Human Consumption
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Define “Human consumption”
The use of goods and services by people to satisfy their needs and wants.
What are some factors that influence human needs? (HINTS: 4 things)
Geographical Environment (importation & exportation)
Career and Income (more income = more purchasing power)
Societal perceptions (culture, beliefs)
Economic and technological progress
Psychological
Personal
What is the “diminishing marginal utility”?
“The more you consume a good, the less extra satisfaction (utility) you get from each additional unit.”
Utility = satisfaction or happiness you get from consuming something
Marginal utility = the extra satisfaction from consuming one more unit
Diminishing = this extra satisfaction gets smaller each time you consume more
What are some factors that contribute to purchase demand? (Give3-5 examples)
Income of consumers
Price of substitutes/complements
Changes in trends
Seasonal
Advertising
Price
Define “substitute goods” and give examples
“goods which can be used in place of one another to satisfy a particular want.”
E.g. tea & coffee, Coke & Pepsi, Domino’s Pizza & PizzaHut

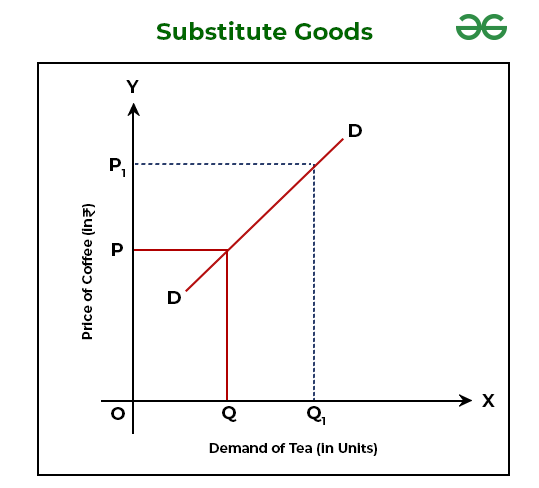
Explain the graph of substitute goods
Price of Good A ↑ → Demand for Good B ↑
(because people switch)
Price of Good A ↓ → Demand for Good B ↓
(because people prefer the cheaper one)
Define “complementary goods” and give examples
“two goods that are used together, so the demand for one depends on the demand for the other.”
If you buy one, you usually need the other.
E.g. sugar & tea, pasta & pasta sauce

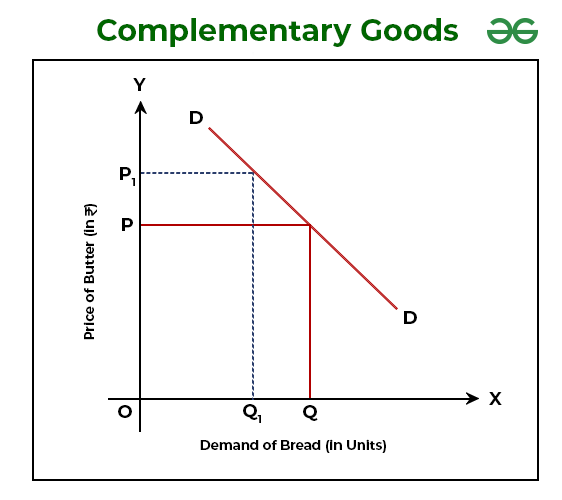
Explain the graph of complementary goods
If price of Good A ↑ → Demand for Good B ↓
(because people stop buying the pair)
If price of Good A ↓ → Demand for Good B ↑
(more people buy the pair)