, light is emitted where the enzyme acts on the substrate
2D electrophoresis
A technique that separates proteins based on their isoelectric point and molecular weight
Mass spectrometry
A technique where proteins can be excised from the gel, digested with trypsin, and then analyzed by comparing the experimentally derived mass to trypsin fragments of known proteins