TV4101 - Bovine - Nervous 3 - Young Calves
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Alpha-Mannosidosis
Signalment?
How does it work?
Control?
Affects Angus and Murray Grey
Autosomal, recessive deficiency of the
enzyme α-mannosidase is inherited → widespread storage of mannose-containing oligosaccharides
Large scale genetic screening programmes within pedigree nuclei
Alpha-Mannosidosis
CX?
Can be normal for several months b4 getting prog neuro signs
- a wide-based stance
- ataxia
- incoordination
- head nodding
- a tendency towards aggressiveness

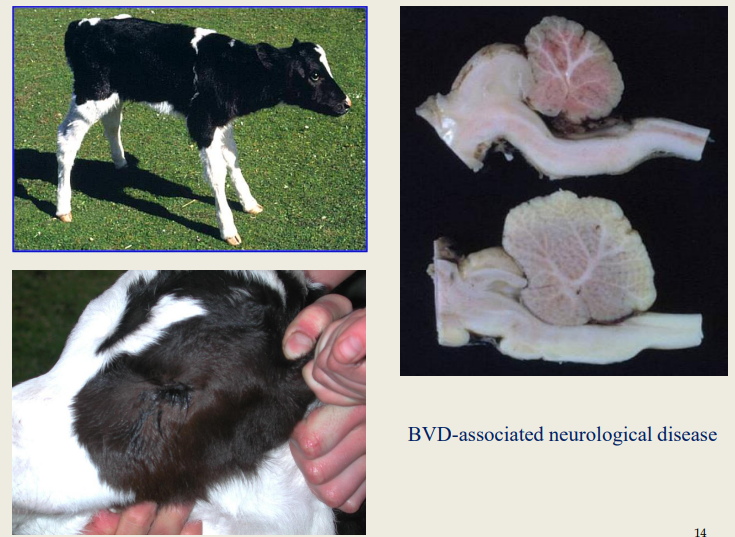
BVD-ass. neuro dz in calves
How work? When?
Infection of a naïve dam around 90-130 days of gestation
BVDV inf in pregnant cow → inf foetus
BVD-ass. neuro dz in calves
CX
Brain changes?
- cerebellar hypoplasia
- less commonly hydranencephaly, internal hydrocephalus,
microencephaly, porencephaly, or hypomyelinogenesis
BVD-ass. neuro dz in calves
CX
Eyes?
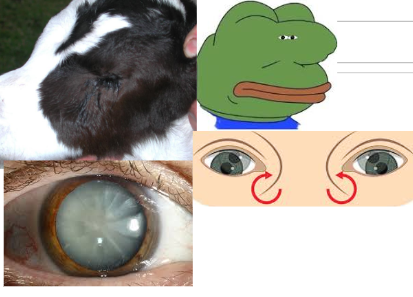
Eyes
oscillating nystagmus
No menace
Micropthalamia
Cataracts
Retinal degen
BVD-ass. neuro dz in calves
CX
Movement issues?
Incoordination (characterised by a wide-based stance &
ataxia) is usually the most prominent sign
Dysmetria
BoHV - ass neuro dz
BoHV-1 usually causes?
Respiratory (IBR) or genital (IPV/IPB) diseases in cattle; less commonly it may be ass. with encephalitis
BoHV - ass neuro dz
BoHV-5 infection may cause?
Encephalomyelitis in young calves in Aus
BoHV - ass neuro dz
Disease is characterised by?
- incoordination
- occasional circling or licking of the flanks
- recumbency & death
BoHV - ass neuro dz
DX?
brain sample submitted for standard virus isolation procedures or virus identification by fluorescent
antibody techniques
BoHV
Diff types and dz they cause"?
BoHV-1
IBR: Infectious bovine Rhinotracheitis
IPV: Infectious pustular vulvovaginitis
IBP: Infectious balinoposthitis
BoHV-2
Bovine Herpes Mammillitis
Pseudo lumpy skin disease
BoHV-5
Encephalomyelitis in young calves

Akabane Virus-asso dz
Prevalence?
Akabane virus is a major cause of epizootics of?
Transmission?
Endemic in N AUS
Congenital dz in calves → either hydranencephaly and/or arthrogryposis
Present at birth → euth only option mostly
Spread by biting arthropods; major carrier is the biting
midge Culicoides brevitarsis
Akabane Virus-asso dz
In outbreaks occurring in herds with year-round or extended calving periods, what may we see?
First (early) cases seen are the result of viral infection in late gestation →Arthrogryposis
Towards the end of an outbreak are due to infection that
occurred when the foetus was in an early stage of development → Hydrancephaly
Akabane Virus-asso dz
In case of restricted seasonal breeding (or limited periods of exposure to infected vectors), abnormalities may be limited to?
Only one type
Akabane Virus-asso dz
The diff types of defect and when it happens?
Arthrogryposis is usually seen in the early stage of an outbreak (it is the result of infection late in gestation – between 105 and 150 days)
Hydranencephaly is usually seen towards the end of an outbreak (it is the result of infection early in gestation – between 30 and 105 days)
Calves showing both defects occur in the middle of an outbreak (it is the result of infection between 100 and 120 days of gestation)
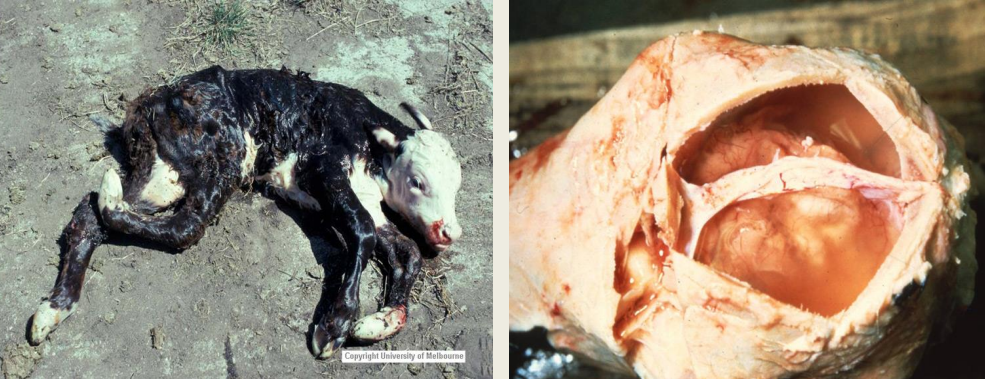
What is this Dz?
Describe each photo
Akabane Virus-asso dz
Left - Severe arythrogryposis
Right - Small brain (microencephaly) surrounded by CSF
Clostridial (haemorragic) entertoxaemia
Agent? Features?
Affected calves age?
Clostridium perfringens
5 genotypes (A, B, C, D and E), but only Type D is important in cattle
Ass with exotoxin prod in GIT lumen
1-2 wks old (but can be as old as 10 wks)
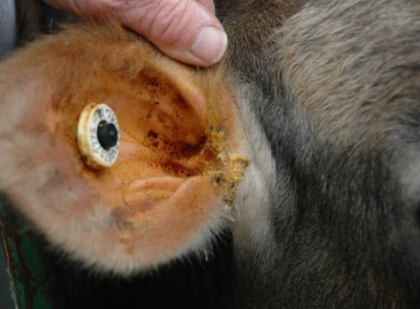
Otitis media (and vestibular Dz)
Commonly secondary to?
Neurological signs associated with otitis media include?
Most cases will?
TX?
Respiratory disease, (particularly bronchopneumonia) → bacteria reach middle ear via Eustachian tube
- head tilt
- drooping eyelids (ptosis)
- paralysis & drooping of the ear
Have discharge from affected ear
Treatment → broad-spectrum antibiotics & NSAID
Clostridial (haemorragic) entertoxaemia
CX?
- sudden death
- frothing at the mouth
- haemorrhagic diarrhoea
- abdominal discomfort
Neuro
Stagger
Appear blind
Recumbent
Some cases → opisthotonos, rigid muscles, convulse
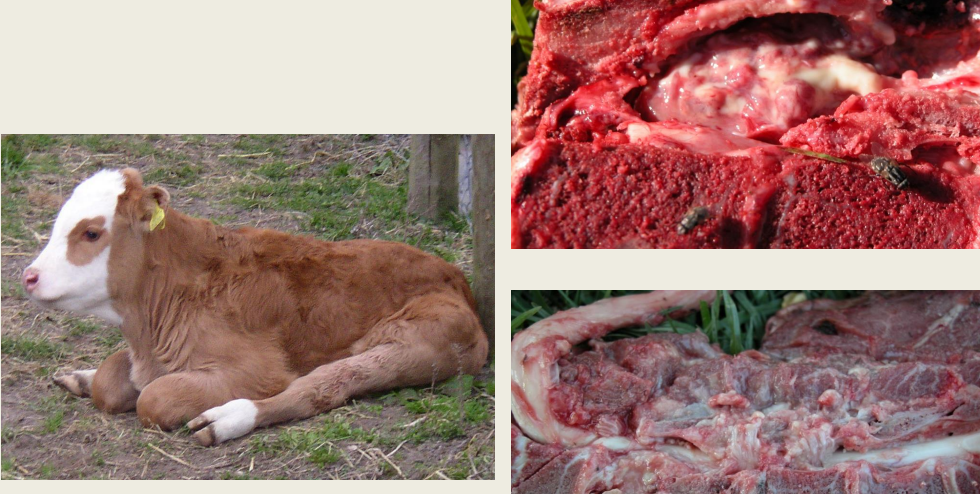
Clostridial (haemorragic) entertoxaemia - DX
PM?
Definitive diagnosis requires identification of?
What else can we see?
Post-mortem examination → small intestine may be
haemorrhagic (associated with ischaemic necrosis)
β- or ε-toxin in small intestinal contents
Large numbers of Gram-positive rods in impression smears from duodenal or jejunal mucosa is strongly supportive (Clostridium spp are not normal inhabitants of upper SI)
Vertebral (spinal) abscess
Overview?
Why does it happen?
CX?
Abscessation or osteomyelitis of the spinal vertebrae is most
commonly seen in calves between 2 and 6 months of age
• Infection is usually the result of haematogenous spread
• Compressive lesion on the spinal cord → ataxia & paralysis

Vertebral (spinal) abscess
CX
Vary based on location of lesion
describe each
Lesion btw - T2 and L3
Hindlimb ataxia and paresis
W/O dysfunction of
peripheral ns of hindlimbs and paralysis of rectum, bladder & tail
Cranial to T2
Rigidity of forelimbs or tetraparesis
Lesion between C6 and T2
Weak/para forelimbs with poor/absent reflexes
HL less weak with normal/exaggerated reflexes

Where is lesion?
Lesion between T2 and L3
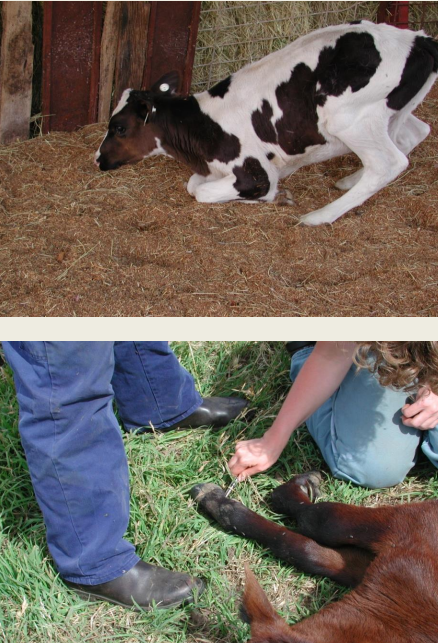

Where is lesion?
Lesion between C6 and T2
Many congenital diseases have been reported in cattle
May be ass with?
infectious, genetic, endogenous biochemical, and exogenous toxic causes
Congenital neuro dz in calves
cerebral disorders → primarily associated with changes in?
Mental status or behaviour, functional disturbances and abnormal postures
Congenital neuro dz in calves
cerebellar disorders → primarily characterised by?
incoordination
Congenital neuro dz in calves
Spinal defects ass with?
Affected peripheral control
Steps to follow when dealing with possible congenital neuro dz?
ID and confirm dz is neuro and ass. with changes b4 birth
Do good ante-mortem investigation to find lesion site
Submit animal for further PM exam and lab investigation
Citrullinaemia
How work?
Inherited as an autosomal, recessive disorder of HolsteinFriesian calves → def of urea cycle
enzyme argininosuccinate synthetase → Affected calves have greatly elevated concentrations of citrulline and ammonia in the blood
Citrullinaemia
Control?
Screening of heterozygous bulls that enter AB centres, using a DNA-based test
Citrullinaemia
CX?
Neuro?
Diagnosis is based on?
Calve normal at birth → 4 days shit goes down
Quick death
Neuro
Stupor
Wander aimlessly
Head pressing
Collapse
Convulse
Paddling
Bellowing
Elevated levels of serum citrulline (1-3 mM) by Day 3