National Income, Aggregate Demand + Aggregate Supply (Theme 2: The UK Economy - Performance + Policies)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is Macroeconomics?
Study of interrelationships between economics variables at an aggregate (economy-wide) level
What is the Circular Flow of Income?
Model showing the flow of goods, services, money + factors of production between households + firms
What is equal in the Circular Flow of Income?
National Income = National Expenditure = National Output
What are Withdrawls + Examples?
Withdrawls - money removed from the economy
Savings
Taxes
Imports
What are Injections + Examples?
Injections - money added to the economy
Government Spending
Investment by firms
Exports
What are the three states of the Economy?
Injections = Withdrawls → Equilibrium
Injections > Withdrawls → Growing
Injections > Withdrawls → Shrinking
What is Income + Wealth?
Income - amount of earnings during a period
Wealth - a stock of assets (e.g property + shares)
What is the Wealth Effect?
Increase in wealth (e.g) or perceived increase → increased in spending
What is Aggregate Demand?
Total spending on goods + services in the economy
What is the equation for Aggregate Demand?
AD = C + I + G + (X - M)
C - Consumption (~60%)
I - Investment (~15%)
G - Government Spending (~18%)
X - Exports
M - Imports
(X - M) - Net exports (~5%)
What are the influences on Consumption?
Level of disposable income
Level of saving
Interest rates
Consumer confidence
Wealth effect
What are the types of Investment?
Gross Investment - amount a company invests in assets without accounting for depreciation
Net Investment - accounts for depreciation (e.g if 5 machines bought but 2 old removed → net investment is 3 machines)
What are the influences on Investment?
Rates of economic growth
Business expectations + confidence
Keynes + ‘Animal Spirits’ - emotional + psychological factors drive decisions
Demand for exports
Interest rates
Access to credit
The influence of government + regulations
What is Government Spending?
Current spending (wages to public sector works)
Capital spending on investment goods (e.g roads)
Not transfer payments (e.g pensions)
What are the influences on Government Spending?
Trade cycle - booms, recessions + recovery cycle
Fiscal policy preferences - expansionary + contractionary fiscal policies (e.g decrease or increase taxes)
What are the influences on Net Exports?
Real income
Exchange rates
State of the world economy
Degree of protectionism - how protected country is from imports (e.g tariffs/quotas)
Non-price factors - e.g brand loyalty, advertising
Why is the AD Curve that shape?
If prices increases:
Real Balance Effect - saved money worth less → decreased C → AD decreases
Interest Rate Effect - inflation → decreased C → AD decreases
International Competitiveness - increased imports + decreased exports → X-M decreases → AD decreases
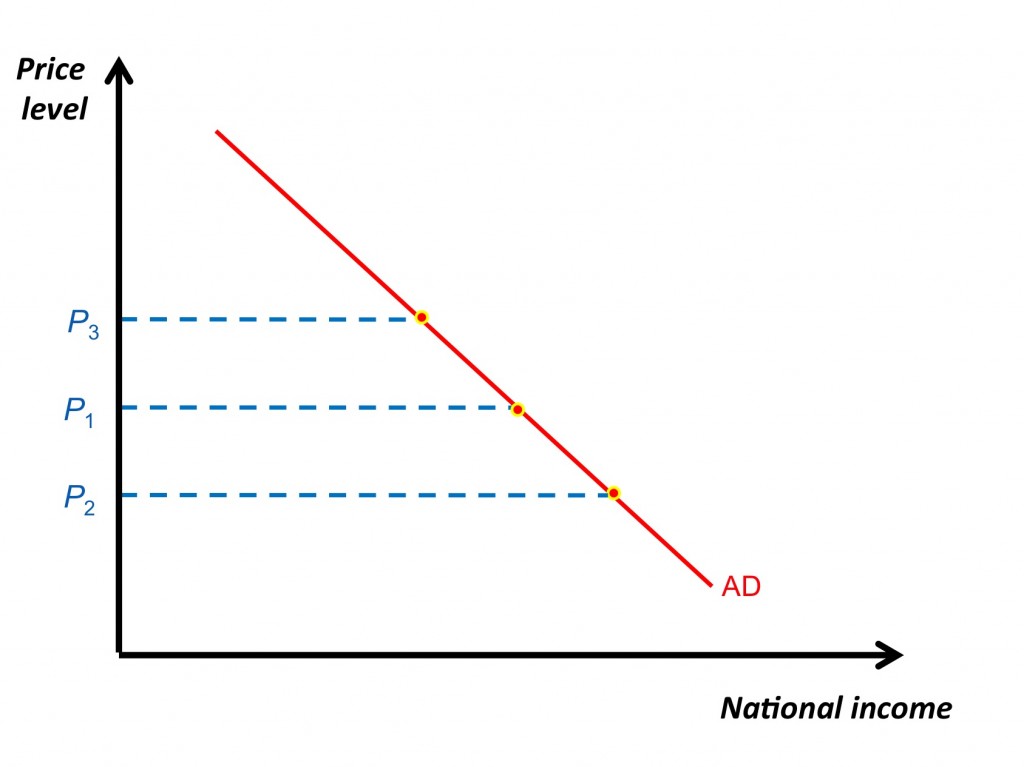
What causes a Movement along the AD Curve?
Price changes → Extension or Contraction of AD
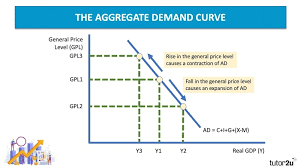
What causes a Shift in the AD Curve?
Changes in:
Consumption
Investment
Government
Net Exports
What can affect the level of Shift in the AD Curve?
Multiplier effect - increased AD → increased household income → increased C → even higher AD
Time lags - takes time to affect AD
Accelerator model - increased AD → so business invests → even higher AD
What does Marginal Propensity mean?
Proportion of additional income that is used to ____ (e.g consume/save/tax/import/withdraw)
What are the five Marginal Propensities?
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS)
Marginal Propensity to Tax (MPT)
Marginal Propensity to Import (MPM)
Marginal Propensity to Withdraw (MPW)
What is the Multiplier Formula?
Multiplier = 1 / (1 - MPC)
OR
Multiplier = 1 / MPW, where MPW = MPS + MPT + MPM
What are the four problems of the Multiplier?
Difficulty measuring
Time to come to into full effect
Size of leakages
Impact of trade cycle
What is Aggregate Supply?
Total goods + services produced in the economy at a given price level
What does the Short Run Aggregate Supply Curve look like + why?
If output increases in the short run, firms have to pay overtime/more money for quick delivery → increased costs
This is because at least one factor of production is fixed in the short run (e.g labour → have to pay overtime)
What does the Keynesian Long Run Aggregate Supply Curve look like + why?
When there is mass unemployment, output can be increased without an increase in prices
At full employment, the economy cannot produce any more output, even if the goods can be sold for more
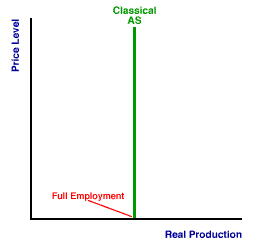
What does the Classical Long Run Aggregate Supply Curve look like + why?
At full employment, the economy cannot produce any more output, even if the goods can be sold for more
What causes a Movement along the AS Curve?
Price changes → Extension or Contraction of AS
What causes a Shift in the Short Run AS Curve?
Changes in:
Costs of raw materials / energy
Exchange rates
Indirect tax rates
What causes a Shift in the Long Run AS Curve?
Changes in:
Relative productivity
Education/skills
Government regulations
Demographic changes / migration
Competition policy
Technological advances
What could an increase in the level of AS cause?
Spare Capacity - unemployed people
Bottlenecks - constraint which causes costs of AS to rise as the economy grows