GB1- Chapter 3
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Water’s four properrties that facilitate environment for life
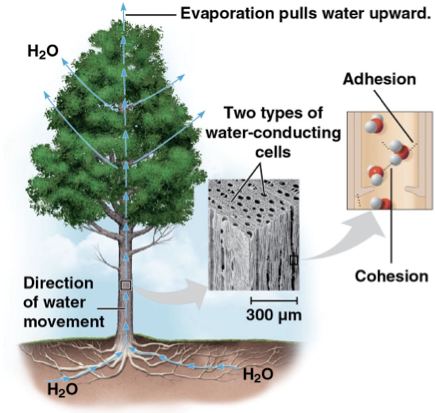
cohesive behavior
ability to moderate temperature
expansion upon freezing
versatility as a solvent
cohesion
hydrogen bonds holding water molecules together
transports water and dissolved nutrients against gravity in plants
results in high surface tension
surface tension
how difficult it is to stretch or break the liquid’s surface

adhesion
attraction between different substances
ex) water and plant cell wall
kinetic energy
energy of motion
thermal energy
kinetic energy associated with random motion of atoms or molecules
temperature
average kinetic energy of the molecules in a body of matter
heat
transfer of thermal energy
calorie (cal)
amount of heat required to raise the temperature 1g water by 1ºC
amount of heat released when 1g of water goes down 1ºC
specific heat
amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1g of substance to change 1ºC
water resists temperature change because of its high specific heat of 1 calorie
heat of vaporization
amount of heat 1g of liquid must absorb to be converted to gas
evaporative cooling
cooling of the surface after evaporation because the molecules with the greatest kinetic energy leave as gas
stabilizes temperature in organisms and bodies of water
ex) sweating
water’s density
water is more dense as liquid than solid
at 0ºC water molcules lock into crystalline lattice- hydrogen bonds keep the molecules far apart = makes ice 10% less denser than water
water’s greatest density is at 4ºC
solution
homogeneous mixture of liquid substances
solvent
dissolving agent
solute
substance that is dissolved
aqueous solution
water is the solvent
hydration shell
water molcules surrounding ionic compound
hydrophilic
affinity for water
“water loving”
hydrophobic
doesn’t have affinity
ex) oil molecules are hydrophobic because of their nonpolar composition
molecular mass
sum of all atom masses in a molecule
molecular mass: 1 mol
Molarity
number of moles of solute per liter of solution
mol/L
number of molecules
1 mole = 6.02 ´ 1023 molecules
hydrogen ion (H+)
leaves electrion behind and becomes a proton
hydroxide ion (OH–)
lost proton = anion
hydronium ion (H3O+)
extra proton
acid
increases H+ concentration in soltuion
lower than 7
base
reduces H+concentration in solution
higher than 7
pH
pH = –log [H+]
most biological fluids have 6-8 pH
Buffer
substances that minimizes change in concentration’s H+ and OH–
contains weak acid and corresponding base; combines reversibly with H+ ions