The Objectives of Firms
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is arguably the most important objective for most firms?
Profit, which is difference between total revenue and total cost - reward that entrepreneurs yield for taking risks
When do firms break even? When TR = TC
When does profit maximisation occur?
When Marginal Revenue = Marginal cost. This is because, producing one extra unit would now incur a loss, as MC would be > than MR, therefore production should be kept constant at the point where MC and MR meet.
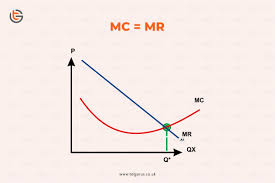
Benefits of profit maximisation
Give employees higher wages and shareholders larger dividends
Cheap source of finance, can use profits to invest in the future rather than taking out potentially expensive loans.
Why is short run profit maximisation particularly important to PLCs?
They could lose their shareholders if they don’t receive a high dividend, therefore need short run profits to keep them happy.
What are other important objectives for firms?
Satisficing
Sales revenue maximisation
Survival
Growth
Increasing market share
Satisficing principles, what are they?
A mix between satisfy and suffice, it suggests that decision makers settle for the option that meets a minimum acceptable level, rather than trying for better outcomes.
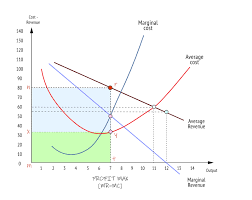
Revenue maximisation - what is it, link to graph
At the point where Marginal Revenue = 0, as producing anymore would actually make a loss.
Revenue is the area bounded by the MR = 0 dashed vertical line, which meets the AR curve.
Survival - why do firms aim for this?
Some firms, particularly those entering competitive markets, may aim to simply survive, a short term view.
During periods of economy decline, consumer spending plummets, so firms need to just survive until there’s growth again
Firms may aim to sell as much as possible to keep market position, even if it’s at a loss in the short run.
Growth - why do firms aim for this?
Firms may aim to increase their size to take advantage of economies of scale. This would lower their AC in the long run , making them more profitable.
May also expand their product range, or take over existing firms. Large firms may increase R&D to make them more competitive in the long run.
At what point on the graph is sales maximisation achieved?
When AR = AC.
Increasing market share - why do some firms aim for this?
Can be achieved by maximising sales to increase chance of survival.
E.g. amazon sold kindles at a loss to gain market share, in the long run gaining customer loyalty and are now the leading e-reading producer.
What are some other more uncommon objectives?
Society
Environment
Ethical - when there are philanthropic owners
Managerial for personal gains, like holidays
Worker welfare
What are examples of Corporate social responsibility (CSR) obligations?
Reducing carbon emissions
Waste reduction and recycling
Community projects like supporting schools hospitals or infrastructure
Philanthropy - charities/social causes
What is the difference between shareholders and stakeholders ?
Shareholders - own shares of a company’s stock
Stakeholders - parties with diverse interests in a company’s operations, reputation and outcomes
What are different stakeholders
Shareholder, manager, employee, supplier, customer, creditor, government, community
Effect on shareholders of Profit, revenue and sales maximisation
Profit: highest returns
Revenue: lower
Sales: lowest
Effect of profit, sales and revenue maximisation on consumers
Profit: prices higher and output lower reduces consumer surplus (worst)
Revenue: '‘ Better
Sales: ‘‘Best
Effect of profit, revenue, sales maximisation on wider stakeholders
Profit: more tax revenue for govt.
Revenue: close to allocative efficiency which benefits society
Sales: maximises output, benefit firm employment