Pathophysio Quiz 2
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
What are types of cellular injuries?
Reversible cellular injury
Irreversible cellular injury
What are the etiologies of cellular injuries?
Nutritional deficiencies / imbalances
Infectious agents and immunological response
Physical trauma, chemical injuries, radiation-induced injuries
Ischemia and hypoxic injury
Perfusion
Good blood flow; Delivery of oxygen, nutrients, and removal of waste
Ischemia
Inadequate blood flow causing tissue hypoxia and waste build up
Hypoxia
Results from ischemia, oxygen deprivation
What will happen to the cell?
Hypoxic tissue injury → oxygen decreases → decrease ATP
Sodium potassium pump fails and sodium enters cell
Cell swells and cell death occurs in normal perfsuion isn’t returned
What is reversible cellular injury characterized by?
Intracellular accumulation of substances such as fluids, fats, proteins, glucose, pigments, or minerals.
What causes intracellular accumulations?
Altered metabolism
Genetic disorders
Enzyme deficiencies.
What are examples of cellular accumulation?
Fat accumulation: caused by altered metabolism → build up fat globules in cell → fatty liver
Lack of enzyme: accumulation of endogenous material → lysosomal storage disease (Gaucher disease)
Pigment / minerals: ingestion of indigestible materials → build up exogenous materials
Abnormal proteins: mutation → build up of abnormal proteins
How can cells repair abnormal proteins?
Chaperones (reshape proteins) or ubiquitin (break into small pieces)
What is cellular adaptation?
Structural or functional change that cell undergoes in response to environmental stressors to allow them to survive and function better
What are the types of adaptive cellular response?
Normal
Hypertrophy
Metaplasia
Atrophy
Hyperplasia
Dysplasia
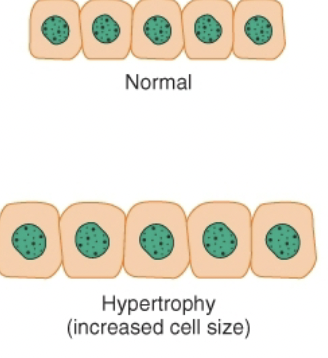
Hypertrophy
Increase in cell size and functional capacity due to increased demand
Metaplasia
Replacement of one cell type with another better suited to stress.
ex. esophageal cells changing to columnar cells in acid reflux.

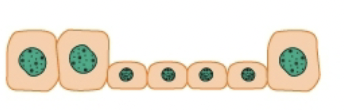
Atrophy
Decrease in cell size and function
ex. muscle atrophy
What causes atrophy?
Disuse, denervation (lack of nerve stimulation), ischemia, nutrient starvation, loss of endocrine signals, persistent injury.
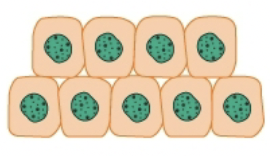
Hyperplasia
Increase in number of cells, increasing functional capacity. Cells response to increase demand by dividing
What causes hyperplasia?
Increased physiologic demand
Hormonal stimulation
Chronic irritation or injury
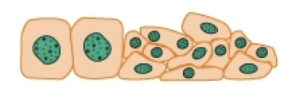
Dysplasia
Disorganized appearance of cells (size, shape, arrangement) due to adaptive effort gone astray; may progress to cancer (preneoplastic)
What are the types of irreversible cell injury?
Necrosis
Apoptosis
What is necrosis?
Irreversible cell injury with swelling, membrane/organelle breakdown, leakage of contents, and inflammation.
What are the types of tissue necrosis?
Coagulative
Liquefactive
Fat necrosis
Caseous necrosis
All caused by ischemia or toxic injury
What is coagulative necrosis?
Necrosis due to ischemia, tissue structure preserved.
ex. heart
What is liquefactive necrosis?
Necrosis from rapid cell death, often due to infection, forming pus (combination of WBCs and dead tissue)
ex. brain
What is fat necrosis?
Death of fat tissue
ex. pancreas.
What is caseous necrosis?
Cell death in lungs caused by tuberculosis
ex. lungs
What is gangrene?
Necrosis of large tissue area, results from interruption of blood supply to a particular part of body
What are the types of gangrene?
Dry gangrene
Wet gangrene
Gas gangrene
Dry gangrene
Coagulative necrosis characterized by blackened, dry, wrinkled tissue
Wet gangrene
Liquefactive necrosis often found in internal organs; fatal
Gas gangrene
Results from infection of necrotic tissue. Form gas containing bubbles
What is apoptosis?
Programmed cell death without inflammation; part of normal development or response to injury.
What are the two pathways that trigger apoptosis?
Signals inducing apoptosis
Intrinsic pathways
Cellular aging
How do signals induce apoptosis?
Withdrawal of survival signals that normally suppress apoptotic pathway
fas lingang → trigger death cascade
How does intrinsic pathway trigger apoptosis
Severe cell damage or to cellular DNA → increase in protein
What is the cellular basis of aging?
Progressive decline in cells’ ability to repair and divide due to cumulative environmental and metabolic damage.
What are the theories of aging?
Damage / error theory
Programmed senescence theory
What is the damage/error theory of aging?
Aging results from accumulated damage and limited cell repair capacity.
Aging results from accumulated damage and limited cell repair capacity.
Aging is genetically programmed; cells have finite replications due to telomere shortening.
What are the physiologic changes of aging?
Age-related decrease in functional reserve
Decreased ability to adapt to environmental demands
What is somatic death?
Death of the entire organism with cessation of heartbeat and respiration.
What are key features of somatic death?
Rigor mortis (0–6 hrs, then flaccidity 24–48 hrs),
Release of lytic enzymes in body tissues: postmortem autolysis
Brain death (no brainstem reflexes, flat EEG).
What are the layers of the skin?
Epidermis
Dermis
Hypodermis (subcutaneous fat)
What is the function of the skin?
Protective barrier for internal organs
Senses changes in temp, pressure, or pain
Regulates body temp
Excretes fluid and electrolytes (sweat)
Stores fat
Synthesize vitamin D
Provide site for drug absorption
What external factor is primary cause of age related changes of the epidermis?
Exposure to sunlight
What are the changes that happen in the epidermis?
Epidermis thins
Prickle cells have less orderly arrangement
Cells will reproduce more slowly
How does these epidermis changes manifest on the skin?
Age spots / liver spots: uneven distribution of melanin
Seborrheic keratosis: build up of old skin cells
What are the changes that happen in the dermis & subcataenous tissue?
Dermis becomes less elastic
Collagen fibers become cross-linked and rearranged into thick bundles (skin folds on itself)
Decresed subcutaneous fat (fat under skin)
Decreased perfusion (blood flow to skin from shorten capillary loops)
What changes happen to hair?
Hair thinning for both sexes after 40
Male inherit baldness trait from mother (x-linked)
Loss of melanocytes in hair follicles → gray / white hair
Woman have increase facial hair post menopause due to loss of estrogen
What changes that happen nails?
Become dull, brittle, hard, and thick
Diminished vascular supply to nail bed
Increase in longitudinal striations can cause splitting of nail surface
Common fungal infection—onychomycosis
What are the changes that happen to glands?
Decrease in number of sebaceous glands and sebum secretion → drier, coarser skin
Decrease size, number, and function of sweat glands → less efficient evaporative heat loss
What are the changes to the integumentary system?
Protective function declines
Skin injured easily; heals slowly
Decreased sensation and loss of effective vasoactivity due to decline in sensory nerves and blood vessels
Vasculature more fragile
What are common vascular lesions?
Senile purpura
Venous stasis
Cherry angioma
Venous lakes
Sensile purpura
Spontaneous bruising; can be indicative of bleeding in the skin
Venous stasis
Blood starts pulling to lower extremities, can change appearance of skin over time
Cherry angioma
Overgrowth of capillaries, but not problematic
Venous lakes
Chronic vein ruptures that causes pooling of the vein. Commonly found in face and lips due to UV exposure
What are primary skin lesions?
Macule
Patch
Papule
Plaque
Vesicle
Bulla
Pustule
Macule
Lesion less than 1cm in diameter and is flat; continuous with surface around it, just a color change.
ex. freckle
Patch
Lesion larger than 1cm that is flat; area of color change'
ex. certain birthmarks
Papule
Raised lesion (can be felt), but less than 1cm in diamater
ex. moles
Plaque
Raised lesion larger than 1cm in diameter
Vesicle
Lesion smaller than 1cm with fluid filled bubble
ex. herpes
Bulla
Lesion bigger than 1cm with fluid filled bubble
ex. burns
Pustule
Smaller lesions with visible white head on it (pus)
ex. acne
What are the secondary lesions?
Excoriation
Lichenification
Scar
Excoriation
Scratch marks
Inchenification
Chronic thickening of skin as a result of repeated scratching
ex. eczema
Scar
Primary lesion developed into a scar
What are the distributions of secondary lesions?
Diffuse
Localized
Discrete
Confluent
Linear
Diffusion
Scattered lesions
Localized
Cluster of lesions
Discrete
Lesions are separated from one another
Confluent
Overlapping lesions
Linear
Lesions occurring in aline
What are the common infectious skin conditions?
Bacterial
Viral
Fungal
What are the bacterial infectious conditions?
Impetigo
Syphilis
Cutaneous abscess
Impetigo (staphylococci)
Common staph infection in children. Starts an red itchy sore (cluster of vesicle) that ruptures and heals as a crusty, yellow scab
What is the treatment for impetigo?
Topical antibiotic (mupirocin)
Syphilis (treponema pallidum)
Sexually transmitted bacterial infection that has three stages: primary stage, secondary stage, and latent stage
What is the primary stage in syphilis?
Painless ulcers forming on surface of tongue
What is the secondary stage in syphilis?
Wide spread skin lesions
What is the latent stage in syphilis?
Stage of no symptoms but can reactivate
What is the treatment for syphilis?
Antibiotic (penicillin)
Cutaneous abscess (MRSA)
Infection of skin from break in skin
What is the treatment for cutaneous abscess?
Incision & drainage
Oral antibiotics if MRSA (methicillin resistant staph aureus)
What are the viral infectious conditions?
Verrucae
Herpes simplex (oral / genital)
Chicken pox (varicella)
Herpes zoster
Verrucae
Human papilloma virus; sexuall transmitted warts that can be linked to the development of cancer
Herpes simplex
Two types:
Type 1: oral herpes, cold sores around mouth
Type 2: genital herpes, painful vesicular lesions
What is the treatment for herpes simplex?
Antiviral medication that may reduce severity / duration and supress recurrence but can’t be cured
Chicken pox
Starts as a macule and progresses into a vascular lesion.
What is the treatment for chicken pox>
Preventable with childhood vaccine
Herpes Zoster
Shingles; Stage 2 of chicken pox with painful lesions. Common in unvaccinated person who hasn’t had chicken pox and progresses to shingles.
Treatment for herpes zoster
Antiviral medication (acyclovir / valacyclovir). Will shotern course of outbreak but won’t get rid of it
What are the fungal infectious conditions?
Tinea corporis
Tinea cruris
Tinea pedis
Tinea unguium
Tinea corporis
Fungal infection of body, also known as ringworm
Tinea cruris
Fungal infection of inner thigh, common in men
Tinea pedis
Athletes foot; fungal infection of foot
Tinea unguium (onychomycosis)
Fungal infection of nail; really hard to treat and medication is toxic for liver
What is the treatment for fungal infectious conditions?
Dry skin out (warm, moist environments favorable for fungal infections)
Topical antifungals (clotrimazole) that may require many weeks to month to fully treat