Chem 1C Exam 2 UCSB
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
molality (m)
moles of solute/mass of solvent (kg)
volatile
highly unstable; explosive
has some vapor pressure; does evaporate to some extent
can evaporate and will contribute to the vapor pressure of a solution
nonvolatile
low vapor pressure at room temperature
ex: NaCl, KNO3, C6H12O6
adding a nonvolatile solute to a solvent
lowers the solvent's vapor pressure
Raolt's Law for a volatile solvent and a nonvolatile solute
Psolution = Xsolvent * Ppuresolvent
lower vapor pressure
higher boiling point, higher IMF
boiling point elevation
Adding a nonvolatile solute to a solvent lowers the vapor pressure of the solution, raising the boiling point of the resulting solution above that of the pure solvent
freezing point depression
Adding a nonvolatile solute to a solvent lowers the freezing point of the resulting solution below that of the pure solvent (need to remove more energy for the solution to freeze because nonvolatile solute prevents crystallization)
osmotic pressure
additional pressure needed to prevent or reverse osmosis
osmosis
diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
IMF solution > IMF uncombined
strong solute-solvent interaction
process is exothermic (release energy/heat as a result form of bond formation)
Delta H for combination is a large negative, the overall change in enthalpy is negative (exothermic)
form IMF
release energy
break IMF
add energy
delta H (change in enthalpy) for expansion
positive (add energy)
Enthalpy
total energy of a system
delta H for combination
negative (release energy)
IMF solution < IMF uncombined
weak solute-solvent interaction
process is endothermic
Delta H for combination is a small negative, the overall change in enthalpy is positive (endothermic)
Delta H positive
endothermic
Delta H negative
exothermic
like dissolves like
polar dissolves polar
nonpolar dissolves nonpolar
ionic compounds ONLY dissolve in polar solutes
Entropy
A measure of disorder or randomness.
positive delta G
non-spontaneous
negative delta G
spontaneous
delta G
delta H - T delta S
T (in K) = always positive
positive delta S
like and like
more disordered
negative delta S
unlike and unlike
less disordered
ex: water and oil- water will arrange itself around the oil to avoid it
solubility of solids ____ as temperature increases
increases
solubility of gases ____ as temperature increases
decreases
Raolt's Law for a volatile solvent and a volatile solute
Pa = Xa Ppurea
Pb = Xb Ppureb
Psolution = Pa + Pb
Psolution= total vapor pressure of solution
assumes IDEAL solution (where IMFs do not play a factor)
Negative deviation from Raoult's law
IMF solution > IMF pure substances
lower vapor pressure than expected (ideal solution)
exothermic
solution feels warm
hydrogen bond donor
hydrogen directly bonded to a N, O, or F atom
hydrogen bond acceptor
any N, O, or F atom with lone pairs
Positive deviation from Raoult's law
IMF solution < IMF pure substances
high vapor pressure than is expected (ideal solution)
endothermic
solution feels cold
non-polar
hydrocarbons, or large hydrocarbons (4+ Cs) w/one O or N
for elements with 4 or 9 d-orbital electrons
move an electron from s orbital into d orbital
when forming metal cations
remove s orbital electrons first
complex ion
charged species consisting of transition metal ion surrounded by ligands
ligands
molecules or ions that bond to the transition metal ion in a complex ion
counter ions
Ions that balance charge. Not part of the complex ion.
ligands attach by
donating a lone pair to form a covalent bond with transition metal
lewis base
electron pair donor
lewis acid
electron pair acceptor
ligand attachment site
any atom with a lone pair
multiple attachment sites are possible only if there are 2+ atoms in between the atoms with lone pairs
coordination number
the number of bonds to the transition metal
CN = 2
linear
CN = 4
tetrahedral
CN = 6
octahedral
Splitting of d-orbitals for octahedral complexes
3 on the bottom, 2 on the top
bottom: xz, xy, yz
top: x^2 - y^2 , z^2
Splitting of d-orbitals for tetrahedral complexes
3 on the top, 2 on the bottom
bottom: x^2 - y^2 , z^2
top: xz, xy, yz
ALWAYS have weak field (high spin case)
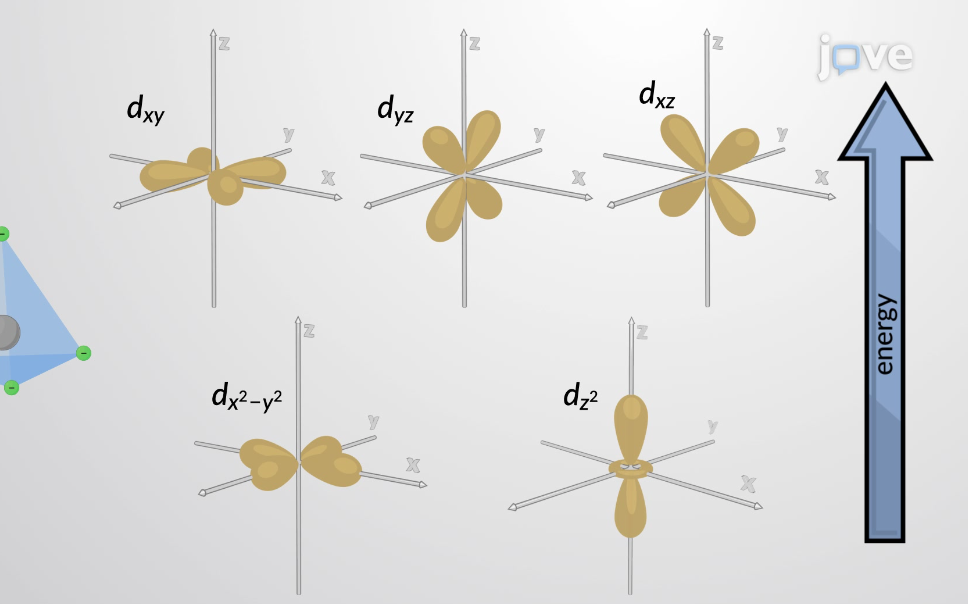
weak field ligands
small delta E
Ligands that cause a small difference in the energies of d subshells
can populate top and bottom energy levels at the ground state (can add e- to the top before the bottom is completely full)
strong field ligands
large delta E
ligands that cause a large difference in the energies of the d subshells
can NOT populate the top and bottom energy levels at the ground state (can only add e- to the top once the bottom is completely full)
delta E (energy of absorbed photon)
hc/lamda (wavelength)
wavelength (lamda)
hc/delta E
you observe the _____ color of light absorbed by the complex
complementary
shorter wavelength
higher energy
diamagnetic
all electrons are paired (repelled by magnetic field)
paramagnetic
unpaired electrons (attracted to magnetic field)
H2O ligand name
aqua
NH3 ligand name
ammine
CO ligand name
carbonyl
NO ligand name
nitrosyl
anion ligands
drop suffix (-ide) and add -o
CO3 2- ligand name
carbonato
1
no prefix
2
di
3
tri
4
tetra
5
penta
6
hexa
Use greek prefixes when naming
ligands that already contain a prefix (ex: en)
write greek prefix then ligand name in parenthesis
1 (greek)
none
2 (greek)
bis-
3 (greek)
tris-
4 (greek)
tetrakis-
when complex ion is an anion
add -ate to the end of the metal name
Fe (in anionic complex)
ferrate
Cu (in anionic complex)
cuprate
Pb (in anionic complex)
plumbate
Ag (in anionic complex)
argentate
Au (in anionic complex)
aurate
Sn (in anionic complex)
stannate
Mo (in anionic complex)
molybdate
Isomer
Compounds with the same formula but different structures.
structural isomers
differ in the covalent arrangements of their atoms (different types of bonds)
ligands swap places in coordination compound
coordination isomers and linkage isomers
Stereoisomers
Compounds with the same structural formula but with a different arrangement of the atoms in space (same bonds, different spatial arrangements)
geometric and optical
linkage isomers
ligand is bound to the metal by a different atom (different binding site on the ligand)
cis (geometric isomer)
same ligands are side by side
trans (geometric isomer)
same ligands are across from each other
MX4X2
octahedral complex capable of forming cis/trans isomers
MX2X2
square planar/tetrahedral complex capable of forming cis/trans isomers
linkage isomers are possible when
there are two distinct attachment sites on ligands
geometric isomers are possible when
MX4Y2
MX2Y2
organic molecules
molecules that contain carbon
alkanes
CnH2n+2
saturated hydrocarbons, single bonds
always non-polar
low boiling points
low reactivity
suffix -ane
1 carbon
meth
2 carbons
eth
3 carbons
prop
4 carbons
but
5 carbons
pent
6 carbon
hex