1(b) Variety of living organisms
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1.2 describe the common features shown by eukaryotic organisms: plants, animals, fungi, and protoctists. 1.3 describe the common features shown by prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria. 1.4 understand the term 'pathogen' and know that pathogens may include fungi, protoctists, bacteria and viruses
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Eukaryotic organisms
Organisms that have a nucleus.
→ Animals, Plants, Fungi, Protoctists
Prokaryotic organisms
Organisms that do NOT have a nucleus.
→ Bacteria
Taxonomy
The study of classification of living organisms.
Characteristics of Animals
multicellular
do not have a cell wall
store carbohydrates as glycogen (=many glucose molecules→polysaccharide)
cells do not contain chloroplasts, not able to carry out photosynthesis
usually have nervous coordination and are able to move from one place to another
Example of Animals
Mammals, e.g. humans
Insects, e.g. houseflies and mosquitos
Characteristics of Plants
multicellular
have a cell wall made of cellulose
store carbohydrates as starch or sucrose
cells contain chlorophyll and are able to carry out photosythesis
Example of Plants
flowering plants such as a cereal
herbaceous legume such as beans, peas
Characteristics of Fungi
not able to carry out photosythesis
body usually organised into a mycelium (network of fibres) made of hyphae (thread-like structure) which contain many nuclei.
some are unicellular, some are multicellular
have a cell wall made of chitin
feed by extracellular secretion of digestive enzymes onto food material and absorption of the organic products(=saprotrophic nutrition)
may store carbohydrates as glycogen
Examples of Fungi
single-celled: yeast
typical fungal-hyphal structure: Mucor (makes bread rise)
Characteristics of 1.Protoctists
microscopic, unicellular
some, like Amoeba, that lives in pond water, have features like an animal cell
others, like chlorella, have chloroplasts and are more like plants
pathogenic example: Plasmodium(causes malaria)
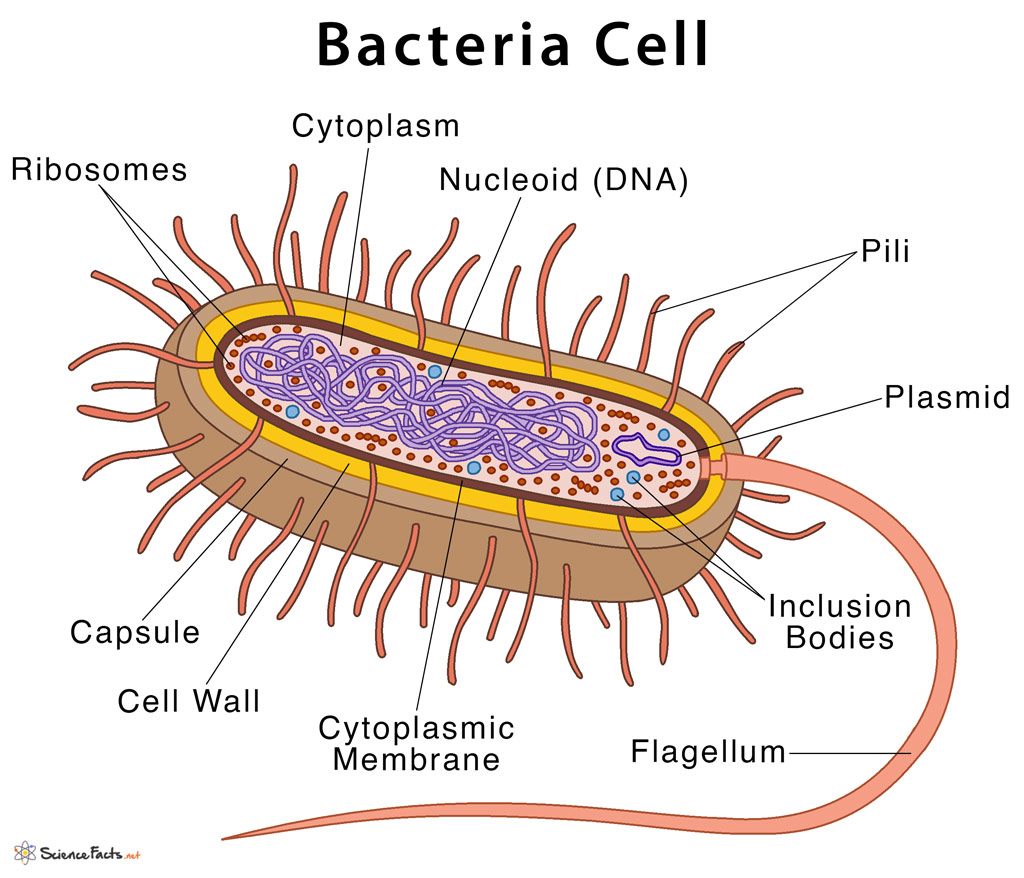
Characteristics of Bacteria
microscopic unicellular organisms
have a cell membrane, cell wall made of peptidoglycan, cytoplasm, plasmids(small loops of DNA)
lack a nucleus but contain a circular chromosome of DNA
some can photosythesise but most feed off other living or dead organisms
some have flagella for movement
some have a slime layer or capsule
Examples of Bacteria
Pneumococcus, a spherical-shaped bacteria that causes Pneumonia
Lactobacillus bulgaricus (latin scientific name, needs to be underlined in the exam!!!!), a rod-shaped bacteria used in the production of yoghurt from milk
Characteristics of Virus
not living organism
small particles, smaller than bacteria
contain one type of nucleic acid, either RNA or DNA
have a protein coat
lack a cellular structure
wide variety of shapes and sizes
infect all types of living organisms
are parasitic- can only reproduce inside living cells
Examples of Virus
Tobacco mosaic virus - causes discolouring of the leaves by preventing the formation of chloroplasts
HIV causes AIDS
Influenza causes flu
Pathogen
Organism or virus that cause disease. May include fungi, protoctist, bacteria, virus.
A pathogenic example of a protoctist
Plasmodium, which causes malaria.
A pathogenic example of a bacterium
Pneumococcus, spherical-shaped bacterium that causes Pneumonia.
A pathogenic example of a fungus
Athlete’s foot