Unit 7: West and Central Asia, 500 BCE–1980 CE
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Art History
AP Art History
Unit 7: West and Central Asia, 500 BCE–1980 CE
Muhammad
Calligraphy
Arabesque
Pyxis-of-al-Mughir
Pyxis-of-al-Mughir
Folio-from-a-Qur’an-Arab
Basin
Ardabil-Carpet
Islamic-Art
Islamic-Art
The-Court-of-Gayumars
Mecca
Islamic-Architecture
Islamic-Architecture
The-Kaaba
The-Kaaba
Great-Mosque
Alhambra
Court-of-the-Lions
Hall-of-the-Sisters
Mosque-of-Selim-II
Taj-Mahal
University/Undergrad
Last updated 7:57 AM on 3/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
Muhammad (570?-632)
The Prophet whose revelations and teachings form the foundation of Islam
2
New cards
Quran
the Islamic sacred text, dictated to the Prophet Muhammad by the Angel Gabriel
3
New cards
Calligraphy
decorative or beautiful handwriting
4
New cards
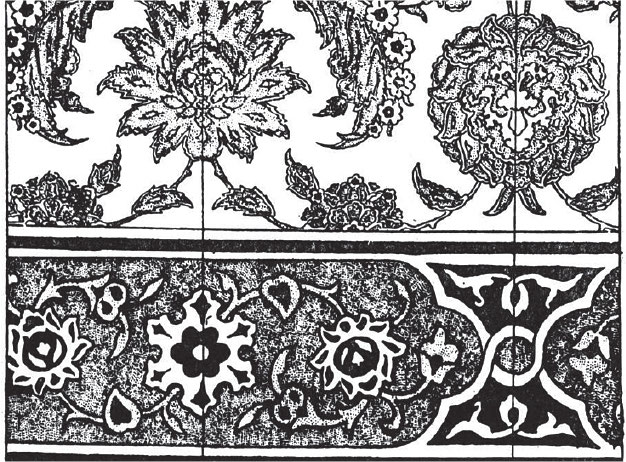

Arabesque
a flowing, intricate, and symmetrical pattern deriving from floral motifs
5
New cards
Kufic
a highly ornamental Islamic script
6
New cards
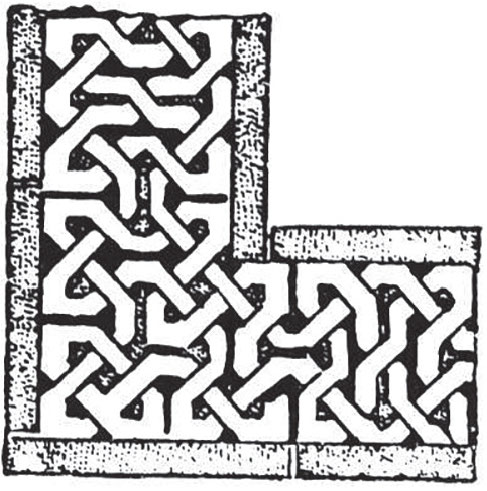
Tessellation
decoration using polygonal shapes with no gaps
7
New cards
Jali
perforated ornamental stone screens in Islamic art
8
New cards
Pyxis
a small cylinder-shaped container with a detachable lid used to contain cosmetics or jewelry
9
New cards
Shahnama, or The Book of Kings
a long epic poem written by the Persian poet Firdawsi between c. 977 and 1010 c.e
10
New cards
Qibla
the direction toward Mecca which Muslims face in prayer
11
New cards
Mecca and Medina
Islamic holy cities;
12
New cards
Mecca
is the birthplace of Muhammad and the city all Muslims turn to in prayer;
13
New cards
Medina
is where Muhammad was first accepted as the Prophet, and where his tomb is located
14
New cards
Minaret
a tall, slender column used to call people to prayer
15
New cards
Muezzin
an Islamic official who calls people to prayer traditionally from a minaret
16
New cards
Hypostyle
a hall that has a roof supported by a dense thicket of columns
17
New cards
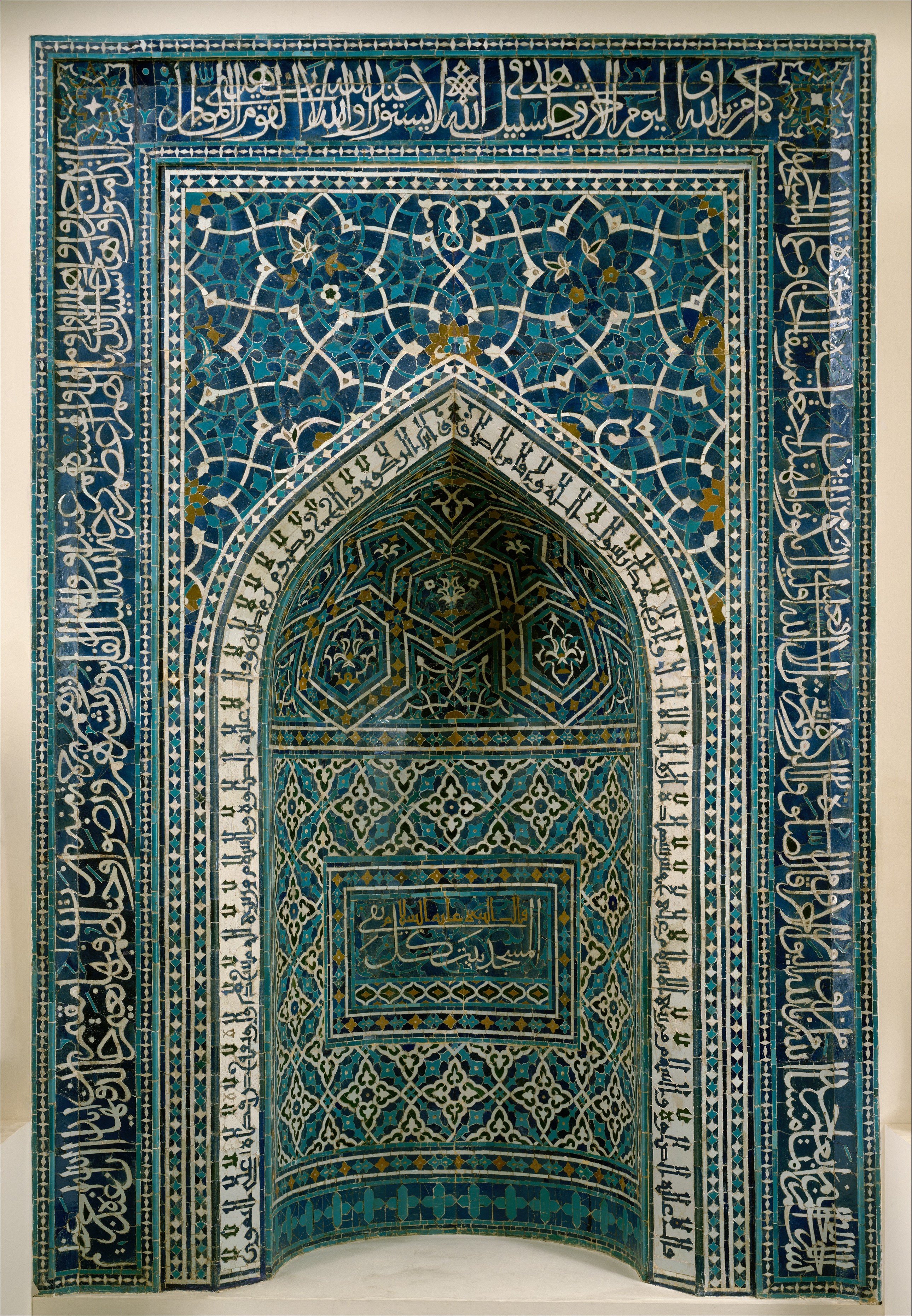

Mihrab
a central niche in a mosque, which indicates the direction to Mecca
18
New cards
Muqarna
a honeycomb-like decoration often applied in Islamic buildings to domes, niches, capitals, or vaults
19
New cards
Iwan
a rectangular vaulted space in a Muslim building that is walled on three sides and open on the fourth
20
New cards
Madrasa
a Muslim school or university often attached to a mosque
21
New cards
Mausoleum
a building, usually large, that contains tombs
22
New cards
Minbar
a pulpit from which sermons are given
23
New cards
Squinch
the polygonal base of a dome that makes a transition from the round dome to a flat wall
24
New cards
Voussoirs (pronounced "vōō-swar")
a wedge-shaped stone that forms the curved part of an arch; the central voussoir is called a keystone
25
New cards
Hajj
an Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca that is required of devout Muslims as one of the five pillars of Islam
26
New cards
Muqarnes
an ornamental and intricate vaulting placed on the underside of arches
27
New cards
Sahn
a courtyard in Islamic architecture
28
New cards
Hypostyle mosque
no central focus, no congregational worship
29
New cards
Charbagh
a rectangular garden in the Persian tradition that is based on the four gardens of Paradise mentioned in the Quran
30
New cards
Prophet Muhammad
The \_____’s powerful religious message resonated deeply with Arabs in the seventh century, and so by the end of the Umayyad Dynasty in 750 C.E., North Africa, the Middle East and parts of Spain, India, and Central Asia were converted to Islam or were under the control of Islamic dynasties.
31
New cards
Abbasid Caliphate
The Islamic world expanded under the \____, which ruled a vast empire from their capital in Baghdad.
32
New cards
Apprenticeships
\____ were exacting, making students master everything including the manufacture of ink and the correct posture for sitting while writing.
33
New cards
acanthus and split leavesscrolling vinesspirals, wheelszigzags.
Favorite arabesque motifs
34
New cards
straightedge and compass
All of these designs, no matter how complicated, were achieved with only \______.
35
New cards
central point
Patterns seem to radiate from a \_____, although any point can be thought of as the start.
36
New cards
geometric elements
Islamic mathematicians were thinkers of the highest order; \____ reinforced their idea that the universe is based on logic and a clear design.
37
New cards
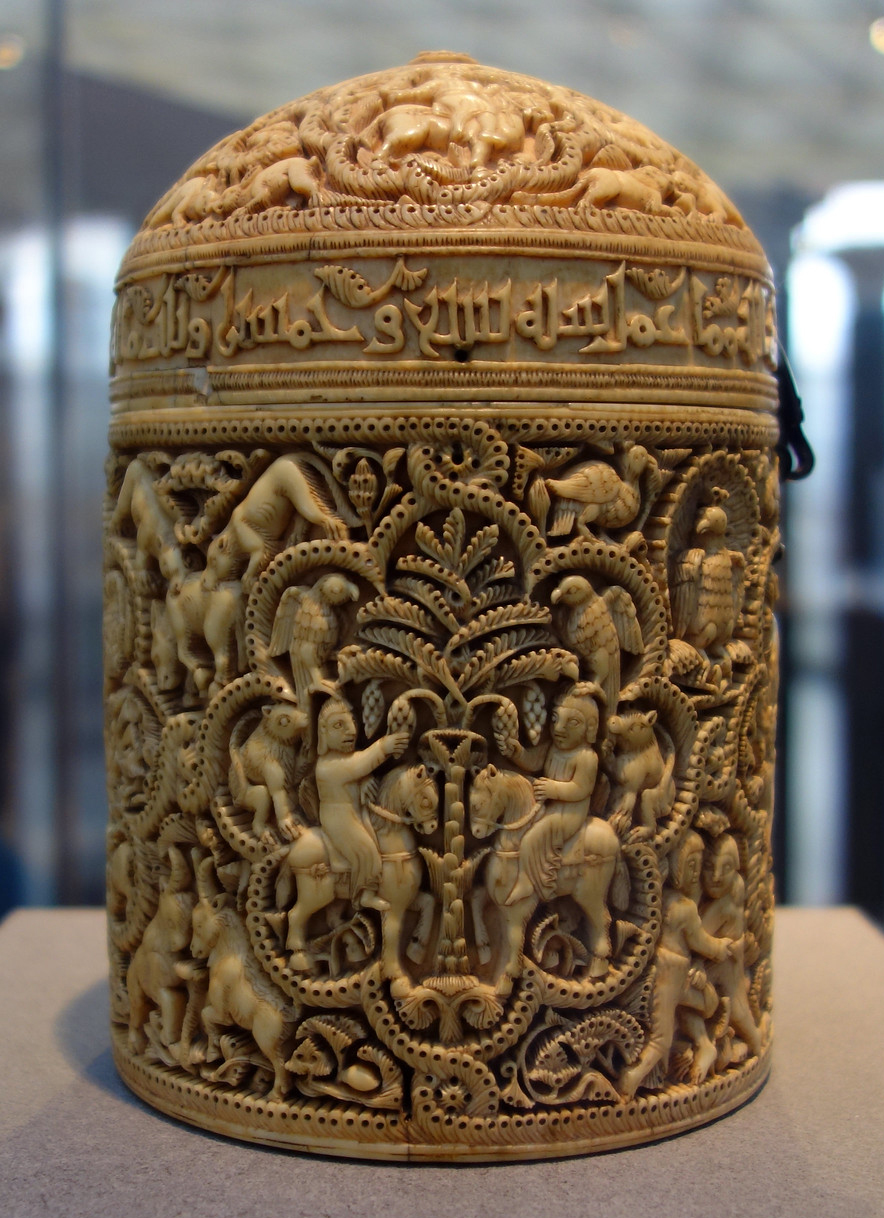

Pyxis of al-Mughir
Horror vacui.Intricately carved container made from elephant ivory. Container for expensive aromatics
38
New cards

Folio from a Qur’an, Arab
The title of each chapter is scripted in gold. Kufic script; strong uprights and long horizontals. Illustrated is the heading of sura 29 (al-’Ankabūt, or “The Spider”) in gold.
39
New cards
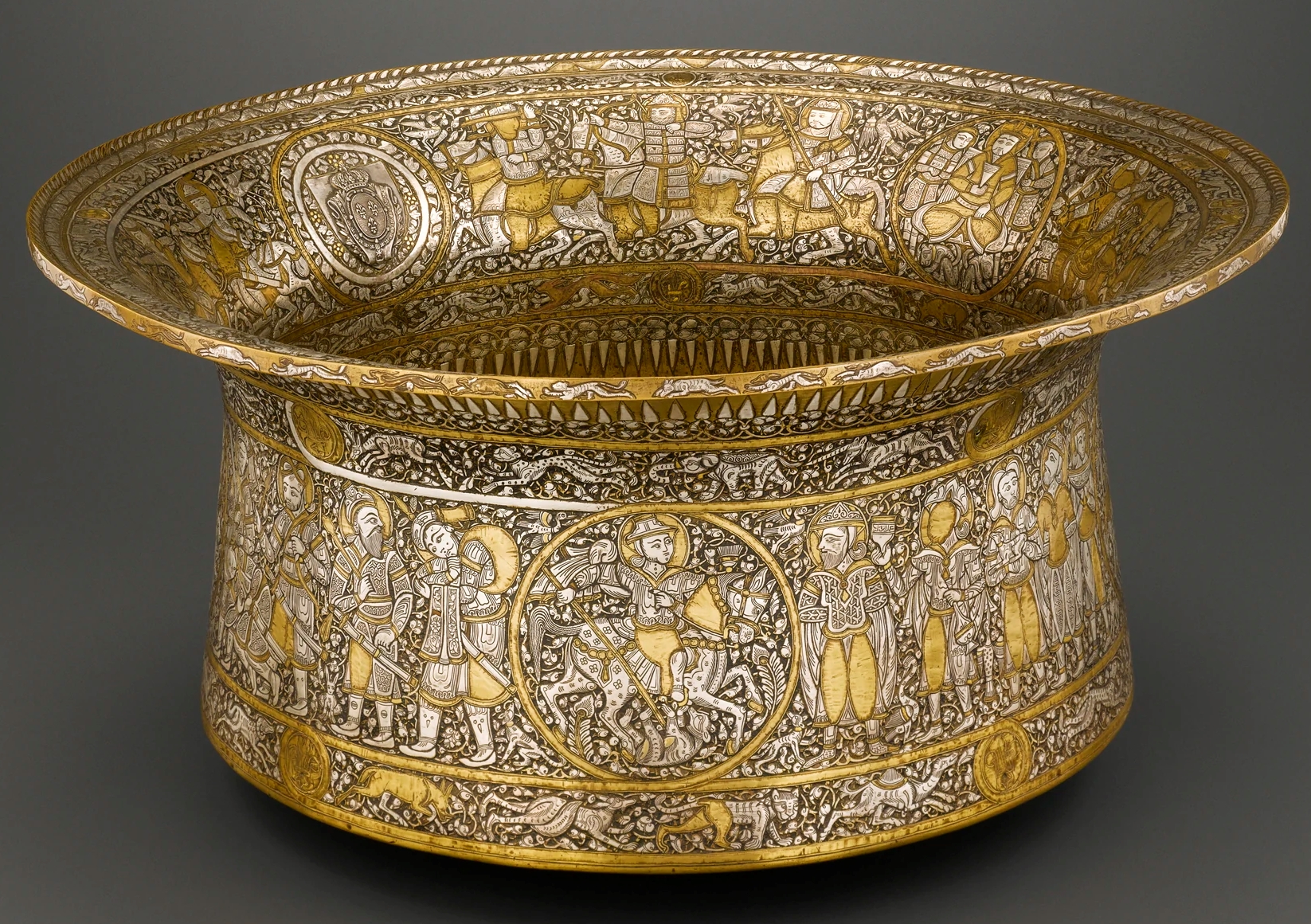

Basin (Baptistère de Saint Louis)
Designed by Muhammad ibn al-Zain. Original use is for ceremonial hand washing. Hunting scenes alternate with battle scenes along the side of the bowl.
40
New cards

The Ardabil Carpet
Designed by Maqsud of KashanPrayer carpet used at a pilgrimage site of a Sufi saint. Wool carpet, woven by ten people, probably menWool pile of 5,300 knots per 10 cm. sq
41
New cards
Bahram Gur
He was an ancient Iranian king from the Sassanian dynasty. He represents the ideal king; wears a crown and a golden halo.
42
New cards
karg
is a kind of unicorn or horned wolf he fought during his trip to India.
43
New cards
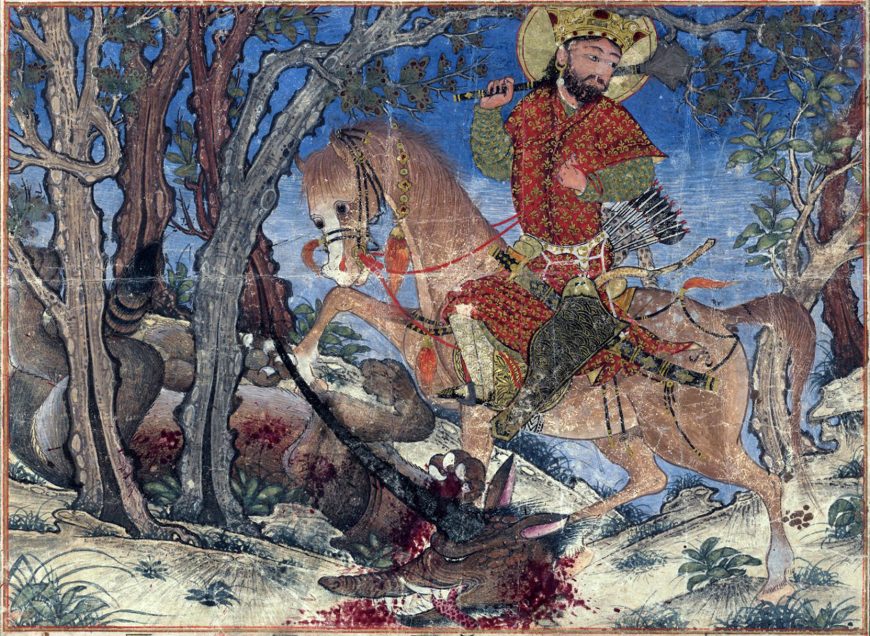

Bahram Gur Fights the Karg
Folio from the Great Il-Khanid Shahnama, Islamic; Persian. The original story by Firdawsi was written around 1010. Commissioned by a high-ranking Ilkhanid court official
44
New cards
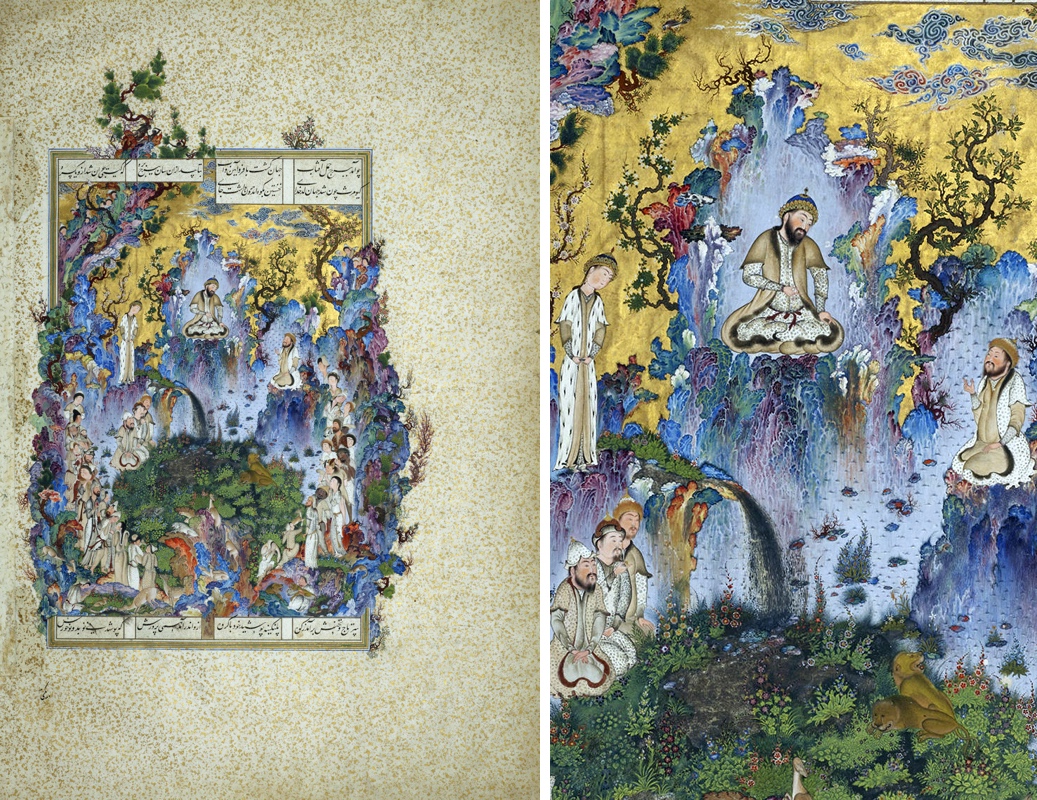

The Court of Gayumars
The original story by Firdawsi was written around 1010. Folio from the text called the Great Ilkhanid Shahnama or the Book of Kings, a Persian epic. Produced for the Safavid ruler of Iran, Shah Tahmasp I Whole book contains 258 illustrated pages.
45
New cards
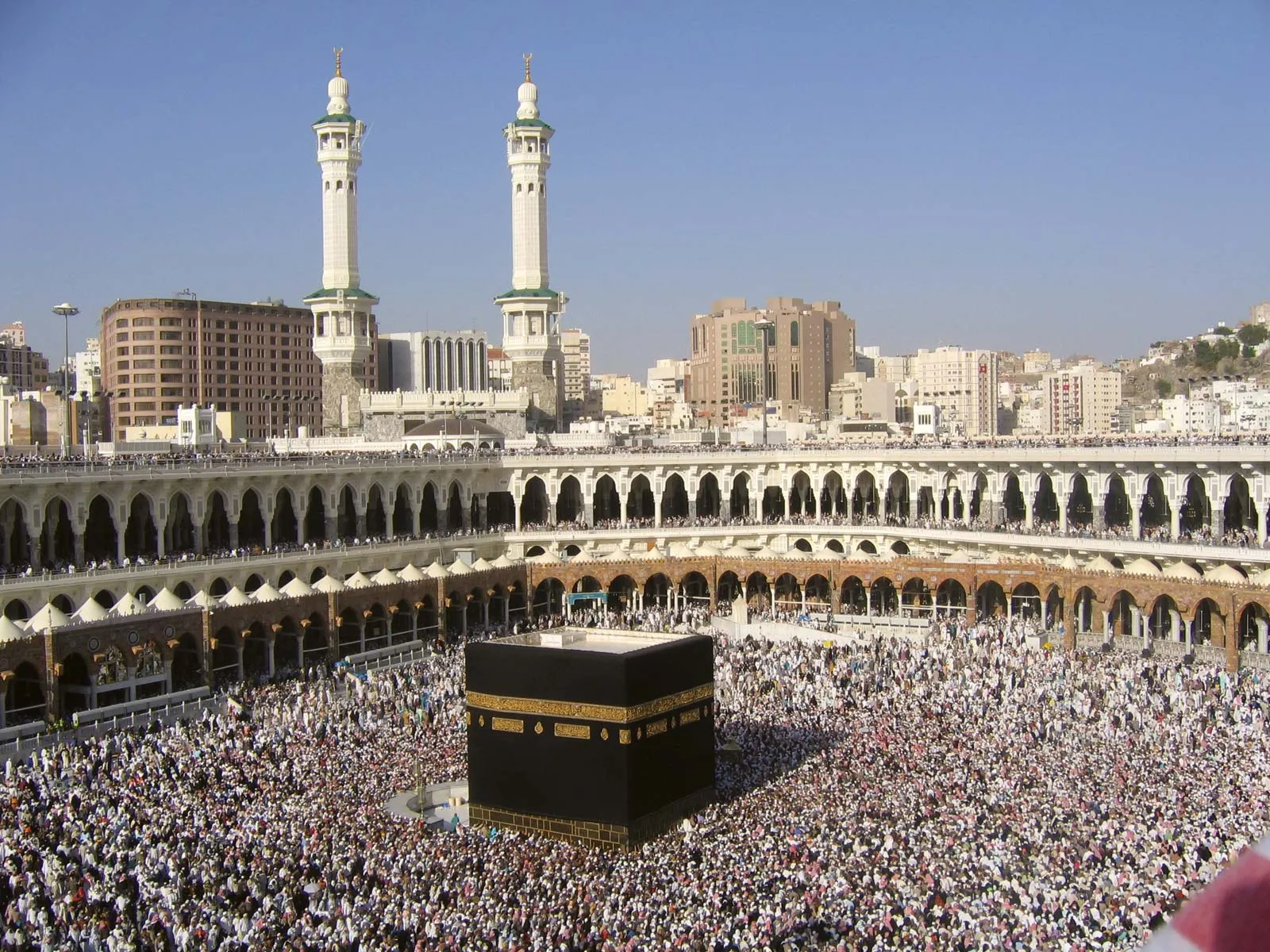

The Kaaba
Rededicated by Muhammad in 631–632Multiple renovations; granite masonry, covered with silk curtain, and calligraphy in gold and silver-wrapped threadbeen built by Ibrahim and Ishamel for God
46
New cards
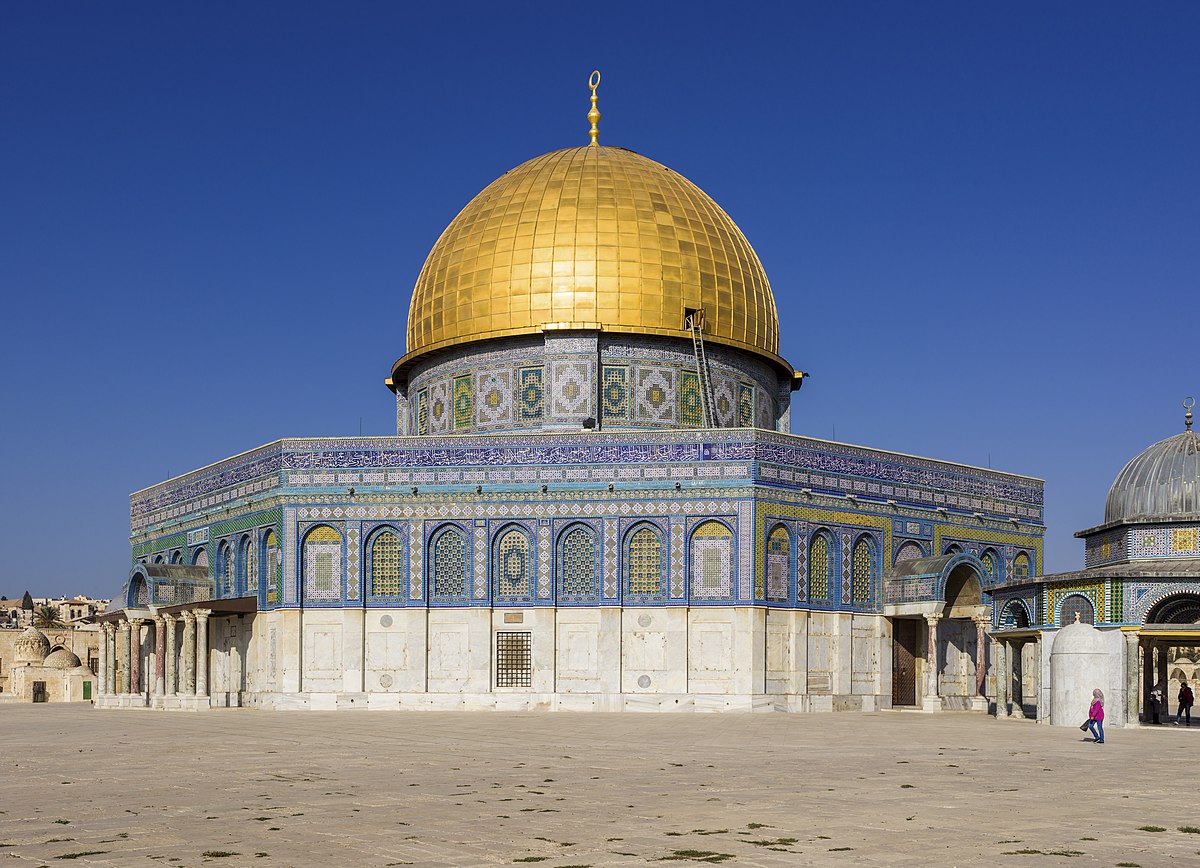

Dome of the Rock
Pilgrimage site for the faithful. Not a mosque; its original function has been debated. Meant to rival the Christian church of the Holy Sepulcher in Jerusalem, although it was inspired by its domed rotunda. Erected by Abd al-Malik
47
New cards
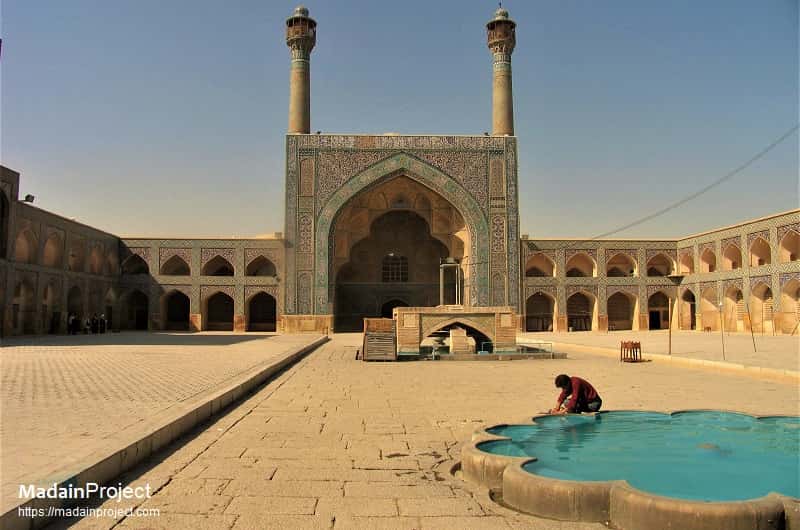

Great Mosque (Masjid-e Jameh)
Muslim mosque. Each side of the courtyard, or sahn, has a centrally placed iwan; may be the first mosque to have this feature. This mosque is nestled in an urban center; many gates give access. The mosque’s outside walls share support with other buildings.
48
New cards
qibla iwan
is the largest and most decorative in the great mosque; its size indicates the direction to Mecca.
49
New cards
Southern iwan
is an entry for a private space used by the sultan and his retinue; its dome is adorned by decorative tiles; this contains the main mihrab of the mosque.
50
New cards

Great Mosque (Umayyad Dynasty)
The site was originally a Roman temple dedicated to Janus, then a Visigothic church, and then the mosque was built. Complex dome with elaborate squinches was built over the mihrab; it was inspired by Byzantine architecture. Kufic calligraphy on walls and vaults.
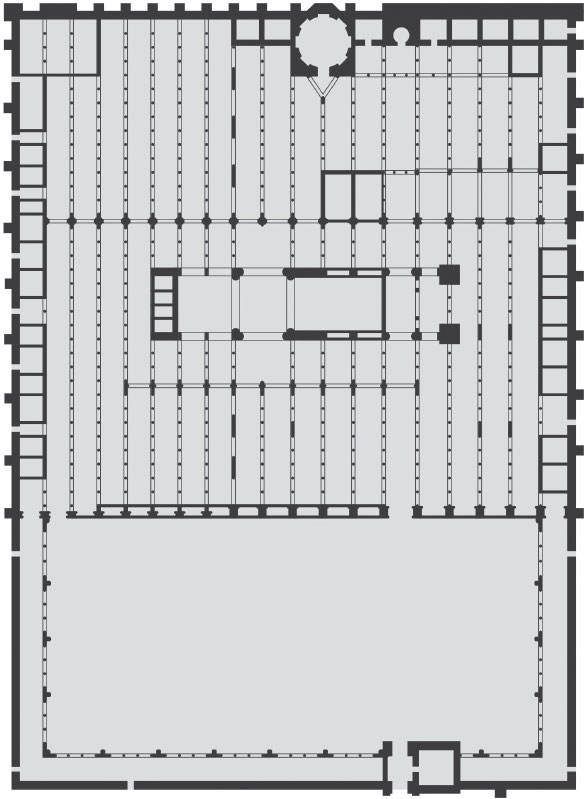
51
New cards
Alcazaba
oldest section and is visible from the exterior.double-walled fortress of solid and vaulted towers containing barracks, cisterns, baths, houses, storerooms, and a dungeon.
52
New cards
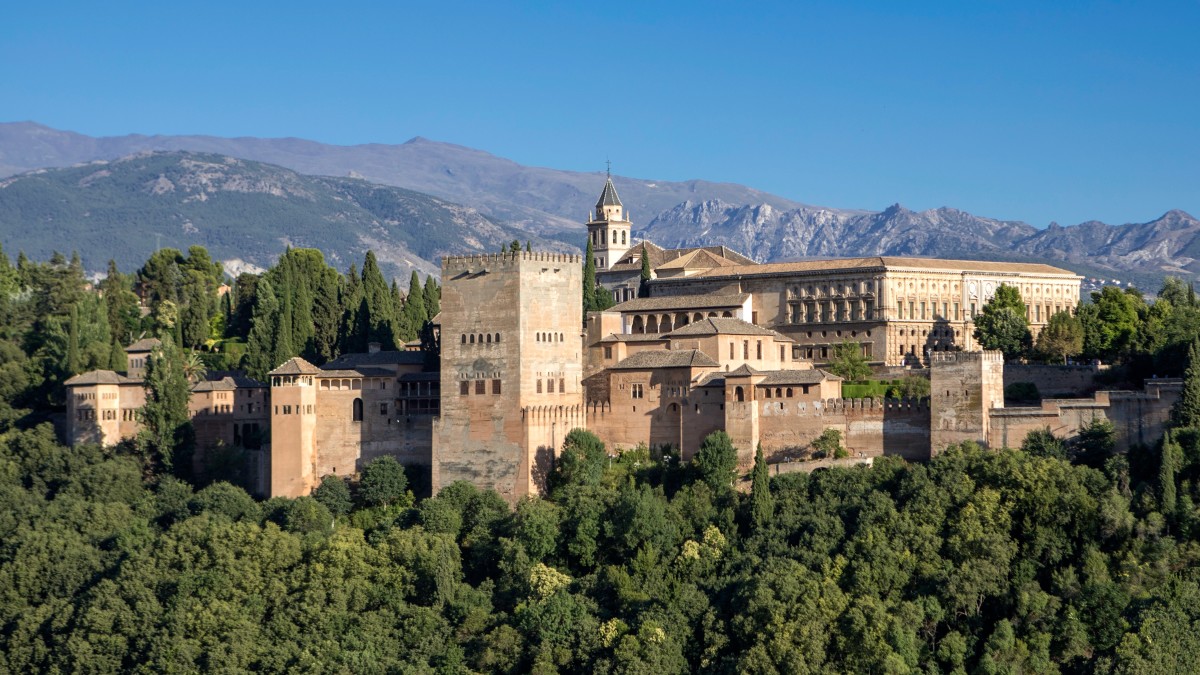

Alhambra
Small, low-bubbling fountains in each room contribute to cool temperatures in the summer. Inspired by the Charbagh gardens from Persia. Light, airy interiors; fortress-like exterior. Contains palaces, gardens, water pools, fountains, courtyards.
53
New cards

Court of the Lions
Form Built by Muhammad V between 1370 and 1391. Intricately patterned and sculpted ceilings and walls. Central fountain supported by 12 protective lions; animal imagery permitted in secular monuments. Parts of the walls are chiseled through to create vibrant light patterns within.
54
New cards

Hall of the Sisters
Sixteen small windows are placed at the top of hall; light dissolves into a honeycomb of stalactites hanging from the ceiling. Perhaps used as a music room or for receptions.The hall was built by order of Mohammed V.
55
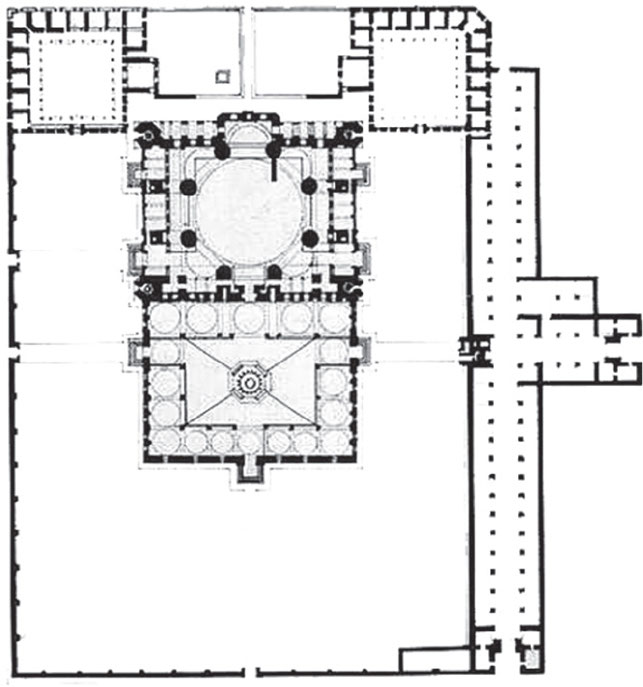
New cards
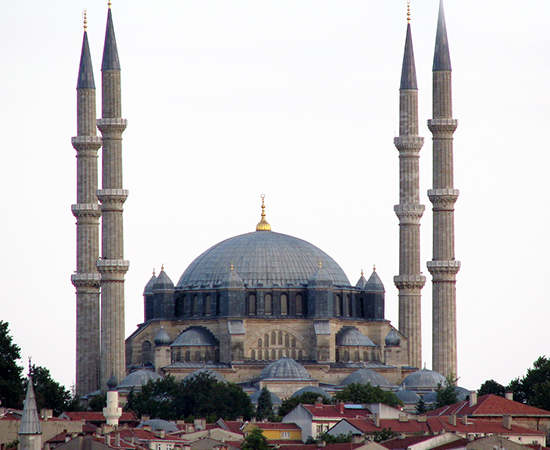

Mosque of Selim II
Designed by Mimar SinanInspired by Hagia Sophia, but a centrally planned building. Open airy interior contrasts with conventional mosques that have partitioned interiors.
56
New cards
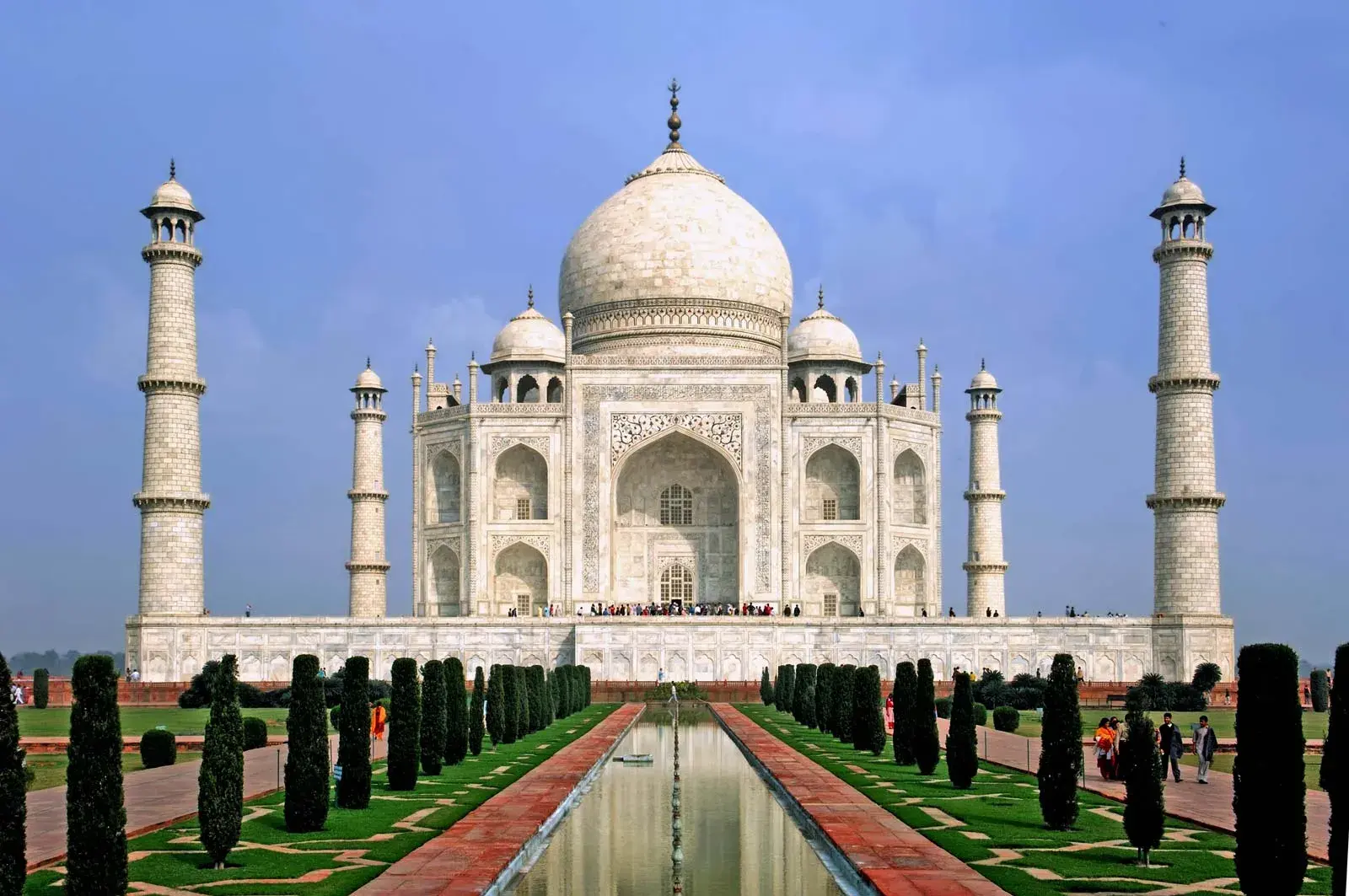

Taj Mahal
Built as the tomb of Mumtaz Mahal, Shah Jahan’s wife; the shah was interred next to her after his death. Translated to mean “crown palace.” Grounds represent a vast funerary garden, the gardens found in heaven in the Islamic tradition.