Anatomy 125 Megee Layers of the Skin
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
hair shaft
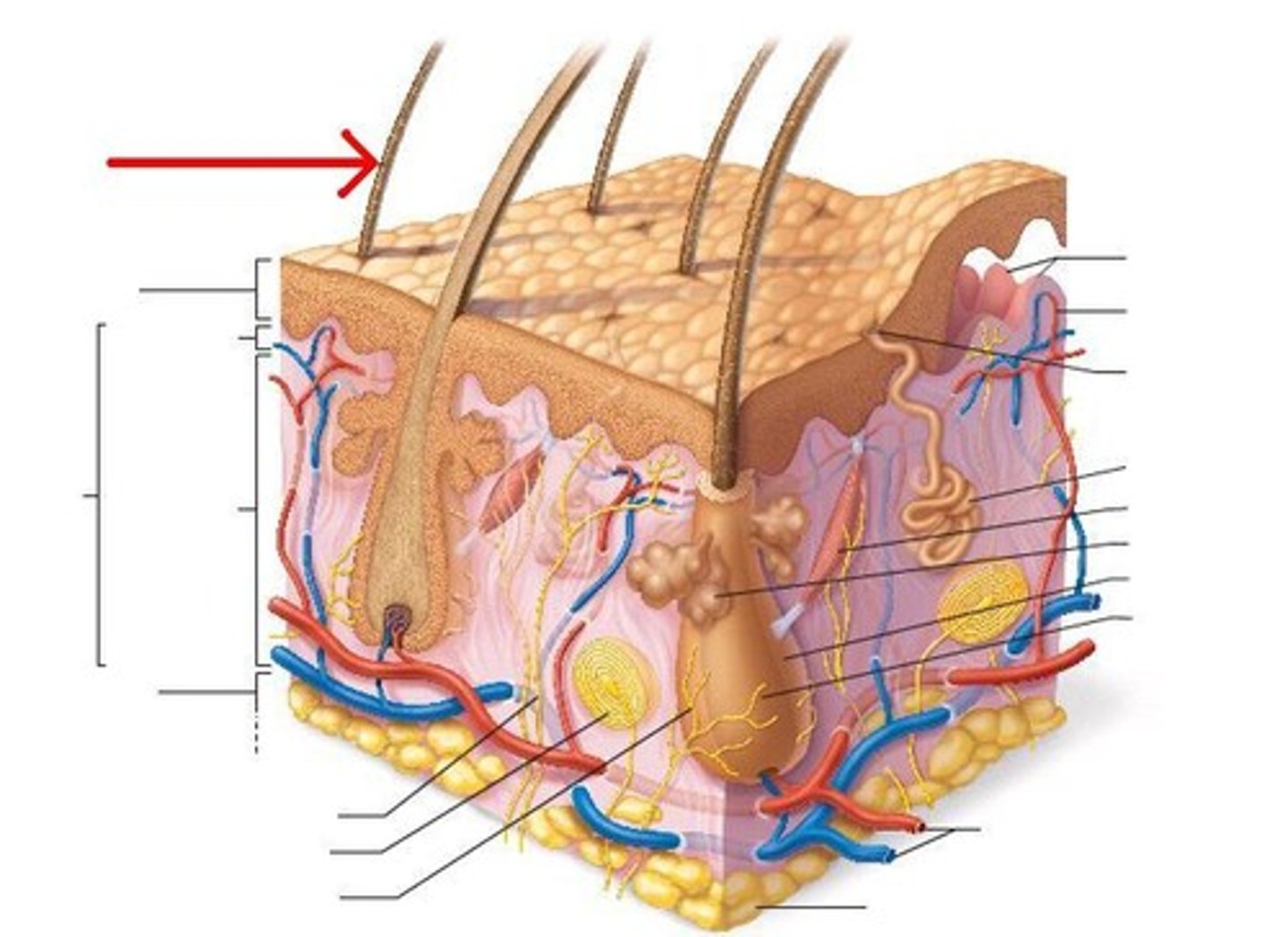
epidermis
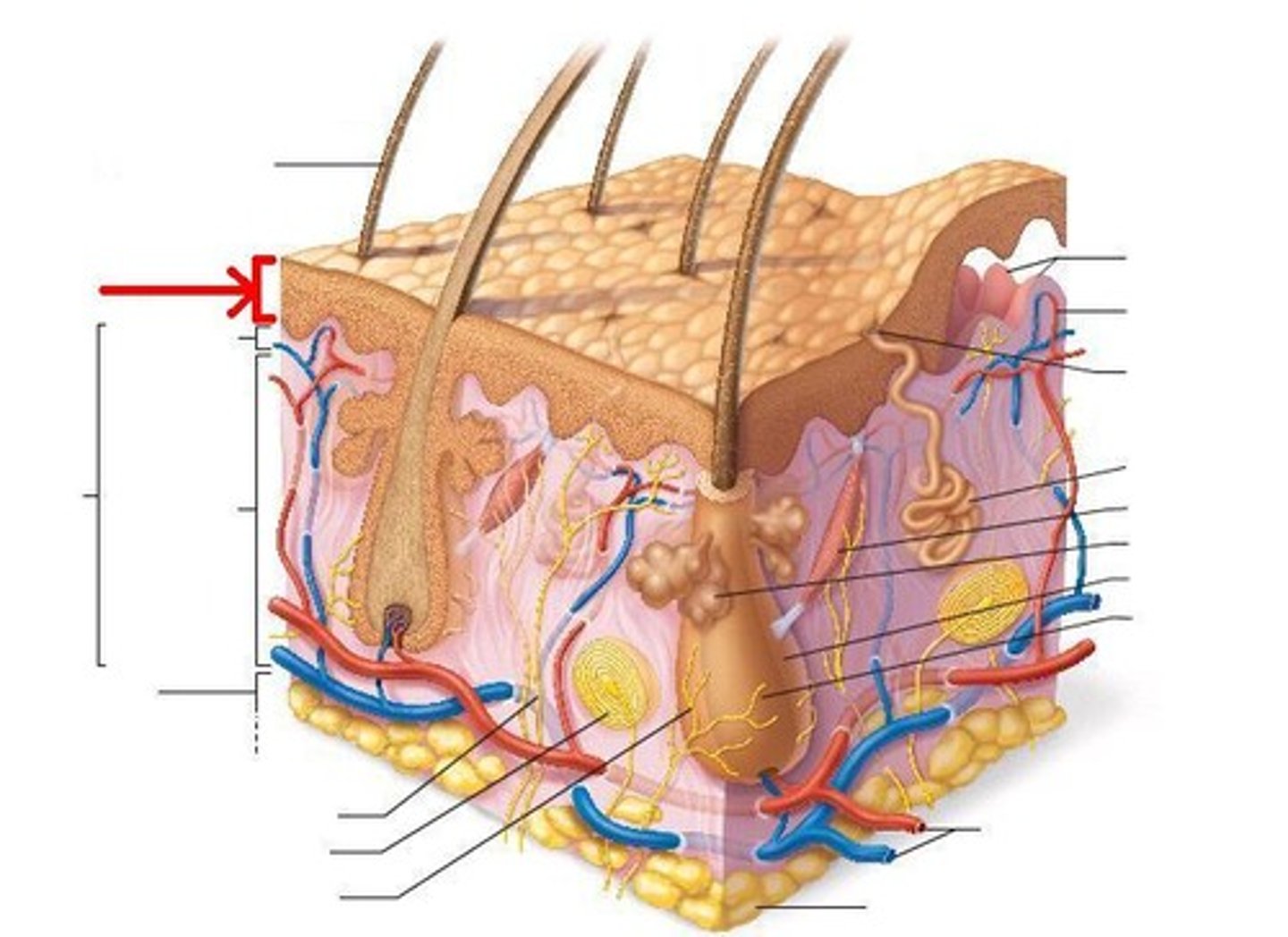
papillary layer
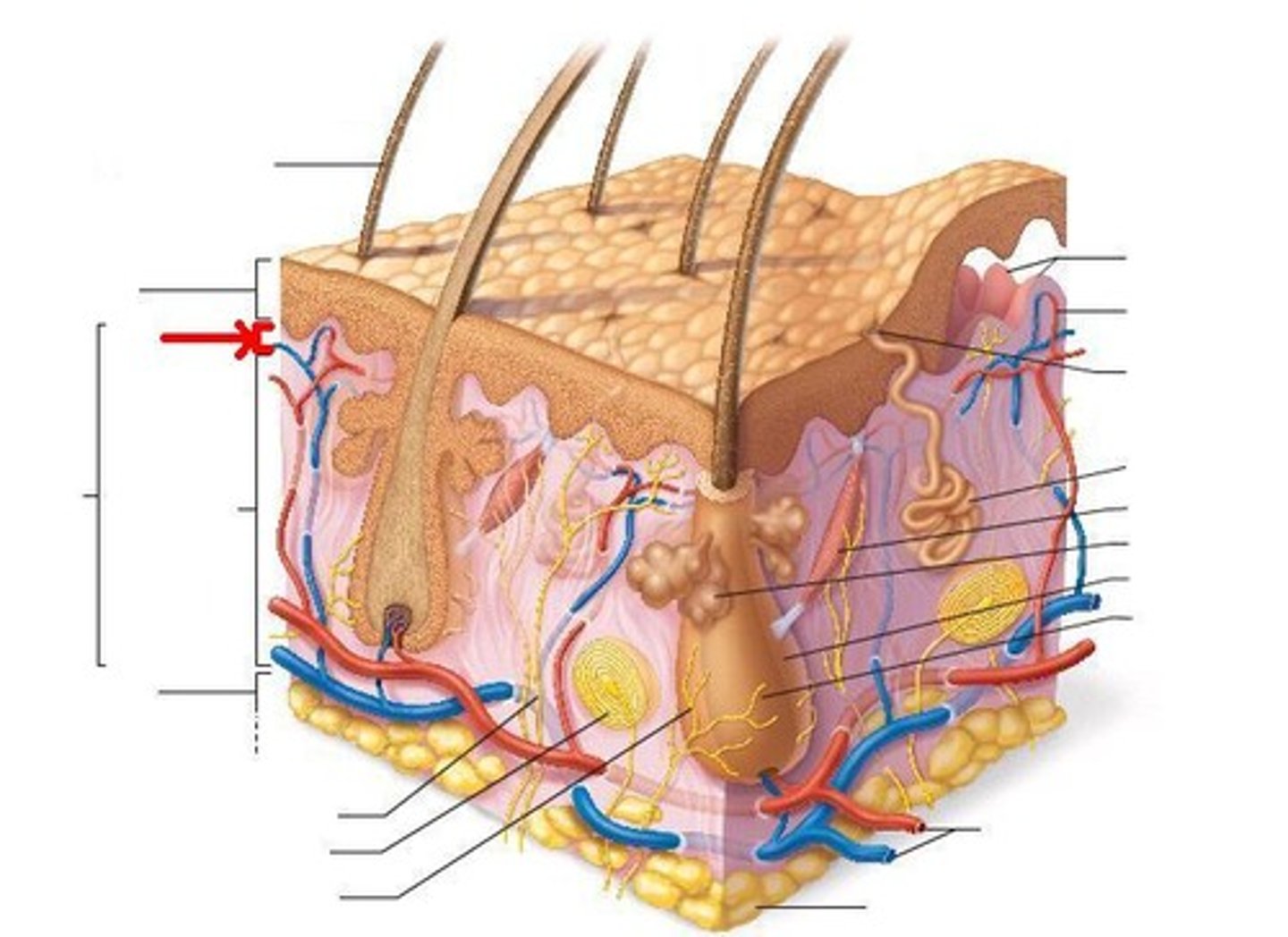
reticular layer
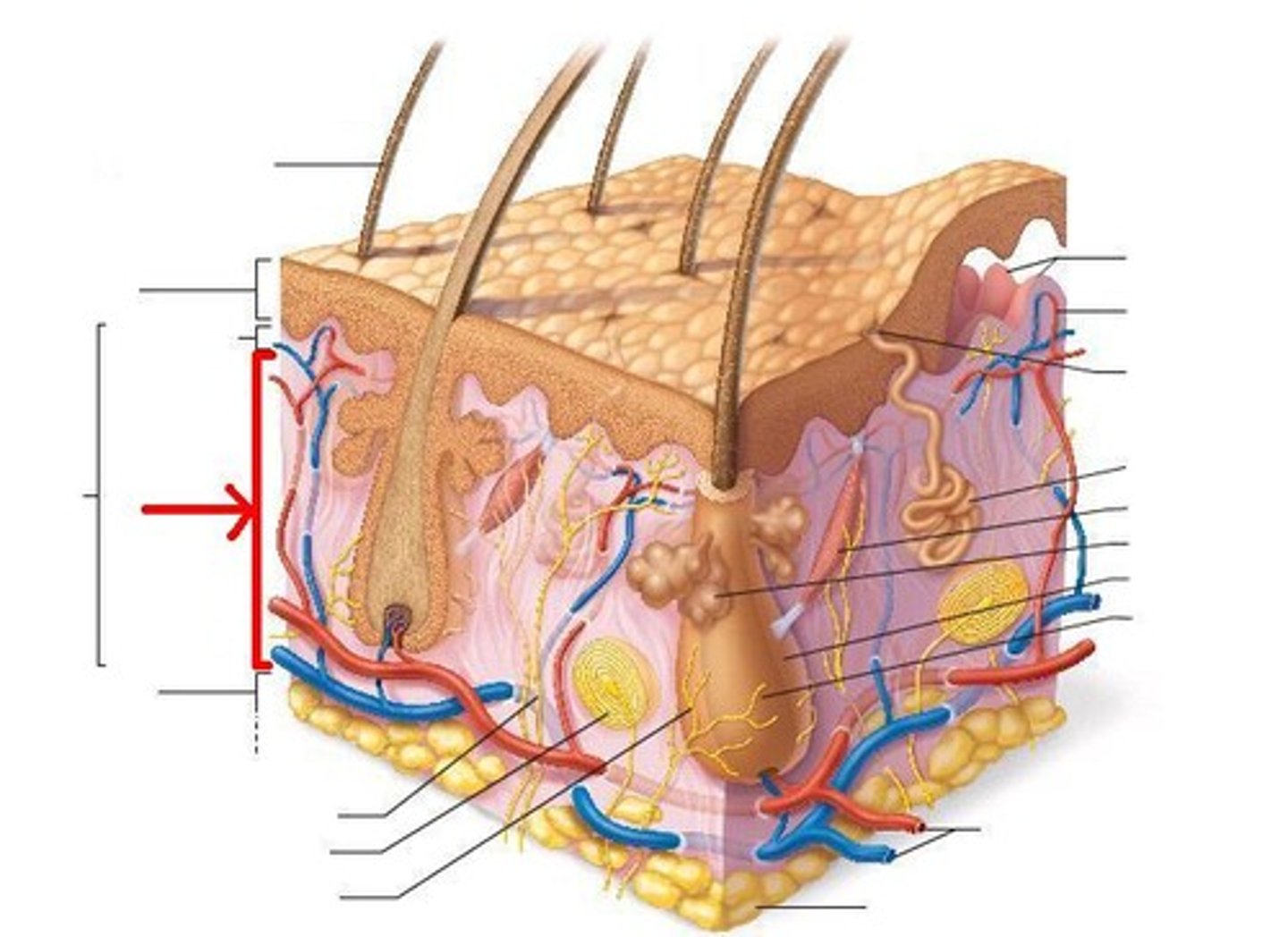
dermis
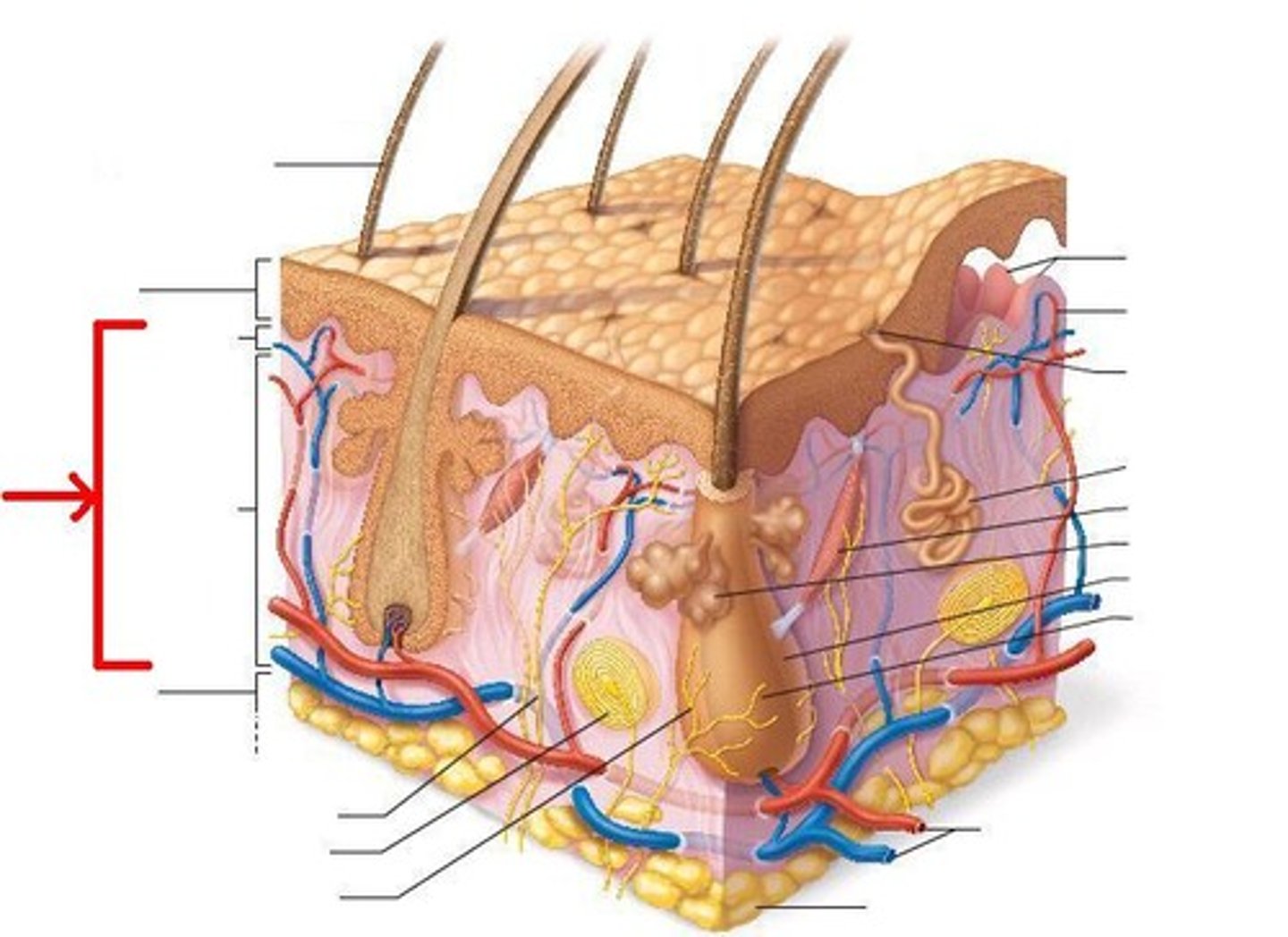
hypodermis (superficial fascia)
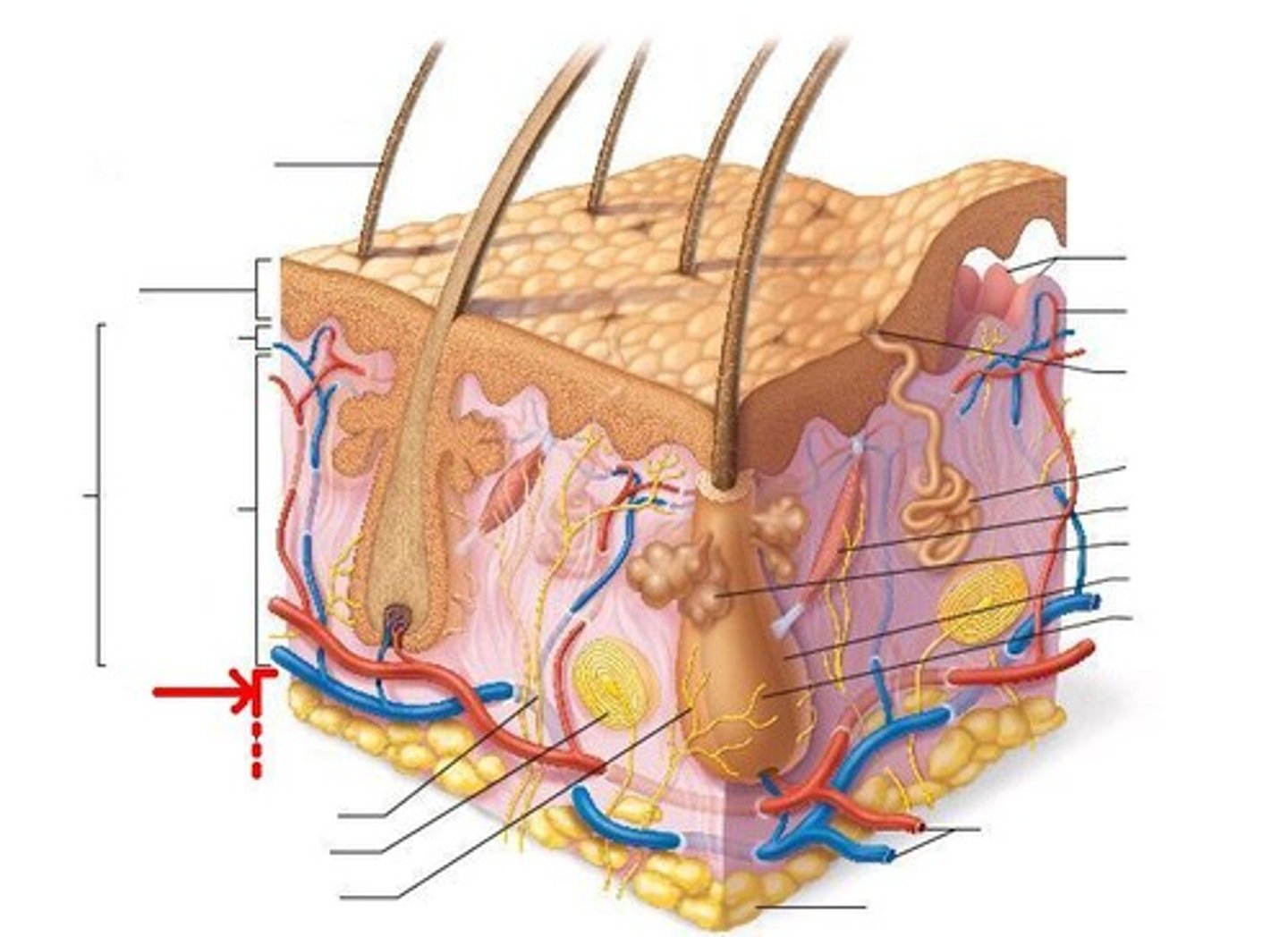
sensory nerve fiber
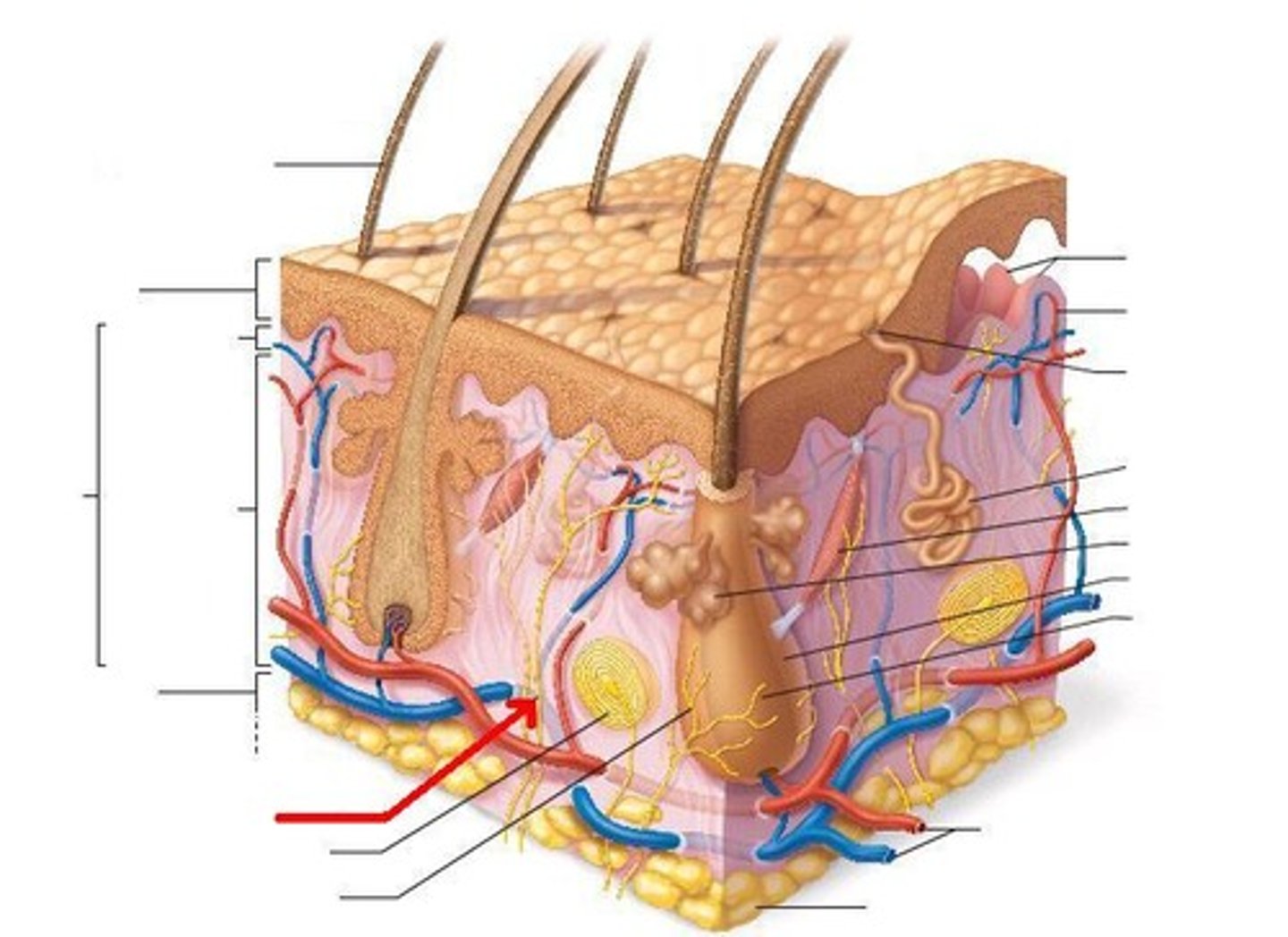
pacinian corpuscle
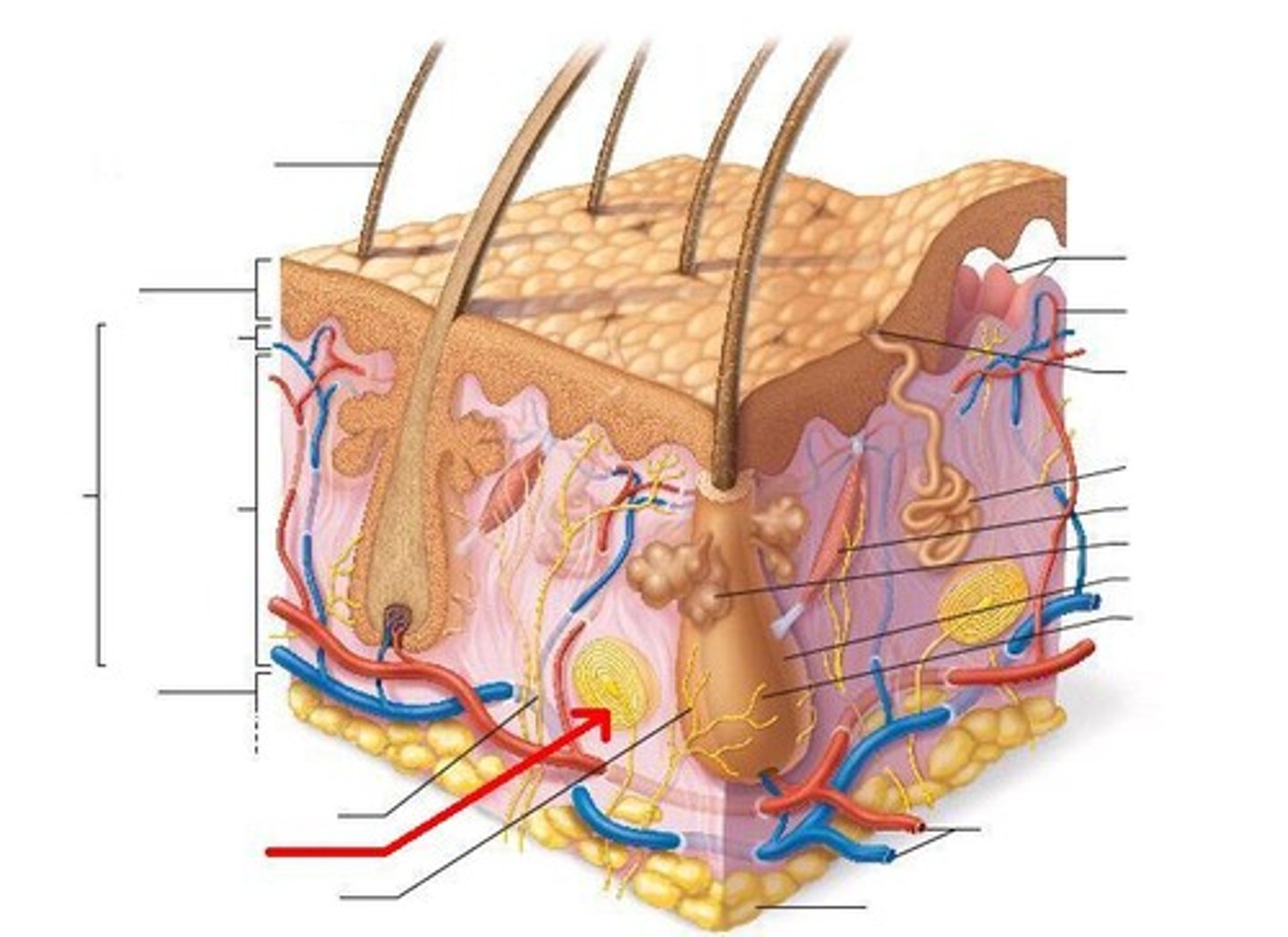
hair follicle receptor (root hair plexus)
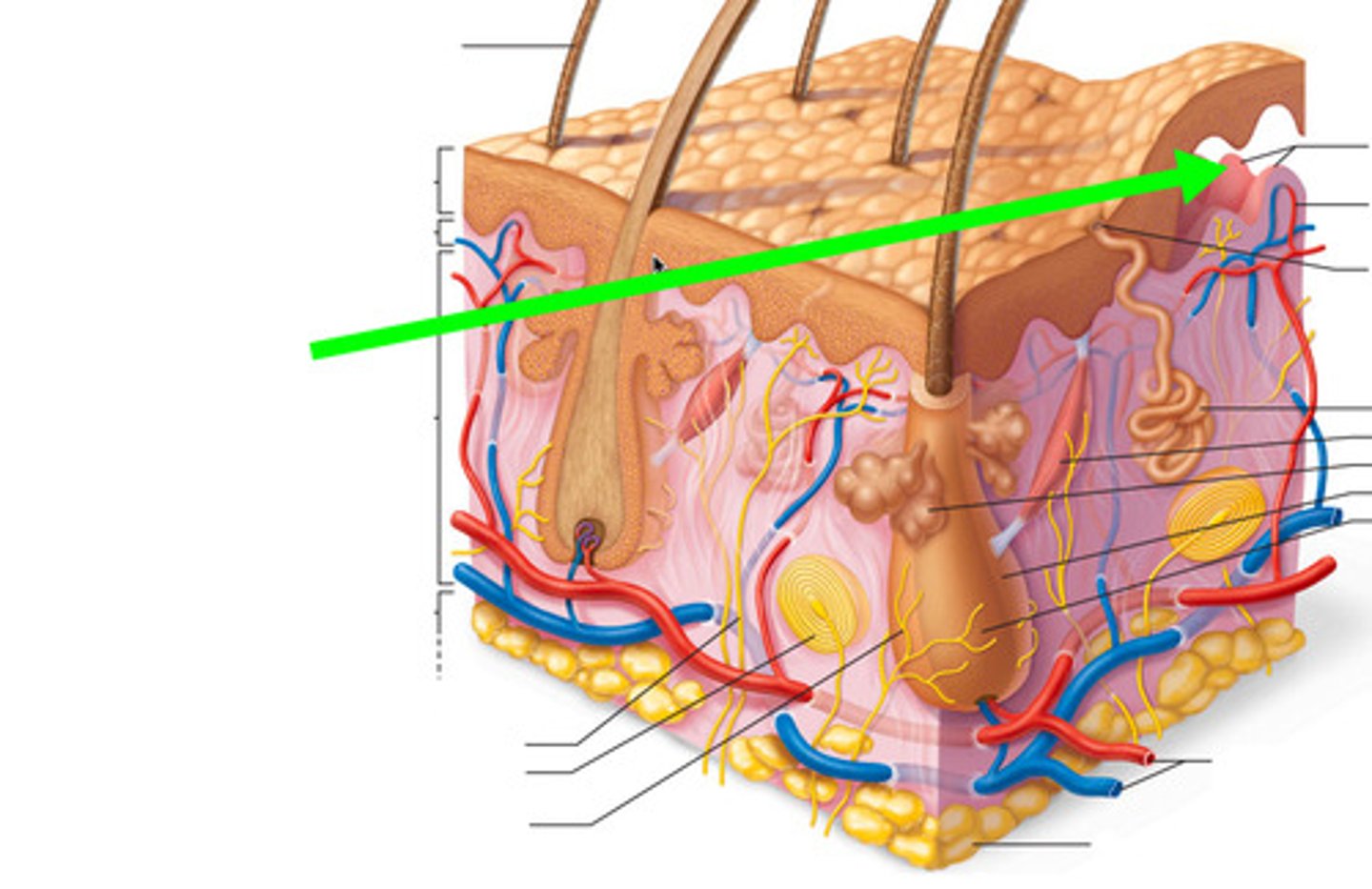
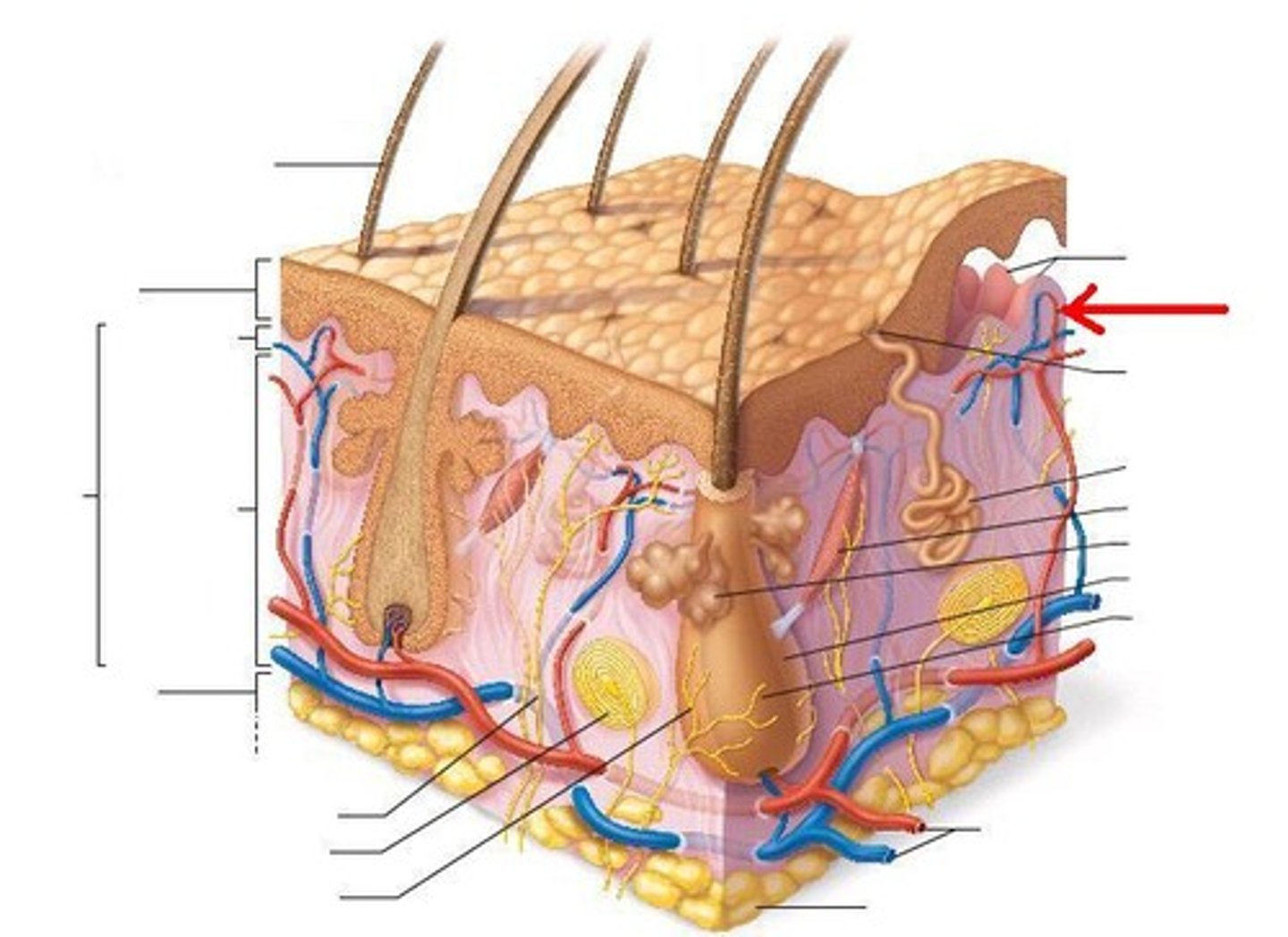
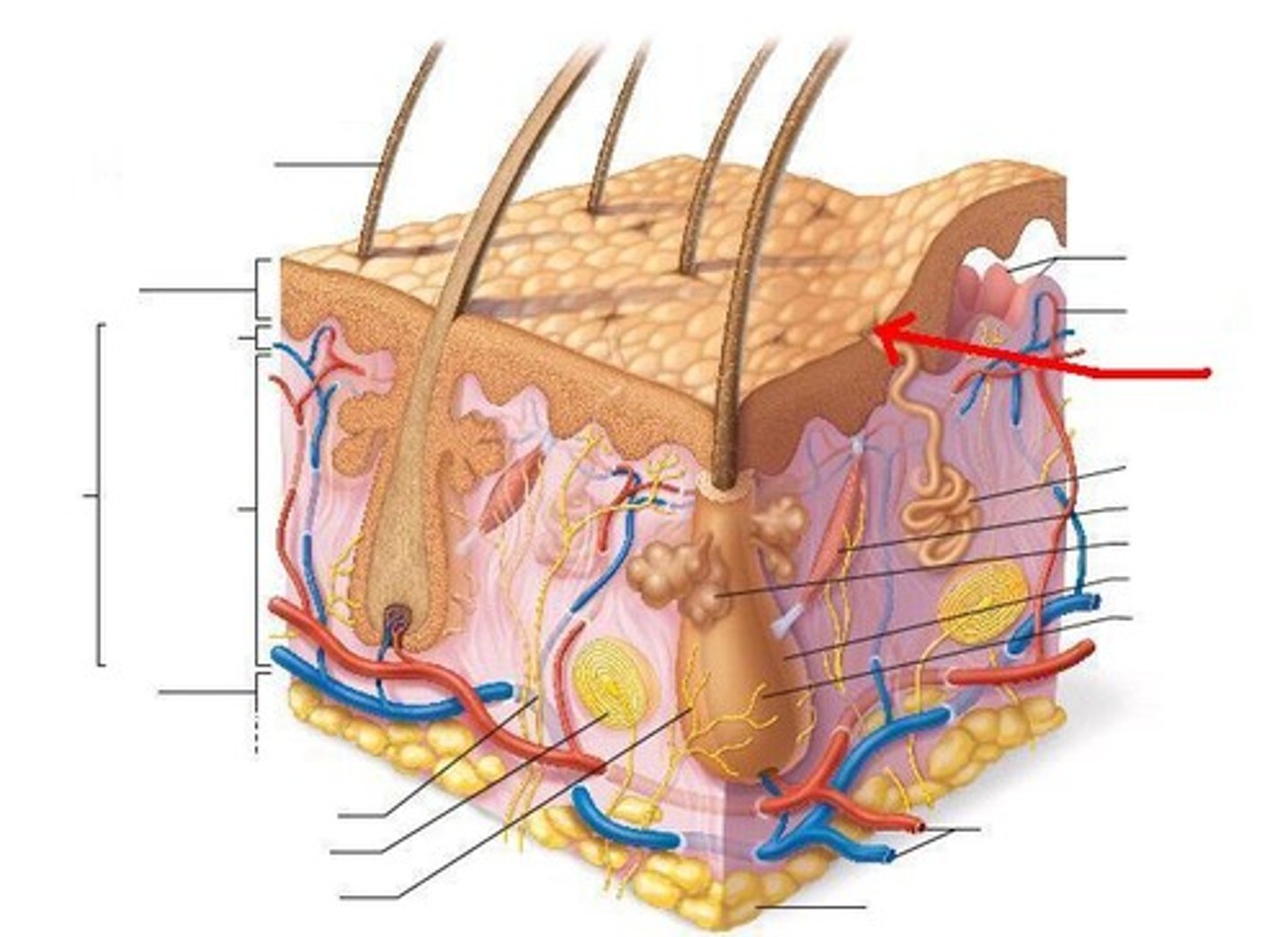
letter J
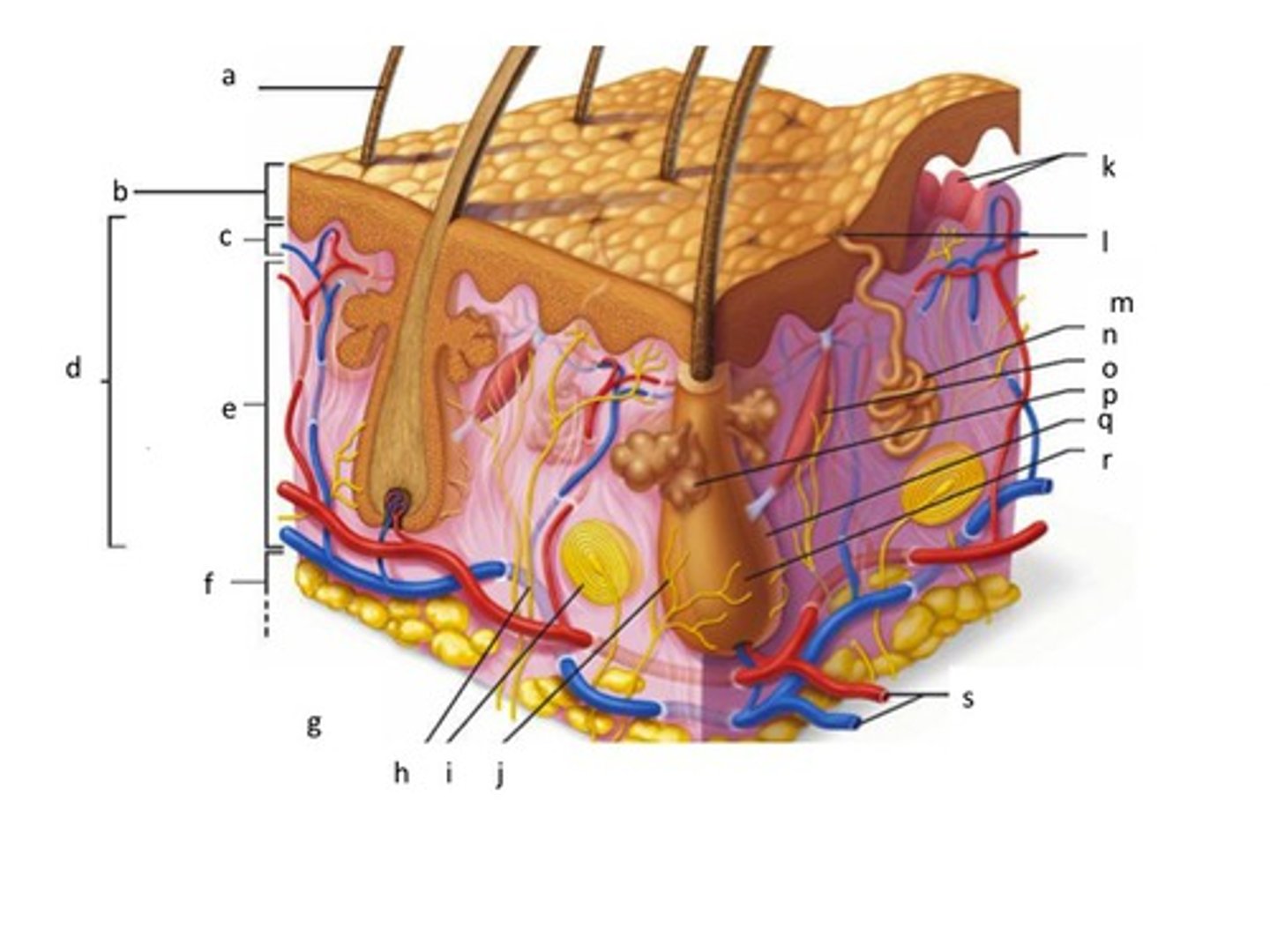
dermal papillae
subpapillary vascular plexus
pore
eccrine sweat gland
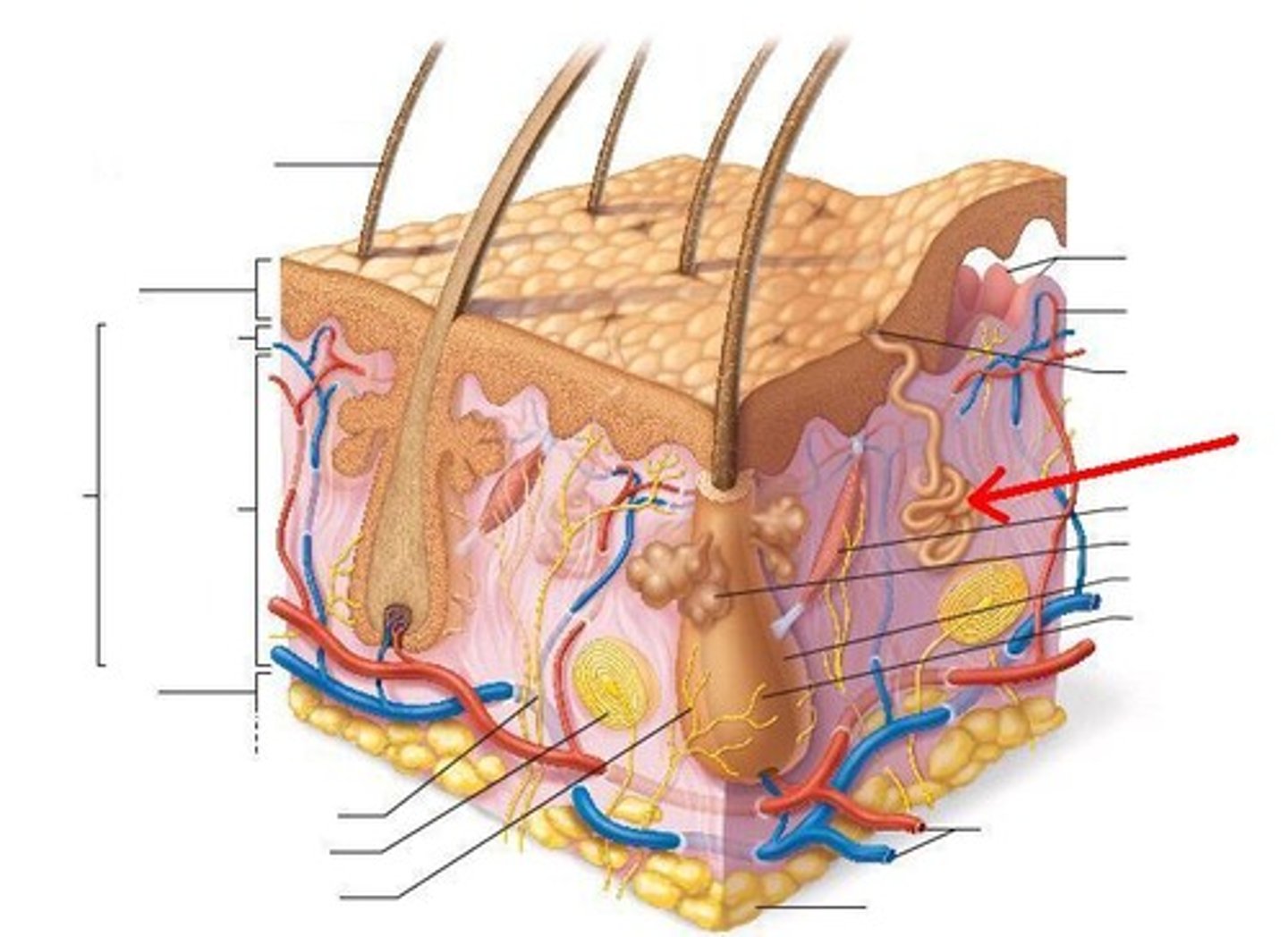
arrector pili muscle
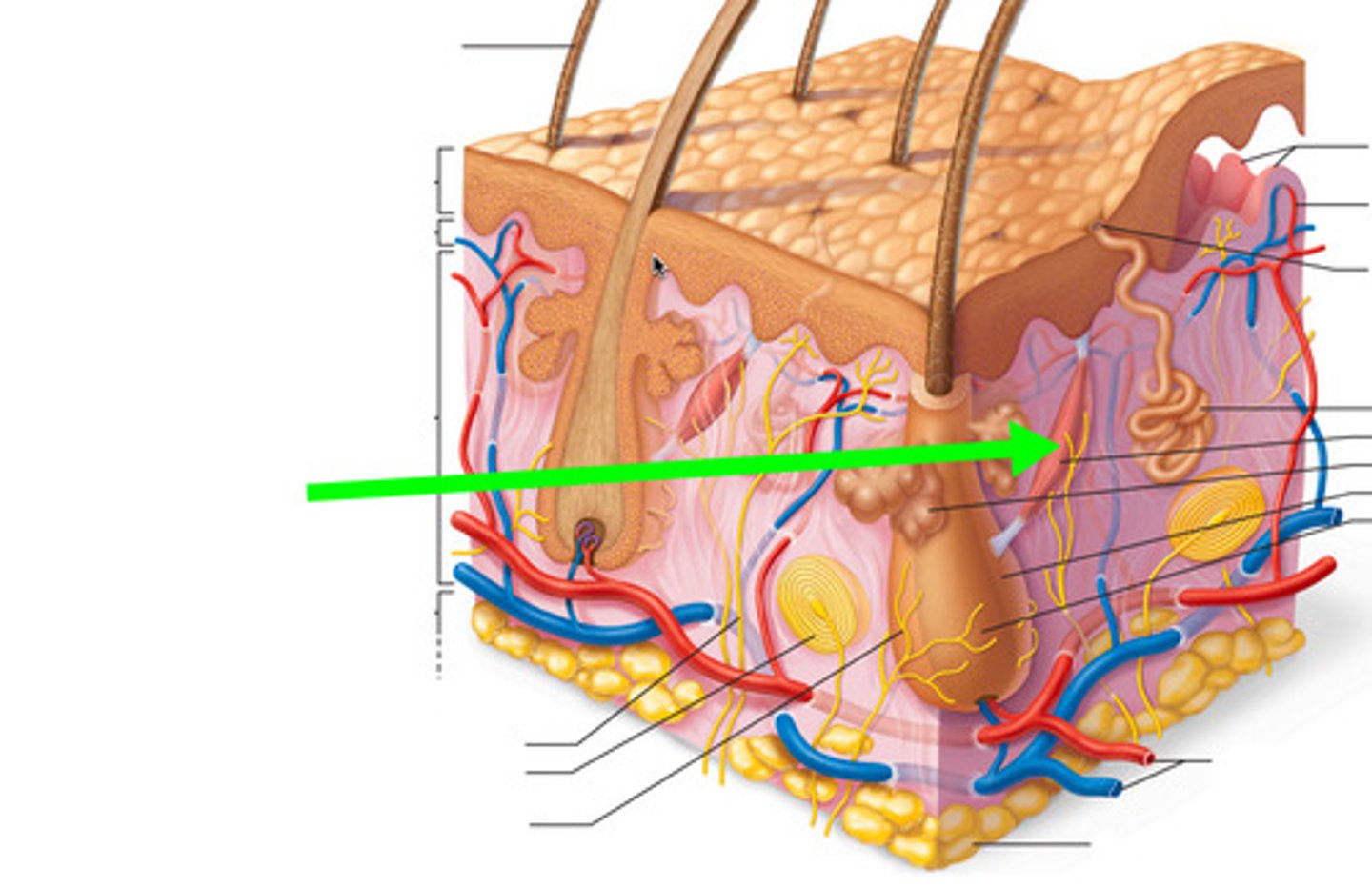
sebaceous (oil) gland
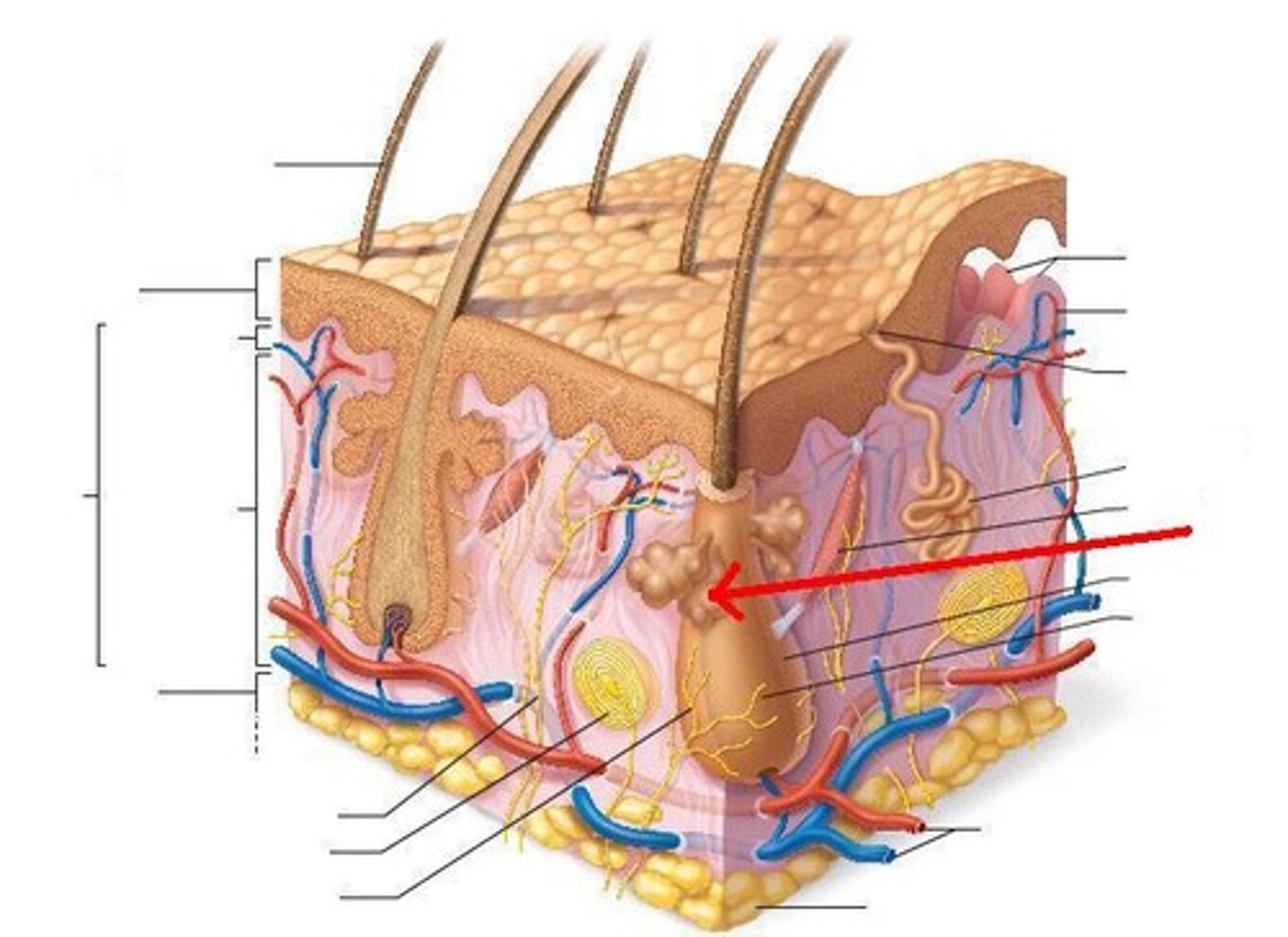
hair follicle
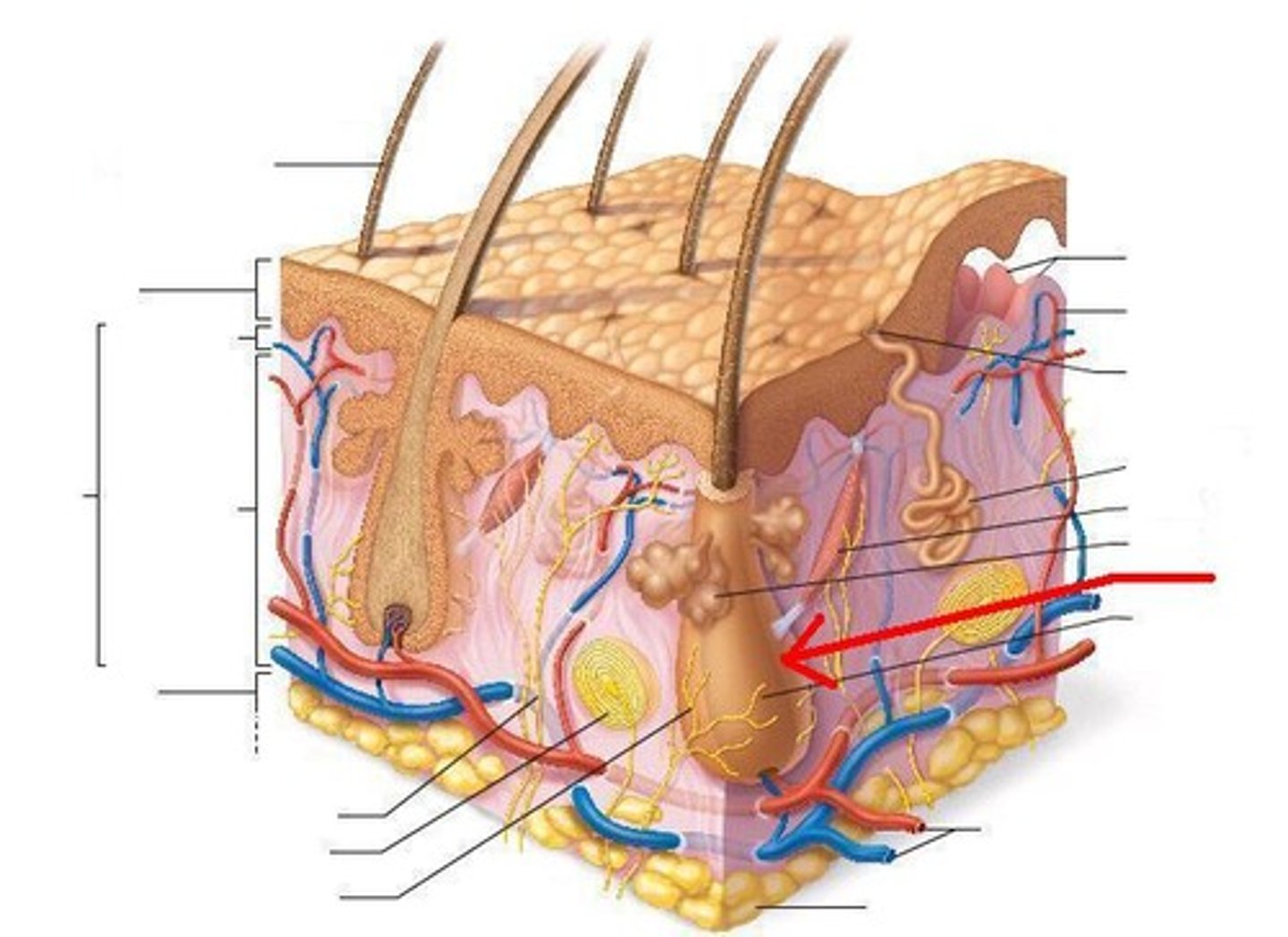
hair root
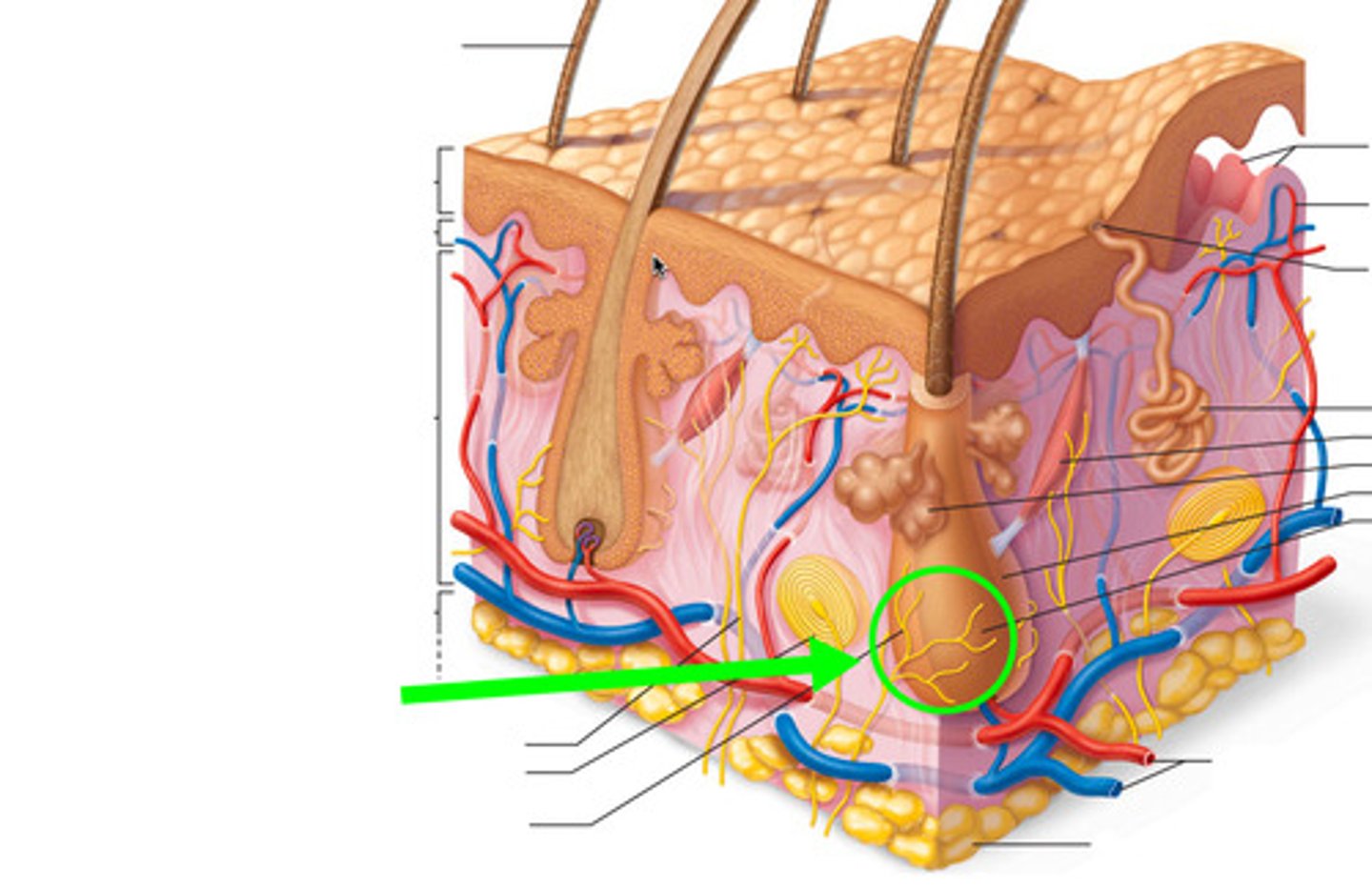
cutaneous vascular plexus
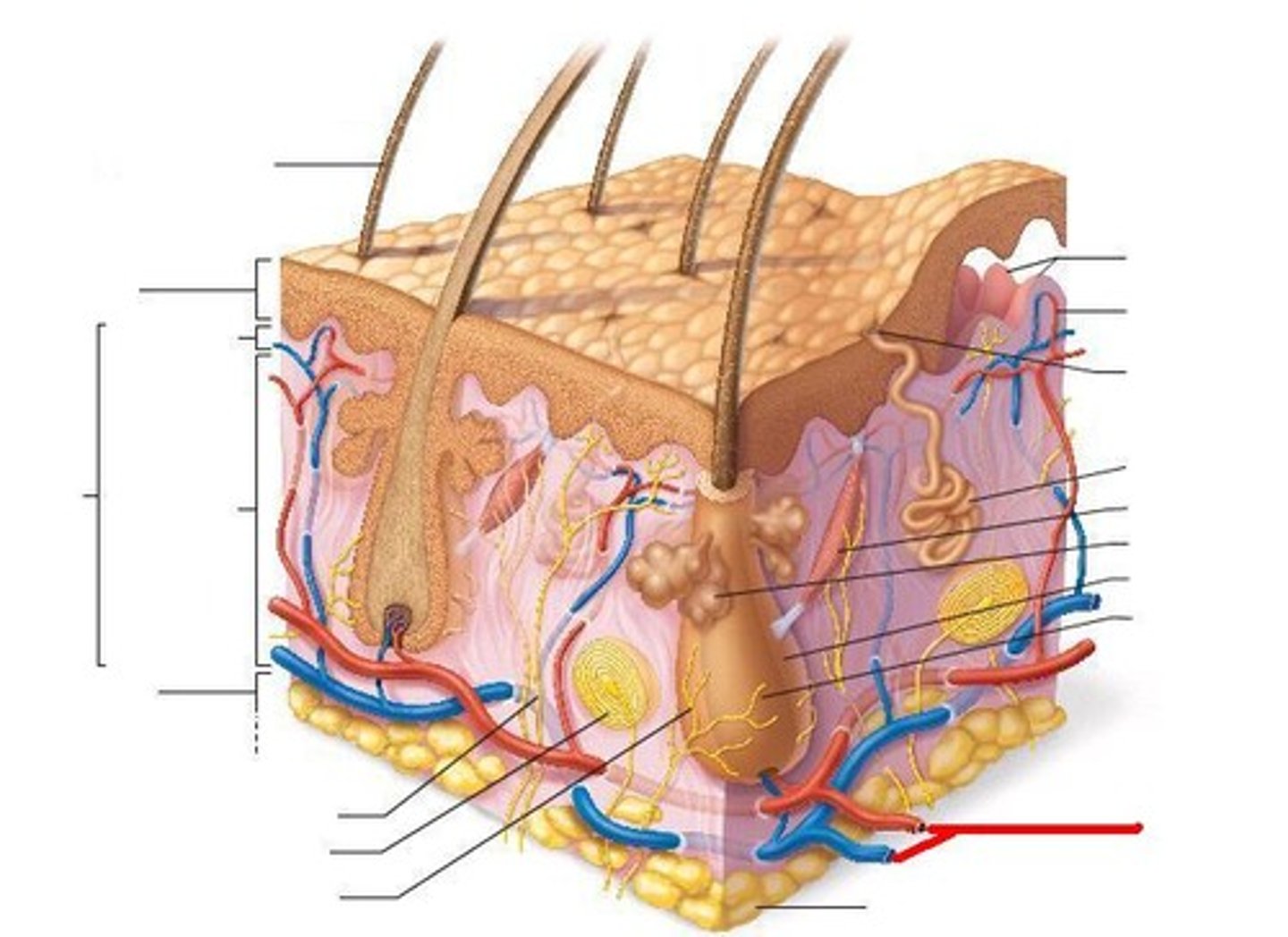
adipose tissue
located on the bottom of the dermis
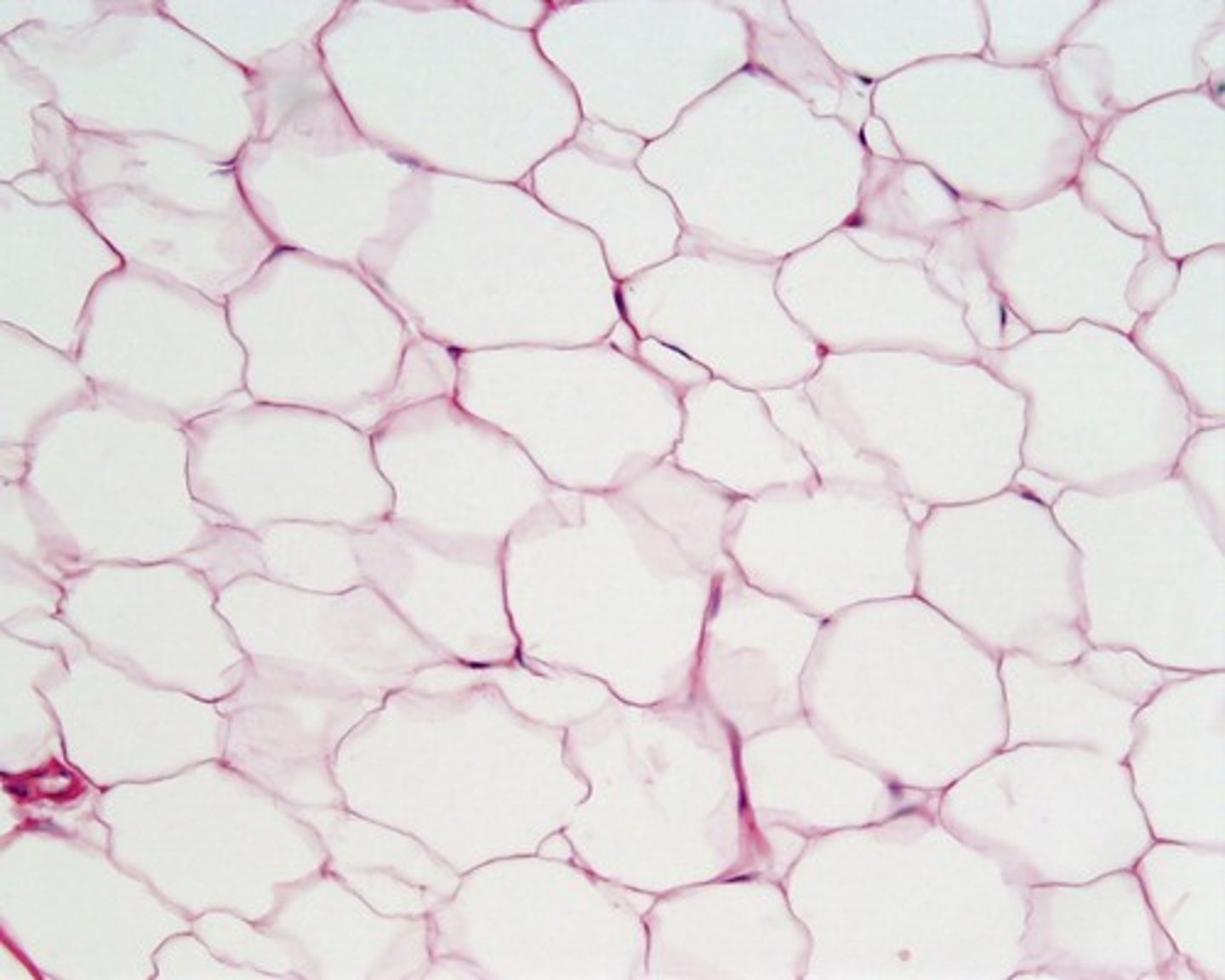
stratum basale (basal layer)
-Deepest epidermal layer firmly attached to the dermis
single row of cell stems above the basement membrane
stratum spinosum (prickly layer)
Many layers of keratinocytes attached by desomomes
stratum granulosum (granular layer)
-thin; three to five cell layers in which cells flatten
-keratohyaline and lamellated granules accumulate
stratum lucidum (clear layer)
Thin layer, of cells superficial to the stratum granulosum
stratum corneum (horny layer)
-20-30 rows of dead, flat, keratinized membranous sacs
Melanocytes
Stratum basale, produces melanin
Thick skin
Contains 5 layers; soles of feet, palms of hands,
Thin skin
Covers most of the body, hair follicles, sebaceous glands and sweat glands
integument functions
Protection, barrier, preventing water gain/loss, regulation temperature, aiding metabolism,
kertain
tough water-repellent protein found in the epidermal cells
subcutaneous layer
connective and adipose tissue layer just under the dermis
arrector pili
tiny muscle that attaches to the hair follicle
tactile cells (merkel cells)
touch sensations
Come, Let's Get Sun Burned
Corneum,
Lucidum,
Granulosum,
Spinosum,
Basale