Science of Sustainability Final Review
1/230
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
231 Terms
Deductive Inference
Apply general rules to infer something about a specific case.
Inductive Inference
Observe specific cases to infer a general rule.
Deductive or Inductive Inference? All men are mortal. Socrates is a man. So Socrates must be mortal.
Deductive
Deductive or Inductive Inference? I’ve bitten several people. No one liked it. So people don’t like to be bit.
Inductive
Absolute Inference
Absolute relationship between variables/parts of a system.
Statistical Inference
Probabilistic relationship between variables/parts of a system.
Absolute or Statistical Inference? Smoking causes lung cancer. Bill smokes. So Bill will get lung cancer.
Absolute Inference
Absolute or Statistical Inference? Smoking increases the likelihood of getting lung cancer. Bill smokes. So, Bill is more likely to get lung cancer than if he didn’t smoke.
Statistical Inference
Weathers et al. definition of an ecosystem?
An interacting system made up of all the living and nonliving objects in a specified volume of space.
Advantages of Weathers et al. definition of an ecosystem: Mass Balance
Makes it possible to use mass balance to track the movement of materials that come into the ecosystem.
Advantages of Weathers et al. definition of an ecosystem: Black Box Approach
Makes it possible to measure the total activity of an ecosystem without having to measure all the parts and exchanges within the ecosystem.
Advantages of Weathers et al. definition of an ecosystem: Importance of ALL Components
Recognizes the importance of both living and nonliving components of the system.
Advantages of Weathers et al. definition of an ecosystem: Boundaries
Gives the investigator the power to select the spatial and temporal boundaries of the system being studied.
How do ecologists regard people?
Ecologists regard people as part of an ecosystem and include people in their studies.
1st Law of Thermodynamics
Energy can change forms, but cannot be created nor destroyed.
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
Entropy of a closed system always increases
Irreversibilities during processes do not allow you to recover the original quality of energy you put in a system.
Ecosystems create order and decrease entropy. Does this make ecosystems an exception from the 2nd Law of Thermodynamics?
No, Earth and ecosystems are open systems.
Which Law of Thermodynamics is concerned with energy quantity?
1st Law of Thermodynamics
Which Law of Thermodynamics is concerned with energy quality?
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
Structure of an Ecosystem
What ecosystems look like.
What is included in the Structure of an Ecosystem?
Components: what is in the ecosystem.
Organization: how the ecosystem is organized.
Examples of Ecosystem Components (part of ecosystem structure):
Bacteria, plants, animals
Air, water, nutrients
Examples of Ecosystem Organization (part of ecosystem structure):
Pathways of matter and energy
Distribution (e.i. patchiness)
Size location
Function of an Ecosystem
How an ecosystem works
Examples of Ecosystem Function:
Consuming energy and transforming materials.
More useful energy:
Solar radiation
Chemical potential energy
Less useful energy:
Heat
Open vs. closed systems
Material function (source or sink).
Ecosystem Dynamics
Ecosystem change over time
Dynamics: External Forces
Forces that act outside a system.
Nutrients inputs, increase in temperature.
Dynamics: Internal Dynamics
Forces that act in a system.
Age of tree strand, succession.
Photosynthesis Equation:
CO2 + H2O + light → (CH2O) + O2
Oxic Respiration Equation:
CH2O + O2 → CO2 + H2O + energy
Example of Anaerobic Respiration:
CH3COOH → CH4 + H2O
Photosynthesis is an ___ of carbon.
Reduction (4+ to 0)
Oxic Respiration is an ___ of carbon.
Oxidation (0 to 4+)
Anaerobic Respiration does not include ____ in it processes.
Oxygen
Oxidation is the…
loss of electrons
Reduction is the…
gain of electrons
Oxidation number of carbon in CO2:
4+ (O is 2-)
Oxidation number of carbon in CH4:
4- (Hydrogen is +1)
What is Gross Primary Productivity (GPP)?
All carbon dioxide fixed into organic matter irrespective of any respiratory losses.
What is Net Primary Productivity (NPP)?
The rate at which organic matter is available for other uses beyond simply supporting energy costs (i.e., respiration) of the primary producers (Ra).
What is Net Ecosystem Productivity (NEP)?
The portion of gross primary production that is not respired by autotrophs or heterotrophs.
What is Ra?
Autotrophic Respiration
What is Rh?
Heterotrophic Respiration
What is Re?
Ecosystem Respiration; Sum of Ra and Rh
Autotrophs
Organisms that produce their own food/energy.
Heterotrophs
Organisms that consume other organisms for food/energy.
GPP =
NPP + Ra
NEP + Re
NPP =
GPP - Ra
NEP =
GPP - Re
What are the terms: dCorg = NEP + I + CM - Ex - Oxnb
dCorg = organic carbon accumulation
NEP = net ecosystem productivity
I = imported carbon that hasn’t been respired
CM = net consumer movement
Ex = exported organic carbon
Oxnb = non-biological oxidation of carbon (i.e. fire)
Climate Change Detection
Demonstrating that climate has changed in a defined statistical sense.
Climate Change Attribution
Identifying the most likely causes of observed change with some level of confidence.
What is the greenhouse effect?
When greenhouse gases absorb the sun's heat that radiates from the Earth's surface, trap it in the atmosphere and prevent it from escaping into space.
How has the greenhouse effect changed?
The greenhouse effect has intensified due to a significant increase in atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations starting around 1900 (industrial revolution).
What are 5 pieces of evidence that show the Earth is warming?
Sea level rise
Increased surface temps
Increased ocean temps
Loss of ice sheets
Retreating glaciers
What role do ice cores play in our understanding of climate change?
Water traps air as it freezes. By sampling air bubbles trapped deep in the arctic ice, scientists are able to see the composition of the atmosphere many years (or millennia) ago.
Helped make the correlation between greenhouse gas concentrations and climate change.
Key Drivers of Climate Change: Milankovitch Cycles
Changes in the shape of the Earth’s orbit, level of axis tilt, and how cleanly the Earth rotates (wobble/precession).
Natural Driver
Key Drivers of Climate Change: Sunspots
Increases and decreases in the sun’s intensity.
Natural Driver
Key Drivers of Climate Change: Albedo
Energy that enters the system but is reflected out immediately.
Natural, but impacted by anthropogenic factors
Key Drivers of Climate Change: Greenhouse Effect
Effect that doesn’t allow heat to escape Earth’s atmosphere.
Billions of years old
Natural, but impacted by anthropogenic factors
What were the key drivers of previous shifts from glacial to interglacial periods?
Milankovitch Cycles
What is the primary driver of contemporary climate change?
Greenhouse Effect; the increase in greenhouse gas concentrations is the primary contemporary driver of climate change.
What is the difference between the rate of climate change today versus previous shifts?
The rate of climate change today is many times faster than previous shifts.
Previous Warming: 4 to 7 C in 5000 years
Past Century: 0.7 C [10x faster]
Projected Next 100 Years: 2 to 6 C [20x faster]
What role does the ozone hole play in climate change?
The ozone hole does not play a role in climate change, but can cause other environmental and social issues.
The 3 Main Greenhouse Gases
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Methane (CH4)
Nitrous Oxide (N2O)
Major Carbon Stocks
Land/Earth
The Ocean
Land as a Carbon Stock
Driven by photosynthesis
Net ecosystem production is substantial and results in the bulk of the stored carbon.
The Ocean as a Carbon Stock
Driven by diffusion (chemical/physical reactions).
Nearly all of gross primary production is respired.
Natural Flows: Rock Weathering
Carbon Inflow
Relatively Small (0.1 to 0.3)
Natural Flows: Volcanism
Carbon Outflow
Relatively Small (0.1)
Natural Flows: Gross Photosynthesis
Carbon Inflow
Relatively very large (123 = 108.9 + 14.1)
Natural Flows: Total Respiration and Fire
Carbon Outflow
Relatively very large (118.7 = 107.2 + 11.6)
Less than Photosynthesis (inflow)
Natural Flows: Freshwater Outgassing
Carbon Outflow
Relatively small (1.0)
Natural Flows: Ocean - Atmosphere Exchange
Both a Carbon Outflow and Inflow
Relatively Large
Inflow is greater that Outflow
Inflow: 80 = 60 + 20
Outflow: 78.4 = 60.7 + 17.7
Anthropogenic Flows: Fossil Fuels and Cement Production
Carbon Outflow
Very Large (7.8 ± 0.6)
Anthropogenic Flows: Net Land Use Change
Carbon Outflow
Relatively Large (1.1 ± 0.8)
Less than fossil fuels/cement
Historic Role of the Ocean
Carbon Source
Modern Role of the Ocean
Carbon Sink
Higher temperatures ___ the concentration of CO2 in water.
Reduces; hotter water decreases the solubility of CO2, causing the ocean to release CO2 into the atmosphere.
Lower temperatures ___ the concentration of CO2 in water.
Increases; colder water can absorb more CO2.
At a constant temp, a(n) ___ in partial pressure increases the concentration of CO2 in water.
Increase
At a constant temp, a(n) ___ in partial pressure decreases the concentration of CO2 in water.
Decrease
A low concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere results in a ___ partial pressure. This partial pressure leads to a ___ CO2 concentration in water.
Low; low
A high concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere results in a ___ partial pressure. This partial pressure leads to a ___ CO2 concentration in water.
High; high
Ocean Acidification
The gradual pH decrease (more acidic) of the ocean.
The ocean’s pH is directly proportional to CO2 concentration.
Increased diffusion of CO2 into the ocean is directly responsible for ocean acidification.
Climate Mitigation
Measures taken to reduce greenhouse gases, thereby decreasing the pace and magnitude of climate impacts.
Climate Adaptation
Measures taken to handle the climate impacts as they come.
Economic Impacts of Mitigation (According to Martinich & Crimmins, 2019)
Climate mitigation would reduce economic damages across all 22 sectors (except 1, urban drainage).
Lessens damages associated with extreme weather decreases
Millions to tens of billions of US dollars in annual benefits are saved by the end of the century.
“S” in a Feedback Loop Means…
Same
“O” in a Feedback Loop Means…
Opposite
Reinforcing Feedback Loop
A process or behavior amplifies the initial action, leading to further growth or intensification of that behavior.
Balancing Feedback Loop
A process of behavior that stabilizes a system by counteracting changes.
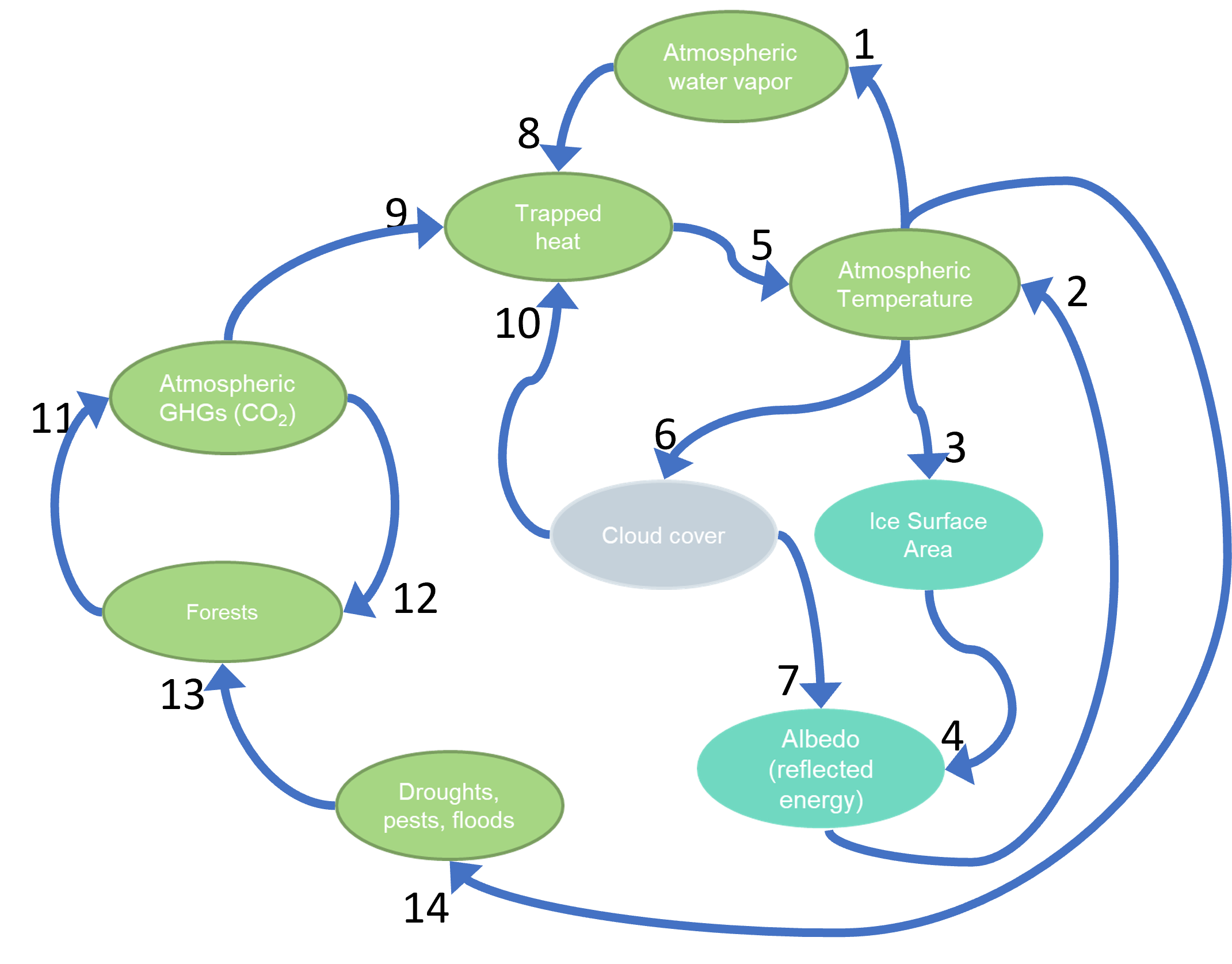
Which numbers would have S arrows?
1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14
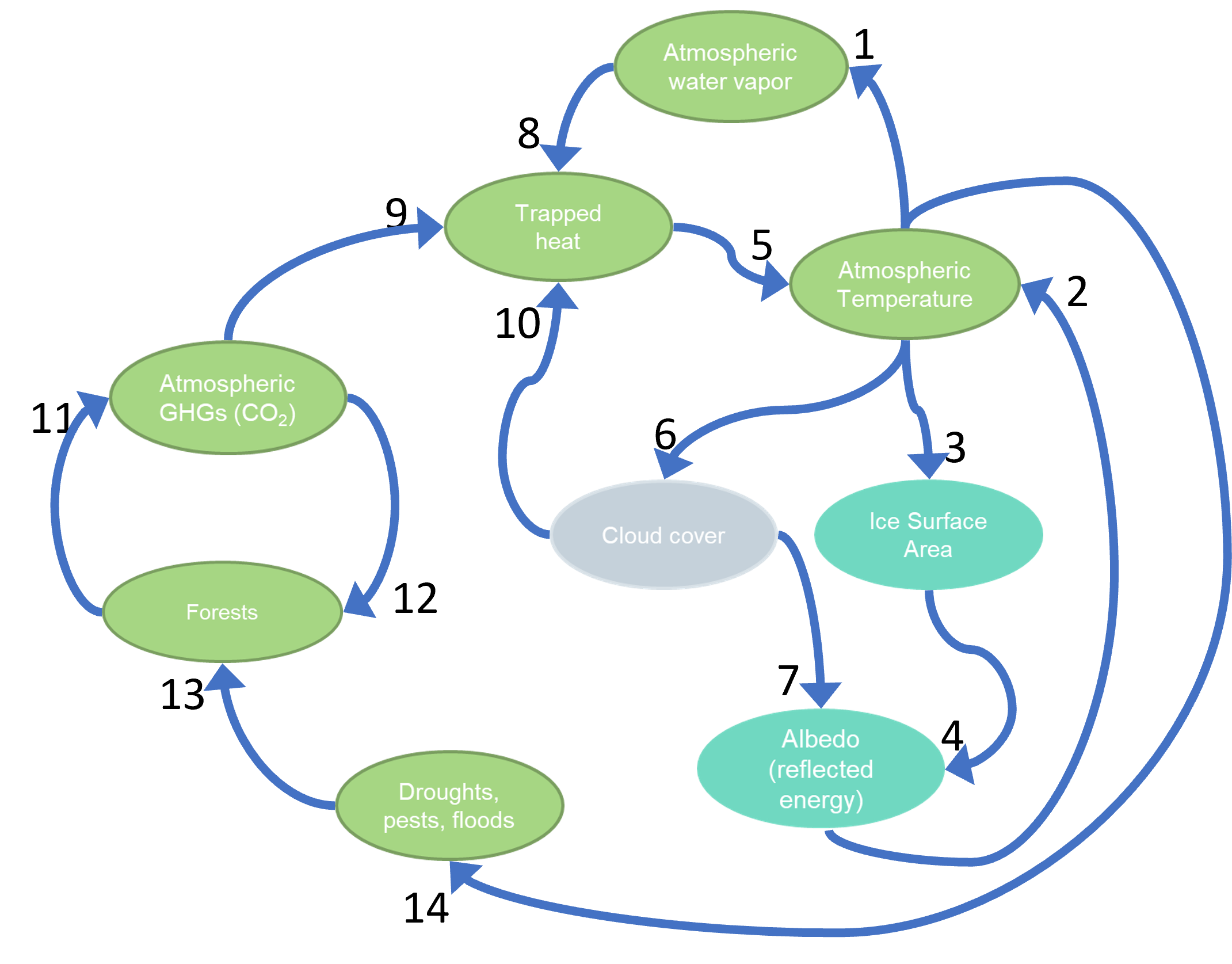
Identify the Reinforcing Feedback Loops.
Loop 8-5-1
Loop 2-3-4
Loop 5-6-10
Loop 5-14-13-11-9
Command and Control
When the government sets specific conditions, such as required equipment or maximum allowable flow rate out of a smokestack.
Market-Based Energy Polices
Use economic incentives to encourage and discourage behaviors.
What are the 3 Market-Based Energy Policies?
Clean Energy Standards
Carbon Tax
Cap and Trade
Market-Based Energy Policies: Clean Energy Standards
The government requires a specific proportion of energy production in a state or country to come from low- or zero-carbon sources.
Doesn’t set specific emission levels or prices.
Market-Based Energy Policies: Carbon Tax
When the government adds an additional fee based on the amount of carbon emissions produced, which raises the price of carbon intensive activities.
Sets price but not emission levels.
Market-Based Energy Policies: Cap and Trade
When the government sets a total allowable level of pollutant for an industry and allows individual actors to buy and sell their individual allowances within that limit.
Sets emission levels but not price.