CH 4: doppler waveform analysis in the upper and lower extremities
1/150
Earn XP
Description and Tags
advanced non-invasive vascular technology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
Doppler waveform analysis helps to confirm the ________, ________, and approximate _________ of arterial occlusive disease.
Diagnosis
Severity
Location
Doppler waveform analysis provides follow-up information about progression of (1)________, results of medical (2)_________, or post-(3)__________ status.
Disease
Therapy
Operative
Advanced non-invasive vascular technology is combined with _________ ________ to produce doppler waveforms.
Segmental pressures
What are some limitations with advanced non-invasive vascular technology? (3)
Casts/Extensive Bandages
Temperature Changes
Uncompensated Congestive Heart Failure
Dampened waveforms on doppler waveform analysis may be due to…
Uncompensated congestive heart failure
Continuous wave dopplers is unable to discriminate (1)_________ from (2)__________.
Stenosis
Occlusion
Arteries affected by hot temperatures or exercise will cause vaso(dilation/constriction).
What waveform will be seen?
Vasodilation
High resistive → Low resistive
Arteries affected by cold temperatures will cause vaso(dilation/constriction).
What waveform will be seen?
Vasoconstriction
Increased pulsatility
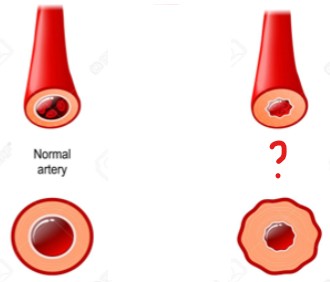
The artery on the left is affected by vaso(dilation/constriction).
Vasoconstriction
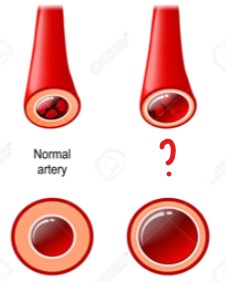
The artery on the left is affected by vaso(dilation/constriction).
Vasodilation
Define the Doppler effect.
When a wave is reflected from a moving target
What is the term for this:
When a wave is reflected from a moving target
Doppler Effect
What is the primary moving target with the doppler effect?
Red blood cells (RBC)
Define the Doppler shift.
Difference between frequency of the wave received and frequency of the transmitted wave
What is the term for this:
Difference between frequency of the wave received and frequency of the transmitted wave
Doppler Shift
There is a _________ _______ whenever there is relative motion between the source and the receiver of the sound.
Doppler effect
With continuous wave doppler, _________ is the moving target.
Blood
With continuous wave doppler, _________ is the stationary source.
Transducer
With continuous wave doppler blood is the…
Moving target
With continuous wave doppler, the transducer is the…
Stationary source
How many piezoelectric crystals are there with continuous wave doppler?
Describe the crystals roles?
2
One constantly sending ultrasound
One constantly receiving reflected waves
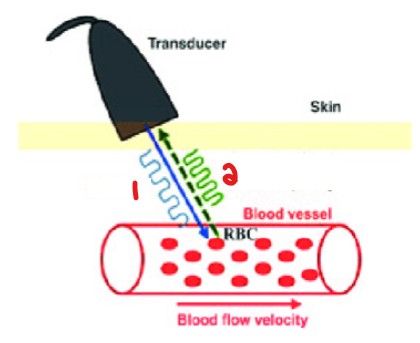
Label the waveforms emitted in this image.
US Wave
Doppler Shift Wave Frequency
List the 2 types of Doppler Velocimetry.
Analog
Digital
What is another term for digital doppler velocimetry.
Spectral analysis
Of the 2 types of doppler velocimetry, which is considered ‘old’ and ‘outdated’?
Analog
Of the 2 types of doppler velocimetry, which is considered better?
Digital (spectral analysis)
Which doppler velocimetry form employs a zero-crossing frequency meter to display the signals graphically on a strip-chart recorder?
Analog
Analog doppler velocimetry employs a (1)_____-_________ frequency meter to display the signals graphically on a (2)______-______ recorder.
Zero-Crossing
Strip-Chart
With analog doppler velocimetry, the (1)_______ counts every time the (2)_____ signal crosses the (3)_____ (baseline) within a specific time span.
Circuitry
Input
Zero
Which form of doppler velocimetry has circuitry that counts every time the input signal crosses the zero (baseline) within a specific time span?
Analog
With analog doppler velocimetry, the number of times the sound waves (1)_______ each second varies and because the (2)_________ of blood flow varies during the cardiac cycle, the equipment estimates the (3)_________ of the reflected signal.
Oscillate
Direction
Frequency
Which form of doppler velocimetry is this?
The number of times the sound waves oscillate each second varies and because the direction of blood flow varies during the cardiac cycle, the equipment estimates the frequency of the reflected signal.
Analog
Why is it hard to distinguish an abnormal waveform with analog doppler?
Due to lack of sensitivity
An analog waveform of the CFA with the absence of flow reversal is hard to distinguish if abnormal due to a lack of _________ with analog doppler.
Sensitivity
It is hard to distinguish abnormal waveforms due to a lack of __________ with analog doppler.
Because of this, it does not allow for the depiction of flow ________.
Sensitivity
Reversal
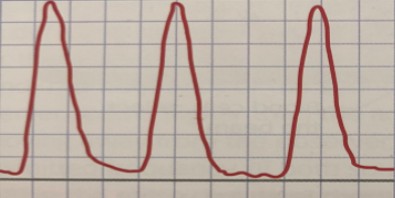
If this waveform was obtained from an analog doppler velocimetry, would this easily be ruled out as abnormal?
If no, why not?
No
Analog has a lack of sensitivity and does not allow for the depiction of flow reversal
With doppler velocimetry, between the two, which has acceptable accuracy and is not as sensitive?
Analog
With doppler velocimetry, between the two, which has more sensitivity?
Digital (spectral analysis)
List the 4 drawbacks of analog.
Noise
Less sensitivity
Underestimate high velocities
Overestimate low velocities
Digital (Spectral analysis) displays (1)_________ on the vertical axis and (2)______ on the horizontal axis.
Frequency
Time
The amplitude of backscattered signals with digital (spectral analysis) can be seen at any given _________ and _____.
Frequency
Time
Digital (Spectral analysis) can display what 3 factors?
Frequency
Time
Amplitude of backscattered signals
Digital (spectral analysis) differs from analog recording in the way that it is more sensitive and is free of…
Drawbacks
Which of the two doppler velocimetry options has more frequency content?
Digital (spectral analysis)
Which of the two doppler velocimetry options allows displays of flow reversal? (i.e., triphasic waveform)
Digital (spectral analysis)
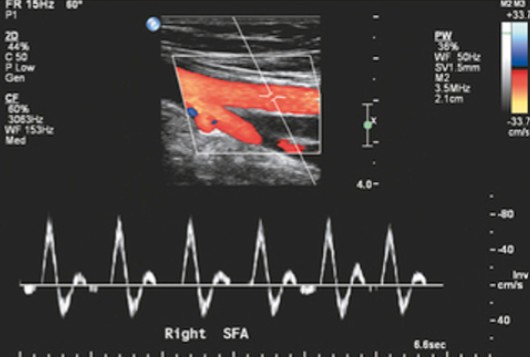
Which form of doppler velocimetry is seen here?
Digital (spectral analysis)
What kind of probe does a continuous wave doppler exam use?
(Be specific on frequency)
8 - 10 MHz doppler probe
Continuous wave doppler waveforms are combined with what else?
Segmental pressures
What upper extremity arteries are examined with continuous wave doppler exams? (5)
Subclavian
Axillary
Brachial
Radial
Ulnar
What lower extremity arteries are examined with continuous wave doppler exams? (6)
CFA
SFA
Popliteal
PTA
DPA
Peroneal
Where is the PTA found?
Medial malleolus
What artery is found at the medial malleolus?
PTA
Where is the DPA found?
Top of foot
What artery is found at the top of the foot?
DPA
Where is the peroneal artery found?
Lateral malleolus
What artery is found at the lateral malleolus?
Peroneal artery
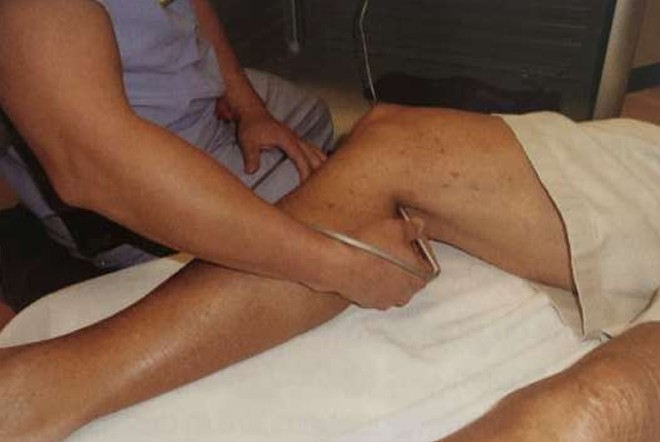
What kind of exam is being performed here?
Continuous wave doppler
List the 6 potential sources of technical errors for a continuous wave doppler exam.
Improper probe position
Inadvertent probe motion
Incorrect angle
Inadequate amount of gel
Excessive pressure on probe tip
Insufficient period of rest by the patient before testing
An insufficient period of rest prior to a CW doppler exam can cause technical errors.
Give an example of what would disrupt that period of rest.
How would that action affect the waveforms?
Exercise
High resistive waveform → Low resisitve waveform
T or F:
With CW doppler exams, you can make a normal vessel look abnormal.
True
T or F:
With CW doppler exams, you can make an abnormal vessel look normal.
False
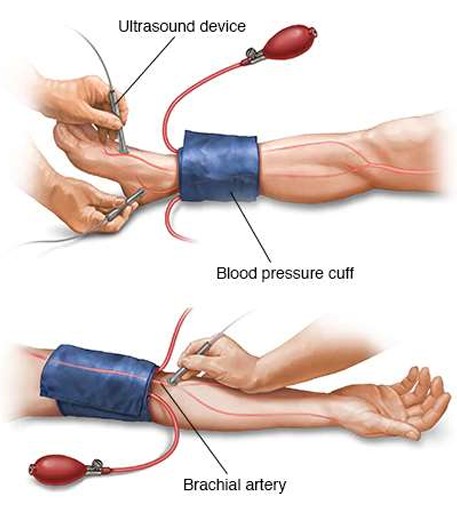
What exam is being performed here?
CW Doppler Exam
What waveform is deemed ‘normal’ when taken on an artery?
Triphasic
What waveforms are deemed ‘abnormal’ when taken on an artery? (3)
Monophasic
Non-Pulsatile
Absent
List the 5 signals/parts of a triphasic waveform.
Rapid Upstroke
Sharp Peak
Rapid Downstroke
Short Peak Below the Baseline
Resumption of Forward Flow
List the 4 signals/parts of a monophasic waveform.
Slow Upstroke
Rounded Peak
Slow Downstroke
No Reversal
What part of a triphasic waveform represents flow reversal?
Short Peak Below the Baseline
A short peak below the baseline with a triphasic waveform represents…
Flow reversal
Which leg is normal?
Which leg is abnormal?
Left
Right
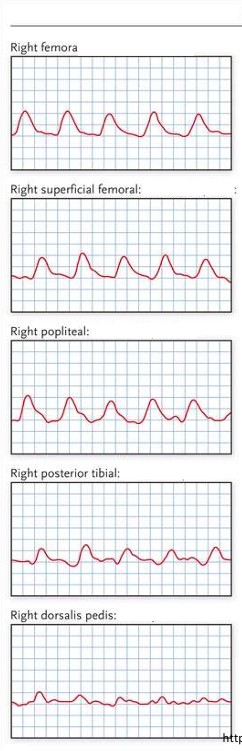
What kind of waveforms are seen here?
If this was taken on a CW doppler exam, is the waveform normal or abnormal?
Biphasic (Due to short peak below baseline)/Monophasic
Abnormal
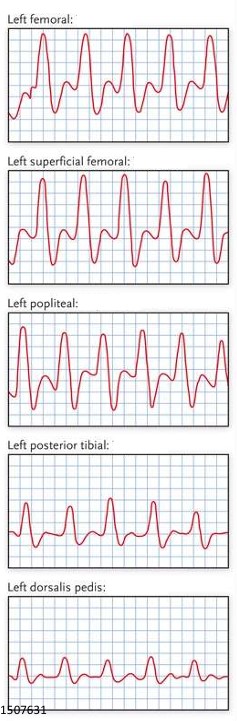
What kind of waveforms are seen here?
If this was taken on a CW doppler exam, is the waveform normal or abnormal?
Triphasic
Normal
What doppler waveform can be considered normal or abnormal (with controversy behind it)?
Biphasic
What is the most essential thing to observe for when obtaining waveforms on a CW doppler exam?
Deterioration of the doppler signal from one level to the next
List 2 examples of waveform changes that indicate deterioration of signal quality from one level to the next.
Triphasic to biphasic
Triphasic to monophasic
Where is disease located if there is a deterioration of doppler signal quality from one level to the next?
Between the 2 levels
A CW doppler exam cannot differentiate between which 2 pathologies?
Explain why.
Stenosis & Occlusion
Cannot detect velocities < 6 cm/sec
CW doppler cannot detect velocities (1)_____ than (2)____ cm/sec.
Less
6
If there is an inability to elicit doppler signals, rather than occlusion, what can it suggest instead?
Slow velocities moving through the vessel (Trickle flow)
What is trickle flow?
Slow velocities moving through the vessel
Inflow or outflow disease?
Blood flowing into the lower extremities
Inflow disease
Inflow or outflow disease?
Blood moving out into the extremities
Outflow disease
Inflow disease represents blood flow…
Flowing into the lower extremities
Outflow disease represents blood flow…
Moving out into the extremities
List 2 examples of inflow disease.
Aortoiliac disease
Iliac disease
List 2 examples of outflow disease.
Femoral-popliteal disease
Tibial disease
If there is deterioration from one level to the next, where is disease most likely?
Between the 2 areas
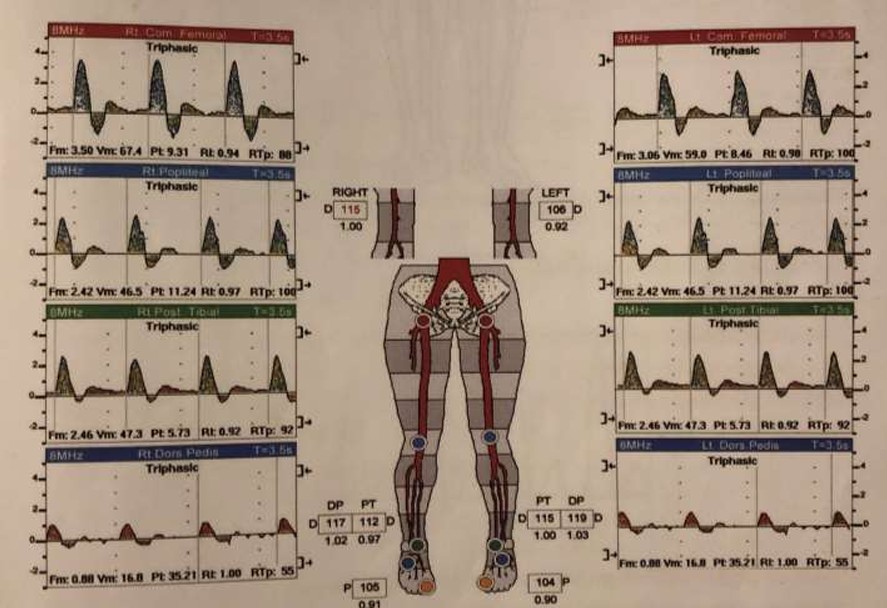
Which leg is normal?
Which leg is abnormal?
Both
Neither
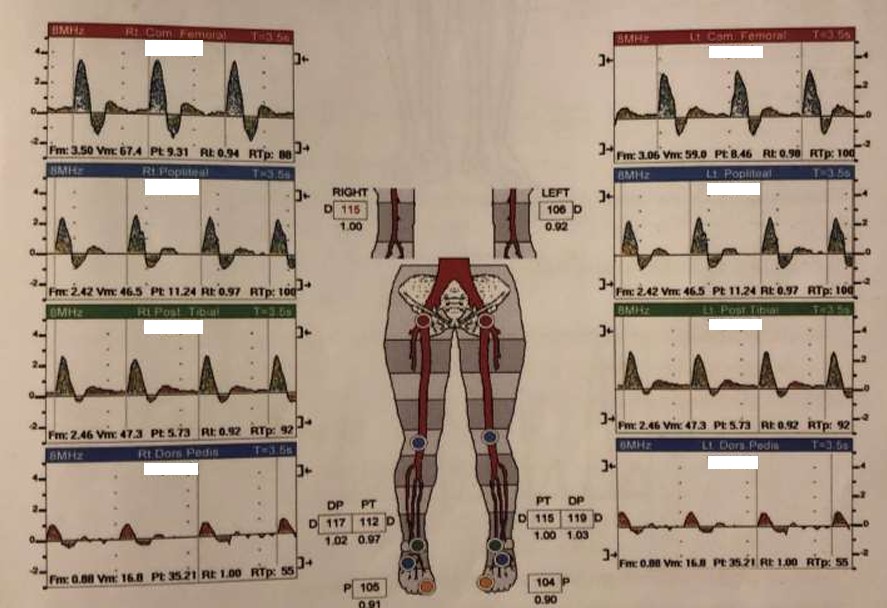
What kind of waveforms are seen in this image?
Triphasic
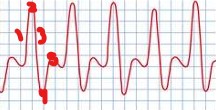
Label the parts of this triphasic waveform.
Rapid Upstroke
Sharp Peak
Rapid Downstroke
Short Peak
Resumption of Forward Flow

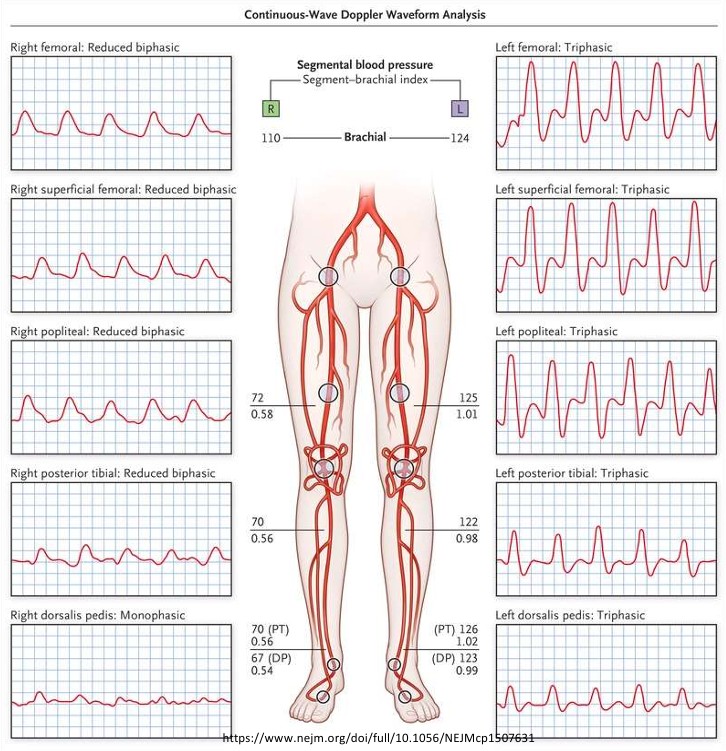
What do the common femoral artery waveforms most likely represent?
Describe L & R waveforms
If diseased, where disease is located and if it is inflow/outflow disease
Left: Normal triphasic waveform
Right: Abnormal monophasic waveform
Proximal disease (iliac artery)
Inflow disease

What do the popliteal artery waveforms most likely represent?
Describe L & R waveforms
If diseased, where disease is located and if it is inflow/outflow disease
Left: Abnormal biphasic waveform
Proximal disease (femoral artery)
Outflow disease
Right: Abnormal monophasic waveform
Proximal disease (femoral artery)
Outflow disease

What do the posterior tibial artery waveforms most likely represent?
Describe L & R waveforms
If diseased, where disease is located and if it is inflow/outflow disease
Left: Abnormal monophasic waveform
Proximal disease (popliteal artery)
Outflow disease
Right: Abnormal monophasic waveform
Proximal disease (popliteal artery)
Outflow disease

What do the dorsalis pedis artery waveforms most likely represent?
Describe L & R waveforms
If diseased, where disease is located and if it is inflow/outflow disease
Left: Abnormal monophasic waveform
Proximal disease (posterior tibial artery)
Outflow disease
Right: Abnormal monophasic waveform
Proximal disease (posterior tibial artery)
Outflow disease
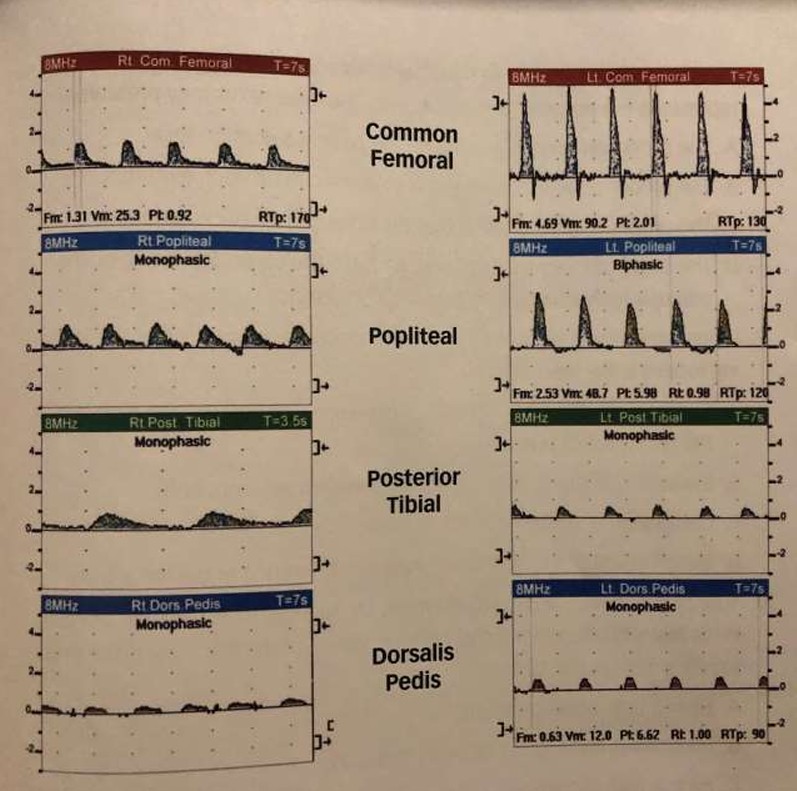
Where is the most significant arterial disease of the left extremity?
Explain why.
What is the name of the diseased area based on location?
Between the popliteal artery and the PTA
Where there is the most dramatic waveform change
Pop-Infrapop arterial disease
A patient with 3-block claudication has an exam done and you are getting triphasic waveforms. Although that is considered normal, the exam is not done because the study needs to be repeated.
What should the patient do prior to repeating the exam?
The patient should exercise first
How should normal post-exercise waveforms seen with CW doppler appear? (3)
Maintain pre-exercise waveform
Augment pre-exercise waveform
All waveform components above the baseline
How does an abnormal post-exercise waveforms seen with CW doppler appear? (4)
Slow upstroke
Rounded peak
Slow downstroke
No reversal
What does exercise produce to the muscles?
Demand for blood flow
Exercise produces an element of arterial…
Vasodilation
Exercise produces arterial vasodilation, therefore post-exercise waveforms will appear how?
Low-resistive