normal cell: structure and function - lecture 1
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
cells are the fundamental units of life. a lot of communication between cells/tissues/systems
why are we interested in the structure and function of the normal cell?
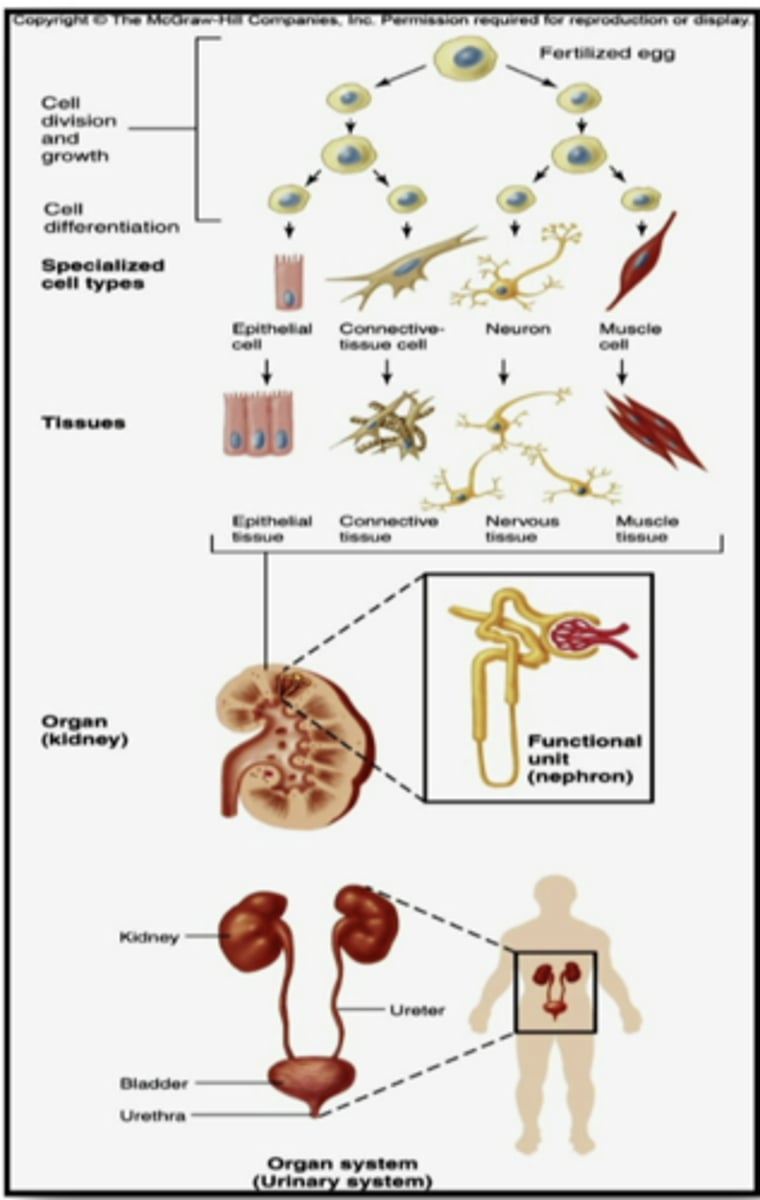
cell
understanding pathophysiology begins with understanding the ...
disease (if not resolved or injury persists)
injury to any cellular component can lead to...
crohn's disease and skin carcinomas
epithelial cells are associated with ...
marfan syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis
connective tissue cells are associated with...
sarcopenia and heart failure
muscle cells are associated with ...
parkinson's and alzheimer's
neural cells are associated with...
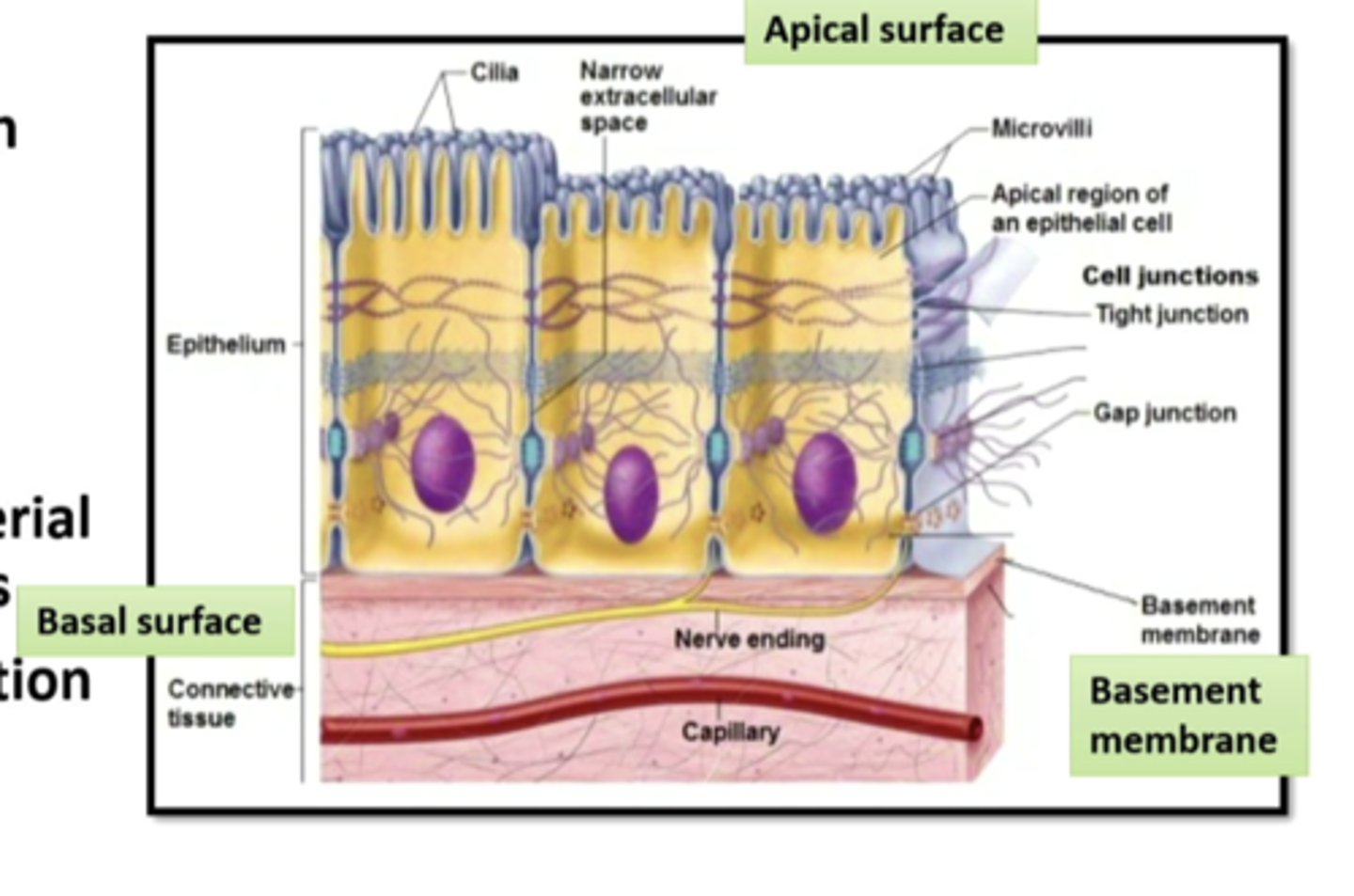
epithelial cells
cover and line body surfaces, specialized for the selective secretion and absorption of ions and organic molecules and for protection, replicate (turnover) often to replace damaged or dead cells, aid in the transportation of filtered material through the use of active transport systems, innervated and provide sensory information, AVASCULAR
stomach lining, skin, etc.
what are some examples of epithelial cells
types of epithelial cells
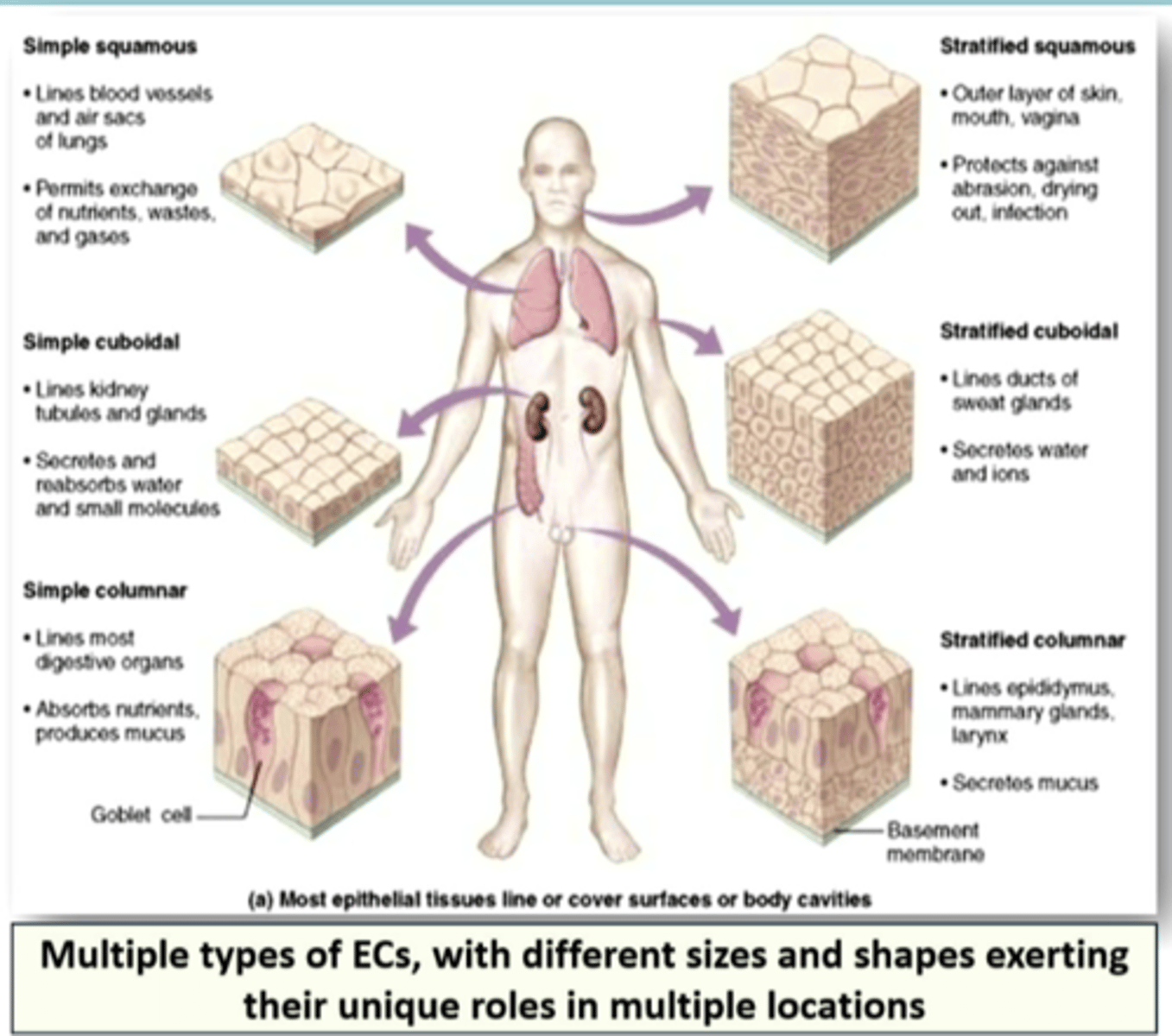
epithelial cells
in diseases such as eczema, psoriasis, dermatitis, peptic ulcers, and barret's esophagus, what cells are the target?
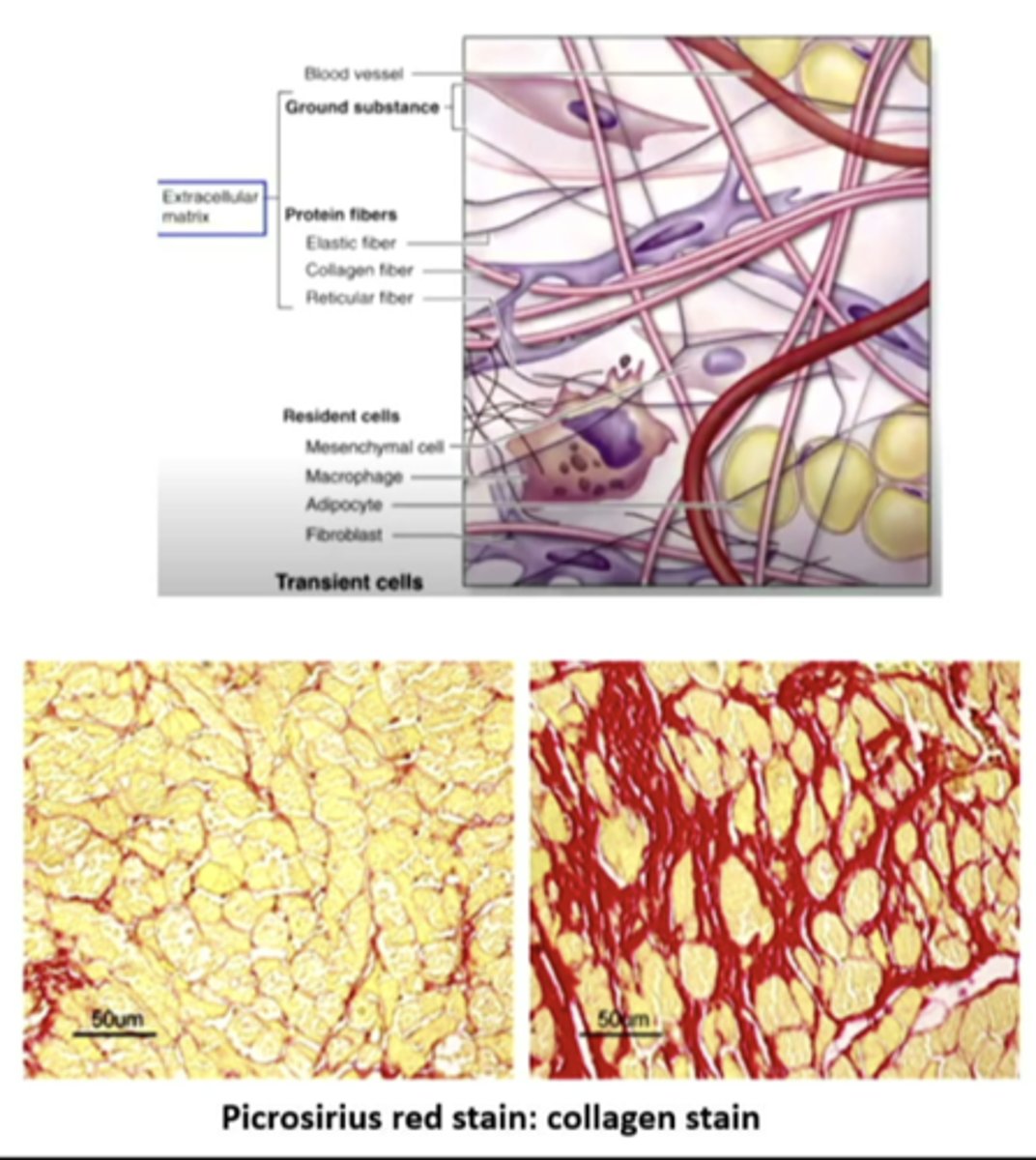
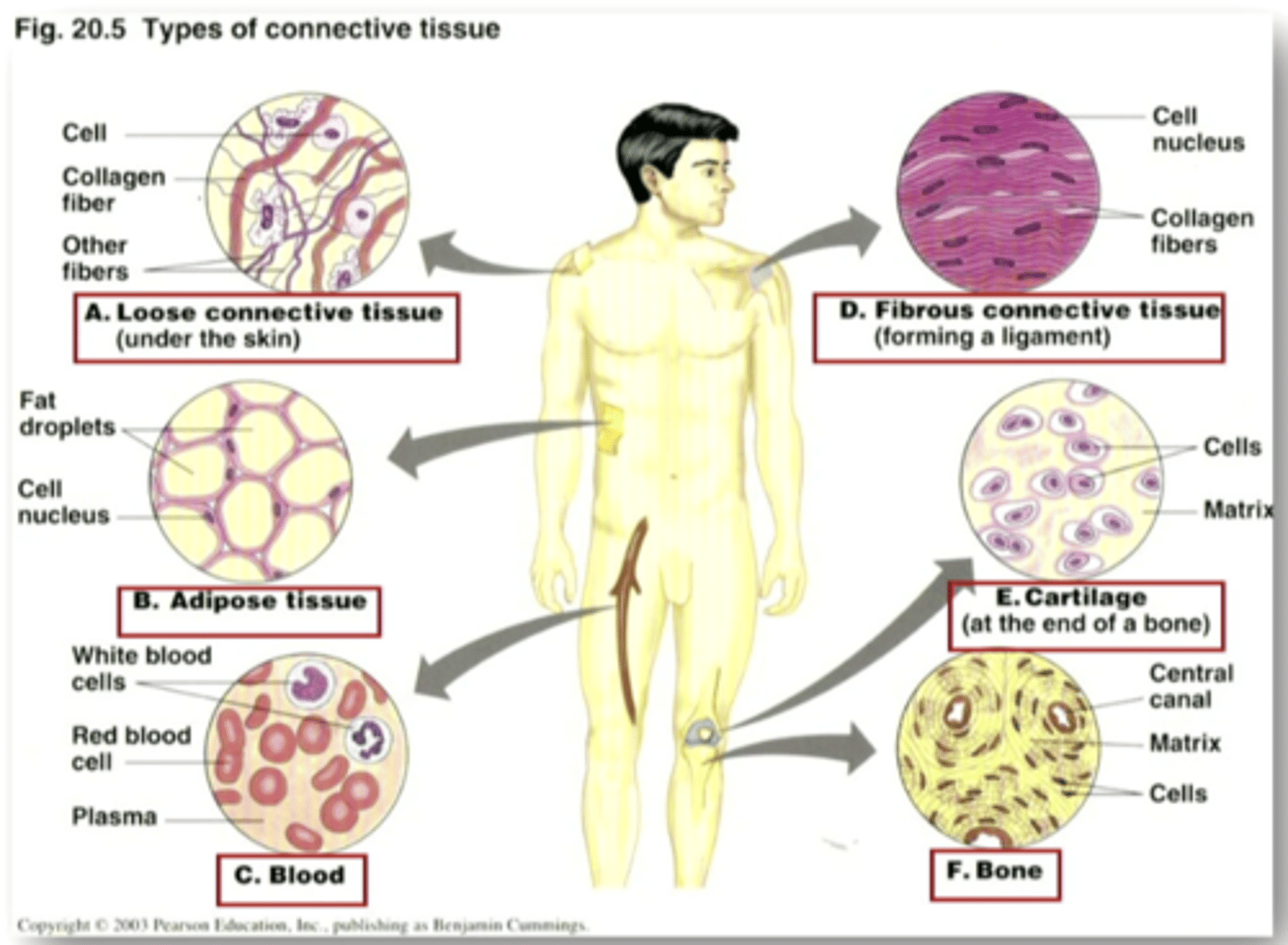
connective tissue cells
connect, anchor, and support the structures of the body. MOST ABUNDANT CELLS IN THE BODY. form a framework of the body. the two major structural proteins are COLLAGEN AND ELASTIN.
connective tissue diseases
any disease that has the connective tissue of the body as a primary target of pathology
leukocytes (white blood cells)
many connective tissue diseases feature abnormal immune cell activity with inflammation called...
collagen
fibroblasts secrete ___________, which is important for maintaining the structural framework of tissues and extracellular matrix (ECM). plays a critical role in wound healing
connective tissue cells
in diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, scleroderma, marfan syndrome, and ehlers-danlos syndrome, what cells are the target?
skeletal, cardiac, and smooth
what are the 3 types of muscle cells in the human body
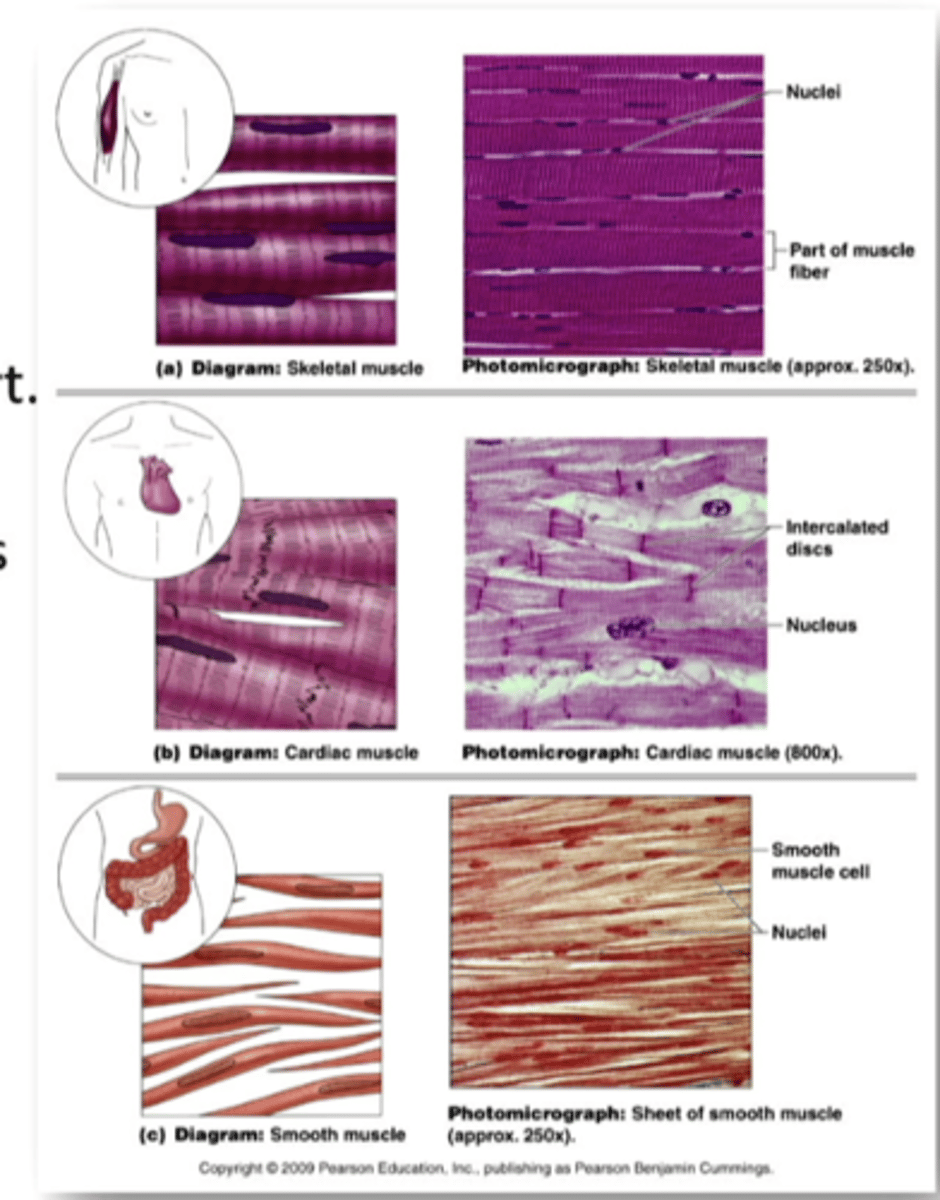
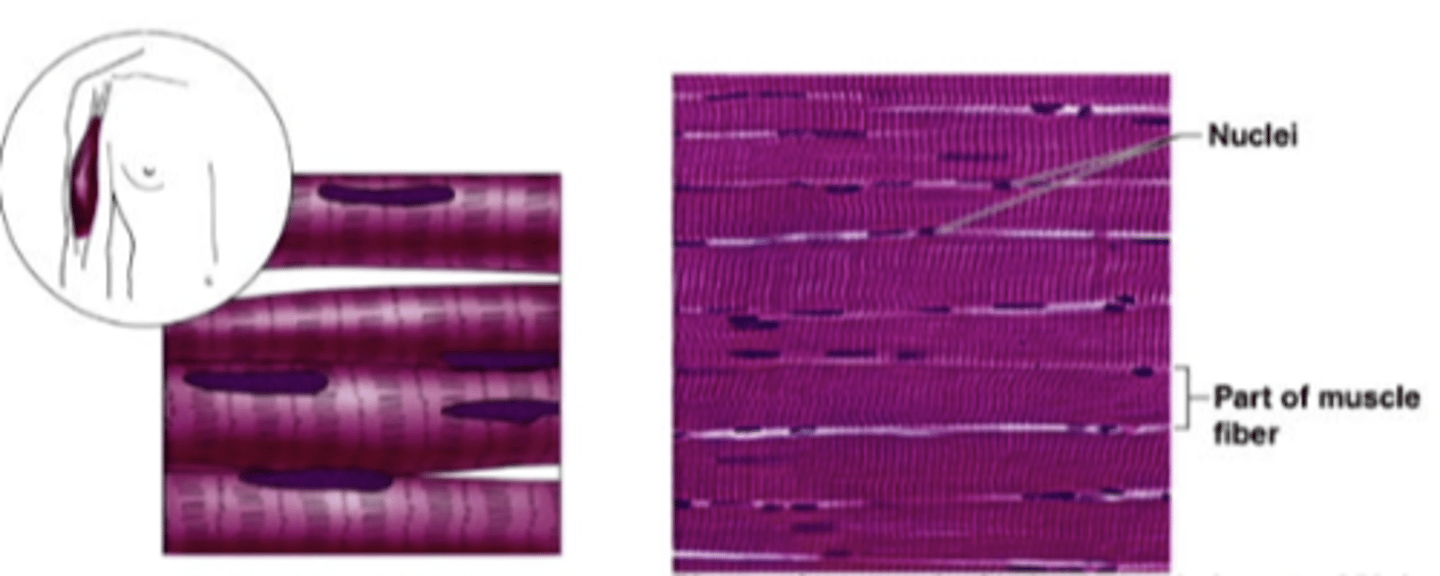
skeletal muscle
anchored by tendons to bone and is used on skeletal movement such as locomotion and in maintaining posture. VOLUNTARY MUSCLE
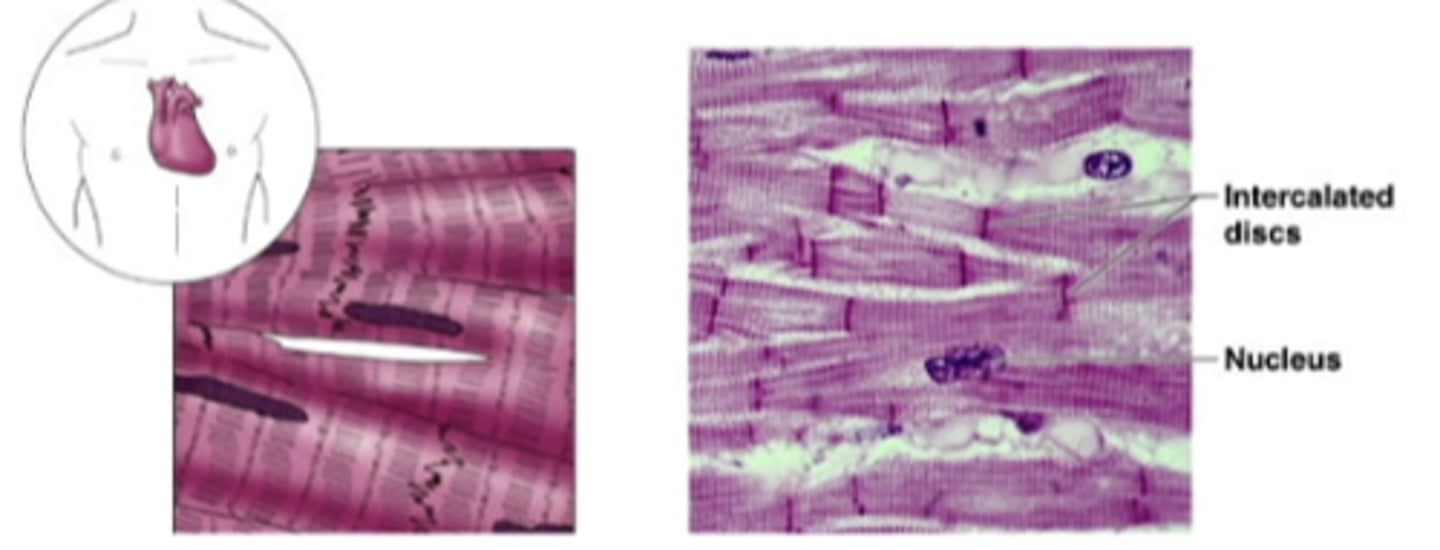
cardiac muscle
similar skeletal muscle but only found in the heart. INVOLUNTARY MUSCLE
smooth muscle
found within the walls of organs and structures such as the esophagus, stomach, intestines, bladder, blood vessels. INVOLUNTARY MUSCLE
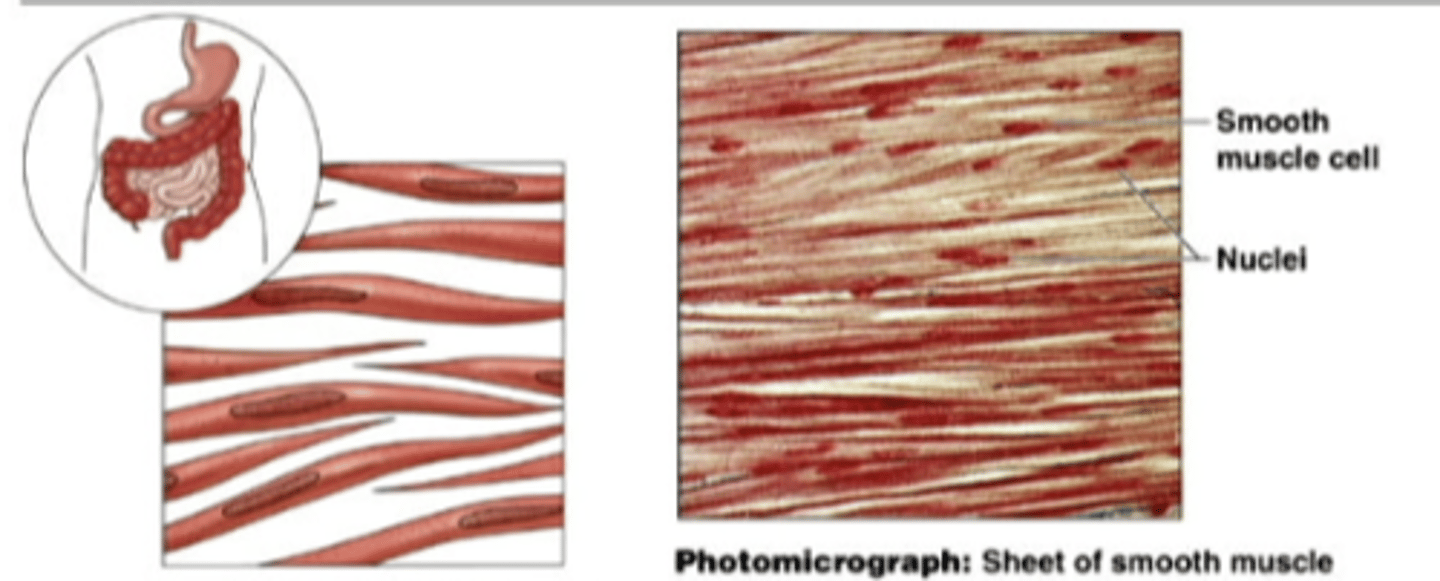
muscle cells
in diseases such as Lou Gehrig's disease, atrophy, muscular dystrophy, myasthenia gravis, and cardiomyopathy, what cells are the target cells?
involuntary muscle
A muscle that is not under conscious control.
voluntary muscle
A muscle that is under conscious control
neuron
a cell of the nervous system that is specialized to initiate, integrate, and conduct electrical signals to other cells
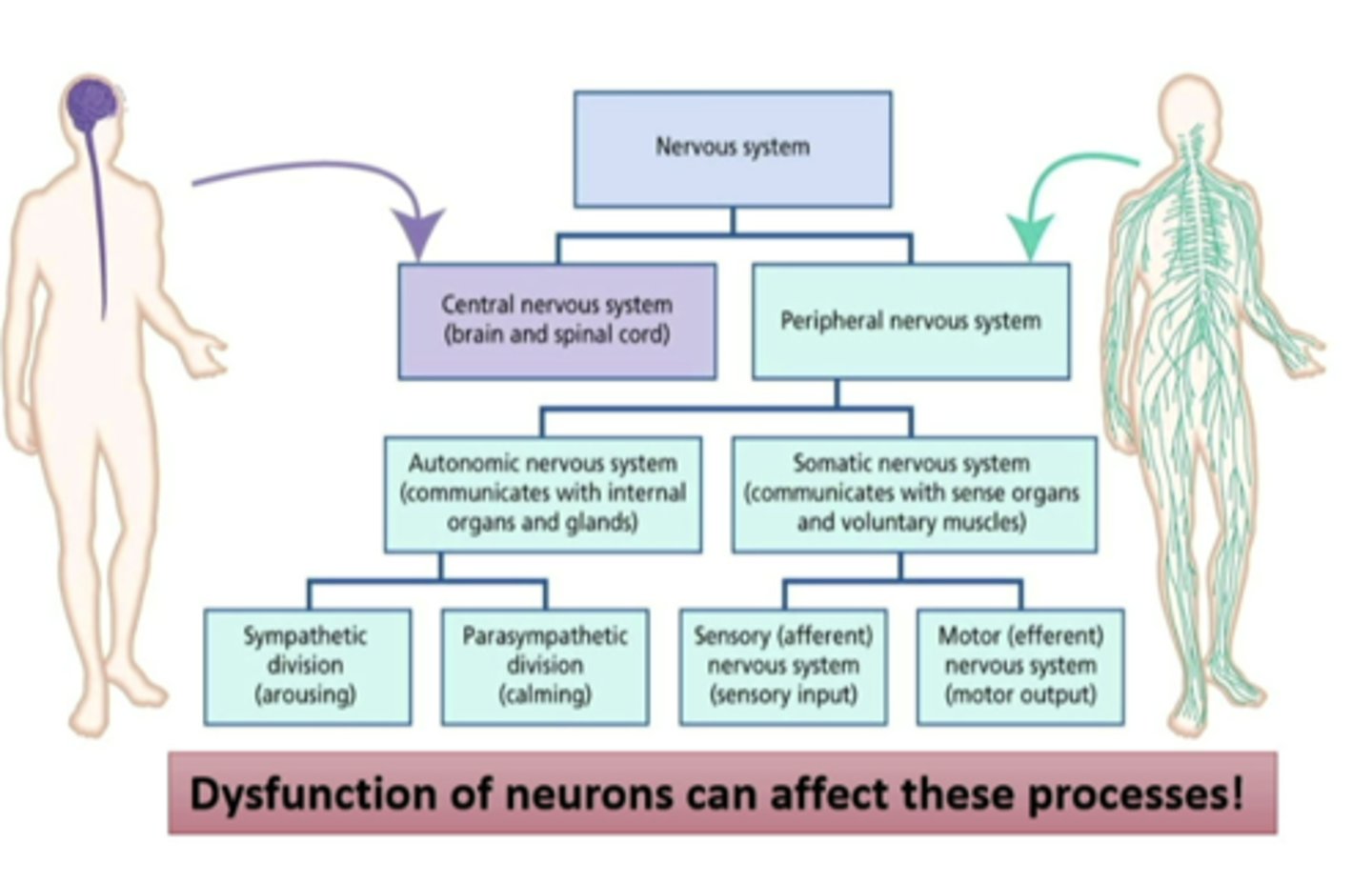
nerve cells/neurons
in diseases such as multiple sclerosis, parkinson's, alzheimer's, stroke, shingles, and depression, what cells are the target?
brain and spinal cord
what are the two parts of the central nervous system
autonomic (sympathetic and parasympathetic) and somatic (sensory afferent and motor efferent) nervous system
what are the two parts of the peripheral nervous system
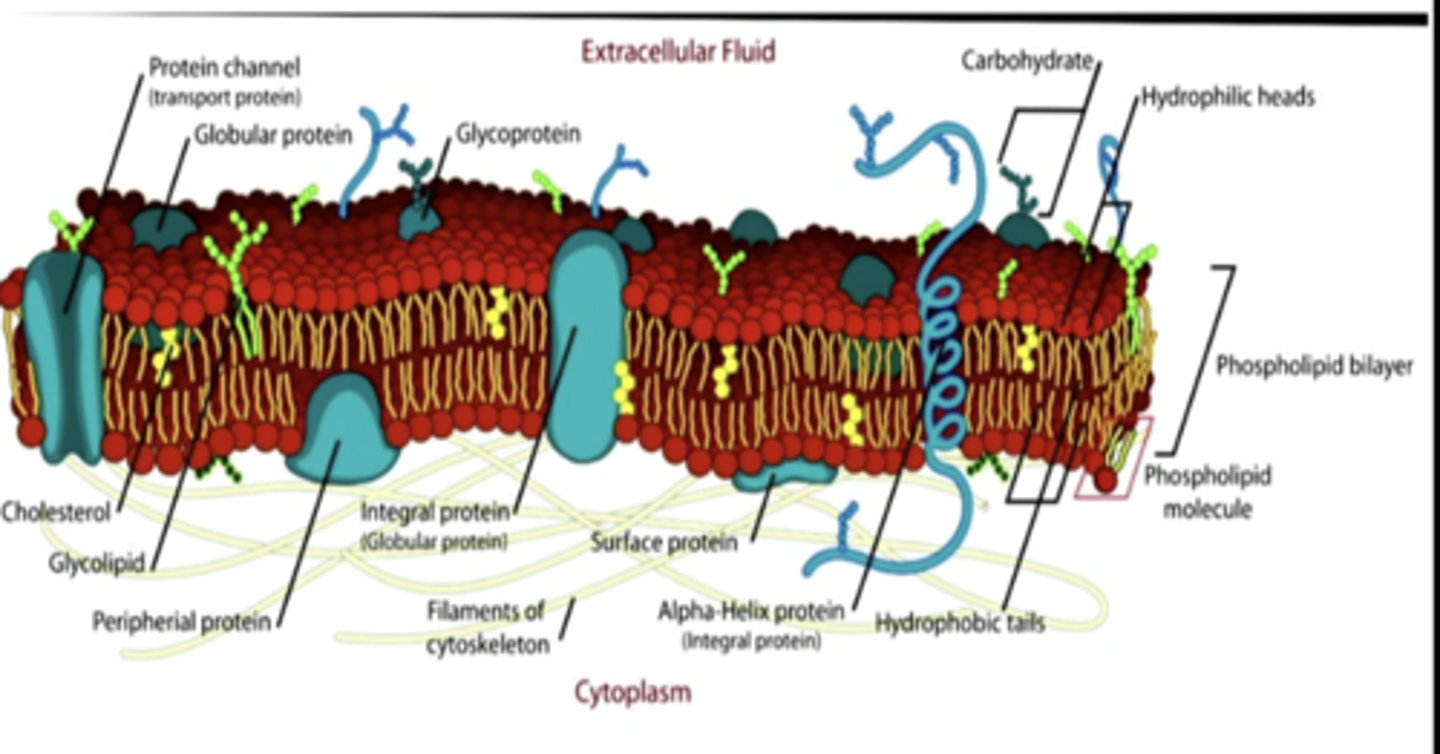
semipermeable membranes
form a major structural element in cells
phospholipid bilayer
cell is surrounded by a ....
1. separate or compartmentalize ions and molecules (allow for the development of fluid compartments in body)
2. detecting chemical signals from other cells
3. link adjacent cells together by membrane junction
what are the 3 functions of cell membranes
fluid compartments
separated by selectively permeable membranes that control movement of water and solutes
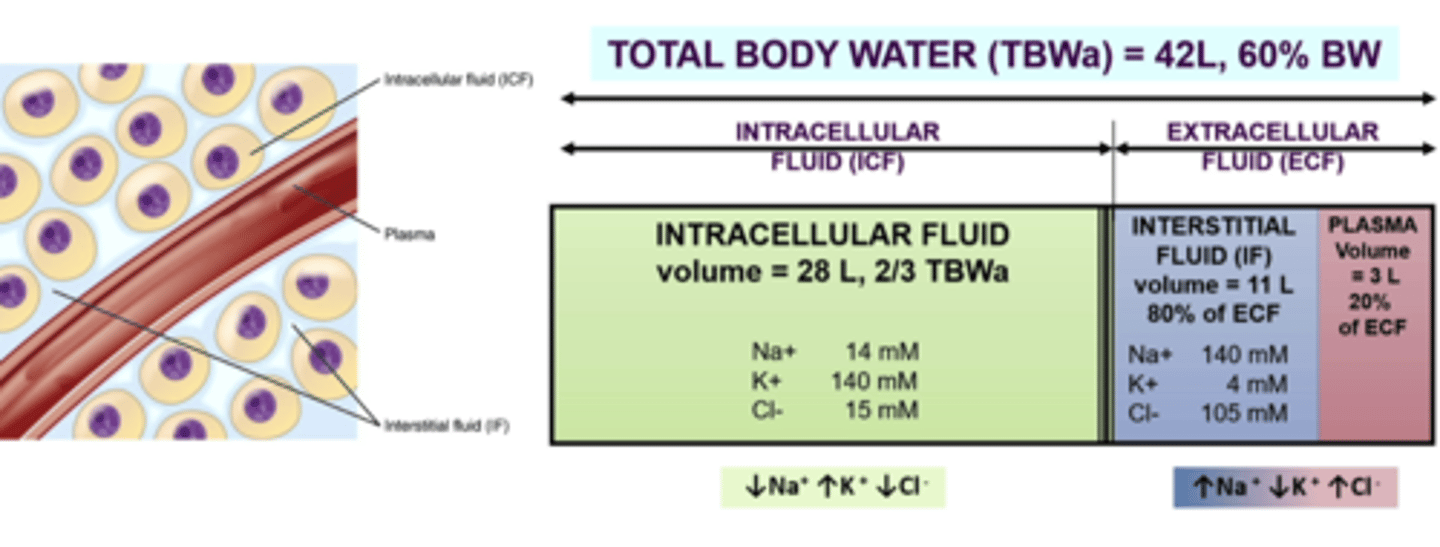
60
____% of our body weight is water
intracellular fluid
fluid within cells
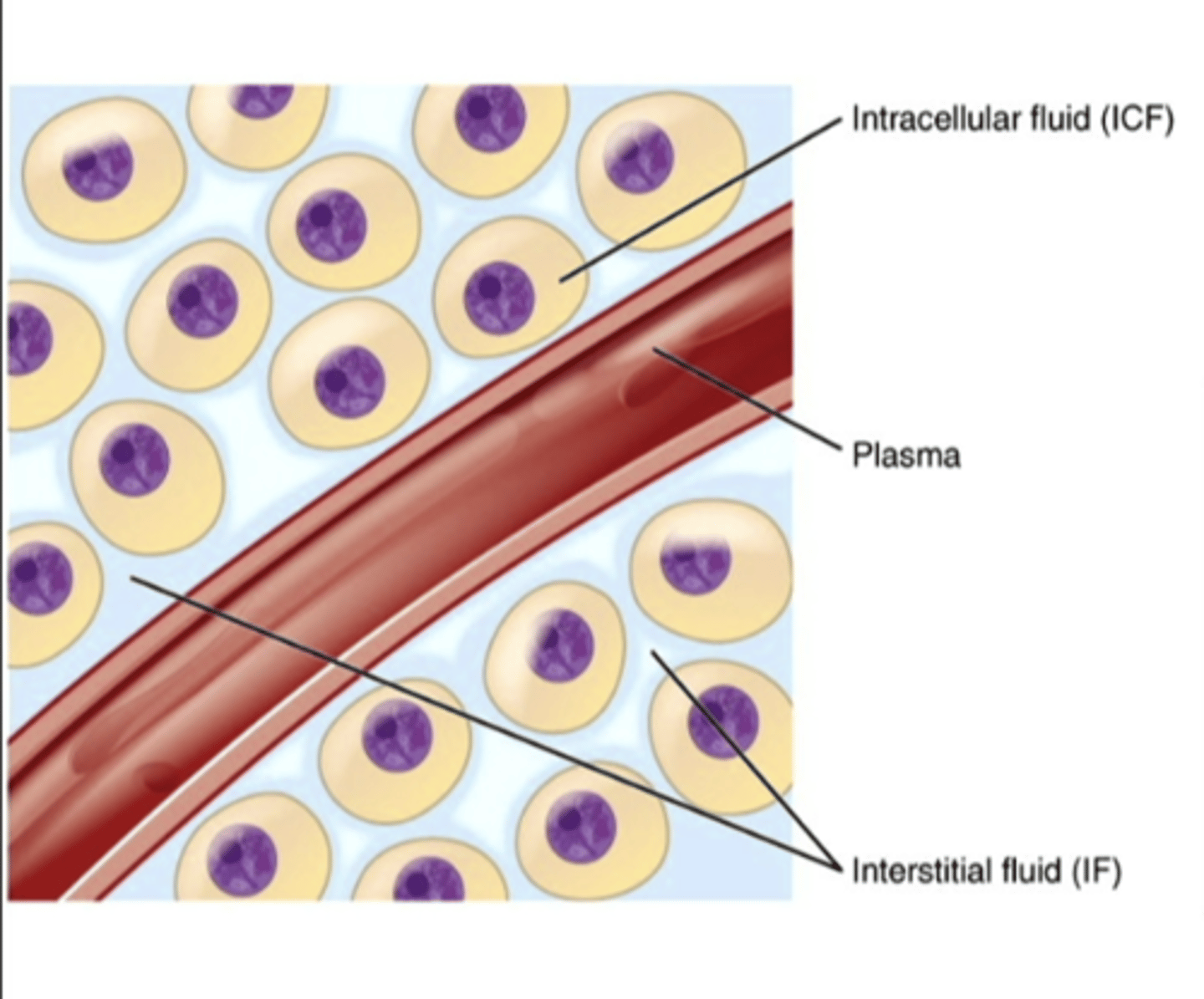
extracellular fluid
fluid outside the cell (interstitial fluid and plasma)
interstitial fluid
fluid between cells
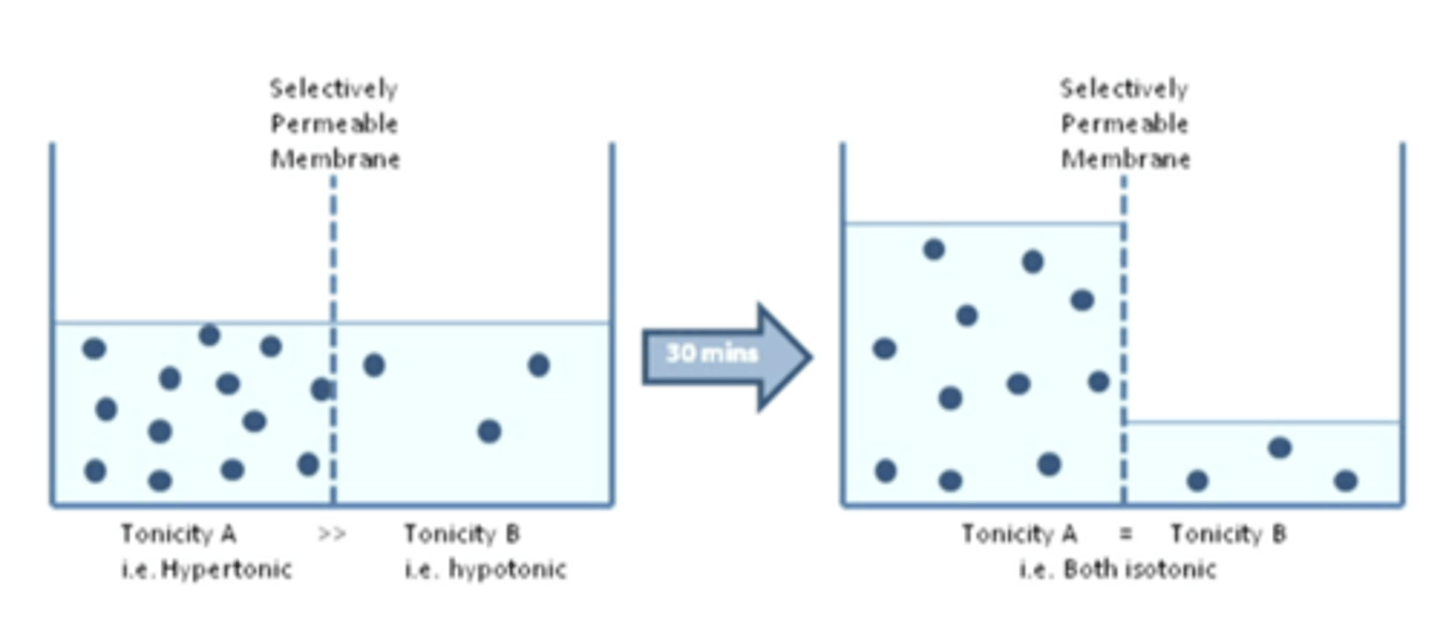
the fluid will start going to the hypotonic compartment to balance the tonicity creating an isotonic environment
if you have two compartments and a selective permeable membrane in between them with hypertonic and hypotonic compartments (as pictured), what will happen?
cell membranes
act as barriers that considerably slow the diffusion of molecules across their surfaces
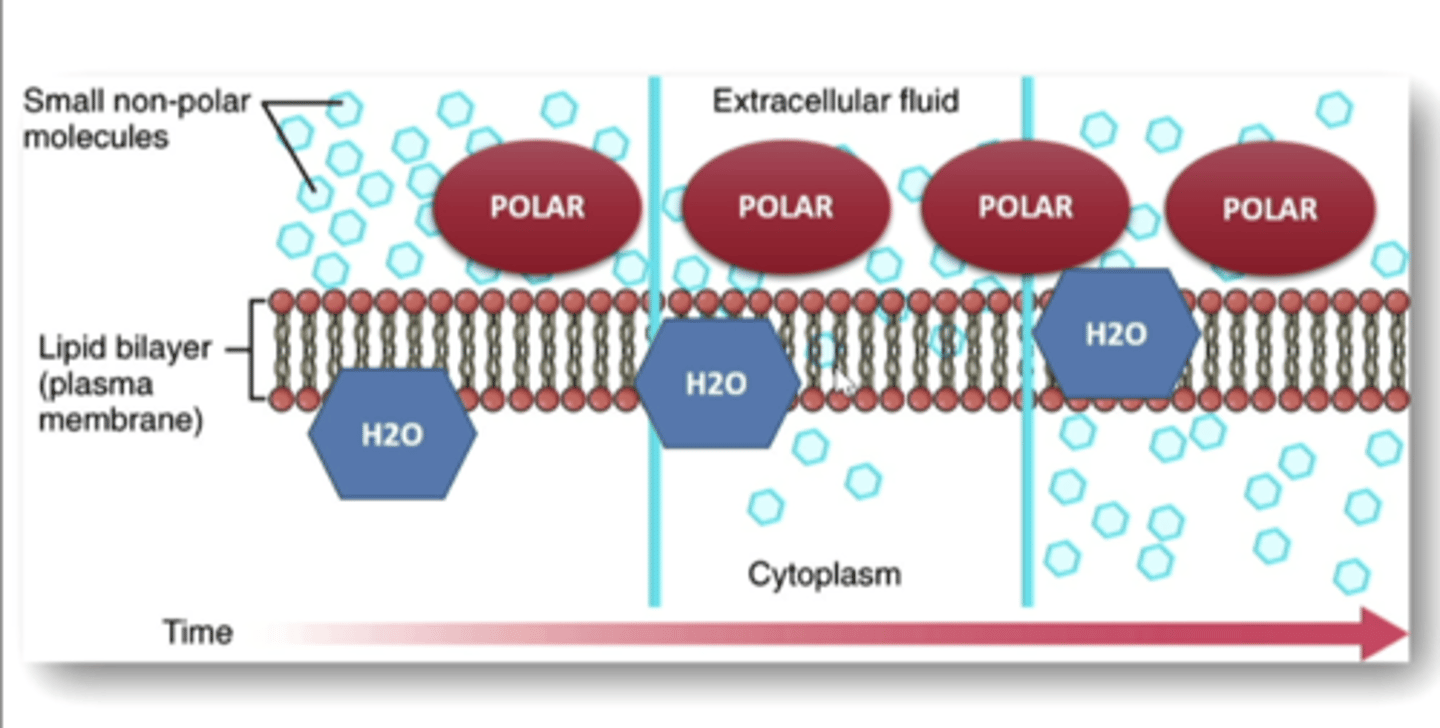
lipophilic (hydrophobic)
____________ compounds can pass through the cell membrane
hydrophilic
_____________ compounds do not pass through
hydrophilic compounds
specialized transporters and channels allow transport of ....
high, low
solutes want to move from area of ______ concentration to area of _____ concentration
proteins imbedded in the cell membrane
control diffusion across the membrane and set up concentration differences
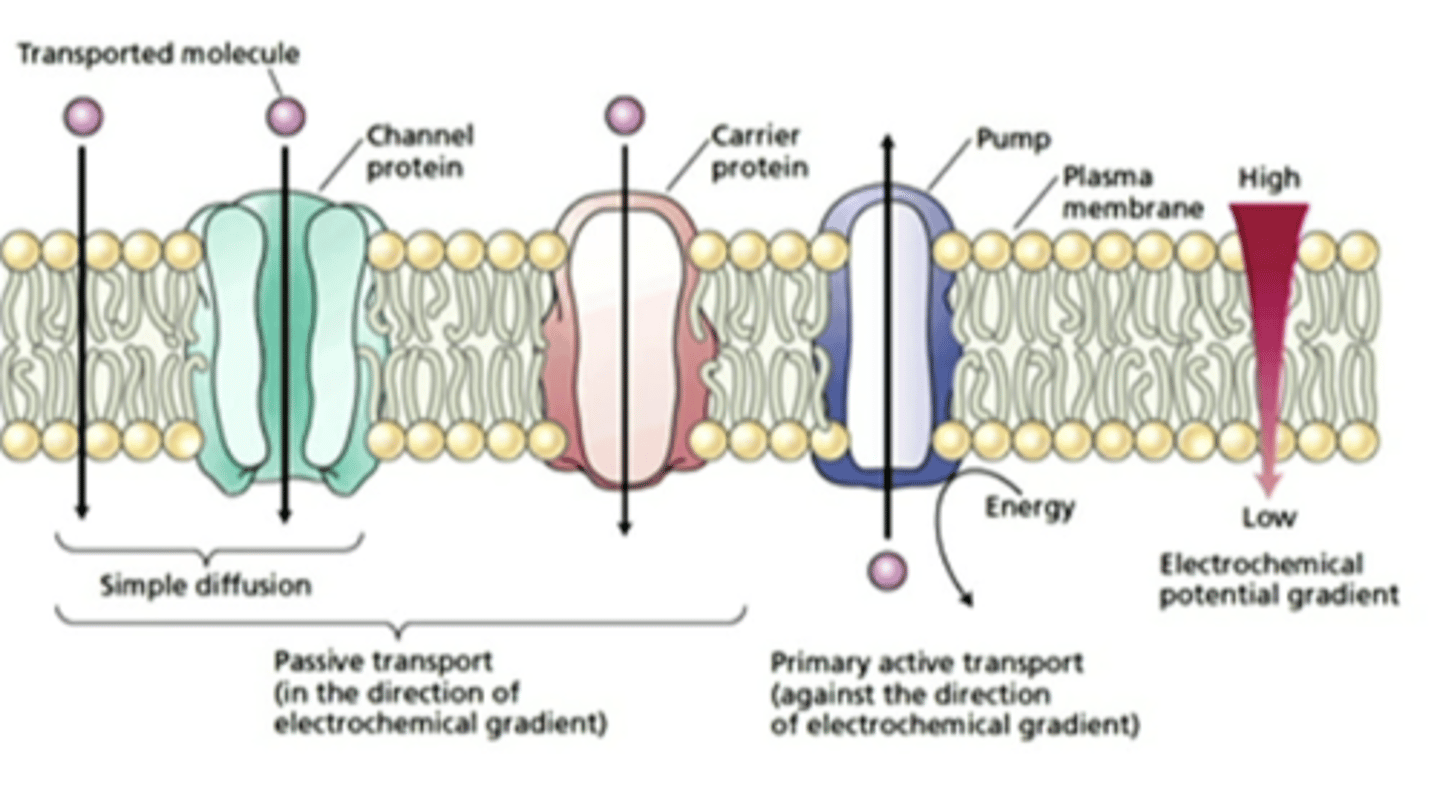
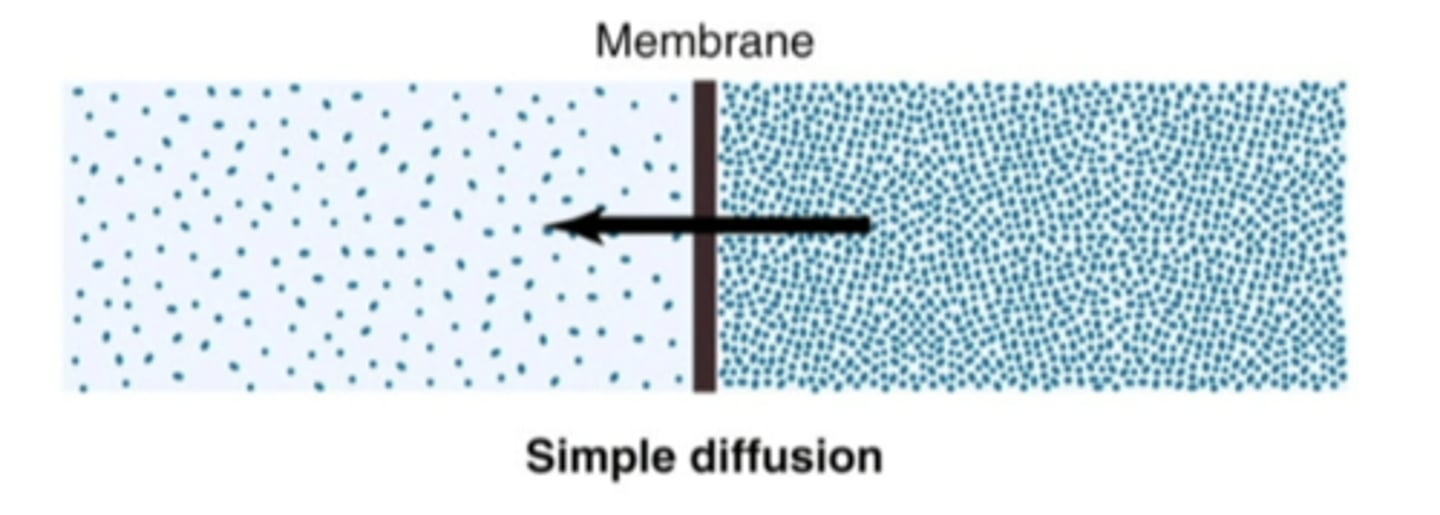
simple diffusion
movement from high to low concentration
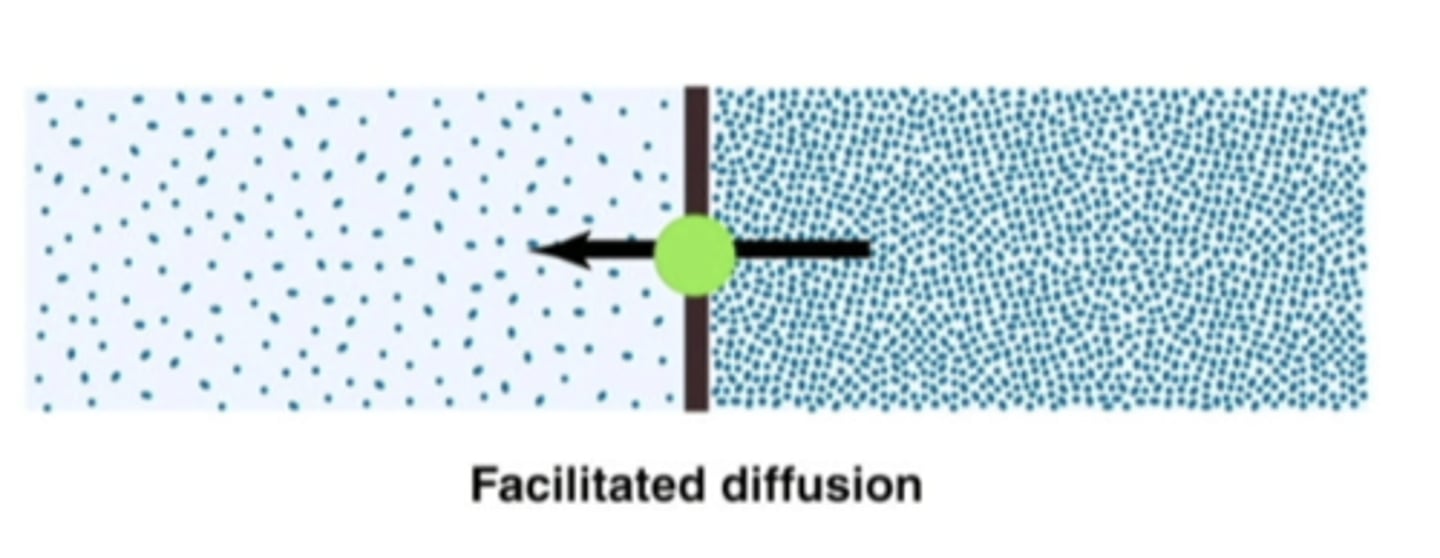
facilitated diffusion
movement from high to low concentration with the help of a transporter
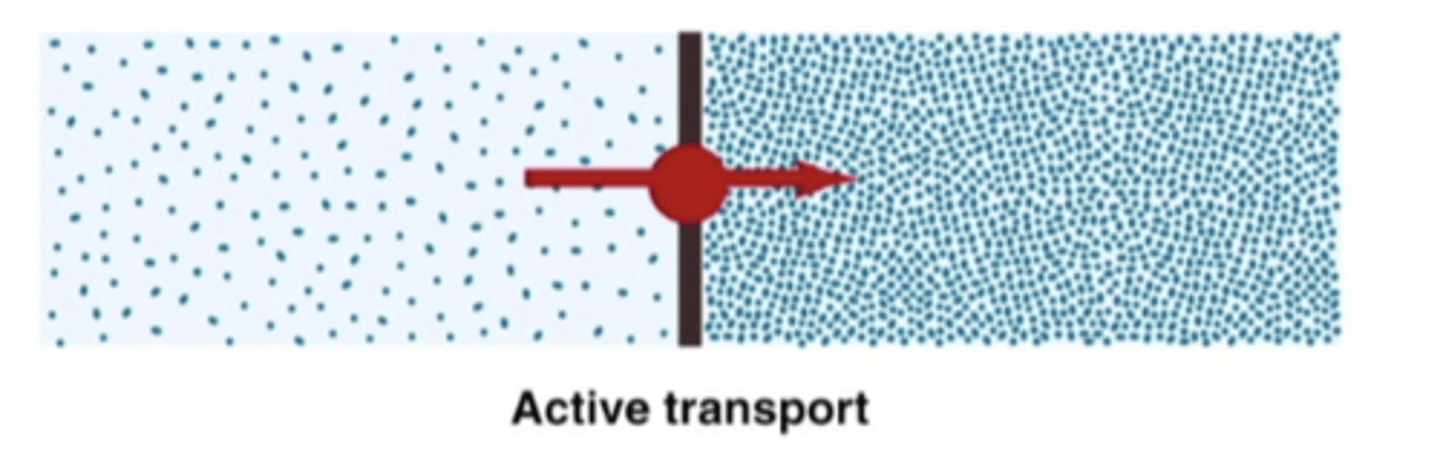
active transport
movement against concentration gradient, with a transporter needing ATP
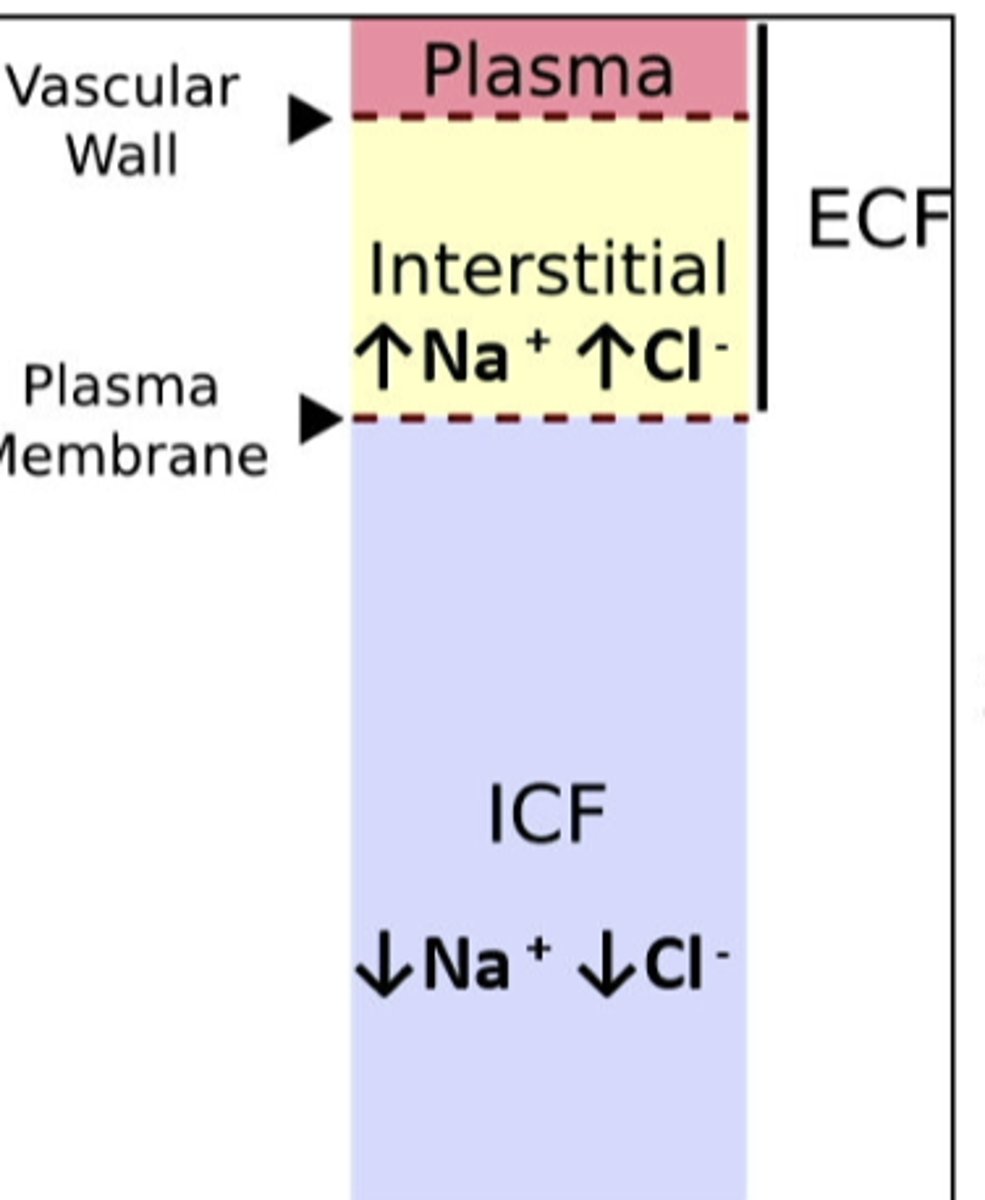
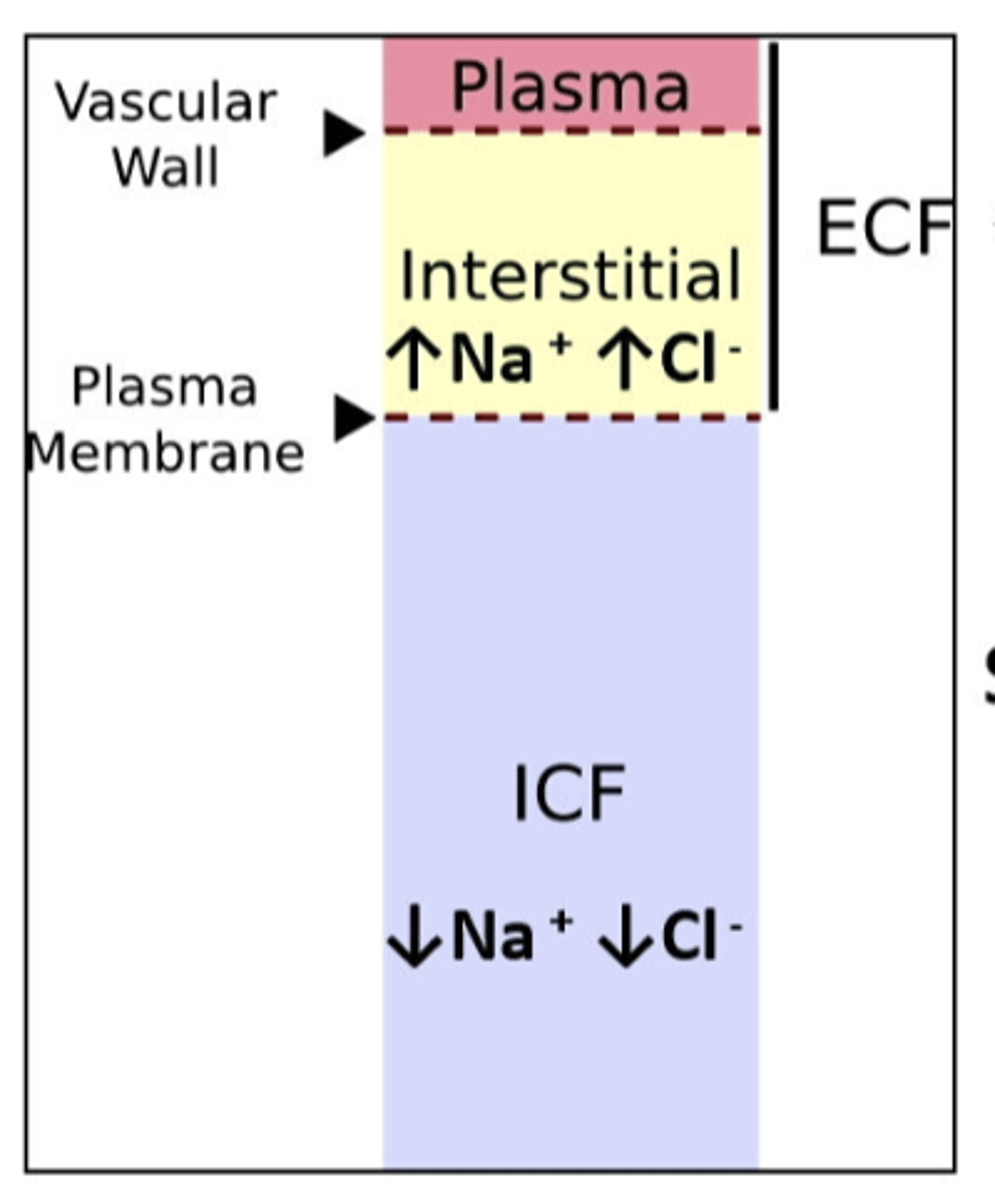
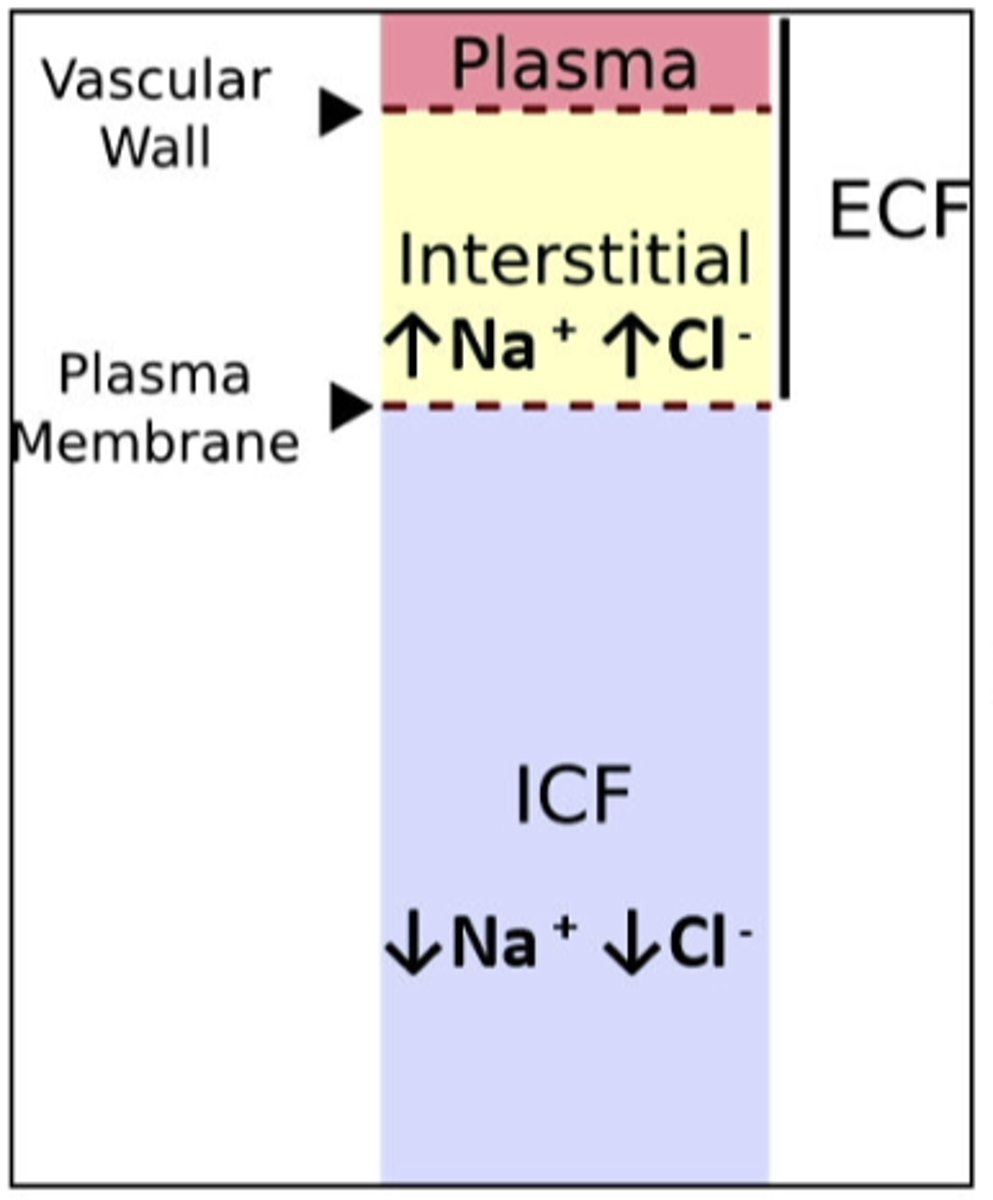
ECF volume
amount of sodium in body is a prime determinant of the ...
ECF
solutes (NaCl) are confined to the
increases
dietary salt (NaCl) overload and ____________ total solute in the ECF
decreases
dietary water overload ___________ total solute in the ECF

increase in plasma volume as a result of increased Na+
an excess of Na+ in the body isnt recognized by alterations in Na+ as you might think, but rather by the ...

osmosis
the movement of water across a semi permeable membrane
osmolarity
the total concentration of all solutes in a solution. defined as the number of osmoles of solute per liter of solution
penetrating solutes (nonpolar) and non penetrating solutes (polar)
osmolarity takes into account the total concentration of...
tonicity
the ability of an extracellular solution to make water move into or out of a cell by osmosis
osmolarity
a solution's tonicity is related to its ...
types of solutions
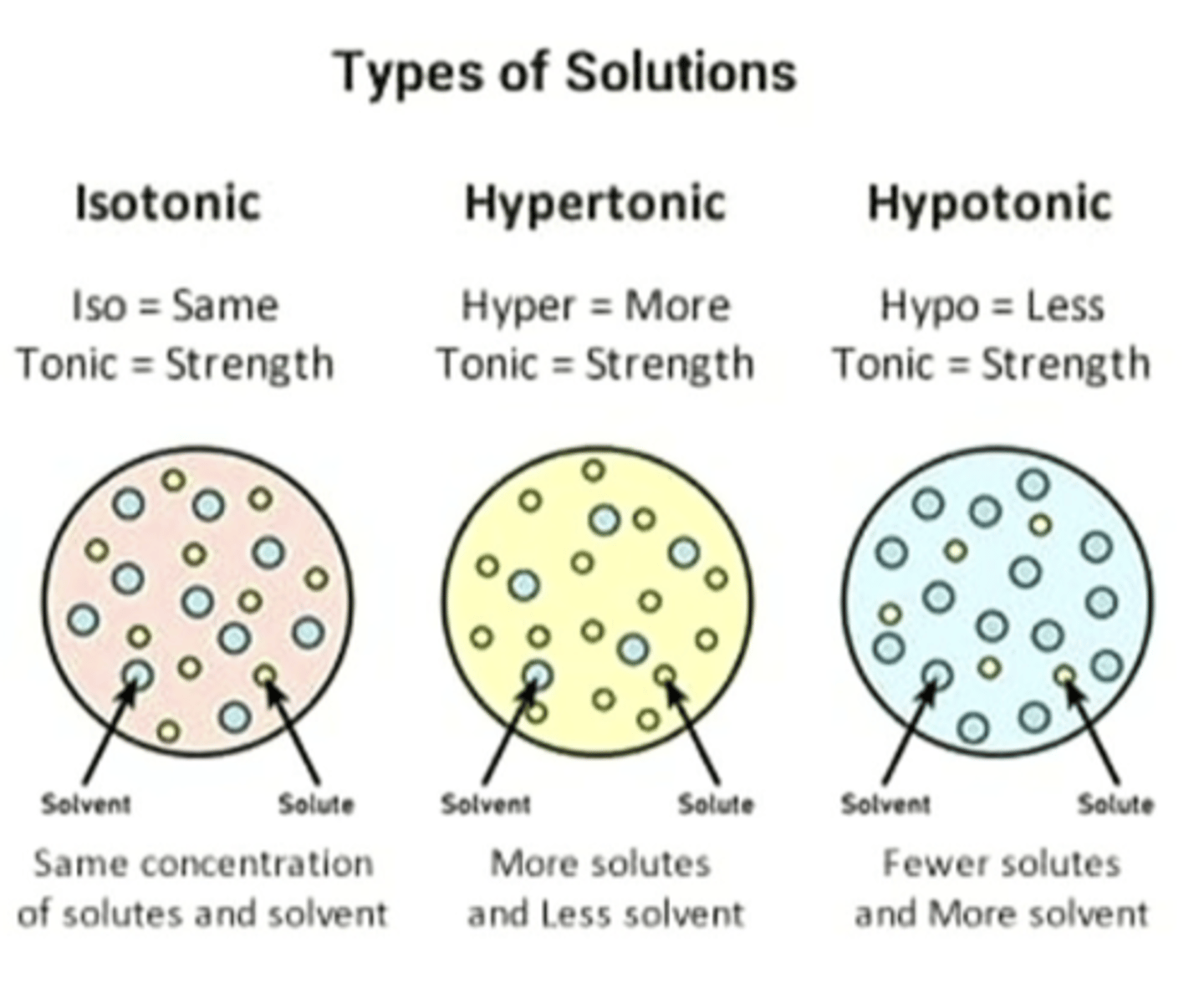
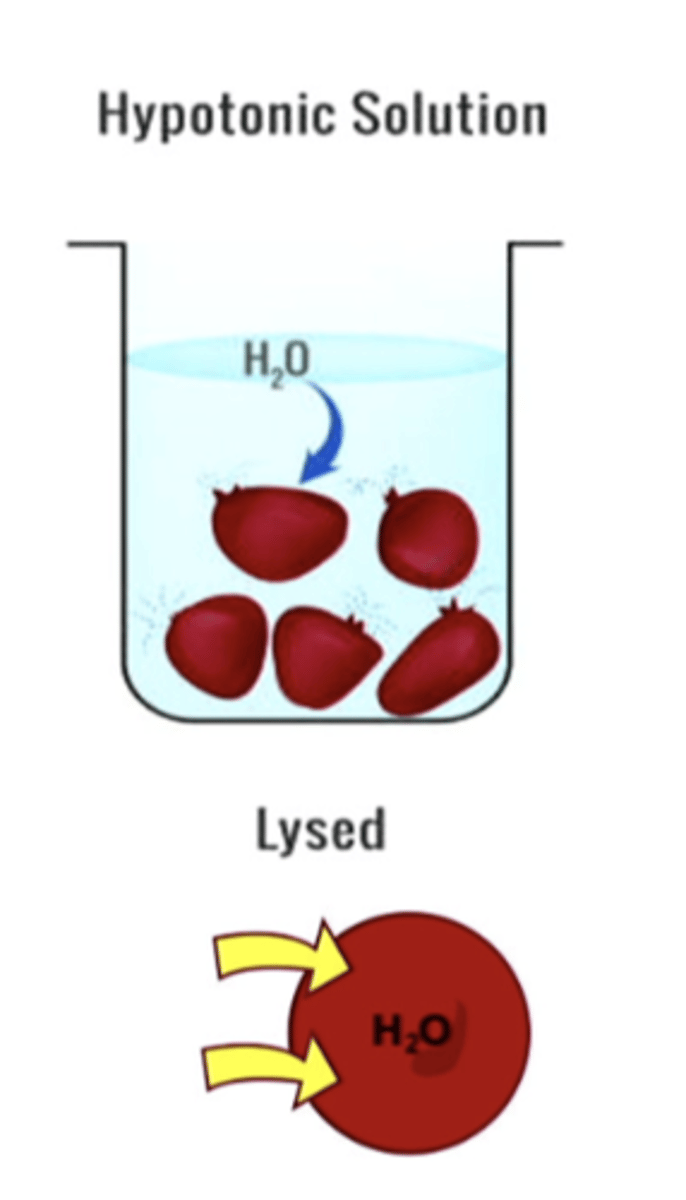
if you add 0.9% of a saline solution (isotonic solution) nothing will happen between the red blood cells and the environment. but if you have a hypotonic solution with low saline, water will come in the red blood cells because it is more concentrated. if you have a hypertonic solution with a higher saline concentration, the water will leave the cell and it will shrink
how can tonicity affect red blood cells
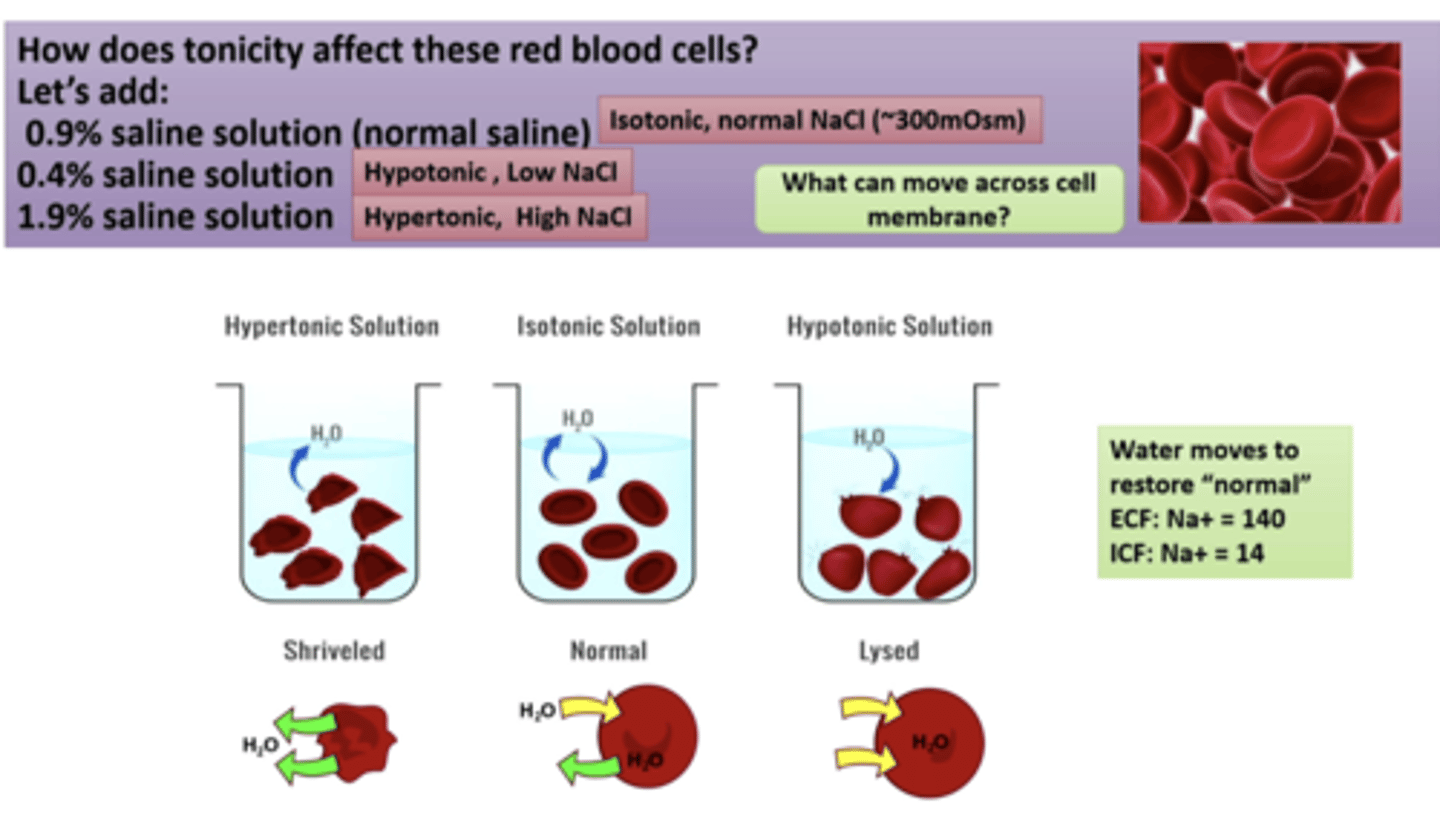
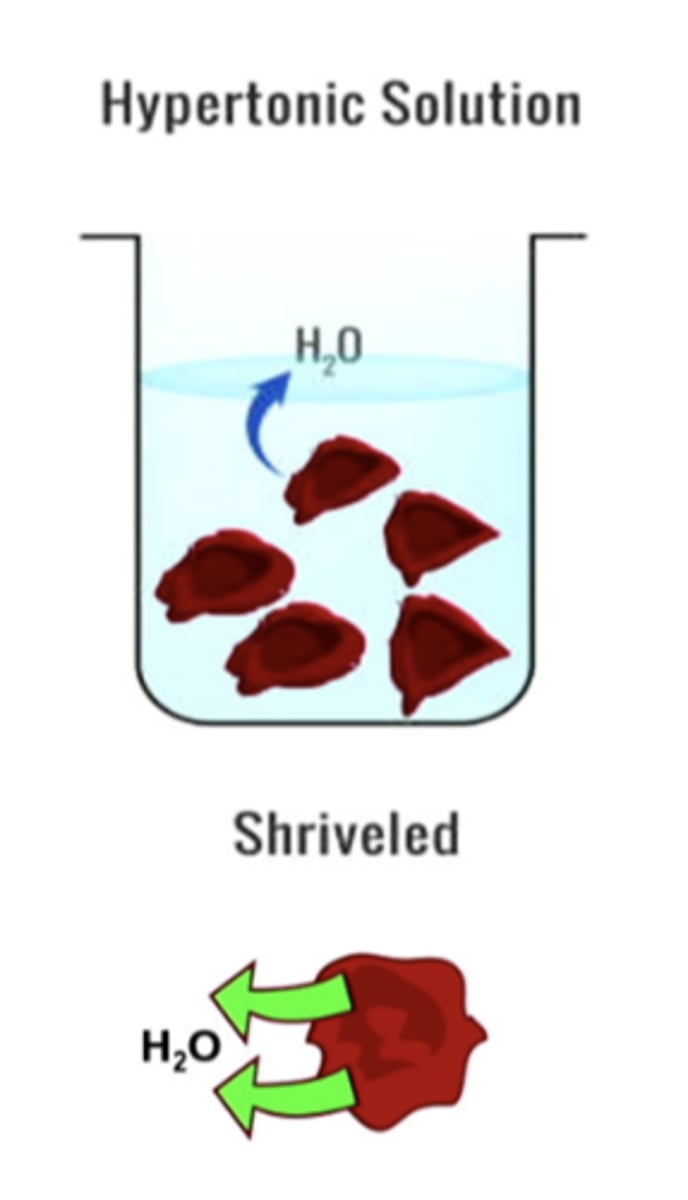
hypertonic solution
causing the cell to shrivel because the fluid will move out
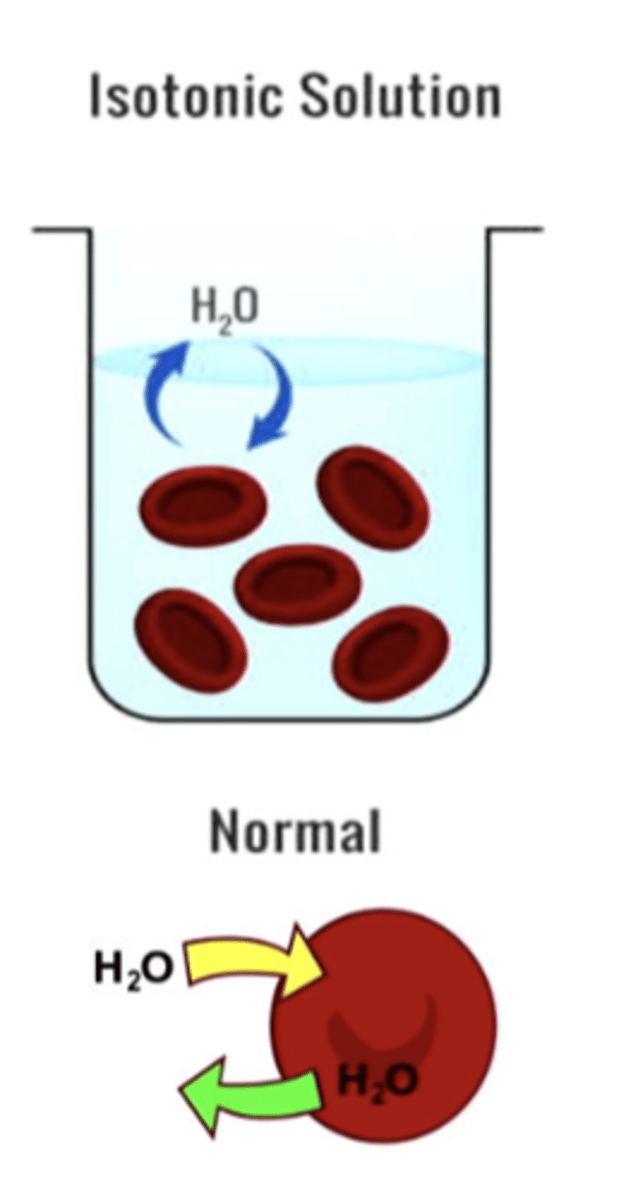
isotonic solution
Equal solute concentration inside and outside cell.
hypotonic solution
a solution that causes a cell to swell because fluid will move into the cell

cells
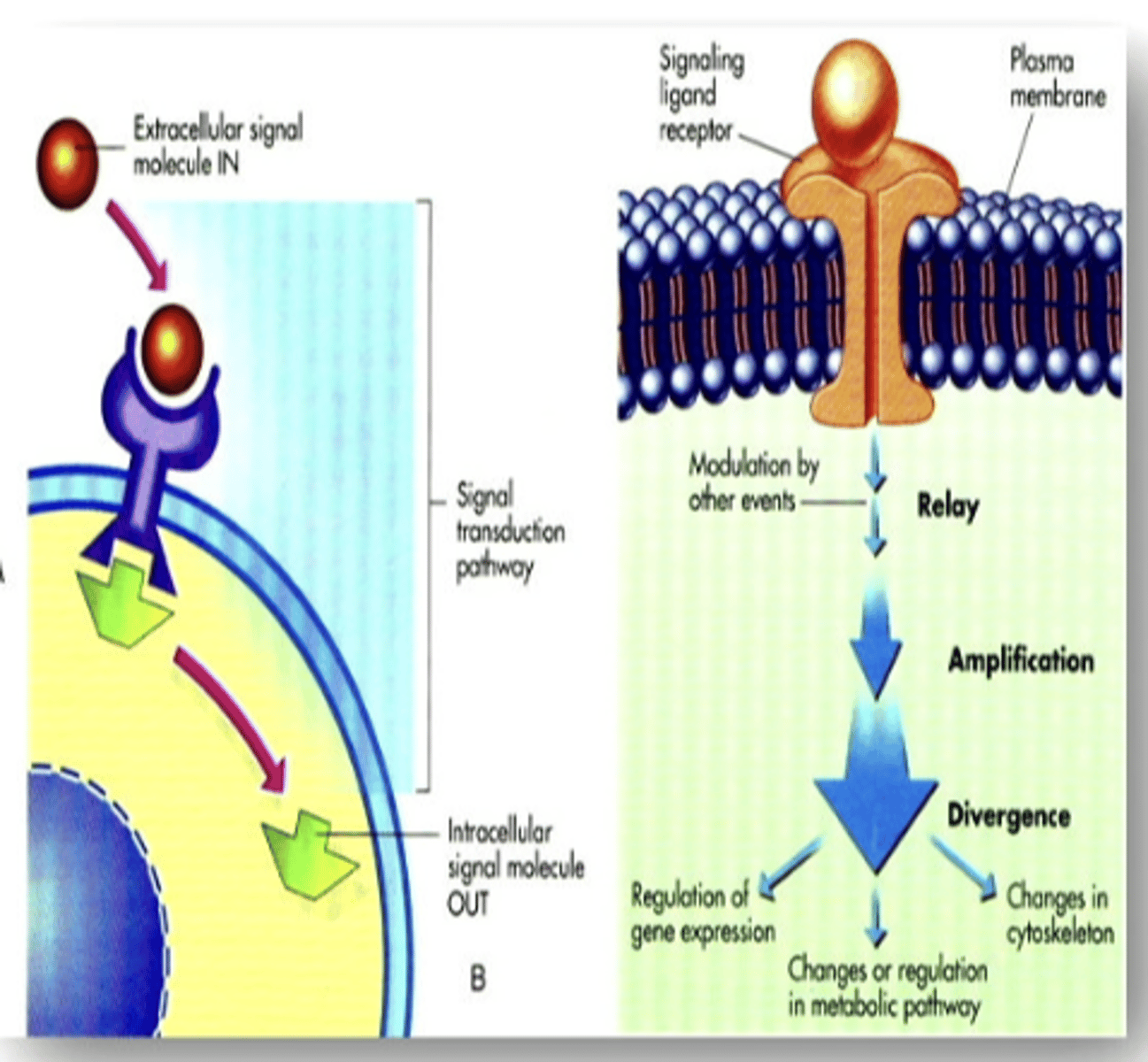
regulate their responses to chemical messengers by increasing (upregulation) or decreasing (downregulation) the number of active receptors on their surface
signal transduction
depends on cell type and location, response can be channel opening, action potential generation, changes in gene expression, etc.
autocrine, gap junctions, paracrine, endocrine, neuroendocrine (responds to NS stimulation), hydrophilic, lipophilic signal
what are the different types of cell communication
autocrine
cell targets itself
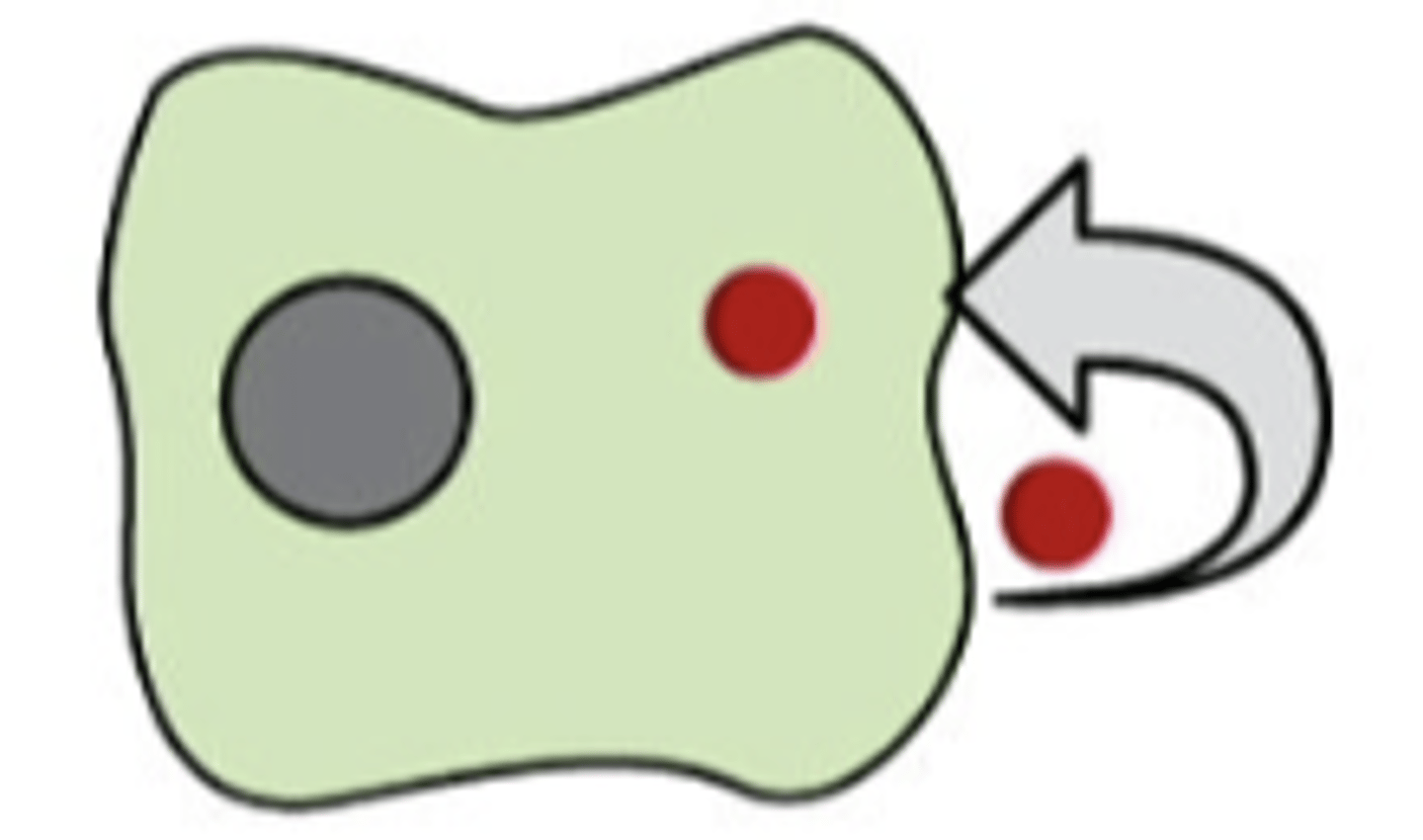
signaling across gap junctions
cell targets a cell connected by gap junctions
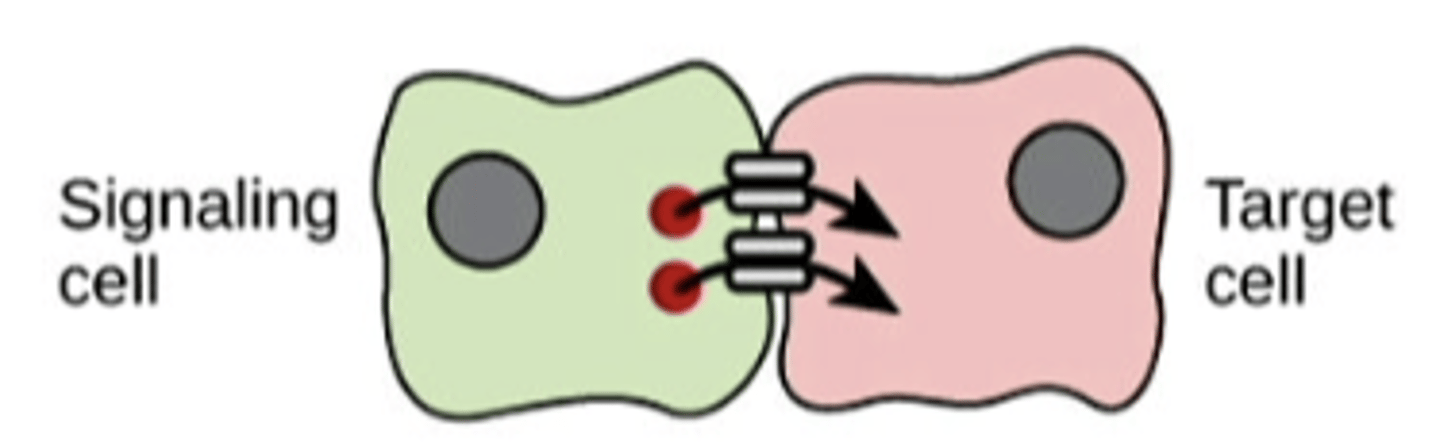
paracrine
cell targets a nearby cell
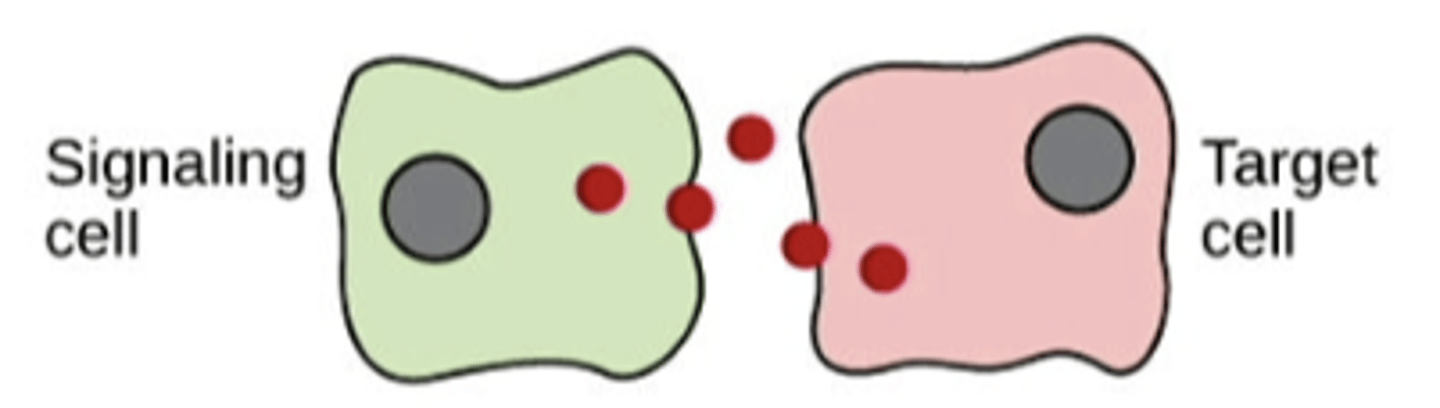
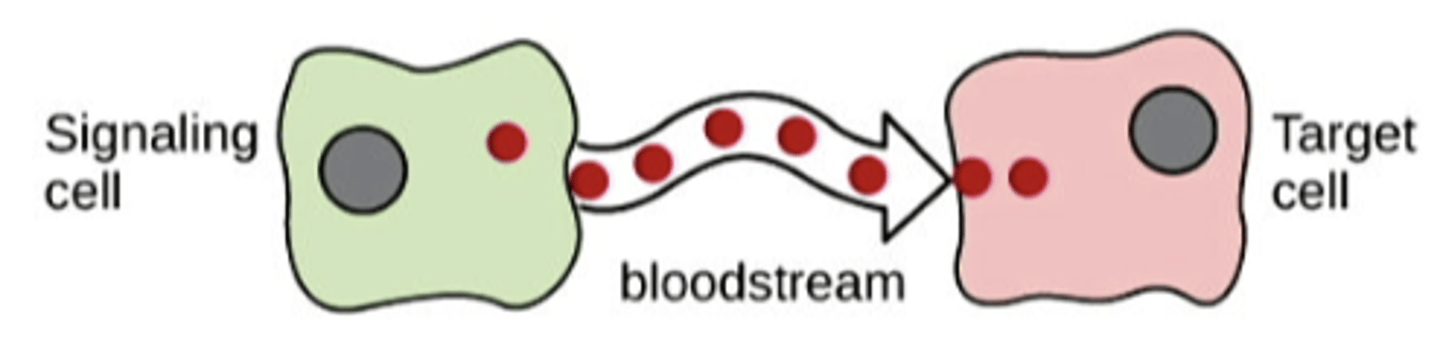
endocrine
cell targets a distant cell through the blodstream
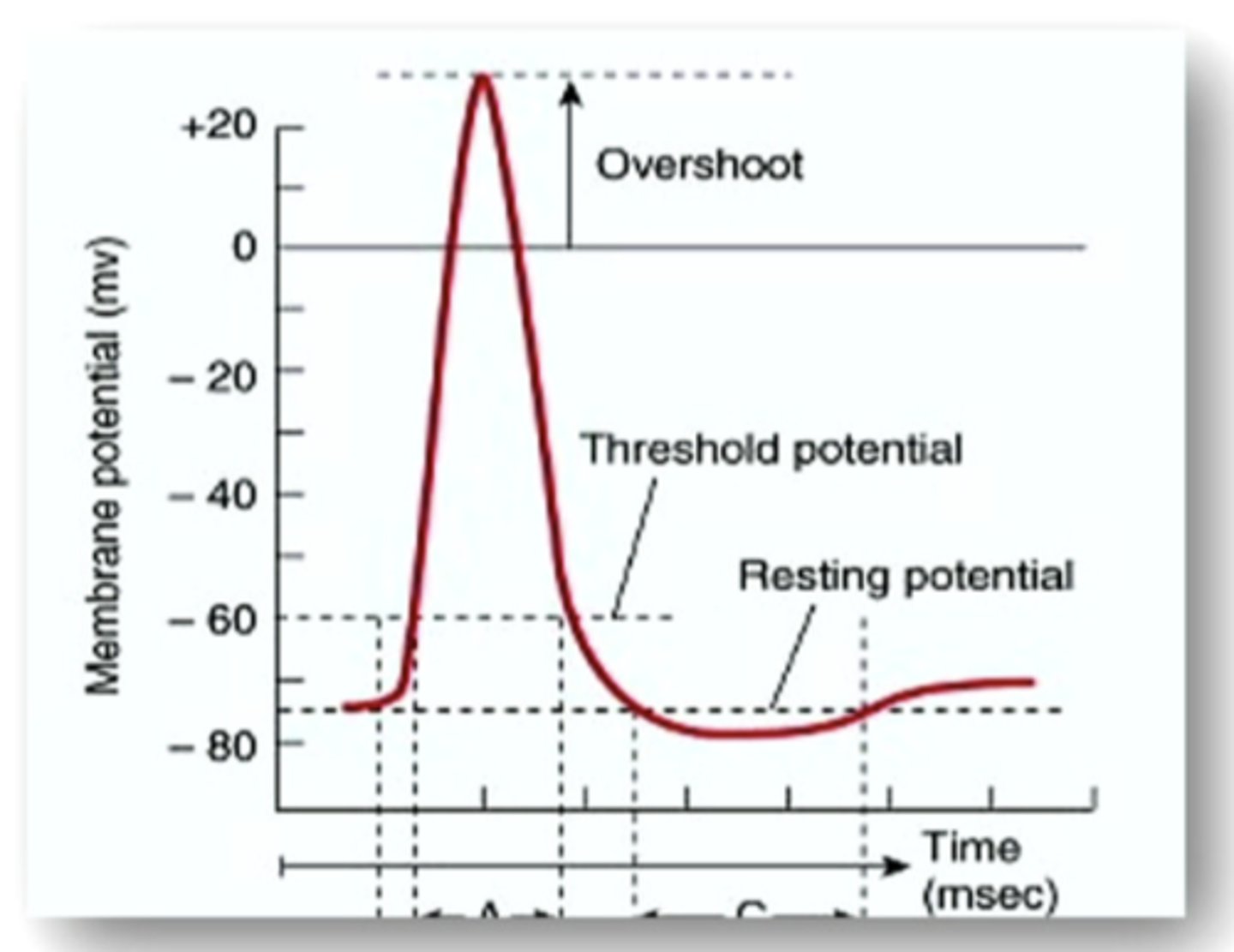
electrical potential
electro-chemical gradient, inside of cell is negative compared to outside
resting membrane potential
the electrical charge of a neuron when it is not active
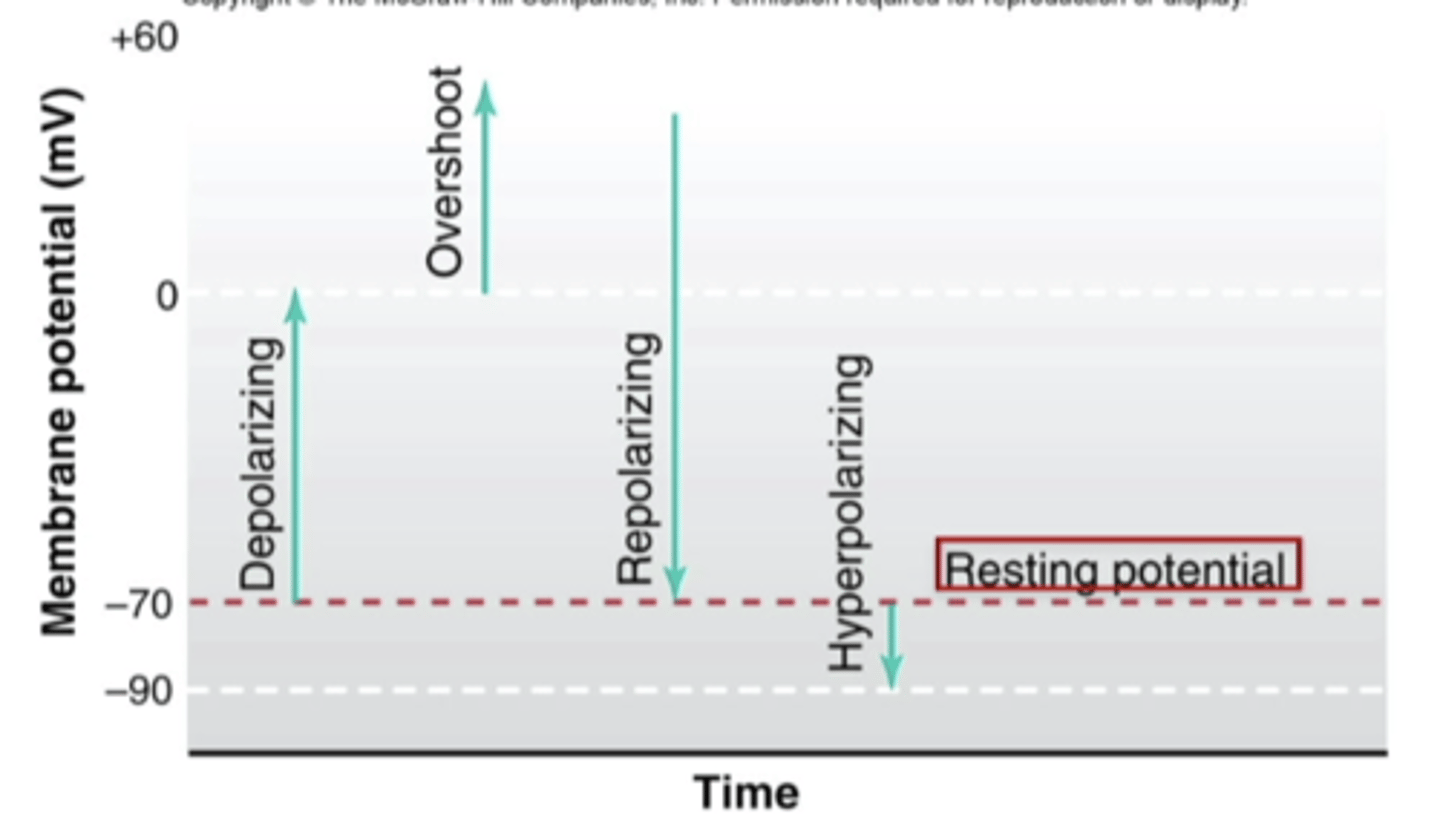
graded potentials
hyperpolarize (IPSP), depolarization (EPSP)
action potentials
short periods of electrical activity at the membrane of a neuron, responsible for the transmission of signals within the neuron
neurons
communicate by chemical and electrical signals
depolarization
Loss of a state of polarity; loss or reduction of negative membrane potential
repolarization
Return of the cell to resting state, caused by reentry of potassium into the cell while sodium exits the cell.