CFP11 - Repetition Structures
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
examsssss
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Repetitive section of code requires four elements:
Repetition statement
Condition
Statement that initially sets the condition
There must be a statement within the repeating section of code that allows the condition to become false
Both defines the boundaries containing the repeating section of code and controls whether the code will be executed or not.
Repetition statement
Forms of Repetition Structures:
while structure
for structure
do while structure
Each structure requires a condition that must be evaluated
Are identical to selections statements, if condition is true, the code is executed; otherwise it is not.
Condition
Must always be placed before the condition is first evaluated to ensure correct loop execution the first time the condition is evaluated.
Statement that initially sets the condition
At some point, the repetitions stops.
There must be a statement within the repeating section of code that allows the condition to become false.
Condition is tested before any statements within the loop are executed.
If condition is true, the executable statements within the loop are executed, if initial value of the condition is false, the executable statements within the loop are never executed and control transfers to the first statement after the loop.
Pretest Loop
Also referred to as entrance-controlled loops.
Example: while & for loop
Pretest Loop
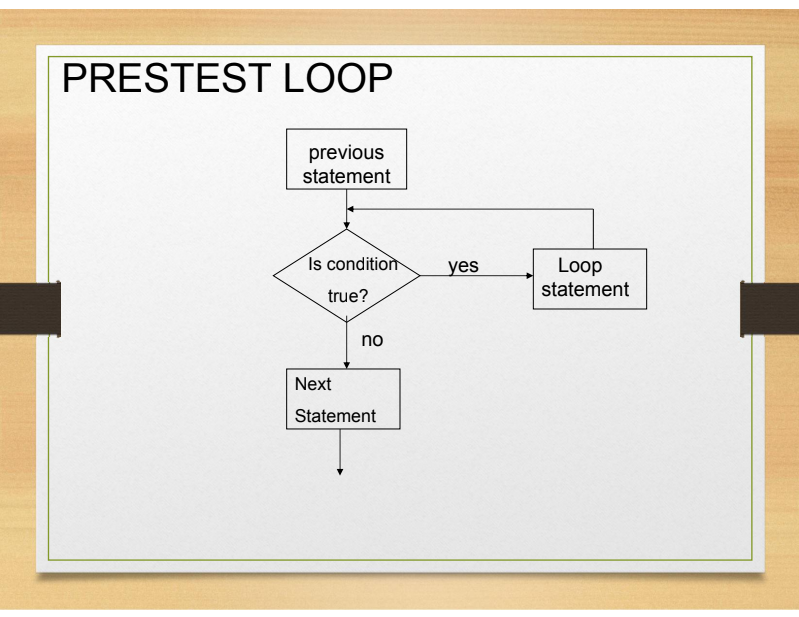
Which loop is this?
Pretest Loop
Referred to as exit-controlled loop
Loop that evaluates a condition at the end of the repeating section of code
Execute the loop statements at least once before the condition is tested. Since the executable statements within the loop are continually executed until the condition becomes false, there always must be a statement within the loop that updates the condition and permits it to become false.
• Example : Do while
Posttest Loop
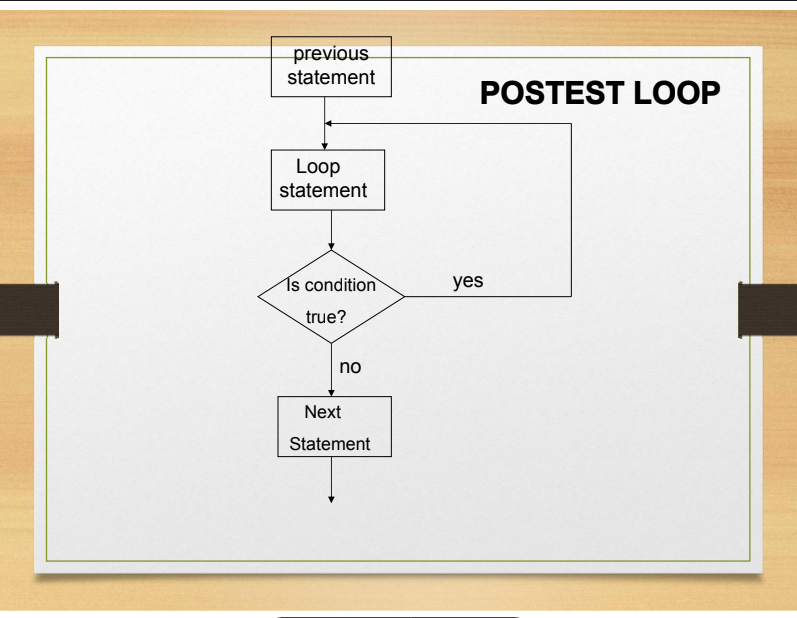
What loop?
Postest Loop
Types of Condition tested:
Fixed count loop
Variable condition loop
The condition is used to keep track of how many repetitions have occurred.
Fixed number of calculations is performed, or a fixed number of lines are printed, at which point the repeating section of code is exited.
Fixed count loop
The tested condition does not depend on a count being reached, but rather on a variable that can change interactively with each pass through the loop. When a specified value is encountered, regardless of how many iterations have occurred repetitions stop.
Variable condition loop
The statement following the expression is executed repeatedly as long as the expression evaluates to a nonzero value
Considering just the expression and the statement following the parentheses.
Literally loops back to itself to recheck the expression until it evaluates to zero (becomes false)
While Loops
Syntax of a While Loop:
while (expression)
statement;
Process used for While:
1. Test the expression.
2. If the expression has a nonzero (true) value.
a. Execute the statement following the parentheses.
b. Go back to step 1.
else
Exit the while statement and execute the next executable
statement following the while statement.
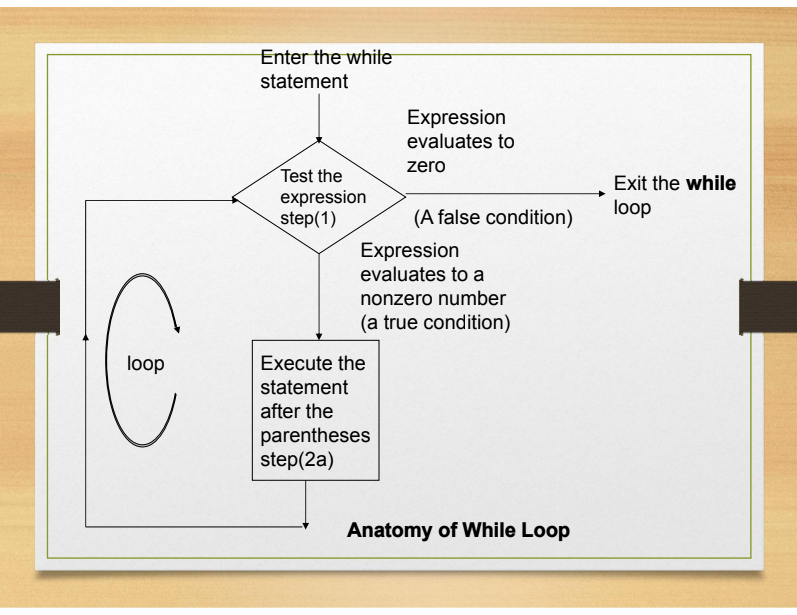
Anatomy of a While Loop:
(okay thanks)
Combining interactive data entry with the repetition capabilities
Used to accept and then display data.
Interactive While Loops
Data values used to signal either the start or end of data series.
Must be selected so as not to conflict
with legitimate data values.
Sentinels
This type of loop is where a counter has been used to control the number of loop iterations by means of a while statement.
Variable condition loops may also be constructed.
Fixed count loops
Two useful statements in connection with repetition statements :
Break
Continue
Forces an immediate break, or exit from switch, while, for and do while statements.
Break
Applies only to loops created with while and do-while and for statements. is encountered in a loop, the next iteration of the loop immediately begun.
Continue
All statements must be terminated by a semi-colon. A semi- colon with nothing preceding it is also a valid statement, called a null statement.
This is a do-nothing statement that is used where a statement is syntactically required, but no action is called for.
Null Statement