Lesson 2.10: Imperfect Competition and Government Regulation
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards made from a presentation segment created as a lesson on imperfect competition and government regulation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms

Monopolistic competition
A market structure in which many firms sell products that are similar but not identical
Many firms with low start-up costs
Few barriers to entry, making it easy to enter the market
Little price control, as consumers may go elsewhere
Differentiated product offerings for greater revenue from production differences
Differentiation
Making a product different from other similar products

Non-price competition
A way to attract customers through style, service, or location rather than a lower price
Can use physical characteristics, location, level of service, or status
Price war
A series of competitive price cuts that lower the market price below the cost of production
Cartel
A formal organization of producers that agree to coordinate prices and production

Oligopoly
A market dominated a few large, profitable firms like an imperfect firm of monopoly
Sometimes defined as the four largest firms producing 70-80% of the output
Can be created by technological or governmental barriers to entry, as in the video game and airline industries which have high start-up costs
May seem like a monopoly to a government despite not truly acting as one
Governments still try to regulate these firms for more competition, however
Price leadership
Situation where a market leader can start a round of price cuts or increases by making its plants clear to other sellers
Depends on other members going along with the policy; disagreement among members can spark a price war
Collusion
An agreement among members to illegally set prices and production levels, also known as price-fixing

Cartel
An agreement by a formal organization of producers to coordinate prices and production, permitted in other countries but illegal in the United States
Seen with OPEC (the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries) coordinating oil prices and production levels
Predatory pricing
Selling a product below cost for a short period of time to drive competitors out of the market
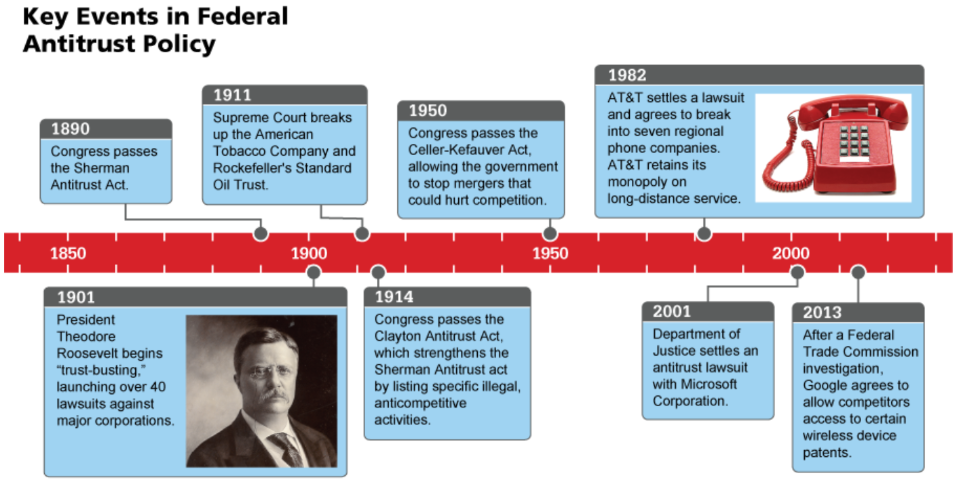
Antitrust laws
Governmental policies that keep firms from controlling the price and supply of important goods
Used to promote competition and lower prices
Trust
An illegal grouping of companies that discourages competition, similar to a cartel
Merger
When two or more companies join to form a single firm

Deregulation
The removal of government controls over a market in response to counterproductive regulation to increase competition
Seen with the Motor Carrier Act of 1980 as well as the Airline Deregulation Act
Market power
A firm’s ability to control prices and production; desired to increase profits