Earth Science Ch6 Study Set
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of vocabulary flashcards derived from Earth Science lecture notes, focusing on key concepts and definitions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Law of Superposition
In geology, it states that in any undeformed sequence of sedimentary rocks, younger rocks lie above older rocks.
Principle of Original Horizontality
Sedimentary layers are originally deposited horizontally under the action of gravity.
Law of Cross Cutting Relationships
Any geological feature (such as a fault or intrusion) that cuts across another feature is younger than the feature it cuts through.
Conglomerate
A sedimentary rock composed of rounded clasts or fragments cemented together.
Relative Age
The age of an event or rock layer relative to another event or rock layer.
Absolute Age
The actual age of a rock or fossil, usually expressed in years.
Half-life
The time required for half of the unstable isotopes in a sample to decay.
Index Fossil
Fossils that are used to define and identify a particular time period in the geologic time scale.
Unconformity
A surface representing a break in the geological record, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous.
Sedimentary Rocks
Rocks formed by the compaction and cementation of mineral and organic particles.
According to _______, a fault or an intrusive rock is younger than the rock that it cuts through and displaces.
Law of Cross Cutting Relations
A stratigrapher studies layers of rocks in order to determine the history of the Earth. What branch of Earth Science is this?
Geology
What kinds of layers do sedimentary rocks generally form?
Horizontal layers called strata.
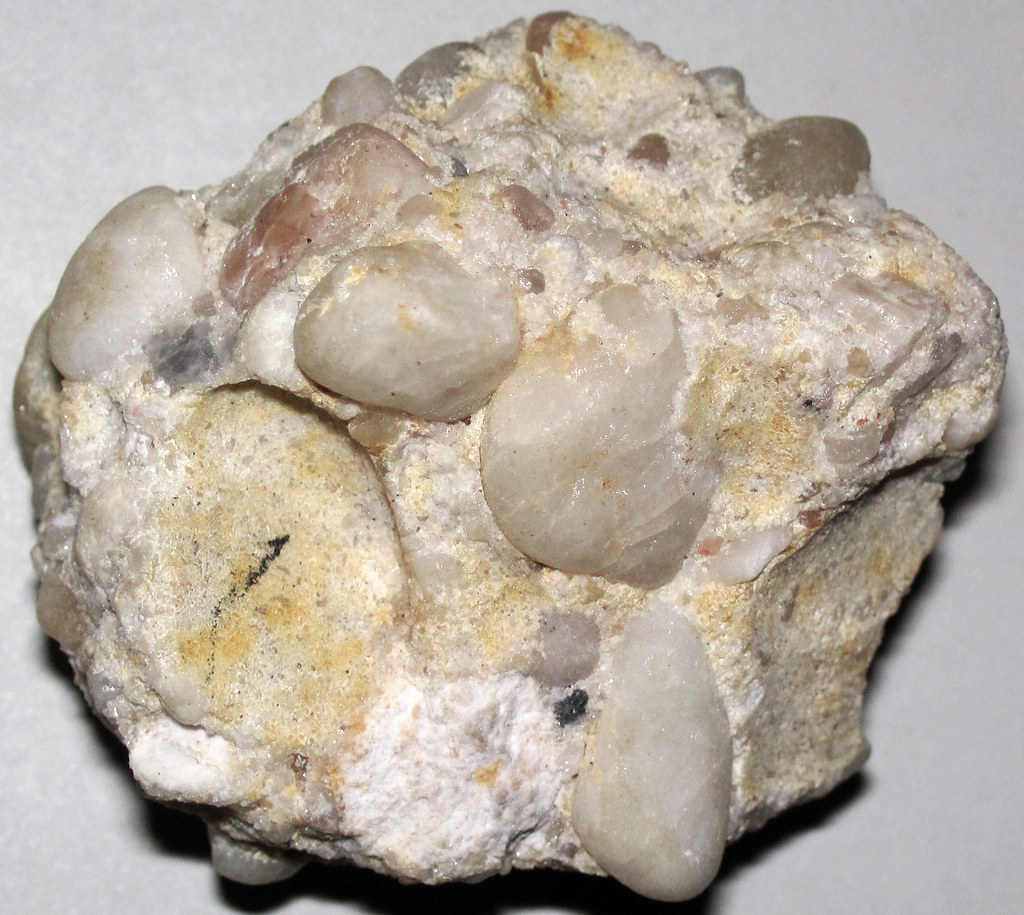

Conglomerate is a sedimentary rock. How do sedimentary rocks form?
It is formed from the compaction and cementation of rock particles.These particles can include gravel, sand, silt, and clay.
When sedimentary rock is tilted or deformed, scientists know that the tilting/deformation occurred _____.
after the formation of the rock.
When a scientist claims that a rock is older than the rock above it, they are describing the rock's _____ age.
relative
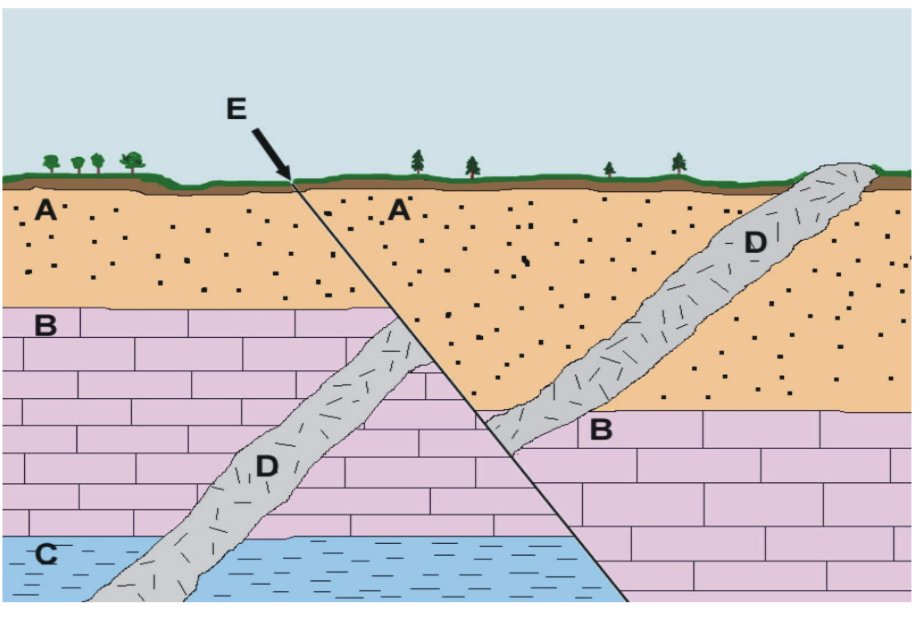
Which letter on the diagram below identifies a rock that demonstrates the Law of Cross Cutting Relationships?
D
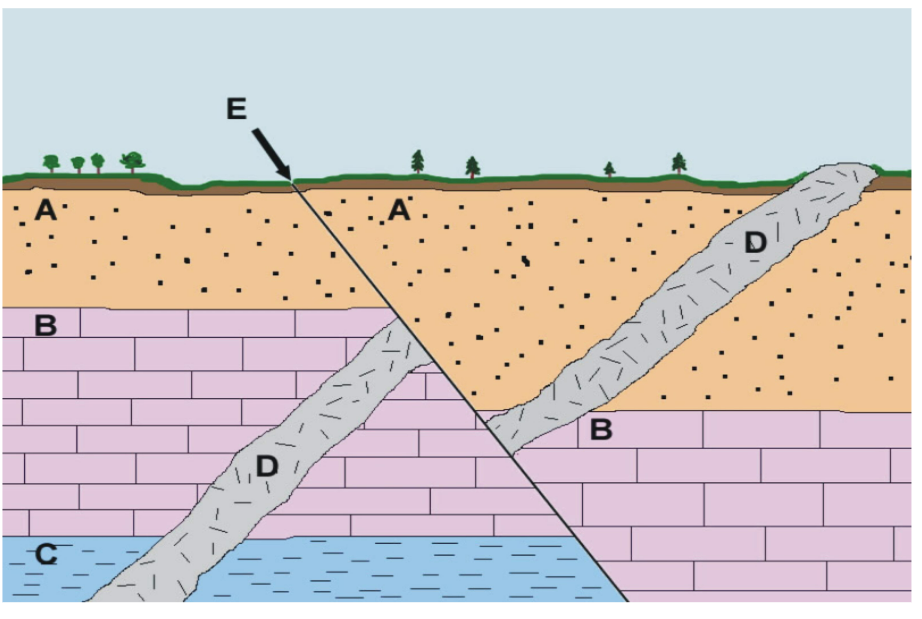
When did Fault E occur?
after A was deposited
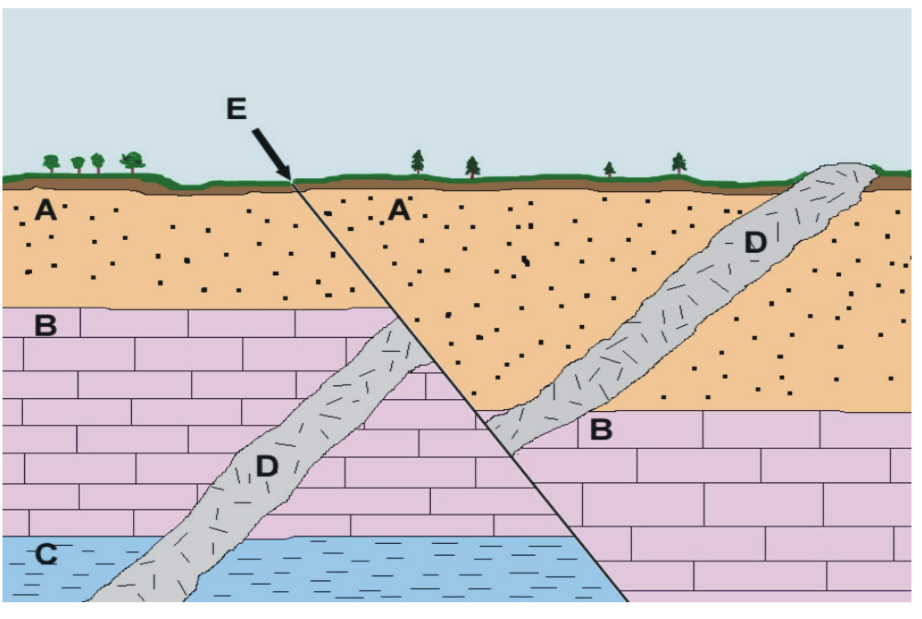
What is feature D called in the diagram?
an intrusion that cuts through surrounding rock layers.
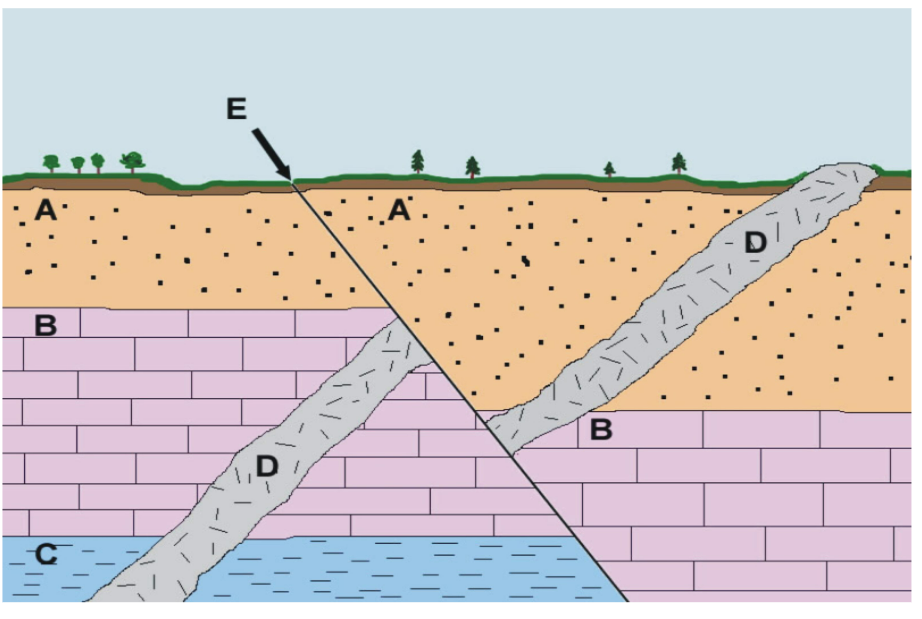
What kind of rock is shown in B?
Limestone a sedimentary rock formed from the accumulation of marine organisms' remains. Typically shown in diagrams as blocks.
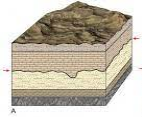
What does the wavy line in the diagram below indicate?
Erosion or sediment deposition processes.
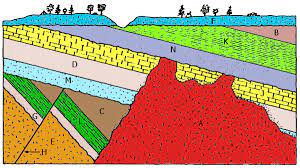
Of the choices provided below, which was the last process to occur in the image?
-tilting of rock layers E, G, L, C
-deposition of rock D
-igneus intrusion A
igneus intrusion A
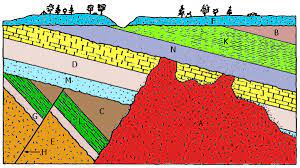
Use the image to help you answer the following question. Which rock type is the oldest?
E
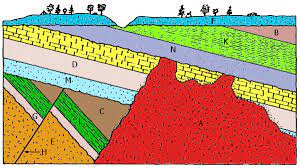
Which two rock layers from these different locations could be the same age. Choose two that apply.
F&I and G&J
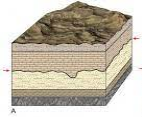
When there is a "break" in the sedimentary rock sequence, a(n) _____ forms.
unconformity
What is half-life?
The time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay. This concept is crucial in radiometric dating and understanding the stability of isotopes. It determines the age of rocks and fossils.
Fossils that are found in the rock layers of a particular geologic period are called ___.
index fossils
In general, what parts of organisms become fossils?
Usually hard parts like bones, teeth, and shells.
Although various types of rocks form layers, what type of rock is commonly used by scientists to determine the relative age of rocks?
Sedimentary Rock
How is relative age different from absolute age?
Relative age refers to the comparison of age between rock layers, where as absolute age is the exact age found by radiometric measurement.
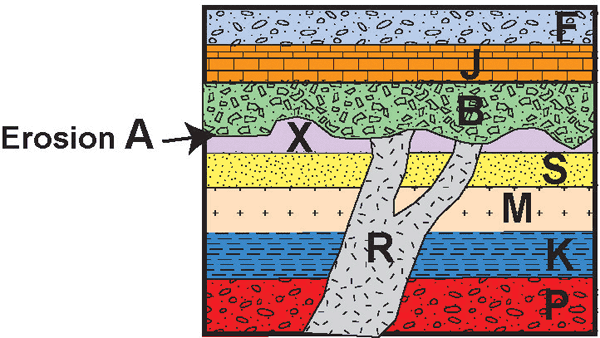
List the order of events from Oldest --> Youngest. There are 10 steps.
P,K,M,S,X, Erosion A, R,B,J,F