Electrical Engineering Exam Review
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards for exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Nyquist Stability Criterion
A stability criterion in control systems that determines the stability of the closed-loop system.
Gate Terminal
To regulate the output current of the FET
High input resistance
Advantage of a FET over a BJT
Purpose of a biasing circuit in a transistor
To establish the operating point of the transistor
Purpose of a decoder in digital circuits
To convert a coded input into a corresponding output
Transformer
A component used to step up or step down the voltage in a transformer
Refractive Index
The ratio of the speed of electromagnetic waves in a medium to their speed in a vacuum
Electromagnetic Induction
The process of generating an electric current in a circuit by varying the magnetic field.
Electromagnetic phenomenon that allows wireless power transfer
Inductive Coupling
Gamma Rays
Cancer treatment
Disinfection
Ultraviolet
X-Rays
Medical Imaging
Radio Waves
Broadcasting
Ampere's Law
The phenomenon where a current-carrying conductor creates a magnetic field around it.
X-Rays
Type of electromagnetic wave used for medical imaging
Transverse and longitudinal waves
Two fundamental types of electromagnetic waves
Diffraction
Bending of waves around obstacles
Refraction
Bending of waves at the boundary between two media
Reflection
Bouncing back of waves from a surface
Absorption
Transfer of energy from waves to matter
Bus in microprocessors and microcontrollers
A communication pathway for data and control signals
Purpose of an interrupt in microprocessors and microcontrollers
To temporarily suspend the normal program execution and handle a specific event
Serial Communication Interface (UART)
Example of an input/output peripheral in microcontrollers
90 degrees
Phase difference between voltage and current in a pure inductive circuit
Flash memory
Memory commonly used for code storage in microcontrollers
I2C
Commonly used communication protocol in microcontrollers
C
Programming language commonly used to program microcontrollers
Commonly used sensor in microcontroller-based systems
Proximity Sensor
Resonance in an RLC circuit
When the inductive and capacitive reactance cancel each other out
Code Segment
Register that defines the starting address of the section of memory holding code
Addressing mode that moves a byte or word between a register and a memory location addressed by an index register, base register plus a displacement
Base relative plus index
Replacing a voltage source in series with a resistor by a current source in parallel with the same resistor, or vice versa
Source transformation in circuit analysis
What happens to the reactance of a capacitor as the frequency increases
Decreases
How a varactor is usually configured
Reverse-biased
Increases
When the light increases, the reverse minority carrier current in a photodiode
Characteristic of Asynchronous Sequential Logic
The outputs change immediately in response to any input change
Primary role of a flip-flop in sequential logic circuits
To store and synchronize binary data
Series Clipper
Half-wave rectifier example
To maintain a constant output voltage irrespective of input voltage variations
Primary function of a voltage regulator circuit
Output frequency of a bridge rectifier if line frequency is 60 Hz
120 Hz
Example of an active transducer
Piezoelectric sensor
USB (Universal Serial Bus)
Example of a commonly used interface circuit
Effect of adding an inductor in series with a resistor in an AC circuit
Increases the impedance
Key characteristic of Finite State Machines (FSMs)
They can be used to model systems with discrete states and transitions
X= (A OR B) AND (A OR C)
Logic gate equivalent to the boolean expression: X = A OR (B AND C)?
Logic gate represented by the following truth table? | A | B |X||-|-|-||0|0|1||0|11| |1|0|0||1|1|1|
NOR gate
512
If three amplifiers with a gain of 8 each are in cascade, how much is the overall gain?
It provides high gain and improved input/output impedance
Benefit of using a cascode amplifier configuration?
Component commonly used to couple two amplifier stages together
Capacitor
The first stage of a preamp
Small signal
conducts current
When forward-biased, a diode
voltage equal to the barrier potential of the diode (0.7V for Si)
For a practical diode model, a forward biased diode is represented as
Anode is more positive than cathode.
A junction diode is said to be forward biased if
About oscillator circuits
They produce a continuous output waveform without any external input
Voltage gain is high, current gain is moderate, and phase shift is 180 degrees
Characteristic of a common-emitter configuration
is necessary in order to establish the proper region of operation for ac amplification.
dc biasing
class B
An amplifier that delivers an output signal of 180 degrees only.
An op-amp inverting amplifier uses a feedback resistor of 100 kilo ohms and input resistor of 10 kilo ohms. If the op-amp's input offset voltage is 2.0mV, approximate the amplifier output offset voltage due to this input offset voltage.
22mV
To stabilize the circuit and reduce distortion
Purpose of negative feedback in an operational amplifier circuit?
Regarding the slew rate of an operational amplifier?
It is the maximum rate of change of the amplifier output voltage
A commonly used communication protocol in building management systems?
BACnet
A commonly used type of occupancy sensor in building automation?
Passive infrared (PIR) sensor
Purpose of daylight harvesting in lighting control systems?
To optimize energy usage by adjusting artificial lighting based on natural light availability
True regarding the frequency response of a common emitter amplifier
The cutoff frequency is determined by the capacitor and resistor values in the amplifier
20 Hz to 20 kHz
An audio amplifier operates in the frequency range of
A commonly used type of occupancy sensor in building automation?
Passive infrared (PIR) sensor
inductive sensor
A proximity sensor that operates under the principle of Faradays Law of Inductance
Regarding the current mirror circuit?
It helps achieve improved accuracy and precision in current matching
In a current mirror circuit, what is the purpose of the emitter resistor?
To stabilize the current against temperature variations
To convert the circuit equations into algebraic equations in the frequency domain
When analyzing a complex linear circuit, what is the purpose of using Laplace transform?
Combinational circuits have output that is solely dependent on current inputs, while sequential circuits have output that depends on both current inputs and previous states
What is the difference between combinational and sequential logic circuits?
Null
In Boolean algebra, the expression X.X' = 0 represents what law?
Which logic gate is equivalent to the boolean expression: X = A OR (B AND C)?
X= (A OR B) AND (A OR C)
What is the Laplace transform used for in control systems?
Analysis of dynamic systems
Feedback control
Which control system technique is used to improve the transient response?
During the half-power frequencies, the current of a series RLC is of the current at resonance.
0.707
2.44 A
If 78 C of charge pass through an electric conductor in 32 seconds, determine the current (Amperes, A) in the conductor.
To represent a node with an unknown voltage
When analyzing circuits using nodal analysis, what is the purpose of a dummy node?
Two SCRS in parallel
The triac is equivalent to
No
Will a SCR turn-off when the voltage at the gate is removed?
10.7V
What is the peak voltage (Vp) if a PUT is connected to a gate supply of 10V?
The diac is a
Bidirectional device
Which of the following is not a characteristic of the UJT?
bilateral conduction
To represent the periodic signal as a sum of sinusoidal components
What is the purpose of using Fourier series in analyzing periodic signals in circuits?
At resonance, what is the total reactance of a series RLC circuit where R is 10 ohms, C is 3mF and L is 1mH?
0

0
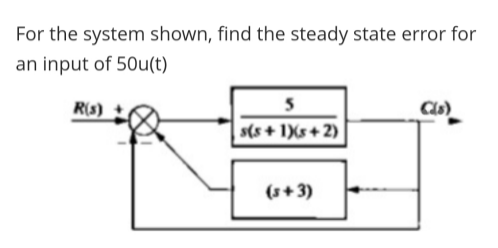
37.5