Body regions/direction terms/body cavaties
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms

cephalic

otic

orbital

oral

frontal

buccal

nasal

mental

cervical

occipital
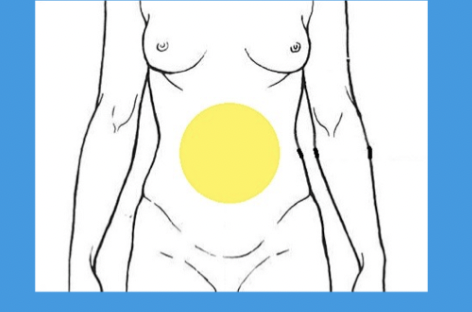
abdominal
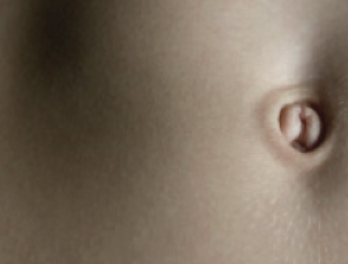
umbilicus
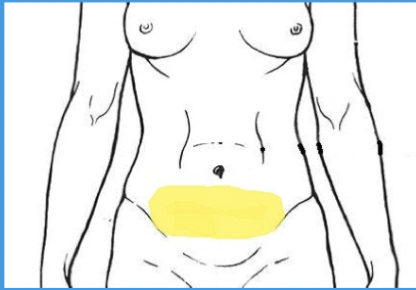
pelvic
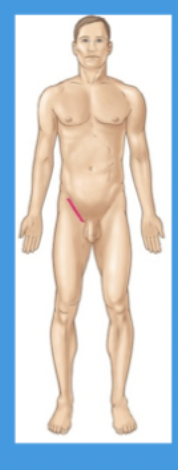
inguinal
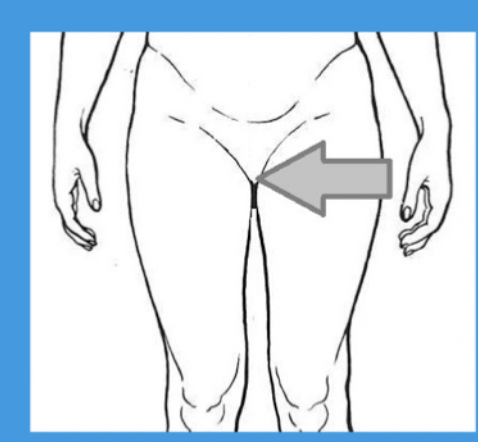
pubic
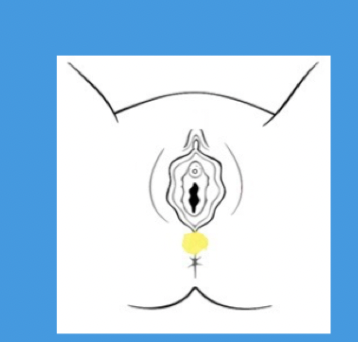
perineal
pectoral
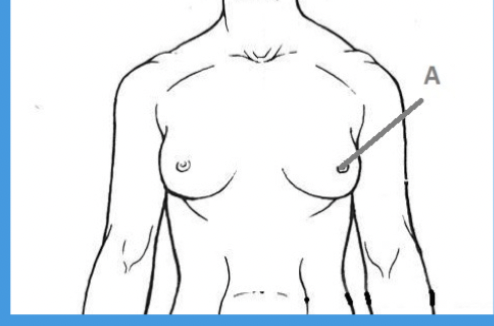
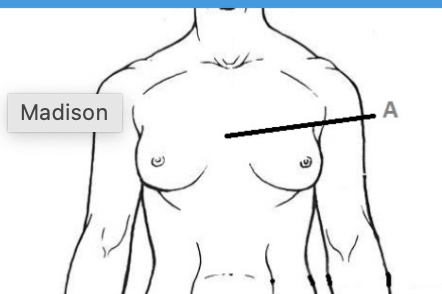
mammary
sternal
vertebral
scapular
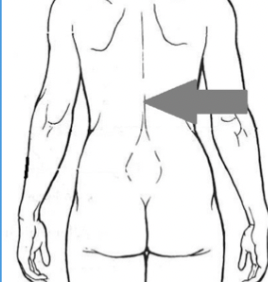
doral
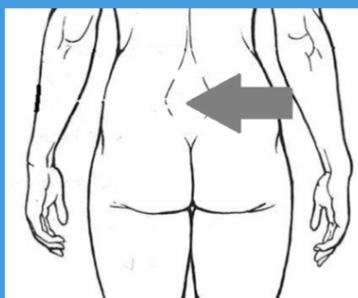
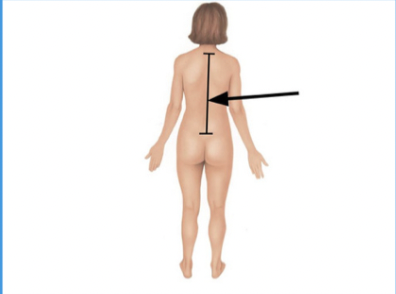
lumbar
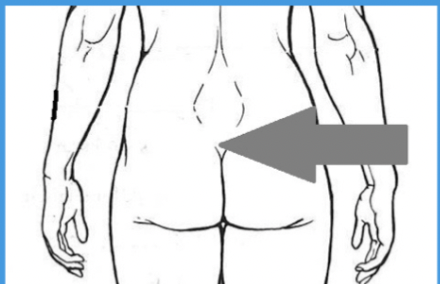
sacral
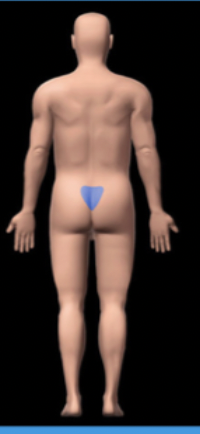
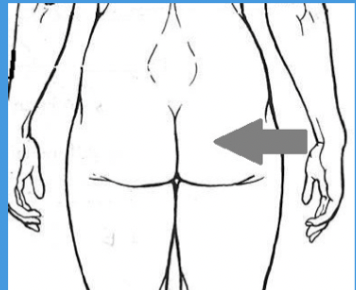
gluteal
upper extremity
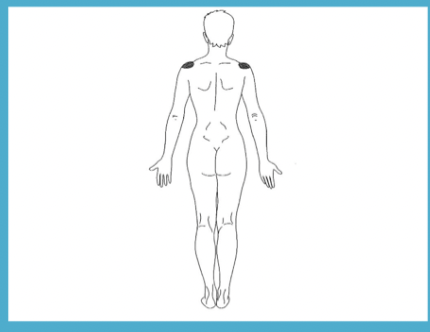
acromial
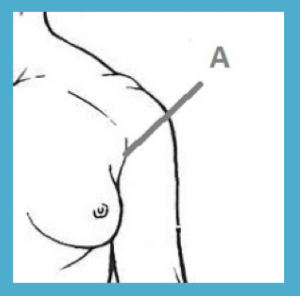
axillary
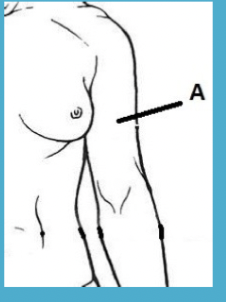
brachial
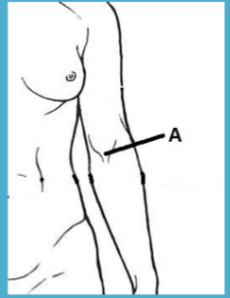
antecubital
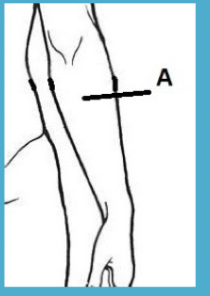
antebrachial
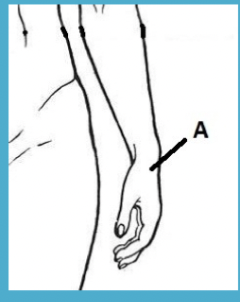
carpal

palmar
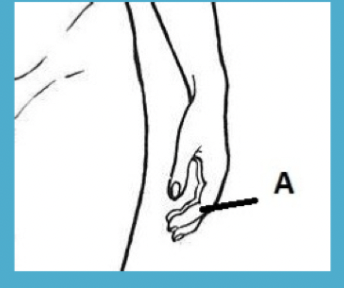
digital

pollex
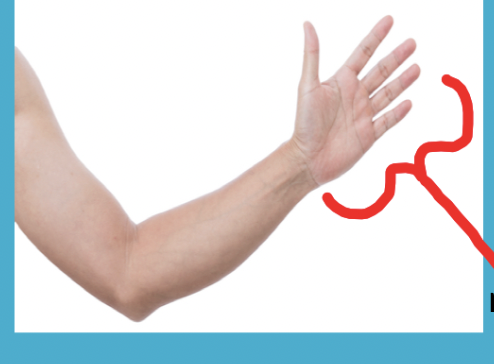
manus
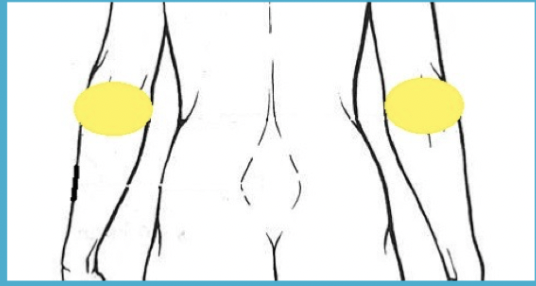
olecranal
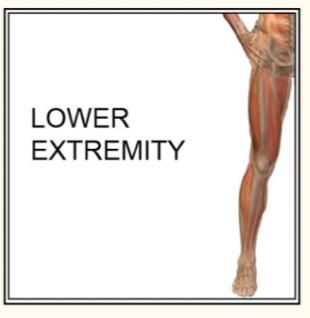
lower extremity
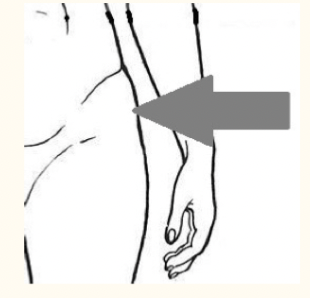
coxal
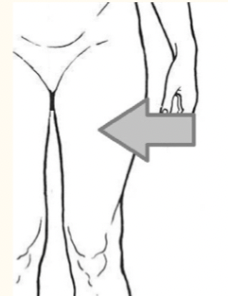
femoral
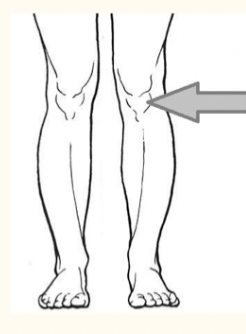
patellar
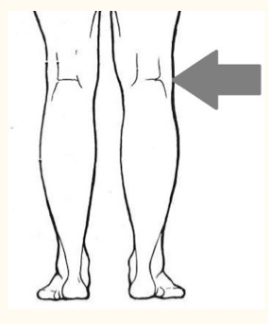
popliteal
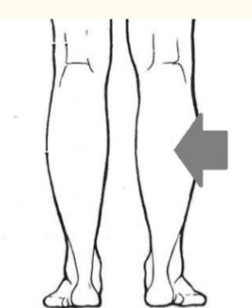
sural
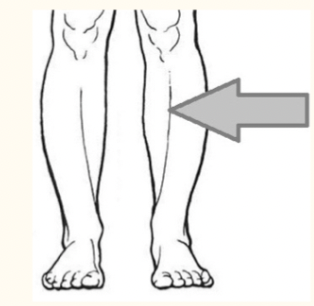
crural
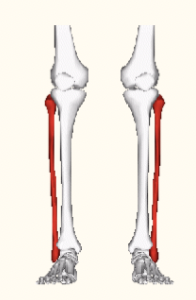
fibular (peroneal)
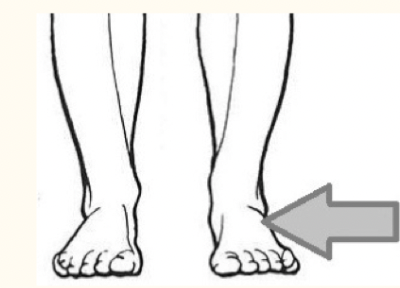
tarsal
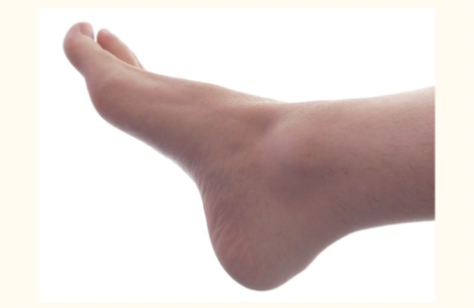
pedal
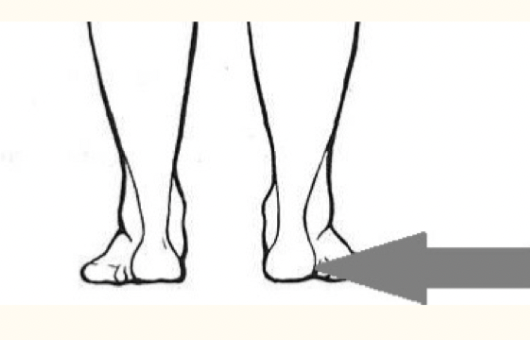
calcaneal
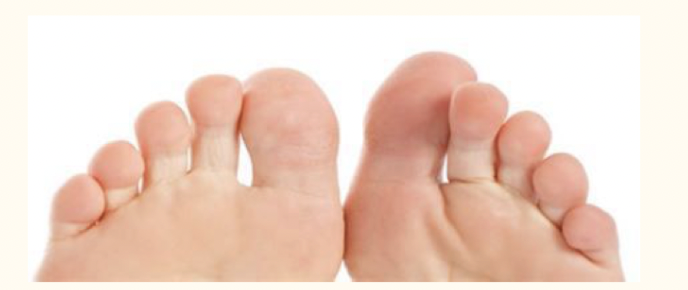
hallux (big) and digits
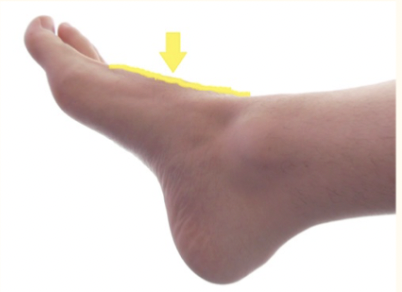
dorsum of foot
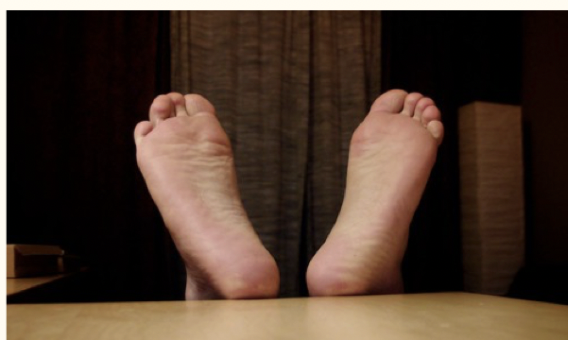
plantar region
directional terms
are used to precisely locate on part of the body relative to another and to reduce length of explanations
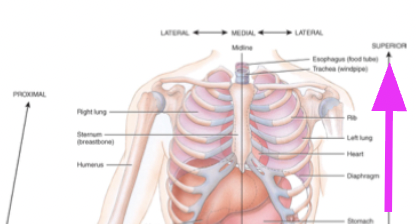
superior
towards the head or towards top on an organ
→ the eyes are superior to the mouth
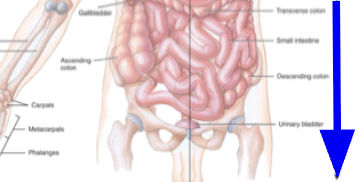
inferior
away from the head or the bottom on an organ
→ the stomach is inferior to the heart
cranial
AKA SUPERIOR- toward the head
caudal
AKA INFERIOR- toward the lower part of the structure or body
medial
towards the midline of the body
→ the heart lies medial to the lungs
lateral
father from the midline of the body
→ the thumb is lateral to the pinky
proximal
nearer to the attachment of the limb to the trunk
→ the knee is proximal to the ankle
→ USE IN UPPER AND LOWER EXTREMITY ONLY
distal
farther from the attachment of the limb to the trunk
→ the wrist is distal to the elbow
→ ONLY USE IN UPPER AND LOWER EXTREMITY
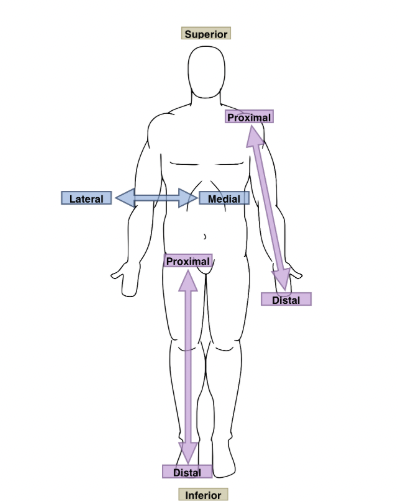
dorsal
→ toward the back of the body
→ AKA POSTERIOR
→ ex: the spinal cord is dorsal to the heart
ventral
→ towards the front of the body
→ AKA ANTERIOR
→ the sternum is anterior to the heart
intermediate
→ between a more medial and more lateral structure
→ the collar bone is intermediate to the breast bone and shoulder
superficial
→ toward the body surface
→ AKA EXTERNAL
→ the skin is superfical to the muscles
deep
→ away from the body surface
→ AKA INTERNAL
→ the bones are deep to the skin
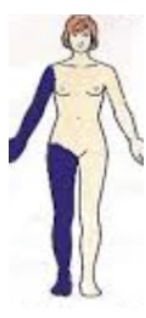
contralateral
→ structures on opposite sides of the body midline
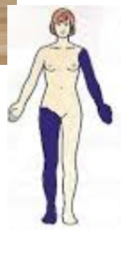
ipsilateral
→ same side of the midline
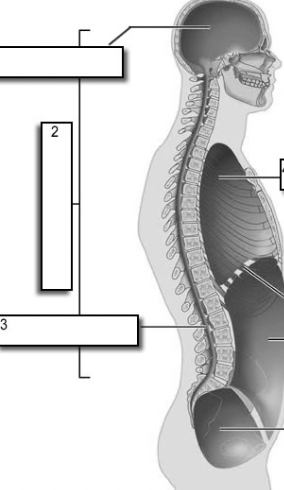
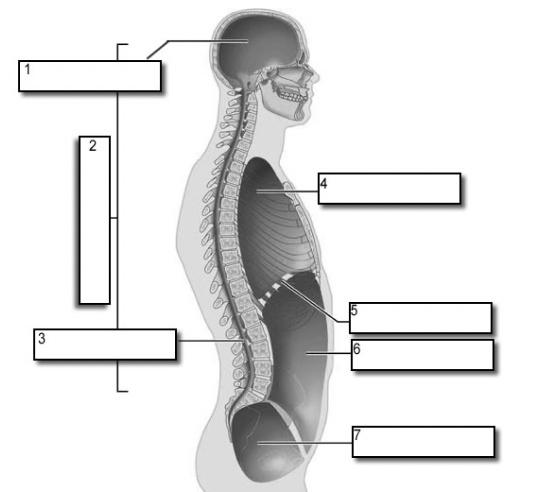
dorsal cavity
protects the nervous system, and is divided into two subdivisions
→ CV
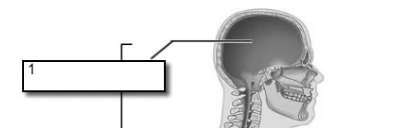
cranial cavity
within the skull; encases the brain
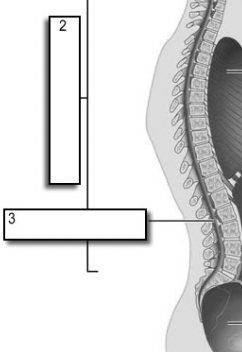
vertebral cavity
runs within the vertebral column; encases the spinal cord
ventral cavity
houses the internal organs (viscera) and is divided into two subdivisions
→ TA
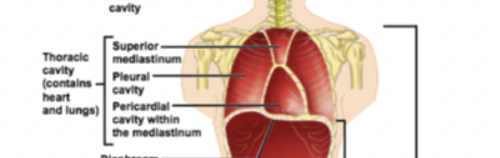
thoracic cavity
→ contains heart and lungs
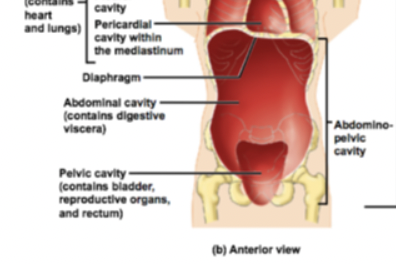
abdominalpelvic cavity
→ contains digestive vicera, bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
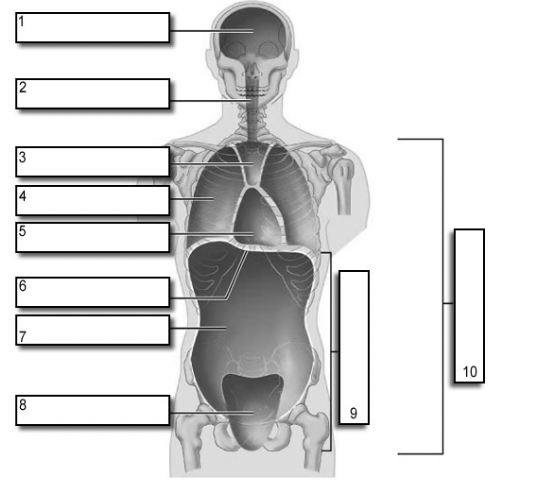
diaphragm muscle
seperates (#6, and #5)
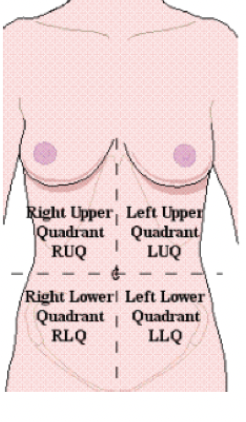
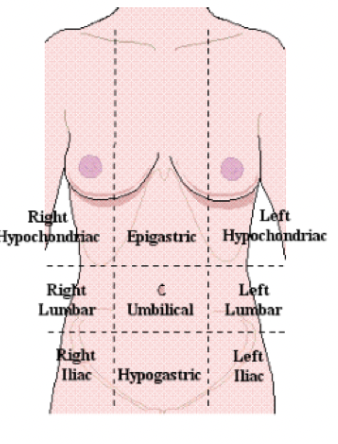
abdominal quadrants
→ GLASS
RUQ- GL (gaulbladder, liver)
RLQ- A (appendix)
LUQ- BIG S LITTLE S (stomach, splene)
LLQ- BIG S (stomach)