ESS chap.6 Atmospheric systems and societies
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Atmosphere
gases that surround the earth’s surface and are retained by the gravitational field
roles of the atmosphere
provides a shield from meteorites
protects us from harmful sun radiation
moderates and stabilizes our climate (temperature with greenhouse gases)
source of the oxygen we breathe and the carbon dioxide plants use for photosynthesis
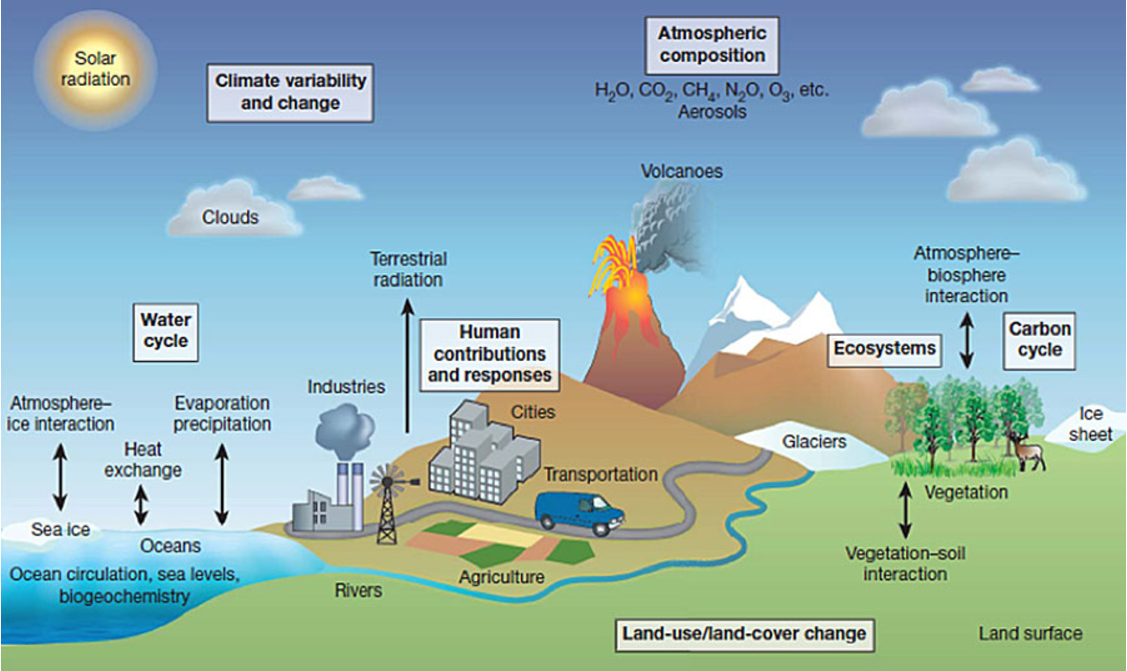
how is the atmosphere connected to other Earth systems?
litoshpere
hydrosphere
biosphere
through biogeochemical cycles (carbon cycle)
structure of the atmosphere
multiple layers with varying pressure and temperature : troposphere + stratosphere + mesosphere + thermosphere
sunlight is higher at the tropics than polar regions → temperature differences that drive air movement and circulation
atmospheric circulation : distributes and spread heat and polllutants (turns local issues into global problems)
Earth’s initial condition
4.6 billion years ago
extremely hot, volcanic activity and radioactive decay
environment not suitable for life
Eras
Hadean era
from 4.6 to 4 billion years ago
after greek god Hades - “hellish” conditions
ended with the Earth’s cooling that allowed water vapor to condense and form oceans
Archean era
from 4 to 2.5 billion years ago
cyanobacteria changed oxygen levels (increase)
Proterozoic era
from 2.5 billion to 542 million years ago
increase of oxygen levels - decrease of carbon dioxide levels
formation of the ozone → more complex organisms (eukaryotes) and movement of life from oceans to land
composition of the atmosphere
early atmosphere
hydrogen and helium
escaped due to solar winds and weak magnetic field
today
nitrogen (78%)
oxygen (21%)
argon, carbon dioxide, water vapor and other gases (1%)
birth of life
3.8 billion years ago
anaerobic bacterias (methane-producing prokaryotes)
stratosphere
10-50km
temperature at -60°C
air is dry
winds and temperature increase with height
ozone layer
Albedo effect
The albedo effect is about how much sunlight a surface reflects. Bright surfaces, like ice and snow, reflect most sunlight, keeping things cooler. Darker surfaces, like oceans or forests, absorb more sunlight, making things warmer. When ice melts and exposes darker surfaces, more heat is absorbed, which can make the planet warm up faster.
High albedo effect = cool temperatures
Low albedo effect = warm temperatures
Troposhere
less than 10km
where we live
air gets cooler as you go higher
contains most of the atmosphere’s air, clouds, weather system
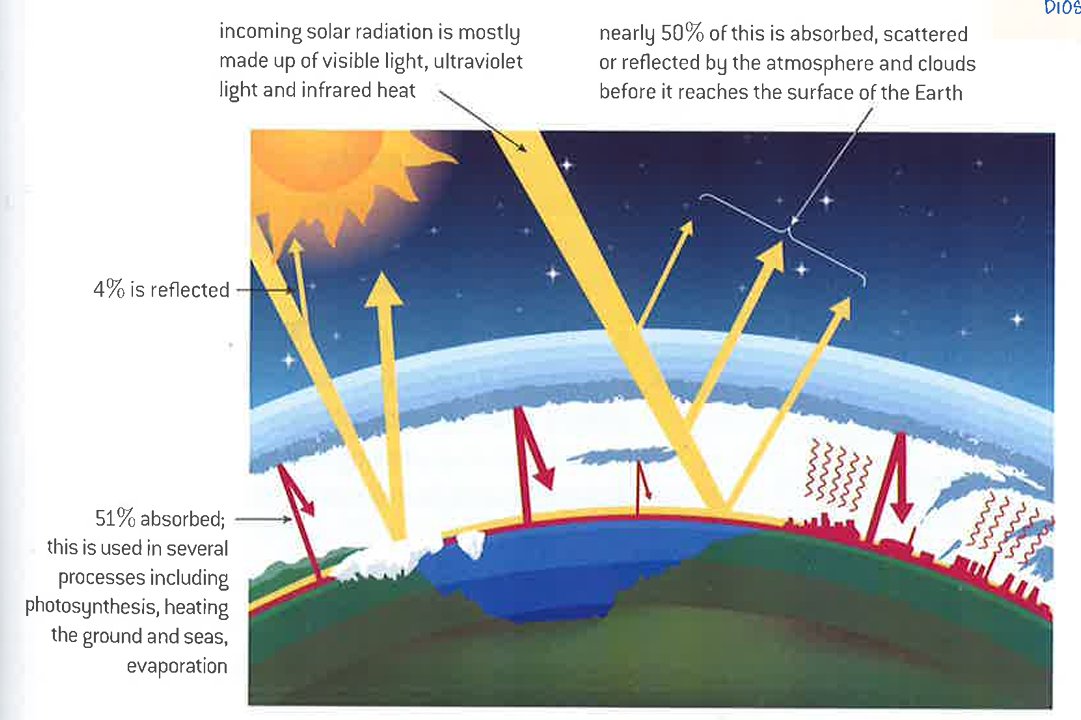
what is solar radiation made up of?
visible light
ultraviolet light
infrared heat
greenhouse gas effect diagram
atmospheric system model
where is ozone located?
lowest part of the stratosphere - good ozone
troposphere - bad ozone
highest concentrations of ozone are located above Antarctica
chemical composition of ozone
3 atoms of oxygen
role of the ozone
filters and protects from harmful UV lights (that damage living tissue)
allows UVA (wrinkles) and UVB (skin cancer) but blocks UVC (destroys DNA)
What are some ODS (ozone-depleting substances)?
CFCs (chlorine, fluorine, carbon) - found in aerosols and plastic
halons - found in fire extinguishers
What are the effects of ODS?
increased skin cancer, cataracts, immune issues
ecosystem harm
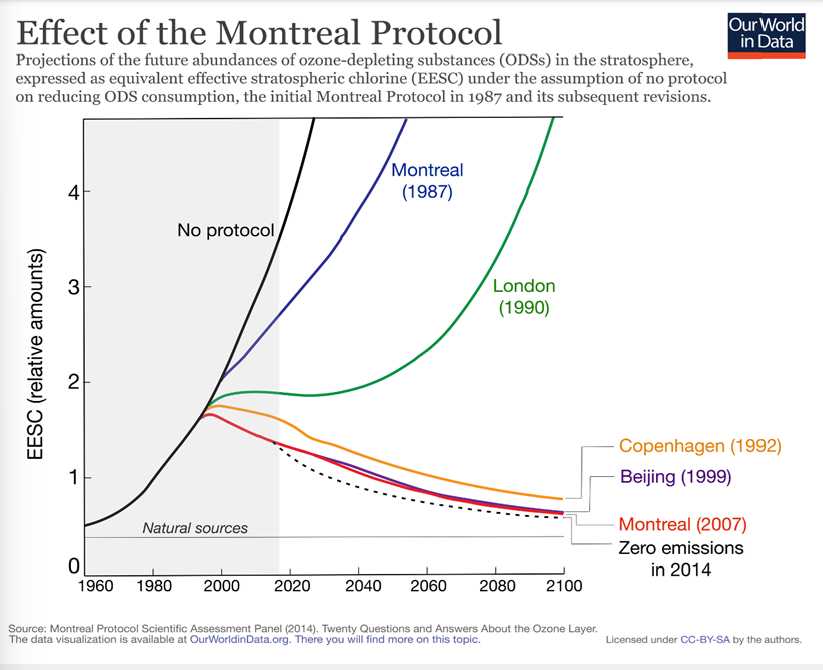
the Montreal protocol
WHEN - 1987, then 1992 ( new amendment in Copenhagen)
WHY - reduce ozone-depleting substances/protect the ozone layer/propose alternatives
WHO - all 198 UN member countries
Chemical processes: how CFCs destroys ozone
1 molecule of CFC = 1 atoms of carbon + 2 atoms of fluorine + 2 atoms of chlorine
UV light breaks down the molecule and releases chlorine atoms
chlorine atom (Cl) + ozone (O3) → oxygen (O2) + chlorine monoxide (ClO)
chlorine atom is regenerated in another reaction and can repeat the process
What is photochemical smog and how does it form?
a mixture of pollutants that are formed when nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) react to sunlight, creating a brown haze above cities
Primary pollutant
air pollutants which are directly emitted from their source
examples
carbon monoxide
water vapour
sulfur dioxide
nitrogen oxide
Secondary pollutant
pollutants formed when primary pollutants react with UV light in the atmosphere
acid rain
tropospheric ozone
Catalytic converter
reduce the amount of nitrogen oxide released by cars
What are the impacts of the smog?
pollution
irritated eyes
lung cancer
Industrial smog
caused by smoke and sulfur dioxide emissions mixing with fog
In December 1952, London experienced industrial smog over four days, contributing to around 4,000 deaths.
What is acid deposition?
result of primary pollutants of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) reacting with water in the atmosphere to form secondary pollutants of sulphuric acid and nitric acid respectively
it can be :
Wet deposition occurs when pollutants are incorporated into the clouds or falling raindrops, resulting in acidified rain or snow.
Dry deposition occurs when atmospheric pollutants are removed by gravity or direct contact under dry conditions
Causes of acid deposition
composition of fossil fuels
Effects of acid rain
Direct effects
degradation of coniferous forest
Ocean acidification
degradation of rivers and lakes
degradation of buildings made of limestone and marble
Indirect effects
dissolve aluminium in the soil which is then leached out
nutrients and minerals are leached out (dissolved)
→ impacts plant growth as they lack aluminium, nutrients, and minerals
pH
acid - between 0 and 7
neutral = water - 7
alkaline - between 7 and 14
rain is usually between 5 and 6 (presence of carbonic acid = CO2 + H2O): when the acidity is lower than 5, it is considered acid rain
Role of lichen
indicator species - only grows in non-polluted environments
dies as pollution level rise
Solutions and management of acid rain
transboundary issue but not as much as climate change
tools used to reduce acid deposition
policies/legislation (regulations)
changing human behaviors (reducing emissions of sulfur dioxide)
economic instruments (e.g. tax on polluting cars)
technology
UN Geneva Convention - 1979
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
include methane or ethane
they enter photochemical reactions and contribute to the formation of photochemical smog along with hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides.
Liming
when limestone is used in lakes and rivers to reduce the acidity (but expensive and local – treats the symptom not the cause)