Important LC - Eggs!
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Parasitology, added some others ++
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
?
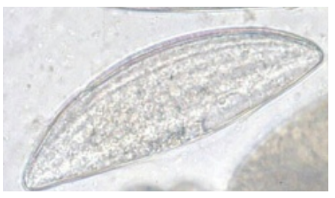
Syphacia obvelata - Parasitic nematode
5 layers of shell?, crescent shaped, flattened on one side, unembryonated, S/M?, grey
?
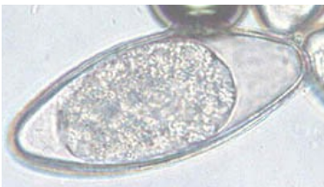
Aspiculuris tetraptera - parasitic roundworm, often found in intestines of lab mice
oval, complex shell of 5 layers, unembryonated, grey, S. ?
?
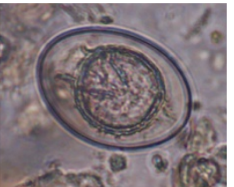
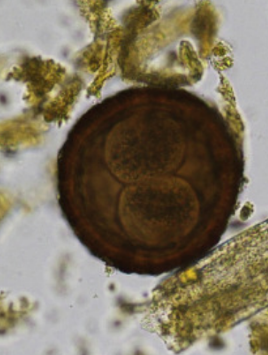
Hymenolepis nana - cestode
oval, S (30-50 um), colorless shell/grey, embryonated,
can be in humans, rodents (mice, rats)
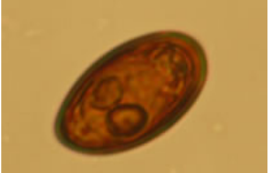
?
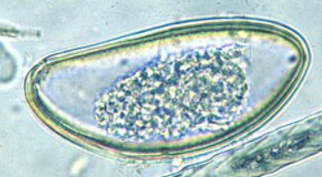
Dicrocoelium dendriticum
liver fluke, affecting primarily livestock
Description: S, oval, asymmetric, 2 thin shells, embryoanated, brown - coffee bean with eyes. With operculum.
Location: bile duct, gall bladder
Trematoda
?
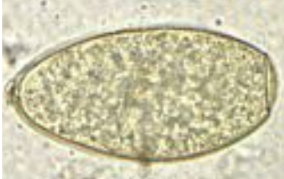
Fasciola hepatica
liver fluke, infects livestock, causing fascioliasis
Description: L, oval, symmetrical, 2 thin shells, unembryonated, yellow With operculum
Location: Bile duct, liver
Trematoda
?
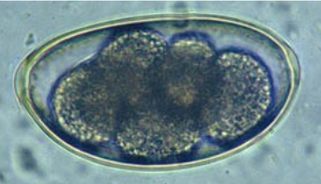
Syngamus trachea “gapeworm” - primarily affects birds, causing resp. issues
ellipsoidal shape, S (85-93um), red/brown, thick shells with 2 plugs at either ned, contains morula?
?
Passalurus ambiguus - pinworm found in rabbits, linked with intestinal infections.
M/L, oval, asymmatrical, mucoid plug at one pole, 2 thin shells, unembryonated, grey
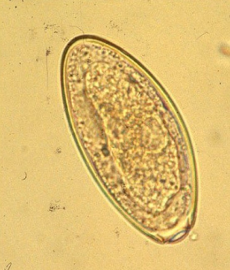
?
Oxyuris equi - equine pinworm, infests large intestine of horse
Description: M, elliptical, 3 thick shells, unembryonated, light brown, unipolar plug
Location: Large intestine
nematoda
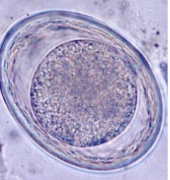
?
Toxascaris leonina - roundworm, infects dogs/cats
description: M, spherical, 3 thick shells, unembryonated (1 light blastomere), light brown/pinkish/colorless
Location: SI (EHP migration)
Nematoda
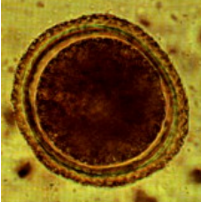
?
Toxocara canis - roundworm in dogs
Description: M, subspherical, 3 thick shells, unembryonated (1 dark blastomere), dark brown
Location: SI (EHP migration)
Nematoda
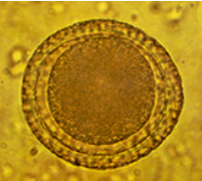
?
Toxocara vitullorum - roundworm, in cattle
M, Spherical, 3 thick shells (rough surface), unembryonated (1 cell), dark brown
location: SI (calf)
Nematoda

?
Trichuris spp. - genus of roundworms, including whipworms parasitic in the intestines of many animals
T. ovis, T. suis, T. vulpis
M, lemon-shape, symmetrical, 2 thick shells, unembryonated, red-brown, 2 prominent pole plugs
location: Large intestine
Nematoda (T. suis, T. vulpis (dog), T. campanula (cat), T. ovis (cattle, sheep, goat, ru), T. trichiura (humans)
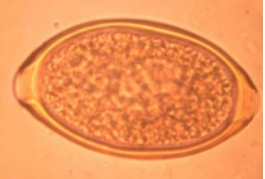
?
Capillaria spp. - genus of nematodes that infect urinary system of mammals
M, barrel-shaped, asymmetrical, 2 thin shells, unembryonated, light brown/yellow-green, 2 flat polar plugs
Location (depends on species):
Aerophilia: resp. system
Plica: bladder
Hepatica: liver
Nematoda
?
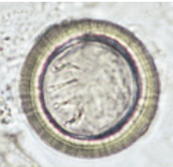
Taenia spp. - genus of tapeworms (cestoda)
S, rounded, 3 thick shells, embryonated, light-brown-gray
Location: SI
?
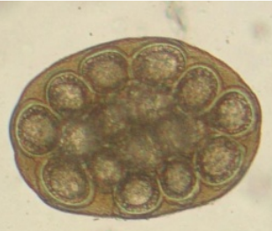
Dipylidium caninum - tapeworm, infests dogs/cats
“egg packets” inside proglottids, usually containing clusters of eggs
spherical, thin shelled, contains an oncosphere (hexacanth larvae) with six hooklets, brown.
?
Parascaris equorum - roundworm
M, spherical, 3 thick shells, unembryonated (1 blastomere), dark brown
location: SI (EHP migration)
Nematoda

?
Ascaris suum - roundworm (nematoda) - pigs
M, spherical, 3 thick shells (rough surface), unembryonated (1 cell), brown
Location: SI
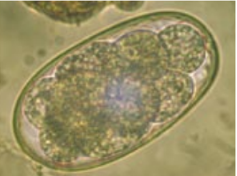
?
Trichostrongylidae - family of nematodes that typ. infect the GIT of Ru. (many blastomeres)
Eq: Strongylus spp. (few blastomeres)
Su: Oesophagostomum spp. (many blastomeres)
Ca: Ancylostoma caninum (4-8 blastomeres)
M, oval, symmetric, 2 thin shells, unembryonated, gray
location: Large intestine
Nematoda
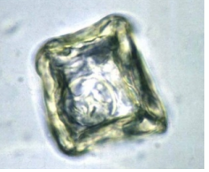
?
Moniezia spp. - cestode, Ru
Small ru: M. expansa
Large Ru: M. benedeni
M, 3-4-5 angulate, 3 thick shells, embryonated (oncosphere), transparent/grey + pyriform apparatus.
Location: SI
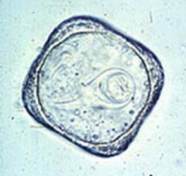
?
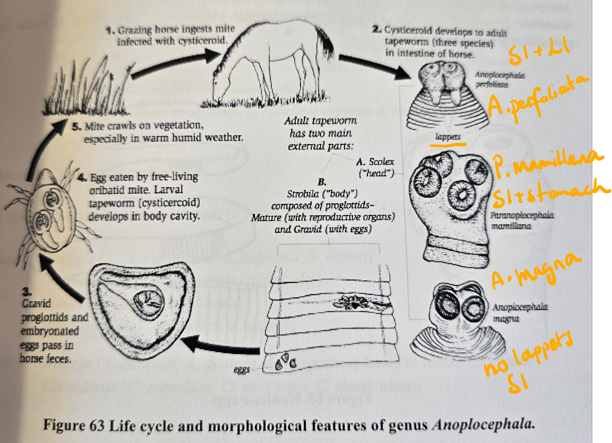
Anoplocephala spp. - tapeworm genus (cestoda)
M, 3-4-5 angulate, 3 thick shells, embryonated (oncosphere), transparent-grey/light brown + pyriform apparatus
Location: Perfoliata - iliocecal junction, magna & mamillana - SI
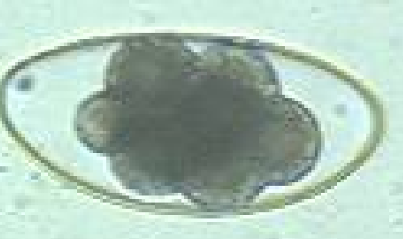
?
Nematodirus spp. - nematodes
XL, oval, symmetric, 2 thin shells, unembryonated (8 dark blastomeres), gray
Location: SI
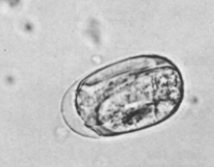
?
Strongyloides spp. - roundworms (nematode)
S, oval, symmetric, 2 thin shells, embryonated (L1), transparent
Location: SI
Animal: Dog, cat, humans (stercoralis)
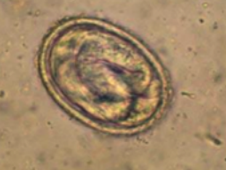
?
Metastrongylus spp. - nematodes, infecting lungs of pigs (Lung worm)
S, spherical, symmetrical, 2 thick shells, embryonated (L1), transparent
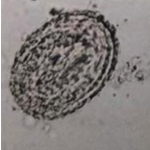
?
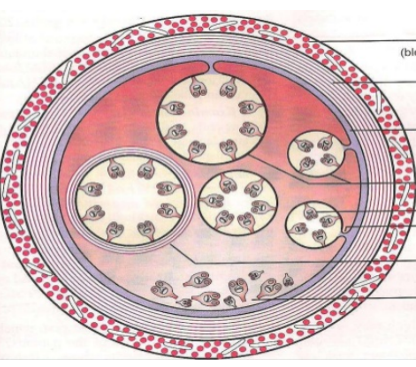
Echinococcus - genus of tapeworms (cestode), causing hydatid disease in humans
Large fluid like, produces multiple infective stages (protoscolies, invaginated scolices containing suckers, hooks)
would maybe describe: S, rounded, 3 thick shells, embryonated, light-brown-gray
fibrous capsule of host and parasite, germinal layer, daughter cyst, hydatid cyst with protoscolex.
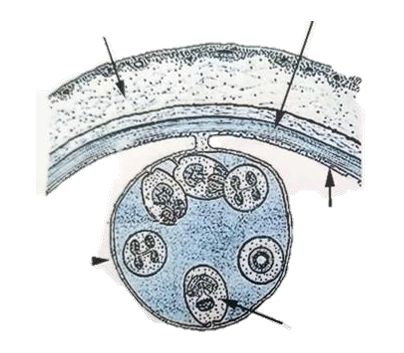
?
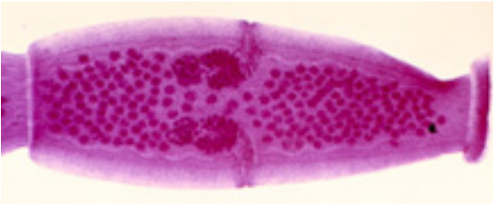
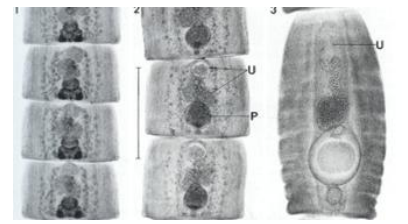
Proglottids of Dipylidium caninum
such proglottids have two genital pores, one in the middle of each lateral margin.
Proglottids may be passed singly or in chains, and sometimes can be seen from anus
They are pumpkin-seed shaped when passed and often resemble rice grains when dried.
Genital pores are visible in carmine-stained proglottid shown in picture
?
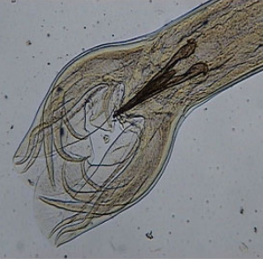
Bursa copulatrix - bell shaped expansion of cuticle of tail of many male nematode worms - functioning as a copulatory structure.

?
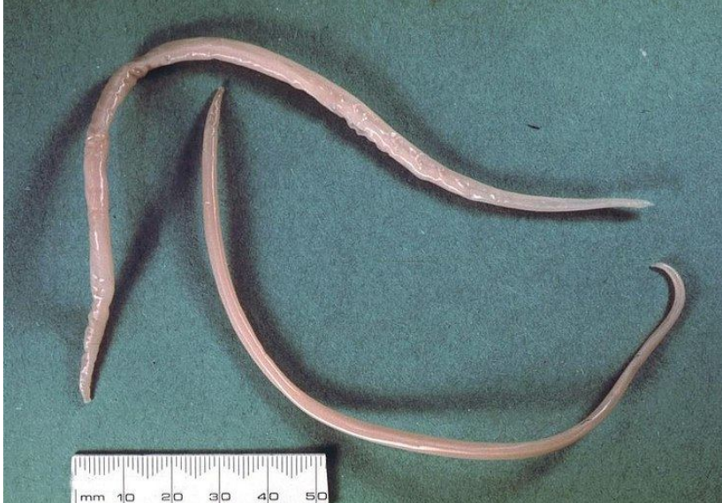
Ascaris suum (large roundworm - nematode) - of pig
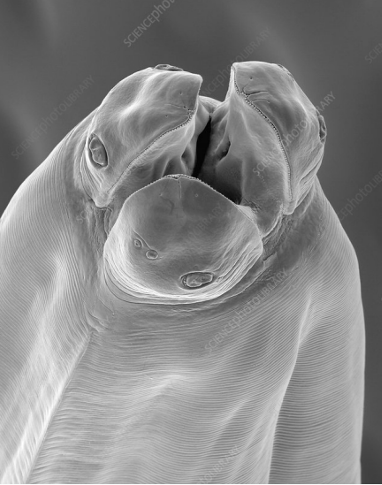
?
Toxocara canis - roundworm (nematode)
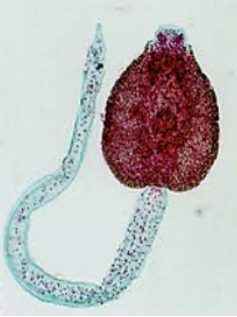
Which stage is this? (trematode developmental stage)
Cercariae (parthenogony)
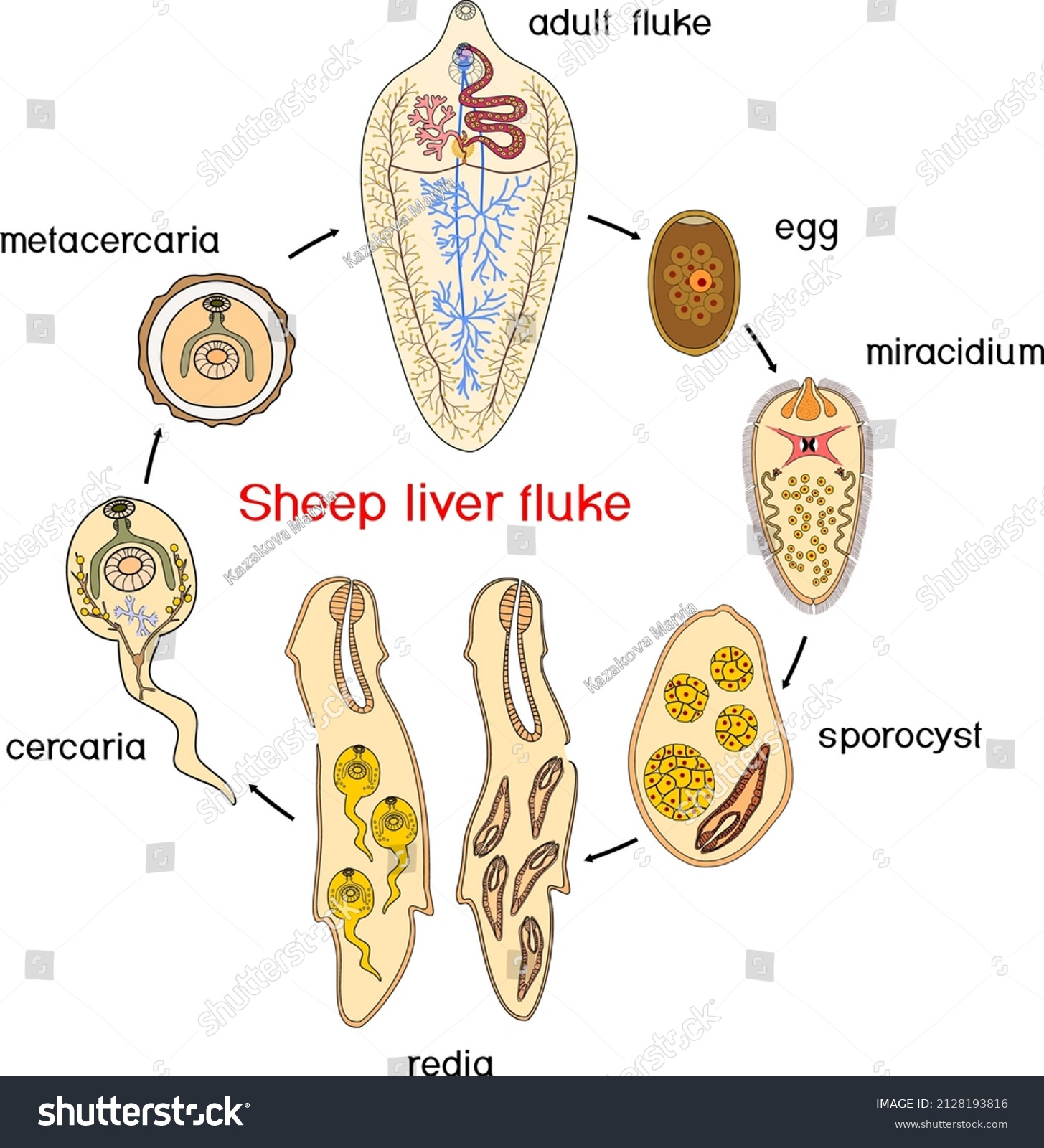
Life cycle of?
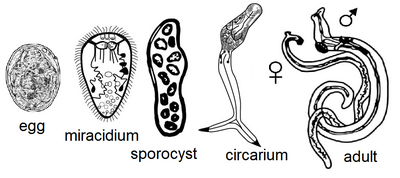
Fasciola Hepatica - Trematode
Indirect, location: bile duct, liver
IH: water snail (lymnaeidae)
FH: Ru, eq, man
Process:
adults release unembryonated eggs → biliary ducts of FH → feces → water → embryonation
eggs release miracidia → infects freshwater snail (IH)
miracidia → sporocysts → rediae → cercariae
cercariae → into water → finds water plants to encyst to form metacercaria
Metacercaria (infective stage) → FH
After FH eats it → excyst in duodenum → intestine → liver parenchyma, develops into adults within bile ducts.
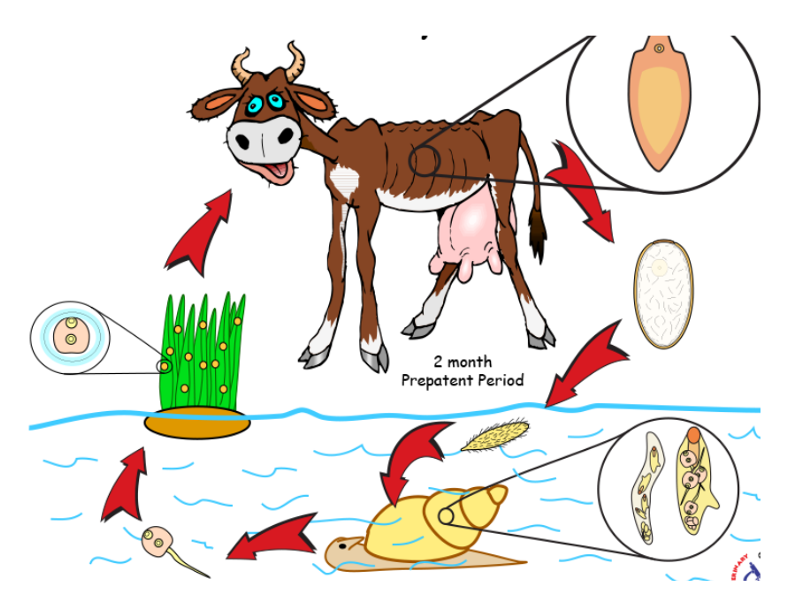
Life cycle of? what is the infective stage called?
Taenia saginata + cysticercus bovis
Taenia - Indirect LC, located in SI
IH: Cattle (T. saginata)
FH: humans
Process:
Eggs → feces from FH
Enters IH (cattle) → oncospheres released from egg → muscles
In muscle, develops into cysticercus bovis
FH eats infected uncooked/raw meat
parasite → SI → matures → released gravid proglottids with eggs by feces
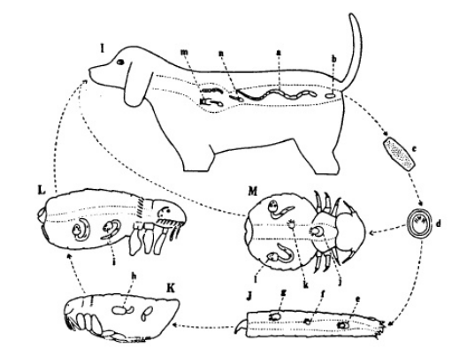
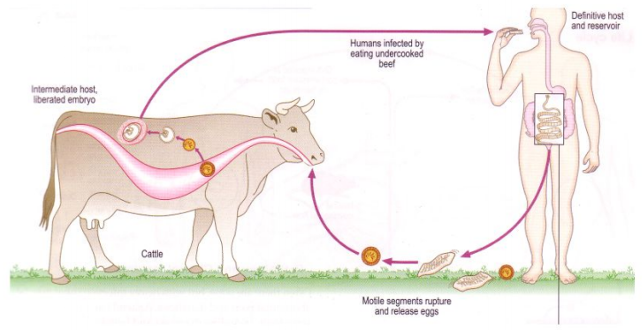
Life cycle of? What is the name of metacestode stage?
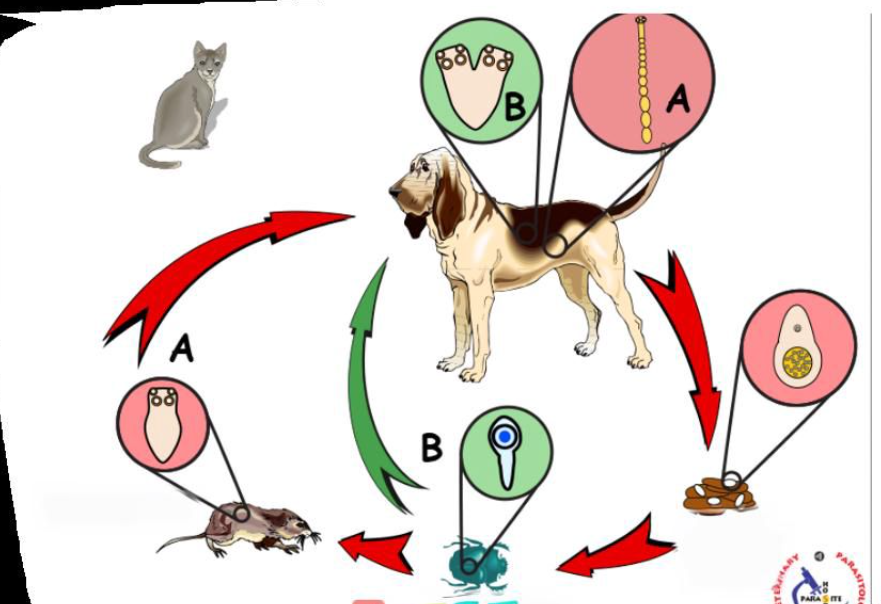
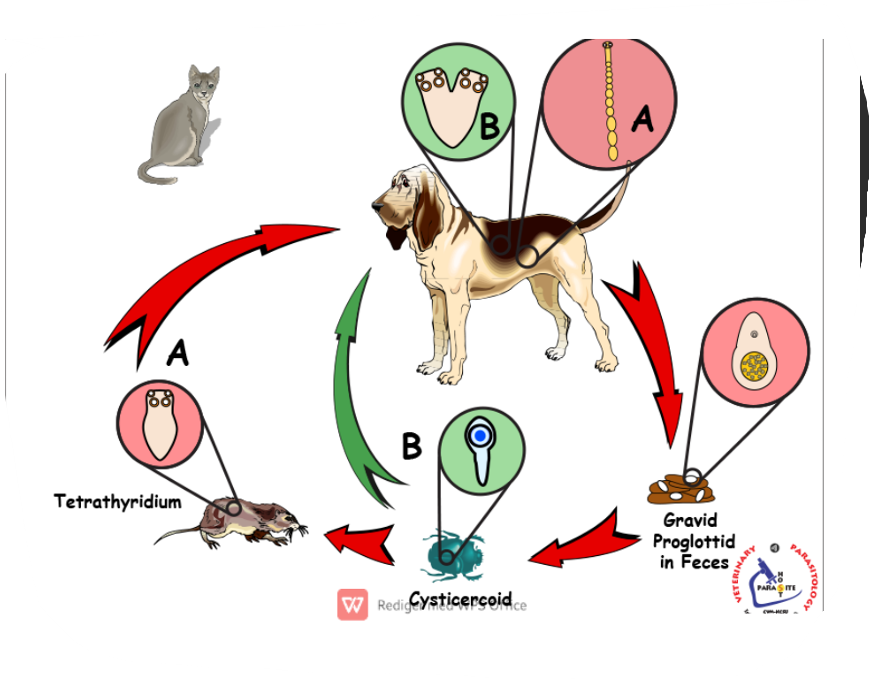
Dipylidium caninum
Indirect LC
FH: dog, cat, wild canids, fox, humans
Location: SI
IH: fleas, louse
Metacestode stage: Cysticercoid (infective stage)
Process:
Adult in FH → SI → gravid proglottids → sheds with eggs by feces
fleas ingest the eggs → egg develop into cysticercoid (infective larvae)
Flea larvae mature into adult → cysticercoid become infective
FH ingest flea → larva is released from flea → adult in intestine
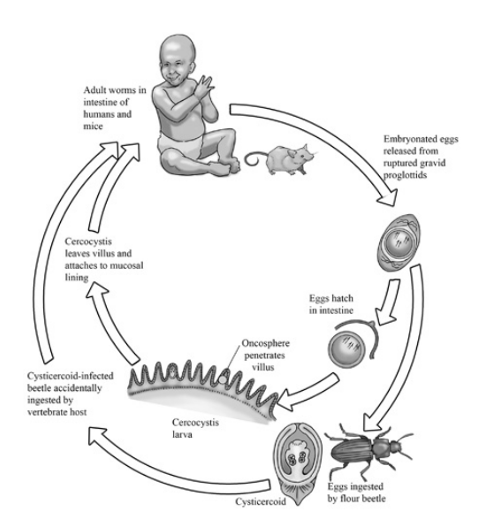
life cycle of?
Hymenolepsis nana (of family Hymenolepididae) - cestode, cyclophyllidae
FH: Rodents, humans
IH: can complete cycle without IH, but can also have beetles, flea, insects as IH
Location: SI
Process:
Direct cycle:
eggs ingested by humans
eggs release oncospheres → intestinal villi → develops into cysticercoids
cysticercoids → mature into adult → in SI → makes gravid proglottids → releasing eggs in feces
Indirect cycle (if IH is involved):
IH: eggs can be eated by arthropods like beetles or fleas → cysticercoids develops
humans get infected by eating these infected insects
life cycle of?
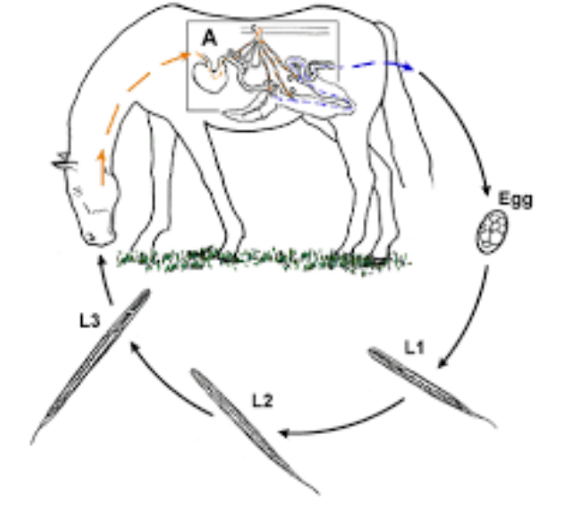
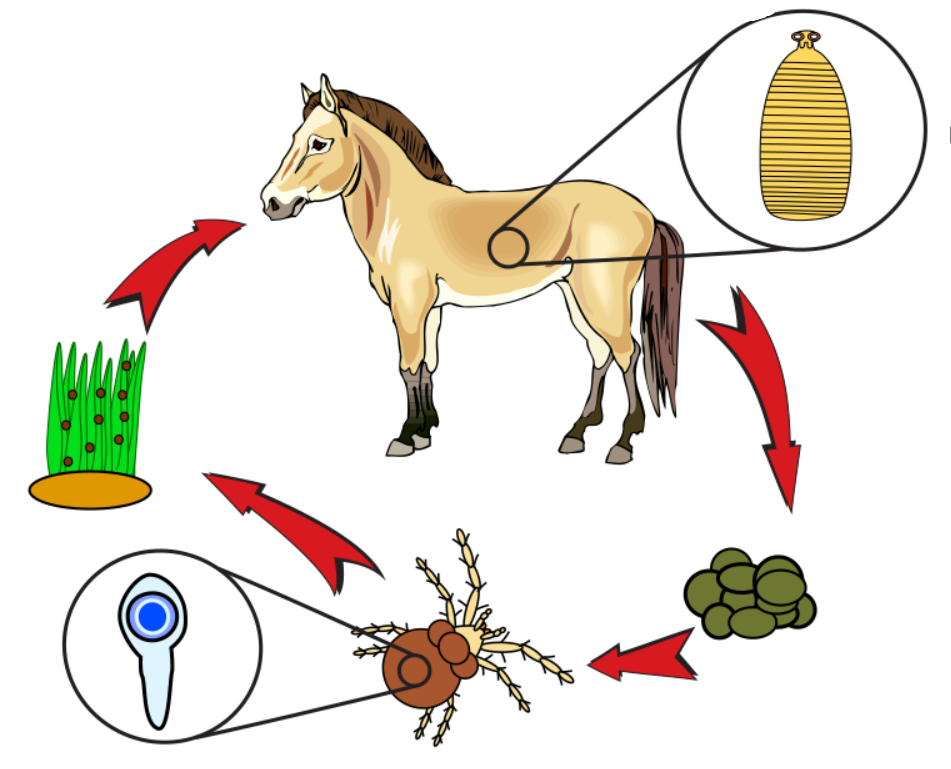
Strongylus spp. (strongylus vulgaris) - nematode
Direct LC, located in large intestine (Colon, cecum)
FH: horse
Process:
Eggs in feces, hatches in environment
Larva → L2 → L3
host ingest L3 larvae when grazing
Larvae → intestine → mucosa and molt into L4
L4 → small arteries → along endothelium to cranial mesenteric artery + branches
After few months → L5 and returns to intestinal wall
matures → eggs release with feces
Life cycle of?
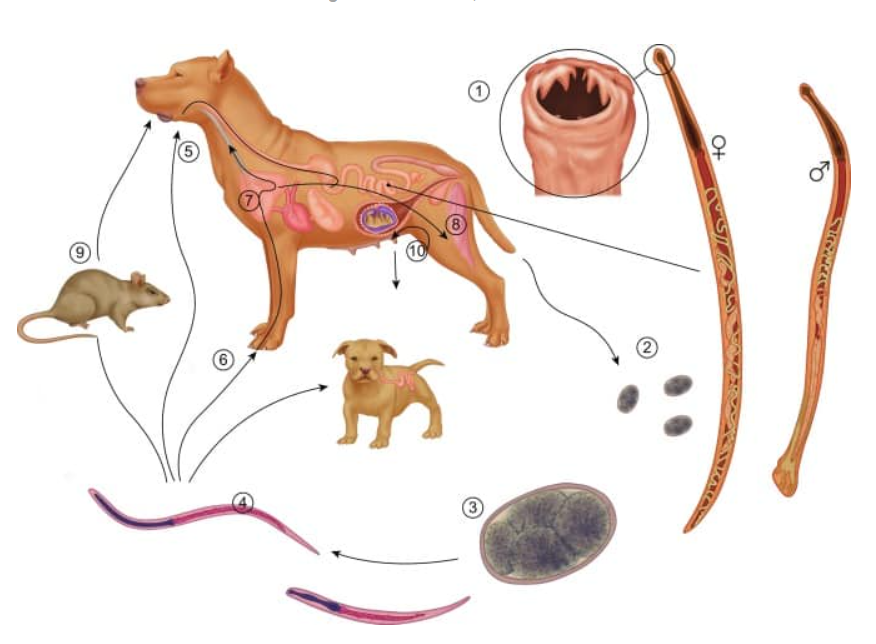
Toxocara canis (canis as there is dog in pic)
direct LC, located in SI, diagnostic stage - umebryonated eggs in feces, infective - embryonated egg with L3
entero-hepato-pulmonal migration
FH: car (canis - dog, cat - cati, leonina - both), accidentally man
paratenic host: various small mammals, can be ingested by dogs (no development of parasite but remains infective)
Process:
eggs shed in feces of FH
eggs embryonate in environment with L3 larvae
Eggs ingested by host → can be FH (dog) or paratenic host (mouse, rabbit etc.)
In FH - larvae mature into adults in SI
vertical transmission: adults can be transmitted from mother to offspring
L3 larvae can get to other tissues → liver, lungs and brain
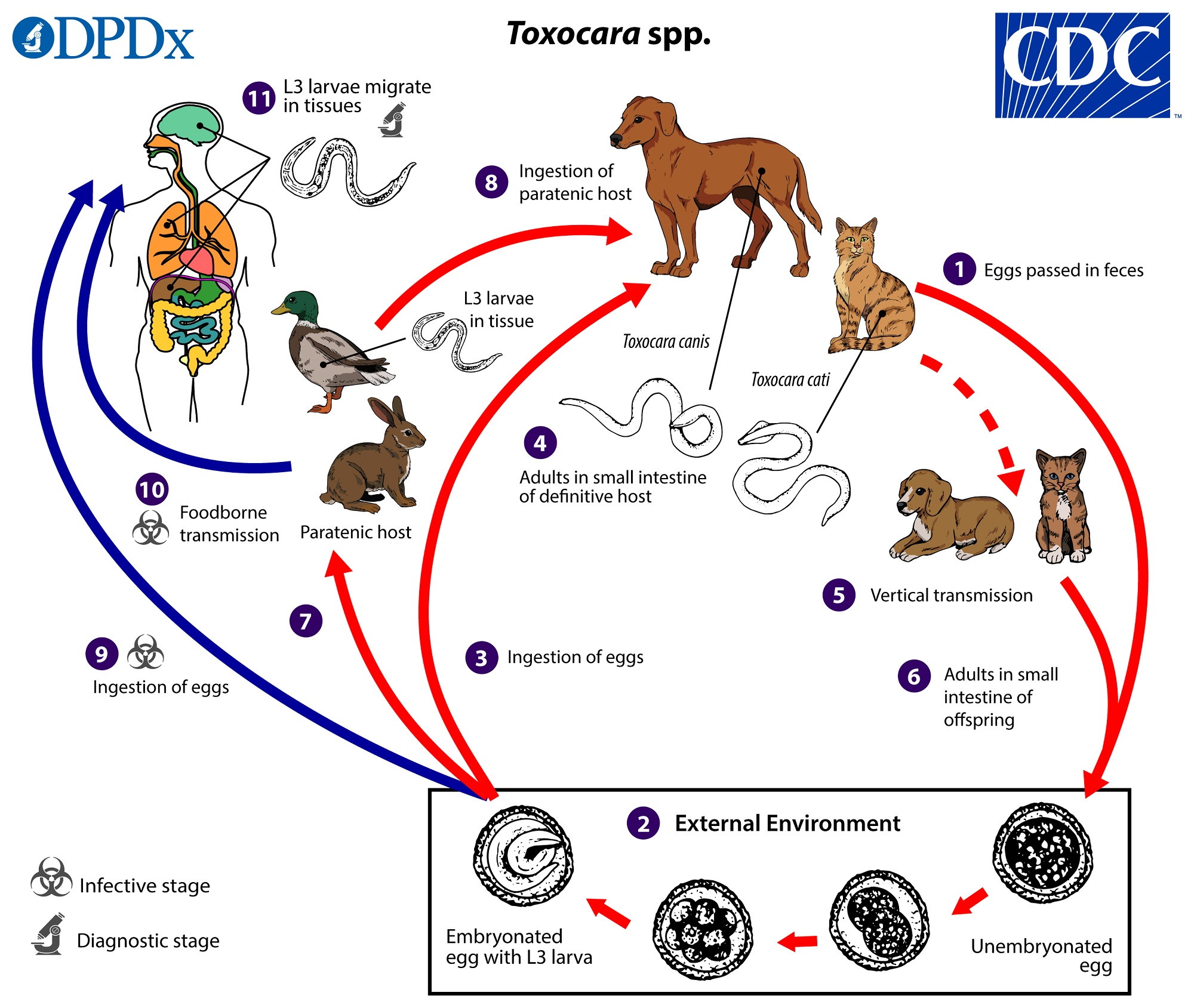
Life cycle of?
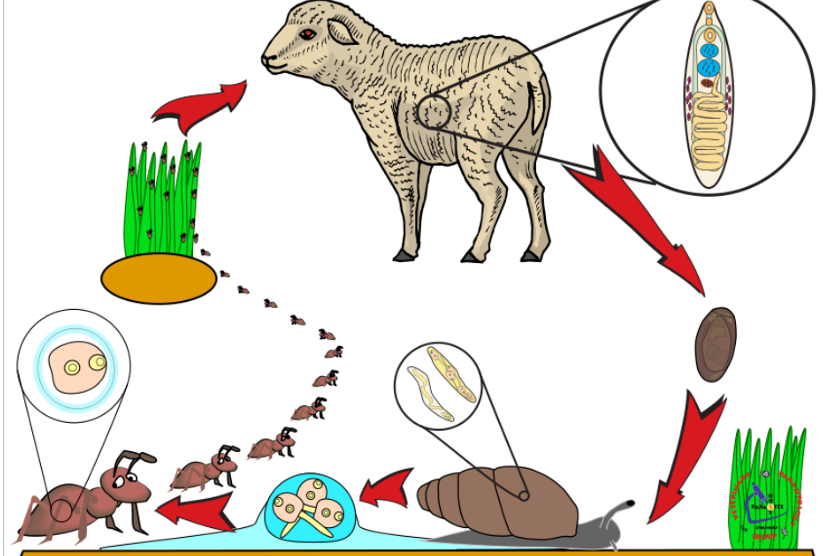
Dicrocoelium dendriticum (dicrocelidae spp.) - trematode
Indirect LC, located in Bile ducts, gall bladder
IH: 1st: land/terrestrial snail, 2nd: Ant
FH: reptiles, birds, mammals
infective: metacercariae
Process:
Eggs with miracidia in feces of FH (ru) → eggs eaten by 1st IH (snail)
miracidia → sporocyst → cercariae → respiratory chamber → shed from snail
ant eat slime ball with cercariae → intestine → metacercariae
FH eats ant, metacercariae excyst in SI. Worms migrate to bile duct and mature.
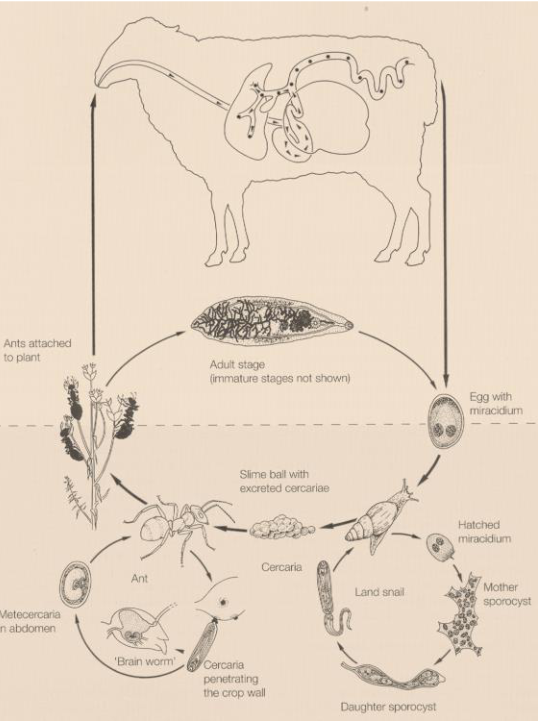
Life cycle of? What is the metacestode?
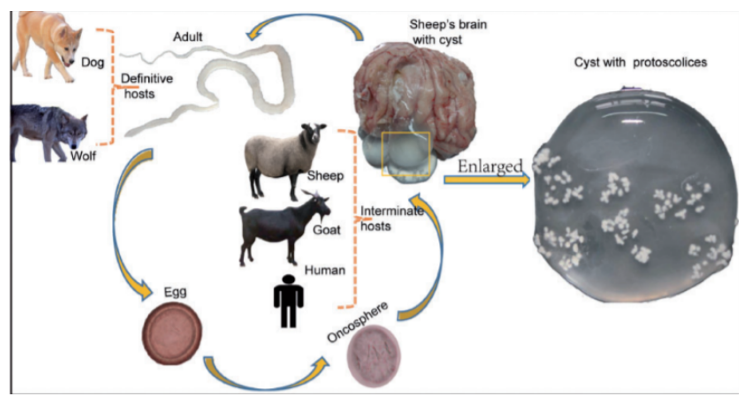
Taenia multiceps + coenurus cerebralis
cyclophyllidae - cestode
FH: Dog, fox, wild canids
IH/larvocyste: Sheep, cattle, goat, pig, horse, deer, camel (coenurus cerebralis)
Location: Brain, spinal cord
Process:
eggs shed in feces of infected FH
eggs are eaten by IH → oncospheres released in intestine → circulate in blood, until they find suitable organs → brain in this case (spinal cord, eyes also).
develops into coenurus cerebralis with protoscolices
FH becomes infected by ingesting tissue of an infected IH with the coenurus.
Protoscolices → attach to SI wall → adult cestodes in FH
Humans get infected after accidental ingstion of eggs in food/water.
coenurus: large fluid-filled bladder with invaginated scolices attached to wall.
Life cycle of?
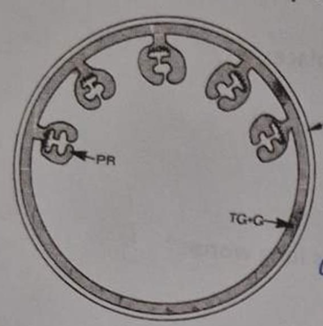
Moniezia spp. - M. expansa/M. benedeni (Cyclophyllidea, cestode)
in this case, it would be M. expansa as this is for small/young ru.
While benedeni is typ. found in medium-large ru
indirect LC, located in SI
IH: oribatid mites (Oribatidae)
FH: Ru
Process:
Eggs with oncosphere are released from FH → ingested by IH where they hatch into cysticercoid in the body cavity
FH ingest infected mite and the cysticercoid travel to SI where they mature into adults
Life cycle of?
Mesocestoides Lineatus (cyclophyllidea, cestode)
Indirect LC, 2 IH, Located in SI
FH: dogs, cats, some wild canids
1st IH: arthropods, such as ants, beetles, oribatid mites etc. - cysticercoid develops here.
2nd IH: small vertebrates like reptiles, amphibians, birds and small mammals - Tetrahyridium.
Process:
1st IH ingests eggs with oncosphere/proglottid → develops into cysticercoid
2nd IH ingest infected arthropod with cysticercoid → tetrahyridium
FH ingest the IH → parasite travels to IH → matures → release gravid proglottids in the feces with many eggs.
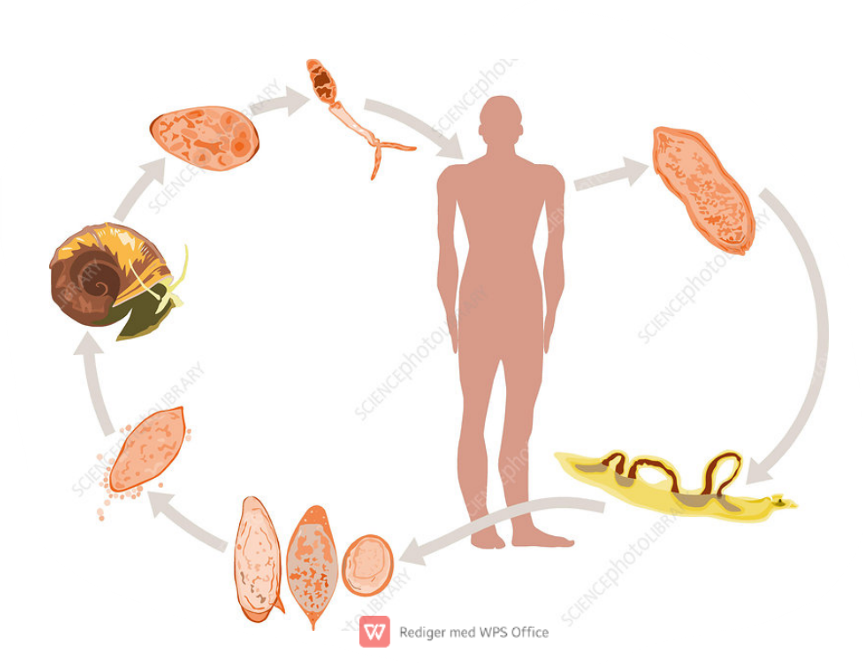
life cycle of?
Schistosoma spp. (S. haematobium, Mansoni, japonicum) - trematode
Indirect LC, located in Blood vessels
IH: water snail
FH: man
process:
eggs hatch into miracidium → IH → pathogony → sporocysts → cercaria with forked tail (furcocercaria) → exits
FH gets infected by furcocercaria → looses their tail and become schistosomulae → circulation → matures.
Worms migrate to mesenteric or vesicular veins depending on species.
S. mansoni: mesenteric veins of LI
S. haematobium: veins of bladder
S. japonicum: mesenteric veins of SI
Embryonated eggs with miracidium released by urine/feces.
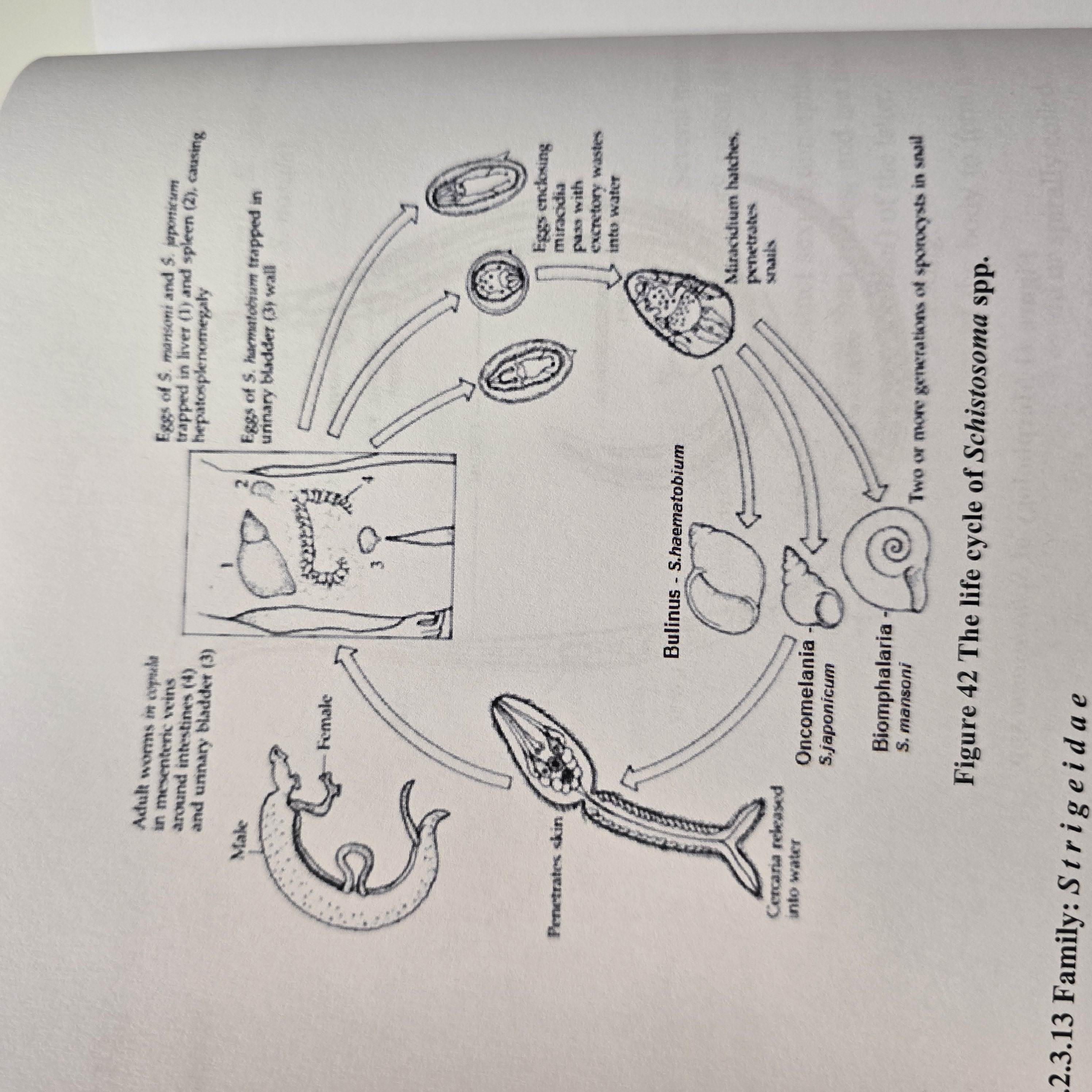
Life cycle belongs to? what is the infective stage?
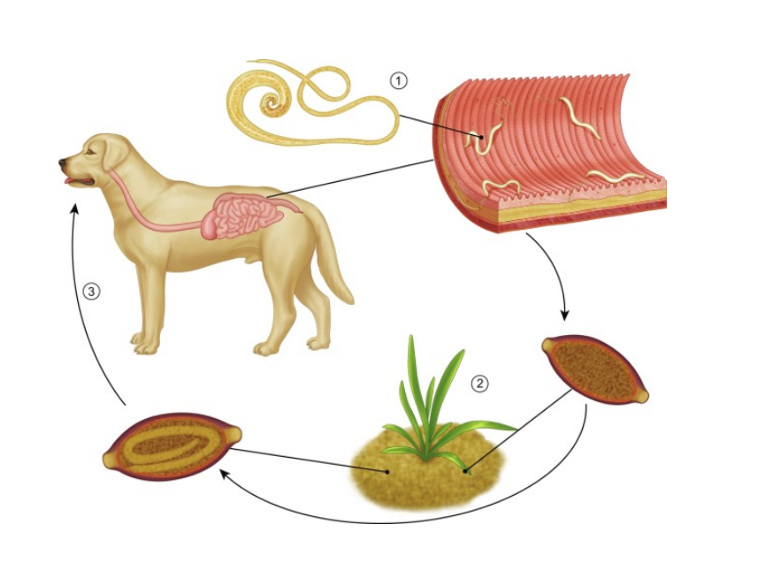
Trichuris vulpis
Direct LC, located in large intestine
FH: Ru, car, su, man (but here it is T. vulpis so FH is dog).
infective: egg with L1 larvae and diagnostic: eggs
Process:
Unembryonated eggs are shed by host`s feces
L1 larvae develop inside the egg in the environment
Host ingest embryonated eggs
eggs hatch and L1 are released in the SI → large intestine (All 4 moults - happens)
The larvae matures into adults within LI → release eggs.
Life cycle of?
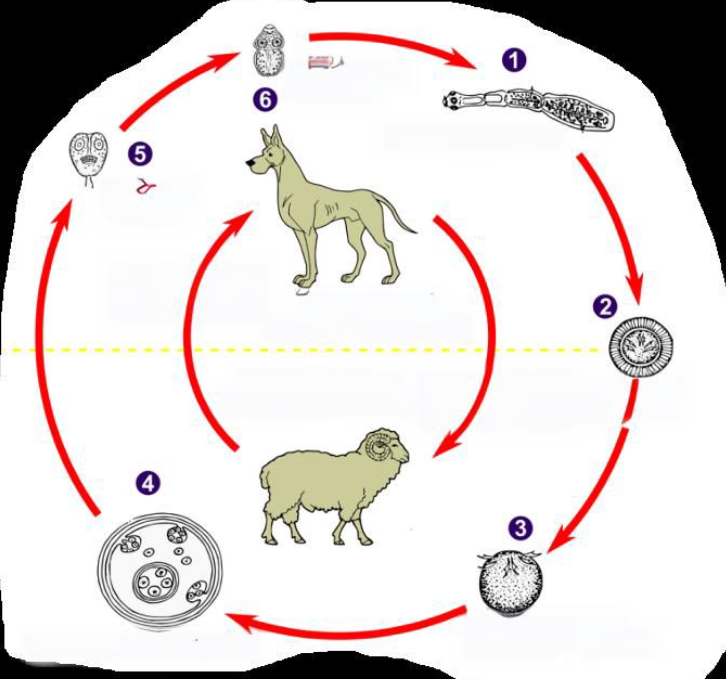
Echinococcus granulosus (also have E. multilocularis but not in this picture case though)
indirect LC, located in liver, lung (both), SI of FH
multilocularis: heart, brain, lymph nodes, SI of FH (primarily liver, but widely also)
IH: granulosus: RU (sheep, cattle, other livestock)
multilocularis: rodents
FH: dogs, wolves, fox, dingoes
multilocularis: fox, dog, wild canids, racoons, cats
Process:
IH ingest embryonated eggs → hatch in SI and release oncospheres
oncospheres → through blood or via lymph to liver, lungs or other tissues → develops into hydatid cyst
cyst grows and releases brood capsules with scolices
multilocularis → develops into a multiocular or alveolar cyst here (metacestode stage)
FH ingest infected tissues with cysts
Scolices attach to intestinal mucosa in SI → matures and eggs are released with feces
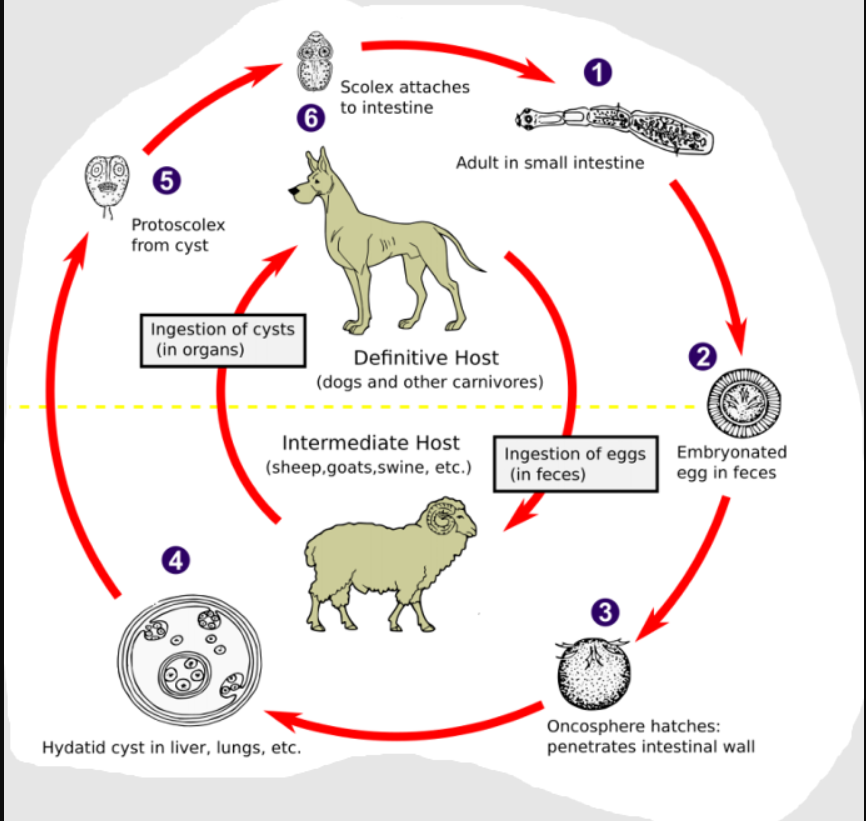
Life cycle of?
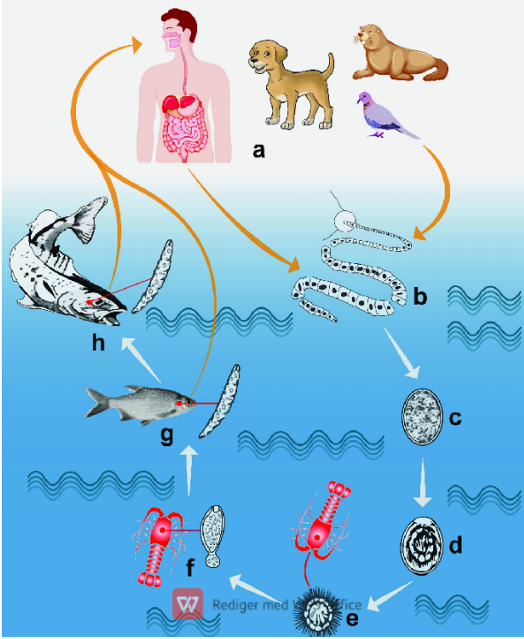
Diphyllobothrium latum (pseudophyllidea, cestode)
Indirect LC, located in SI
IH: 1st: water arthropod, 2nd: fish
FH: fish-eating mammals
infective stage: plerocercoid for FH, procercoid for fish
Process:
eggs embryonate in water → coracidium hatches from eggs taken up by 1st IH
inside 1st IH, coracidium → procercoid larvae
fish ingest infected arthropod and the procercoid → plerocercoid larvae in the muscle
Small infected fish can be then eaten by a bigger carnivorous fish
FH eats raw/undercooked fish → plerocercoid develops into immature worm and then into mature adult in the SI
Unembryonated eggs release from proglottids with feces
FROM HERE - SOME EXTRA
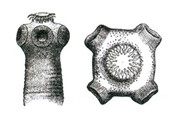
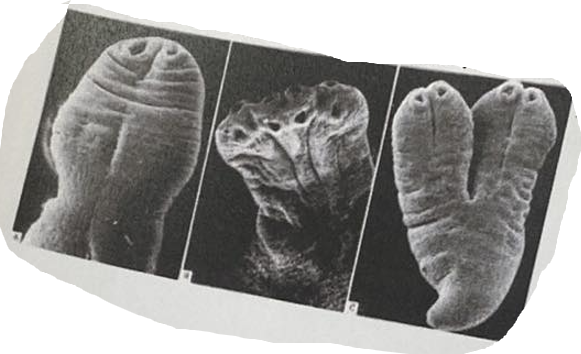
Picture shows the scolex of which tapeworm?
Picture of hook, of Taenia solium (Scolex of tapeworm)
kan være MC
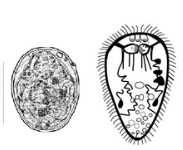
this is picture of?
Larval stages of digenea (trematodes) - egg and redia
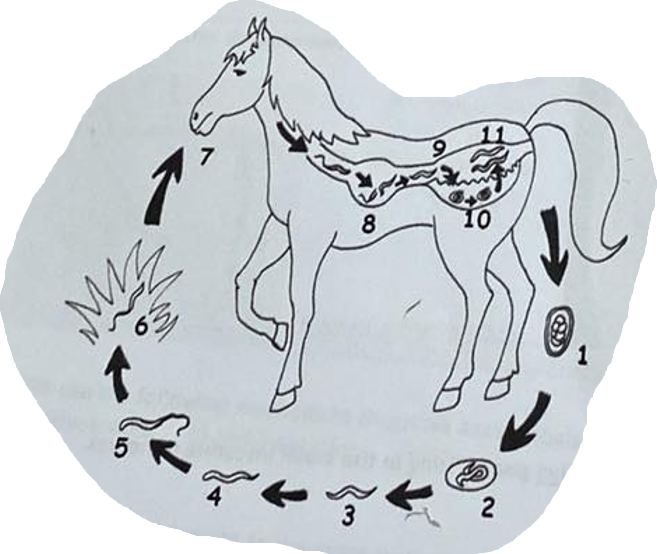
life cycle of?
Cyathostomum (or cyathostomins - broader term) - “small strongyles”, cycliocyclus
Nematode, from family Strongylidae.
Direct LC, located in Large intestine of horses
Process:
Adult cyathostomins live in LI → eggs pass in feces (unembryonated)
larva develops within each egg, then hatches
released larva develops → moults twice to infective L3 stage.
Infection of horse is by ingestion of these larvae → mucosal migration → moults to L4 in LI
Larvae migrates to lumen → moults to L5/adult and release eggs in feces
What is the developmental stage in the picture? To which tape worm belongs?
Tetrahyridium, Mesocestoides lineatus

What is the developmental stage in the picture? Which parasites? (Indicate genus name)
Furcocercariae (cercariae with forked tail)
schistosoma genus
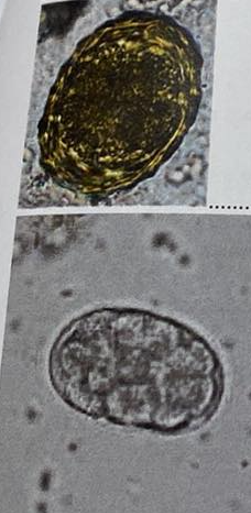
Eggs found in pig examination, name and describe
ascaris suum
M, spherical
3 thick shells, rough surface
unembryonated (1 cell)
brown
Strongyloides ransomi/men ligner og på hyostrongulus rubidus
small, oval, symmetrical
3 thick shells
unembryoanted + few blastomeres
grey color
life cycle of?
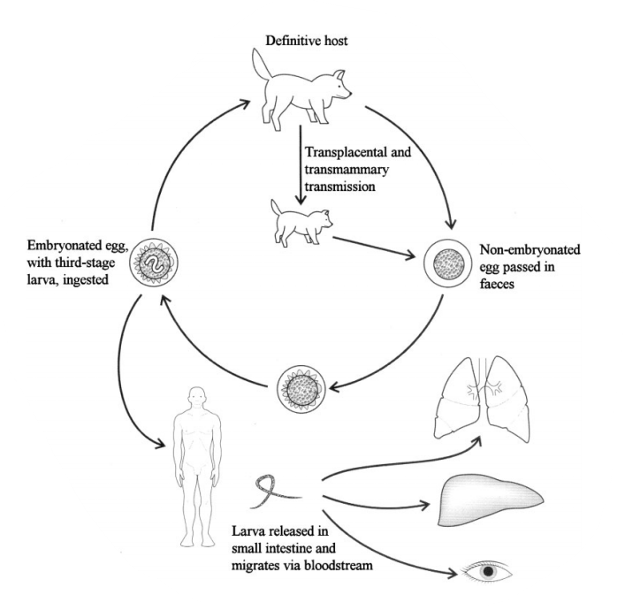
Ancylostoma caninum - hookworm (can see it is ancylostoma due to head of worm)
FH: car, man
Direct LC, located in SI
infective stage: L3 eggs
Infection by ingestion, per skin, and by transmammary, transplacental.
Process:
adult worms live in SI of dog → attach to intestinal wall and feeds on blood
eggs are passed in feces into environment
eggs develop and hatch → L1 released into the soil.
L1 → L2 → L3 developed
Infection happens by:
Dogs ingest L3 → SI (final moult happens here → adults)
Percutaneous infection - enters blood → lungs → coughed up and swallowed → SI
if cat: ancylostoma tubaeforme
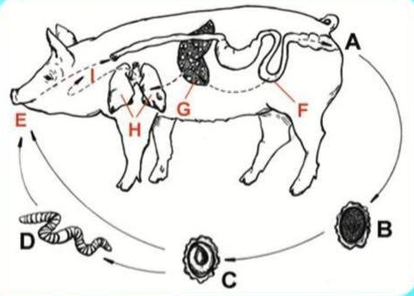
life cycle of?
Ascaris Suum (nematode)
Direct LC, located in SI
Hepato-pulmonary passage of larvae after hatching
Host: pig
Process:
Unembryonated eggs in feces
moults to L3 larvae (infective stage)
ingestion of infective egg by host
hatched larvae → invades intestinal mucosa → hepato-pulmonary migration (to lungs)
further maturation in lungs → swallowing of larvae → SI, develops into adult worms
life cycle of?
Anoplocephala spp. (Perfoliata + magna) - also paranoplocephala mamillana.
Difference is that perfoliata is in SI and LI of horse, cysticercoid in oribatid mites. While magna is in SI of horses, scolex is small, no lappets.
indirect LC, IH: oribatid mites, FH: horse
infective stage: cysticercoid
Process:
grazing horse ingest mite infected with cysticercoid
Cysticercoid develops to adult in intestine of horse
gravid proglottids and embryonated eggs pass in horse feces
eggs eated by oribatid mites → cysticercoid develops here
mites crawl on vegetation → eaten by horse

This is?
Protostrongylus spp.
pointed tail without spines, transparent body
which tapeworm is this?
Mesocestoides lineatus
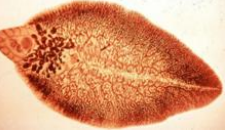
which species is this?
Fasciola hepatica
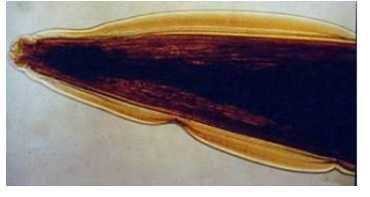
which species is this?
Toxocara canis (10-15cm)
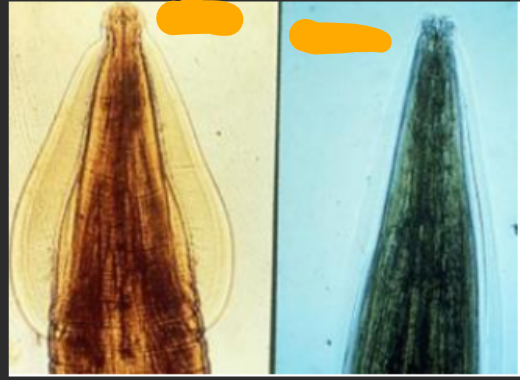
which species is this?
Toxocara cati (left)
Toxocara leonina (7-10cm) - right
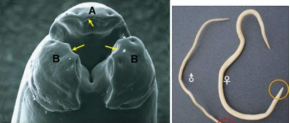
which species? arrows? a, b?
Adult nematoda pig – Ascaris suum
Yellow arrow: rows of tiny denticles on inner surface of each lip;
Mouth opening has one dorsal lip (A) and two ventro-lateral lips (B)

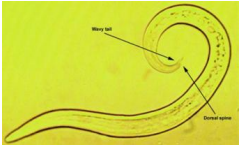
which species?
trichuris suis (ringworm in goat)
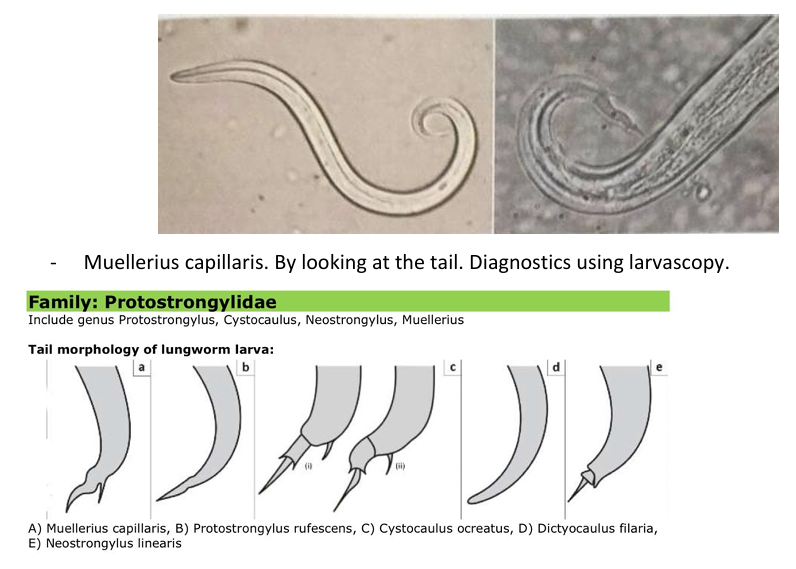
which species?
Muellerius capillaris - can see that by looking at the tail. Diagnostics using larvascopy.
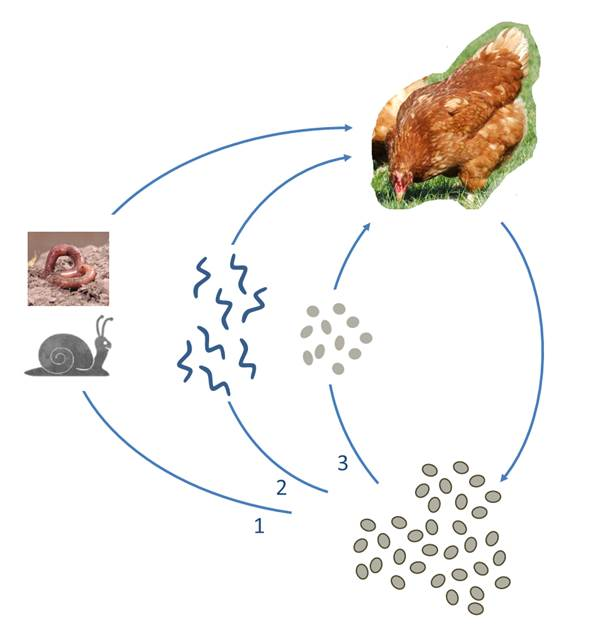
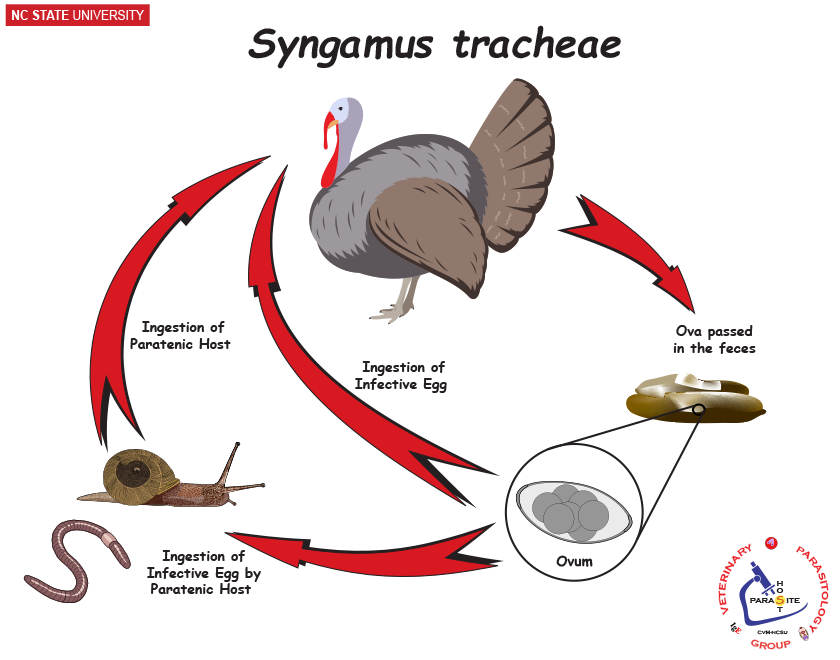
life cycle of?
Syngamus trachea (roundworm)
FH: domestic fowl and game fowl
direct or paratenic earthworm/slug
process:
L1 → L3 in the egg, or a hatched L3 → ingestion by paratenic host → ingestion by FH
L3 penetrate intestine and enter lungs → moults and completes it in the trachea.

eggs - sheep feces?
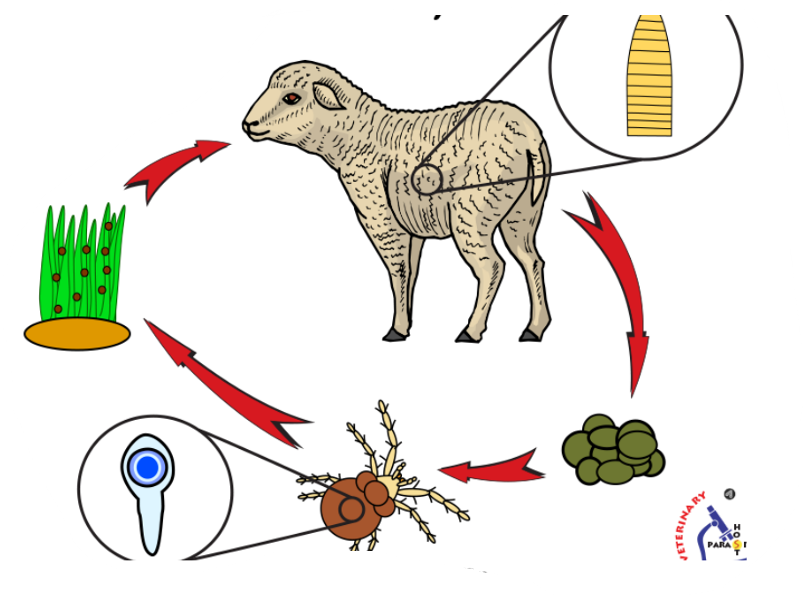
Moniezia expansa
M, embryonated, polyhedral shape, 3 thick shells, transparent.
nematodirus spp.
XL, oval, symmetric, 2 thin shells, unembryonated (8 dark blastomeres), gray
location: SI
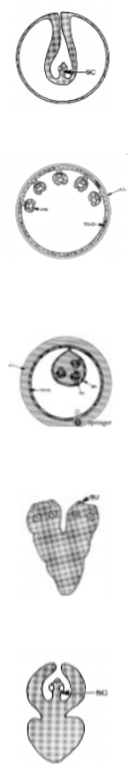
these are?
cysticercus - taenidaee
coenurus - t. multiceps
echinococcus - with protoscolices, suckers, hooks
tetrahyridium - Mesocestoides Lineatus
cysticercoid - D. caninum, moniezia, anoplocephala
Mesocestode stages of cestodes (Cyclophyllidae)
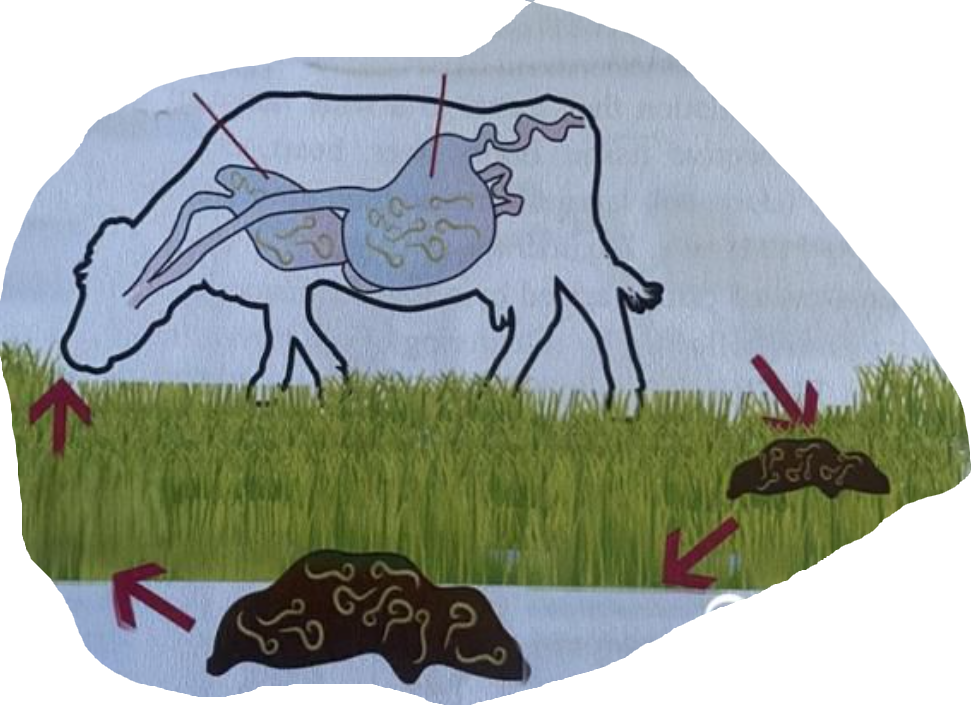
life cycle of?
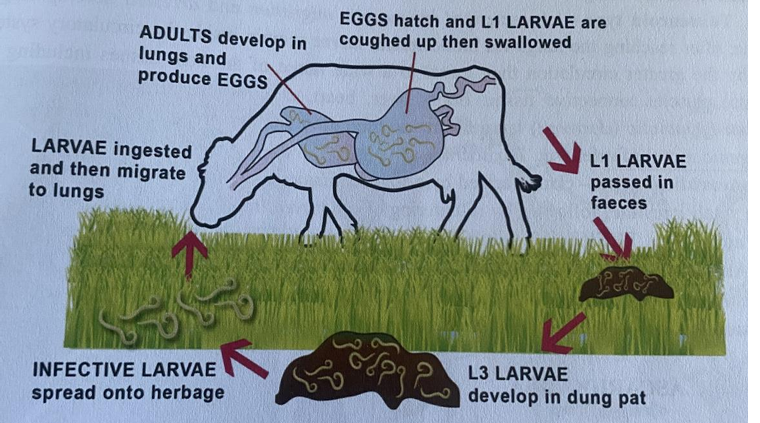
Dictyocaulus viviparus:
FH: Horses, cattle, small ruminants and deer
Location: Trachea and bronchi
Process:
L1 larvae are passed in feces.
L1 → L2 → L3 ➔ FH ingest free L3 larvae
Penetrate intestinal walls and enter lymphatic vessels.
Reaches mesenteric lymph gland.
L3 → L4 ➔ L4 migrates to the lungs.
Migrate through the parenchyma to the airways.
L4 → Adult ➔ Adult lays eggs in the bronchi
Eggs coughed up and swallowed. ➔ L1 hatch in the intestine