Overview of Cardiovascular dynamics. The heart and blood vessels Lab Quiz 3
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
The structure of the blood vessels will affect the ________ ________ and _____________ _____________of the circulatory system.
venous return , pressure gradient
Which vessel experiences the greatest change in pressure?
Arterioles, Under sympathetic control and will constrict or dilate depending on the response.
A _________ __________ _________ refers to a difference in the blood pressure between two points in the vasculature. Note that the absolute value of blood pressure at these points is not relevant to blood flow.
blood pressure gradient
Define Vasocontriction.
a decrease in blood vessel diameter/radius and decreases blood flow
Define Vasodialation
is an increase in blood vessel diameter/radius and increases blood flow
Blood flows if______ _______ (Δ P) is present
pressure gradient
Blood flows from areas of _________ pressure to areas of _________ pressure
high to low
Blood flow is opposed by the ________() of the system.
resistance (R)
What 3 factors affect resistance?
Radius of the blood vessels
Length of the blood vessels
Viscosity of the blood
Flow is usually expressed in either ___ or ___ per minute
liters or mililiters
Velocity of flow is usually expressed in either _________ per minute or _______ per second
centimeters , mililiters
The primary determinant of velocity is the total _______-________- area of the vessels
cross-sectional
Flow of blood in the cardiovascular system is
__________ proportional to the pressure gradient
directly
Flow of blood in the cardiovascular system is
______ proportional to the resistance to flow
inversely
Poiseuille's Law: Resistance is _________ related to the fourth power of the radius (r4) of a blood vessel. For heart valves, it is not possible to use orifice radius because the opening is not circular.
inversely
Resistance is ________ to length
proportional
Resistance is proportional to ______
viscosity
Resistance is ___________ to tube radius to the fourth power
inversely proportional
Resistance is inversely proportional to ___________________________________
tube radius to the fourth power
Define Poiseuille's Law
The velocity of the steady flow of a fluid through a narrow tube (as a blood vessel or a catheter) varies directly as the pressure and the fourth power of the radius of the tube and inversely as the length of the tube and the coefficient of viscosity.
Pressure created by contracting muscles is transferred to blood, driving pressure is created by the _______
ventricles
Pressure created by contracting muscles is transferred to blood If blood vessels dilate, blood pressure _______
decreases
If blood vessels constrict, blood pressure _______
increases
Pressure waves created by ______ contraction travel into the blood vessels
ventricular
Pressure waves created by ventricular contraction travel into the blood vessels. Pressure in the _________side of the circulation cycles but the pressure waves diminish in amplitude with distance and disappear at the _______
arterial, capillaries
Pulse pressure = _______ pressure - ________ pressure
systolic pressure - diastolic pressure
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) = ______________ + _/_ (_________)
Diastolic pressure + 1/3 (pulse pressure)
______________ pressure is the pressure exerted on the walls of the container by the fluid within the container. Hydrostatic pressure is proportional to the height of the water column.
Hydrostatic
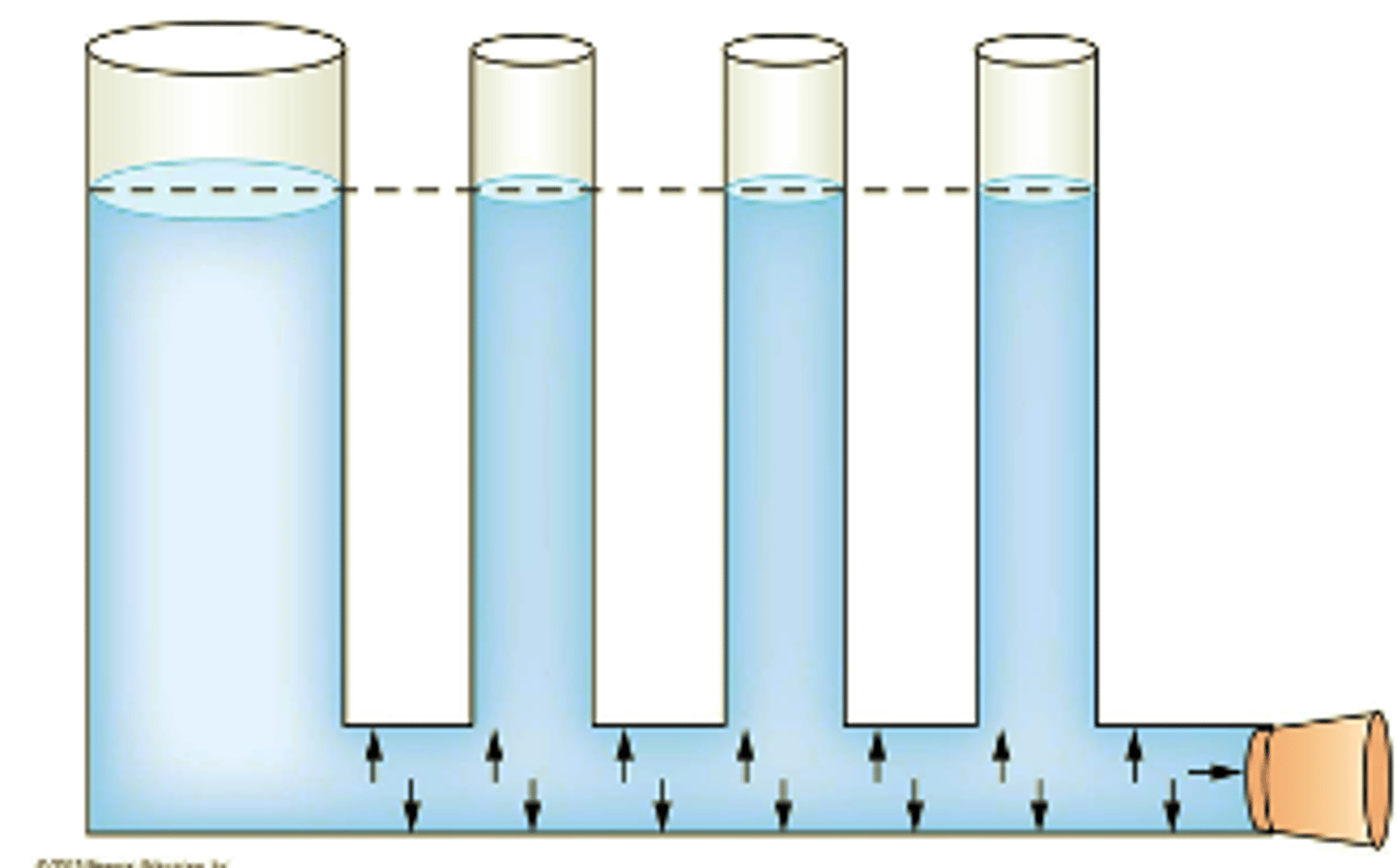
Arterial blood pressure is measured with a _______ (an inflatable cuff plus a pressure gauge) and a stethoscope. The inflation pressure shown is for a person whose blood pressure is 120/80.
sphygmomanometer
What is the primary mechanism by which arterioles regulate blood pressure?
Altering blood volume through fluid reabsorption.
Constricting or dilating under sympathetic control.
Releasing hormones that directly affect cardiac output.
Regulating the viscosity of the blood.
Constricting or dilating under sympathetic control.
Which of the following factors does NOT directly influence mean arterial pressure (MAP)?
a. Blood volume
b. Cardiac output
c. Resistance of the system to blood flow
d. Respiratory rate
Respiratory rate
In the context of cardiovascular dynamics, what is the primary role of the SA node?
To delay the transmission of electrical signals from the atria to the ventricles.
To initiate ventricular contraction.
To control the rate of the entire heart.
To regulate blood pressure by releasing hormones.
To control the rate of the entire heart.
How does vasoconstriction affect blood flow and blood pressure?
Increases blood flow and increases blood pressure.
Increases blood flow and decreases blood pressure.
Decreases blood flow and increases blood pressure.
Decreases blood flow and decreases blood pressure.
Decreases blood flow and increases blood pressure.
Which of the following best describes the function of baroreceptors in blood pressure regulation?
They detect changes in blood pressure and trigger a reflex response.
They directly alter cardiac output.
They regulate blood volume by controlling fluid intake.
They adjust blood viscosity to maintain constant flow.
They detect changes in blood pressure and trigger a reflex response.
What is the effect of increased blood volume on blood pressure, and how does the body compensate for this change?
Decreases blood pressure; compensation occurs through vasoconstriction.
Decreases blood pressure; compensation occurs through decreased cardiac output.
Increases blood pressure; compensation occurs through excretion of fluid in urine.
Increases blood pressure; compensation occurs through increased fluid intake.
Increases blood pressure; compensation occurs through excretion of fluid in urine.
What is the significance of the "leaky Na+ channels" in the SA node cells?
They help maintain a stable resting membrane potential.
They prevent the SA node from generating action potentials too quickly.
They contribute to the self-excitation cycle of the SA node.
They regulate the flow of potassium ions across the cell membrane.
They contribute to the self-excitation cycle of the SA node.
How does the structure of blood vessels contribute to the function of the circulatory system?
The uniform structure of all blood vessels ensures consistent blood flow.
The varying diameter and composition of blood vessels affect venous return and pressure gradient.
The rigid structure of arteries prevents changes in blood pressure.
The thin walls of veins facilitate oxygen exchange with surrounding tissues.
The varying diameter and composition of blood vessels affect venous return and pressure gradient.
What effect does an increase in cardiac output have on arterial blood volume and mean arterial pressure (MAP)?
Decreases arterial blood volume and decreases MAP.
Decreases arterial blood volume and increases MAP.
Increases arterial blood volume and increases MAP.
No effect on arterial blood volume or MAP.
Increases arterial blood volume and increases MAP.
During sphygmomanometry, what causes the Korotkoff sounds?
Silent blood flow through an uncompressed artery.
Pulsatile blood flow through the compressed artery.
Turbulent blood flow in the veins.
Complete cessation of blood flow in the artery.
Pulsatile blood flow through the compressed artery.
How do changes in the diameter of veins affect the distribution of blood between arterial and venous blood vessels, and what is the effect on Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)?
Vein constriction decreases arterial volume and increases MAP.
Vein constriction increases arterial volume and decreases MAP.
Vein constriction decreases venous volume, which increases arterial volume, increasing MAP.
Vein constriction has no effect on arterial volume or MAP.
Vein constriction decreases venous volume, which increases arterial volume, increasing MAP.
How does the viscosity of blood affect resistance to blood flow?
Decreased viscosity increases resistance.
Increased viscosity increases resistance.
Viscosity has no effect on resistance.
Viscosity only affects resistance in capillaries.
Increased viscosity increases resistance.
During the action potential of a cardiac contractile cell, which event is primarily responsible for the rapid depolarization phase?
Opening of calcium channels
Opening of slow potassium channels
Opening of sodium channels
Closing of sodium channels
Opening of sodium channels
Which of the following factors primarily determines cardiac output?
Blood viscosity
Heart rate and stroke volume
Peripheral resistance
Blood volume
Heart rate and stroke volume
Which of the following is NOT a direct factor in determining venous return?
Blood vessel structure
Pressure gradient of the circulatory system
Cardiac muscle action potential duration
Venous constriction
Cardiac muscle action potential duration
The influence of exercise on cardiovascular dynamics primarily involves:
Decreased heart rate and vasodilation
Increased blood viscosity and vasoconstriction
Decreased cardiac output and increased peripheral resistance
Increased heart rate, increased cardiac output, and vasodilation in working muscles
Increased heart rate, increased cardiac output, and vasodilation in working muscles
The Frank-Starling law of the heart describes the relationship between:
Heart rate and blood pressure
Venous return and stroke volume
Arterial pressure and peripheral resistance
Blood viscosity and cardiac output
Venous return and stroke volume
Which of the following best describes the electrical conduction system of the heart?
The AV node controls the rate of the entire heart
Ventricular muscle fibers have a membrane potential of -55 to -60 mV
The SA node controls the rate of the entire heart
Purkinje fibers initiate the action potential
The SA node controls the rate of the entire heart
What effect does vasoconstriction of arterioles have on blood pressure and blood flow?
Increases blood flow, decreases blood pressure
Decreases blood flow, decreases blood pressure
Decreases blood flow, increases blood pressure
Increases blood flow, increases blood pressure
Decreases blood flow, increases blood pressure
What is the effect of decreased blood volume on blood pressure, and how does the body compensate for this?
Decreases blood pressure; compensation occurs through vasoconstriction
Decreases blood pressure; compensation occurs through decreased cardiac output
Increases blood pressure; compensation occurs through increased fluid intake
Increases blood pressure; compensation occurs through excretion of fluid in urine
Decreases blood pressure; compensation occurs through decreased cardiac output
What triggers the activation of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS)?
High blood pressure
High sodium levels in the blood
Low blood volume or low blood pressure
High potassium levels in the blood
Low blood volume or low blood pressure
What effect does low sodium levels in the blood have on RAAS activity?
Inhibition of renin secretion
Increased renin secretion, leading to increased aldosterone release
Decreased aldosterone release and reduced blood pressure
No effect on RAAS activity
Increased renin secretion, leading to increased aldosterone release
How does aldosterone act on the kidneys during low sodium or high potassium levels?
It increases sodium excretion and decreases potassium excretion
It increases sodium reabsorption and increases potassium excretion
It decreases both sodium and potassium reabsorption
It decreases water retention and increases urine production
It increases sodium reabsorption and increases potassium excretion
What is the primary role of angiotensin II in the RAAS?
To promote the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
To decrease blood pressure and reduce blood volume
To inhibit sodium reabsorption in the kidneys
To increase blood pressure by causing vasoconstriction and stimulating aldosterone release
To increase blood pressure by causing vasoconstriction and stimulating aldosterone release
What is the effect of high water intake on the RAAS system?
It decreases renin secretion and lowers blood pressure
It increases renin secretion and raises blood pressure
It increases aldosterone release to promote sodium retention
It activates the system to increase sodium excretion
It decreases renin secretion and lowers blood pressure
What role does the angiotensin II type 1 receptor play in RAAS activation?
It inhibits aldosterone secretion from the adrenal glands
It mediates vasodilation and decreases blood pressure
It stimulates vasoconstriction, sodium retention, and aldosterone release
It enhances the degradation of angiotensin II
It stimulates vasoconstriction, sodium retention, and aldosterone release
Which of the following factors primarily determines blood pressure?
Cardiac output and resistance in the arterioles
Blood viscosity and vessel length
Stroke volume and heart rate
Blood volume and respiratory rate
Cardiac output and resistance in the arterioles
What is the physiological role of Norepinephrine?
It serves as a baroreceptor reflex
What is the source of Norepinephrine?
Sympathetic neurons
What is the physiological role of Epinephrine?
Increases blood flow to skeletal muscle, heart and liver
What is the source of Epinephrine?
Adrenal medulla