1a Leadership in nursing, Theories, & Power
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
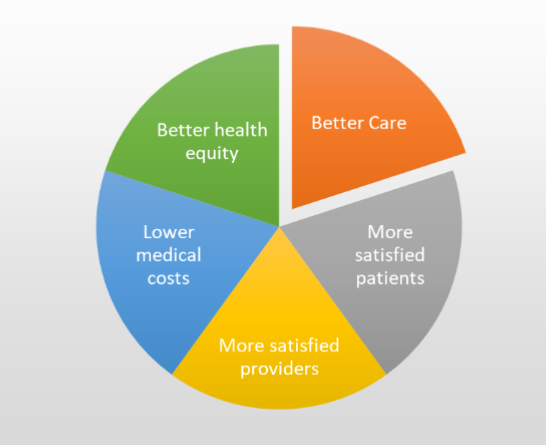
Quintuple aim in healthcare
roles: leader, manager, follower
leader: Inspires and motivates others; helps solve problems
manager: follows protocols and procedures: planning and coordination (eg bedside RN for pt care or unit manager)
followership/followership model: Supports the leader and team; collaborates and actively engages
how nurses support leaders and contribute to the team
traits of a leader
vision for the future (can see what is coming)
able to see possibilities: problem solving)
effective communication
adaptable
Use of experience for judicial decisions
traits of a manager
Plan, direct, control, and evaluate others
Identifies recurring issues and creates evidence-based routines
Monitors self and team consistently
Boosts morale during repetitive or challenging tasks
emotional intelligence
what is it
Ability to recognize, understand, and manage emotions (your own and others’)
social skills, interpersonal competence, psychological maturity, and emotional awareness
Parts of EI
self-awareness: identify your emotions and how they affect your perceptions
self-motivation: internally motivations vs external
managing emotions: identify emotions and not let them out of control
handling relationships: socially appropriate and interact with others with ease
empathy: value differences of others and not one group over another
Application of Roles to Quadruple Aim: just read
leader, manager, follower

theories of nursing management (groups)

trait theory: explain/define
style theory: just explain/list
focuses on the characteristics of individual leaders instead of the characteristics or functioning of the organization.
eg Intelligence, people skills, decisiveness, creativity, trustworthiness
style theory: autocratic, democratic, laissez-faire
autocratic, democratic, laissez faire
autocratic: controlling with less satisfaction
Useful in emergencies
democratic: involves staff in decision making; collaborative
laissez-faire: hands off; Team works independently; Works best with experienced staff/professionals
some leadership needed so everyone moves in the same direction
Transactional
Transformational
Situational-contingency theory T
transational: Focuses on tasks, rules, and performance
uses rewards and consequences
Addresses problems only after they occur; Responds by creating more rules or policies
transformational: Inspires and motivates others
Encourages growth, change, and shared vision
Situational–Contingency Theory: Leadership style changes based on the situation
No one “best” style for all situations
maslow’s
2-factor theory
Maslow: Needs must be met in order (basic → self-fulfillment)
Lower needs first (food, safety)
two-factor: Hertzberg 2 types of factors in organizations (hygiene and motivational factors). both are needed to be satisfied
hygiene factors help employee feel safe and secure/prevent dissatisfaction (working conditions, pay, status)
Motivators increase satisfaction (achievement, recognition)
expectancy theory
Organizational Behavior (OB) Modification
expectancy: Vroom
People are motivated if they believe effort = reward
eg gift card for overtime
Organizational Behavior (OB) Modification
Based on Skinner’s operant conditioning
Rewards increase desired behaviors
Consequences decrease undesired behavior
systems vs complexity theory
systems: A system is the sum of its parts
Changes in one part cause ripple effects in the whole
Focuses on orderly, systematic, and consistent change
complexity: Looks at how parts interact and adapt
Looks for patterns, interactions, and “if/then” scenarios
Focuses on adaptation and work-arounds in unpredictable environments
Focuses on what changes naturally
servant leadership
prioritize the growth and well being of team members
increased job satisfaction and retention rates
supportive work culture
benefits both staff and patients
authentive leadership
strong set of values and morals that they stick to
genuine, self-aware, and transparent of their stances
sinek social contract
Leaders and followers have an unspoken agreement
Leaders protect and support their team
Followers trust and commit to the leader
Authority vs power vs influence
Authority- sanctioned/given by the organization
directs and delegate
Power- ability to get others to do something, whether or not you have formal authority
affects the belief and actions of others: formal and informal
Influence- Process of using power
sources of power: position power
example
types
eg charge nurse/nurse manager
types: CLIRP
Coercive power: Uses punishment or negative consequences to control others
Unpleasant tasks, verbal warnings, termination (must follow protocol
Legitimate: Has formal authority; requests are expected to be followed.
RN asks PCA to carry out task (they do it)
Information power: Has knowledge others don’t.
Manager knows sensitive info that can’t be shared
Reward power: Offers incentives that staff value to encourage performance
Persuasion power: can convince others to follow their leadership
personal power types
CREE
Connection power: Comes from knowing influential people and leveraging those relationships.
Referent power: Comes from personal qualities, like confidence, problem-solving, or giving good advice—not the role itself.
Empowerment: Sharing power with others.
Expert power: Has more knowledge than others.
Example: Managers or educators.
Covey’s 8 Characteristics of Effective, Principle-Centered Leaders (just read -pic)
