Unit 1 - The Chemistry of Life
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
hydrogen bonding
partially positive hydrogen atom in one polar covalent molecule will be attracted to an electronegative atom in another polar covalent molecule
intermolecular bond
bond that forms between molecules
polar covalent bond
when electrons are not being shared equally between atoms (hydrogen pairing w an electronegative)
what bond is between water molecules
hydrogen bonds
polarity
unequal sharing of electrons (happens in water)
cohesion
attraction of molecules for other molecules of the same kind, forces increases due to hydrogen bonds between water molecules holding them together
surface tension
property of allowing liquid to resist external force (cohesion is responsible for it)
what helps water and nutrients travel against gravity in plants
cohesion and capillary action
adhesion
clinging of one molecule to a different molecule, due to water polarity, allows water to cling onto walls in plants
capillary action
upward movement of water due to the forces if cohesion, adhesion, and surface tension, occurs when adhesion id greater than cohesion
transpiration
transport if water and nutrients in plants, adhesion needs to be greater than cohesion
high specific heat (temp control)
water resists in temp due to hydrogen bonds (the bonds release heat when forming and the heat must be absorbed to break those bonds)
evaporative cooling
high heat of vaporization
what do the molecules with the highest kinetic energy leave as
gas
what helps moderate earths climate, stabilize temp in bodies of water, and prevent terrestrial organisms from overheating (ex. sweating) and leaves from becoming too warm in the sun
evaporative cooling
less dense as solid
when water solidifies (freezes), it expands and becomes less dense, due to hydrogen bonds because when water molecules are cooled, they move slowly to break the bonds
what allows marine life to survive under floating ice sheets
water density when solid
what structure does the hydrogen bonds in water molecules form?
crystalline structure
universal solvent
aka versatile solvent, due to polar molecules being attracted to ions and forming hydrogen bonds
solution, solvent, solute
ex. saltwater, water, salt
ionic compounds
partially negative oxygen (or hydrogen) in water interacts with a positive (or negative) atom, dissolves ions
hydrophillic
water lover, polar and/or ionic bonds
hydrophobic
water hater, fats (oils) dont dissolve in water
dehydration reaction
bonds two monomers with the loss of water (h2o), a+b→AB + h2o
hydrolysis
breaks the bonds in a polymer by adding water
isomers
same formula, different structure (making a diff func)
carbohydrates
sugars and polymers of sugars, main energy source for living things
monosaccharides
carbohydrate monomers or simple sugars, 1:2:1 ratio (ch2o), ex. glucose, raw material for building molecules, linear skeletons,
polysaccharides
carbohydrate macromolecules or polymers of sugars, structure n func is determined by its sugar monomers and positions of glycosidic linkages, function as storage or structural polysaccharides
1:2:1 ratio, molecular formula
monosaccharides
dissaccharide
formed when a dehydration reaction joins two monosaccharides, covalent bond in it is called glycosidic linkage
synthesis of maltose
dehydration reaction
starch
storage polysaccharide of plants, made up of glucose monomers
leucoplast/amyloplasy
plants store surplus starch as granules within an organelle
glycogen
storage polysaccharide in animals, humans and other vertebrates store glycogen mainly in love and muscle cells
cellulose
polysaccharide, major component in tough plant cell walls
helical, straight
polymers with a configuration, b confuguration
chitin
polysaccharide, found in exoskeleton of arthopods (shellfish)
lipids
store energy in living things, hydrophobic bc they consist mainly of carbon and hydrogen (non polar covalent bonds), ex. fats, phospholipids, steroids
fatty acids
monomer of lipids, consists of a carboxyl group attached to a long carbon skeleton
glycerol
monomer of lipid, a three carbon alcohol with a hydroxyl group attached to each carbon
triglycerides/tryglycerol
3 fatty acids joined to a glycerol by an ester linkage
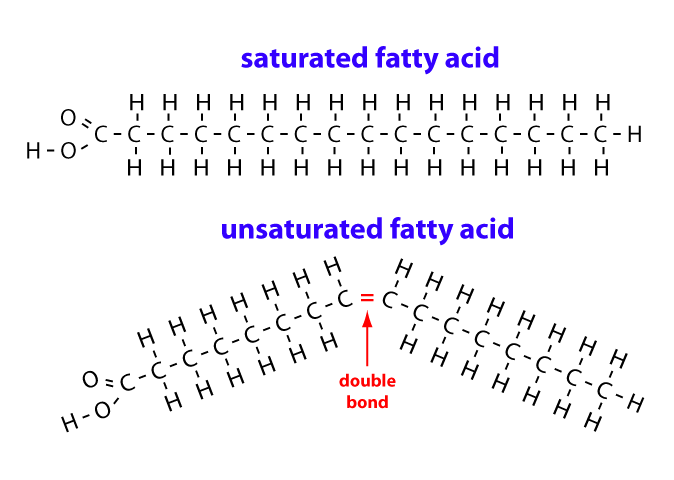
saturated fatty acid
maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible and no double bonds
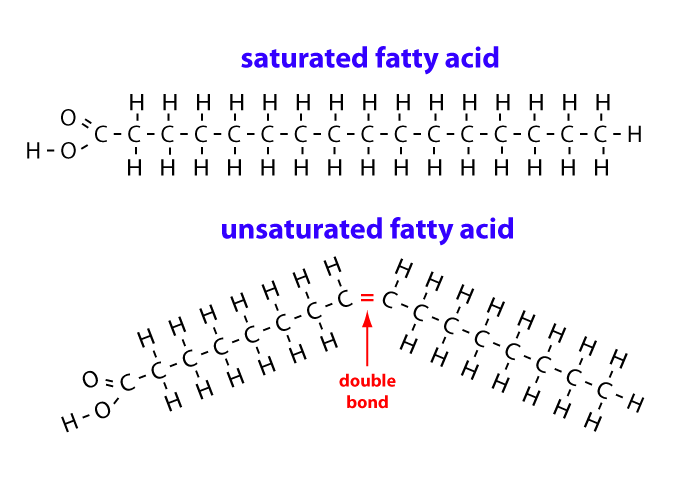
unsaturated fatty acid
has one or more double bond
lard, butter, bacon grease
saturated, solid at room temp, no double bonds, most animal fat
corn, olive oil
unsaturated fat, one or more double bonds between carbons, liquid at room temp, plant fats
trans fat
converting unsaturated fat into saturated (hydrogenation), very bad for you
adipose tissue
cushions vital organs and insulates body, made of fat
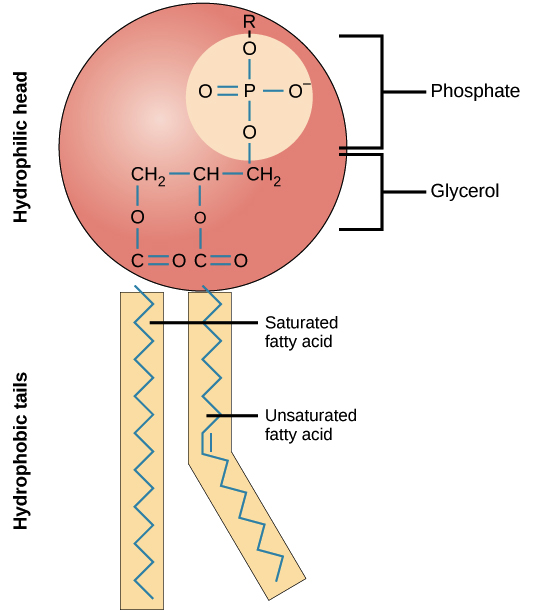
phospholipid
two fatty acids and a phosphate group are attached to glycerol, bilayer, apart of all cell-membranes
steroids
hormonal lipids, ex. cholesterol in animals
waxes
esters made of an alcohol chain and a fatty acid chain, plants have this to prevent water loss
nucleotides
monomers of nucleic acids, consists of a nitrogenous base, a 5 carbon sugar (pentose, and a phosphate group
deoxyribose, ribose
sugar in DNA, sugar in RNA
nucleoside
nitrogenous base and sugar
pyrimidines
cytosine, thymine, uracil (rna only), single rings
purines
adenine, guanine, double rings
3’ and 5’ ends
if it starts as a right side up pentagon, top is 5’, end is 3’
gene
series of bases that code for a particular trait
double helix
dna structure, strands or bases are held together by hydrogen bonds
enzyme
type of protein that acts as a catalyst to speed up chemical reactions
amino acids
organic molecules with carboxyl and amino groups
R groups
amino acids that differ in their properties due to differing side chains
peptide bonds
amino acids are linked by them
polypeptide
polymer of amino acids
proteins
consist of polypeptides folded into a 3d shape, shape determines function
peptide bond formation
carboxyl group of one AA must be positioned next to the amino group of another AA
primary structure
a sequence of amino acids, bonded by peptide bonds, chain shape
secondary structure
coils and folds that result from hydrogen bonds between amino acids in the backbone
alpha helix
coiled every 4th peptide bond
beta pleated sheet
folded, interchain H bonds
tertiary structure
interactions between R groups, bonded with hydrogen and ionic bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and van der Waals interactions, strong covalent bonds called disulfide bridges can reinforce the protein structure
quaternary structure
two or more polypeptide chains form one macromolecule, ex. collagen (fibrous protein) contains 3, ex. hemoglobin (globular protein) contains 4, two of each secondary struc