concentration
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chapter 17
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
concentration
mental effort placed on sensory or mental events. The person can exert deliberate mental effort on what is most important in a given situation
attention
the concentration of mental effort on sensory or mental events
4 components of concentration
focusing on relevant environment cues (selective attention): selecting what cues to attend & disregard
maintaining attentional focus
situation awareness: ability to understand whats going on around oneself
shifting attentional focus when necessary
benefits of external focus
benefits performance in a variety of tasks such as focus on balance, accuracy, speed & endurance & max force production
increases in performance outcomes, movement efficiency, movement kinematics
generalizes across many situations & skill levels
associative attentional strategy
monitoring bodily functions & feelings
internal sensory monitoring: muscle soreness, fatigue, breathing
active self-regulation: technique, strategy, cadence
dissociative attentional strategy
not monitoring bodily functions, distraction & tuning out
focusing on outside sources
maintaining attentional focus
being able to maintain focus for the duration of the competition/performance is part of concentrating
maintaining situational awareness
the ability that allows players to size up game competitions to make appropriate decisions based on the situation, often under acute pressure & time demands
Expert & Novice differences in attentional processing
experts attend more to advance information, & can make faster decisions & better anticipate future actions
experts attend more to the movement patterns of their opponents
expert players search more systematically for cues
experts selectively attend to the structure inherent in their particular sport
expert are more successful in predicting flight pattern of ball
shifting attentional focus
attentional flexibility is know ad the ability to alter the scope & focus of attention as demanded by the situation
information-processing based theories
single channel theory
variable allocation theory
multiple resource pool
single channel theory
information is processed through a single & fixed capacity channel
variable allocation theory
individuals are flexible & can choose where to focus their attention, allocating it on more than one task at a time
multiple resource pool
attention is distributed throughout the nervous system & each microprocessor has its own unique capabilities & resource-performance relationship
3 processes of attentional focus
attentional selectivity
attentional capacity
attentional alertness
attentional selectivity
letting some information into the processing system while other information is screened or ignored
attentional capacity
attention is limited in the amount of information that can be processed at one time
controlled processing
is mental processing that involves conscious attention & awareness of what you are doing when you perform a sport skill
automatic processing
is mental processing without conscious attention
Attentional capacity & Elite athletes
athletes can change from controlled processing to automatic processing as they become more proficient
attentional capacity is compromised by having to perform the cognitive secondary task before the primary task
peak performance when:
in the present & no thoughts about past/future
mentally relaxed & high degree of concentration & control
being in a state of extraordinary awareness of both body & external env.
attentional alertness
increases in emotional arousal narrow the attention field
concentration & optimal performance
focus only on relevant cues in athletic env. & eliminate distractions
ability to automatically process/execute movements
4 types of attentional focus
broad-external focus: used to rapidly assess a situation
broad-internal focus: used to analyze & plan
narrow-external focus: used to exclusively on one or 2 external cues
narrow-internal focus: used to mentally rehearse an upcoming performance/control an emotional state
Internal distracters
attending to past events
attending to future events
choking under pressure
over-analysis of body mechanics
fatigue
inadequate motivation
choking
attentional process that leads to impaired performance & the ability to retain control over performance without outside assistance
the choking process
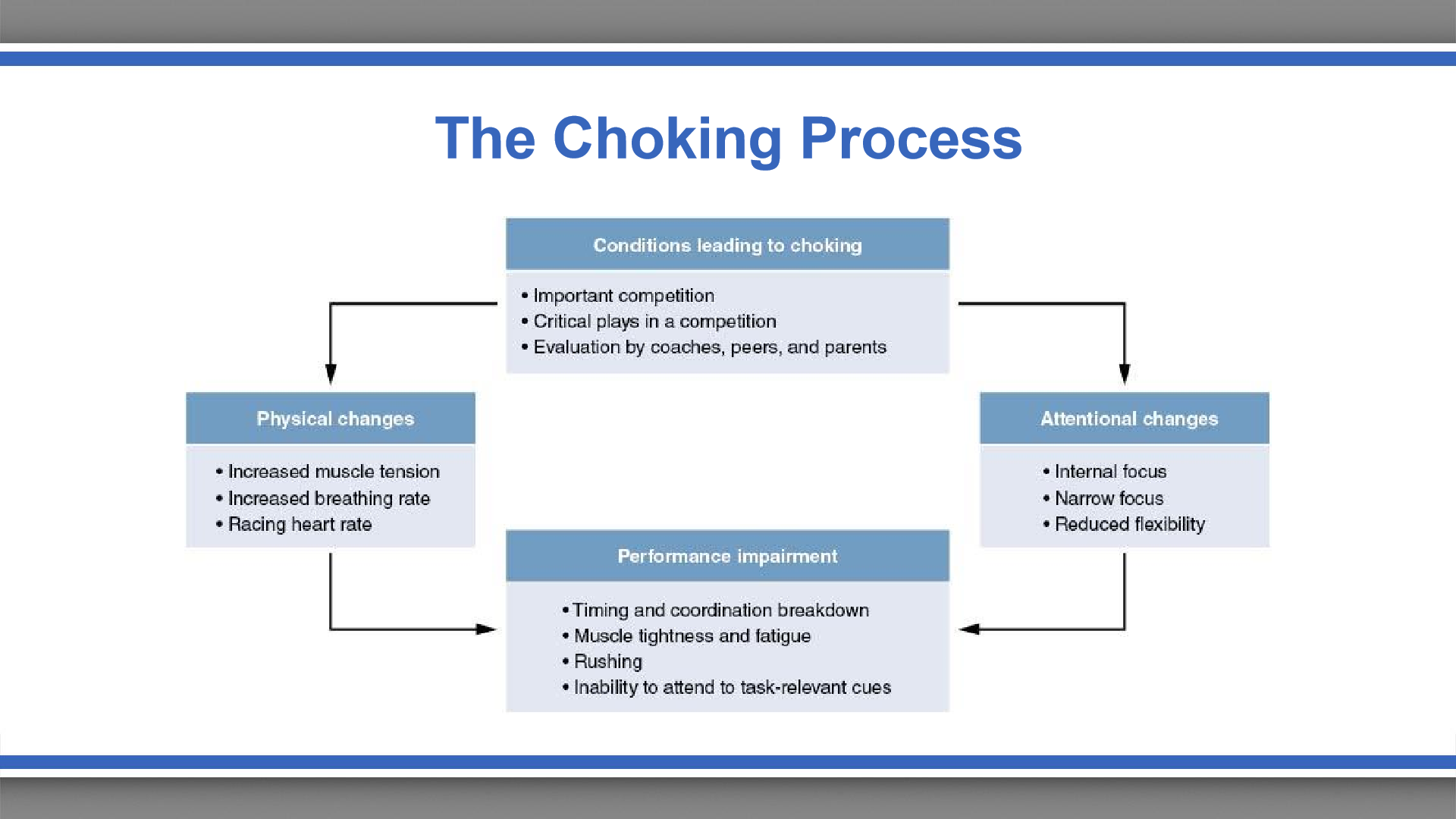
conscious processing hypothesis
choking occurs when skilled performers focus too much of their conscious attention to the task
performance decreases only wit increased focus on several task-relevant cues
once skill is learned an overemphasis on body mechanics is detrimental to performance
interventions to help choking under pressure
imagery builds confidence
pre-shot routines help keep task-focused & relaxed
secondary task focus helps focus on one task-relevant cue
exposure to stressful situations allows athletes to feel more comfortable
Process approach to managing pressure & choking
Before competition: MAPP it
mental & physical preparation
During: ACT on it
accept, center, trust
after competition: GIRD yourself
growth mindset, identity, resolve, defuse
Mindfulness Intervention to help Choking
awareness that emerges through paying attention on purpose, in the present moment, & nonjudgmentally to unfolding experience moment by moment
effective in enhancing concentration, reducing anxiety & improving performance
can reduce emotional reactions to stress
External distracters
inadequate motivation
stimuli from the environment that divert people’s attention from the cues relevant to their performance
visual distracters (audience)
auditory distracters
Self talk to enhance concentration
appropriate self-talk helps one focus on the present & keeps one’s mind from wandering
uses of self talk
motivational
initiating action
sustaining effort
instructional
skill acquisition
breaking bad habits
types of self talk
positive
instructional
negative
organic
strategic
categories of positive self-talk
psych-up (power)
confidence
instruction (focus on technique)
anxiety control
categories of negative self talk
worry
disengagement
somatic fatigue
6 rules for creating effective self talk
keep phrases short & specific
use the first person & present tense
construct positive phrases
say your phrases with meaning & attention
speak kindly to yourself
repeat phrases often
5 Ps of Self talk
Personalized: A person should individually shape the content of self-talk so it has special meaning
Practiced: self talk should be practiced before implementing it in competitive situations. Gain familiarity on how & when to use self talk to make it effective
Purpose: knowing what needs to be accomplished will facilitate superior interventions & help determine the nature of the statements employed based on the task
Positive phrasing: self talk should be positive
Position: tailor self talk to the person’s current situation
Rational emotive behaviour therapy (REBT)
proposes that individuals’ beliefs about diversity that determine whether their emotional & behavioural reactions are adaptive or maladaptive
irrational beliefs lead to dysfunctional emotions & maladaptive behaviour
rational beliefs lead to functional emotions & adaptive behaviours
what is TAIS
Test of Attention & Interpersonal Style
general traits measure
techniques to improve self talk
thought stopping
identify negative thoughts
stop the thoughts
focus on task relevant thoughts
changing negative self talk to positive self talk
combining self talk with self feedback
On-site techniques to improve concentration
use stimulations in practice
use cue words to focus
employ nonjudgmental thinking
establish routines (before & during event)
develop competition plans
overlearn skills
5 step approach to developing pre-performance routines
recording performance on video
clarifying behaviour meaning
developing focus & function for each behavioural component
routine construction & agreement
practice