unit 2 excitatory and inhibitory synapses
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
week 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
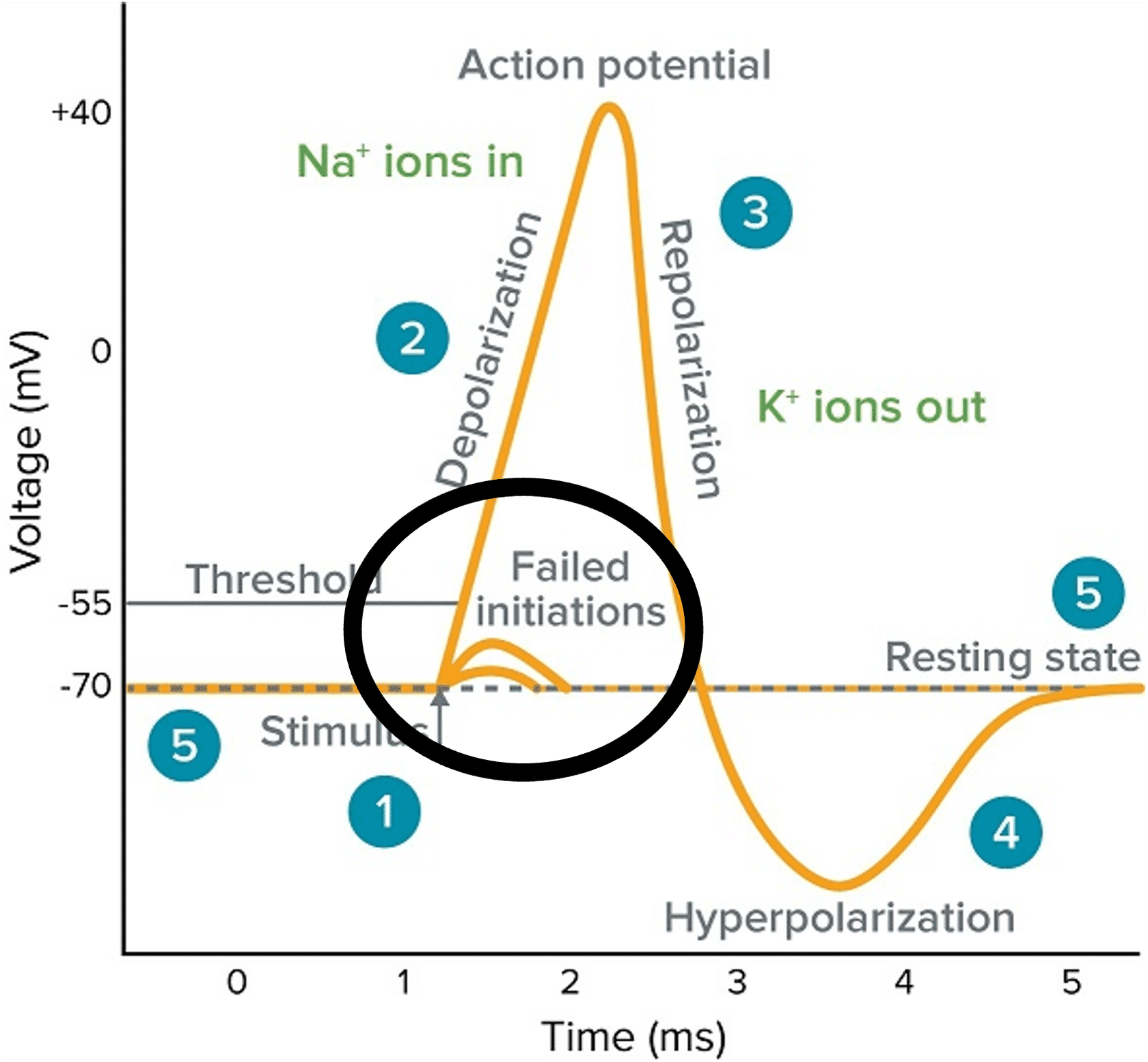
failed initiations/sub threshold depolarizations are also called
excitatory post synaptic potentials (EPSPs)
what are the propertries of EPSPs
dont produce AP
localized - depolarization is confined to one area of plasma membrane
magnitude of depolarization =magnitude of stimulus- meaning they are graded (higher the stimulus, larger depolarization)
they can be summed(stacked up on top of each other producing larger depolarization) multiple epsps are required to produce an AP
bring neuron closer to an AP
decay as they propagate across membrane from point of stimulus - further they are from depolarization, the smaller they become
are produced by neurotransmitters that open na+ and k+ channels
hyperpolarizing potentials are called
inhibitory post synaptic potentials
what are the properties of ipso
localized- hyperpolarization confined to 1 area of plasma membrane
magnitude of hyperpolarization = magnitude of stimulus - meaning they are graded (higher stimulus, larger hyperpolarization)
they can be summed (stacked up on top of each other to produce larger hyperpolarization
brings neuron further away from AP
decay as they propagate across membrane from point of stimulus - further from depolarization, smaller they become
are produced by neurotransmitters that open k+ (moving it out of the cell) or cl- channels (moving cl- into cell)
axon hillock
wether an action potential is generated depends on sum of ipsps and epsps as they reach the trigger zone called the axon hillock
produced by the opening of ligand gated ion channels
graded potential
produced by opening of voltage gated ion channels
action potential
do dendrites and soma have voltage gated channels?
they do not
what are the two ways strength of EPSPs can be increased
temporal summation and spatial summation
why do epsps have to be strong
in order to cause a sufficient depolarization to open voltage gated na+ channels at the axon hillock, positive current of the epsp must be strong enough to spread all the way from the synapse where it originated from to the axon hillock
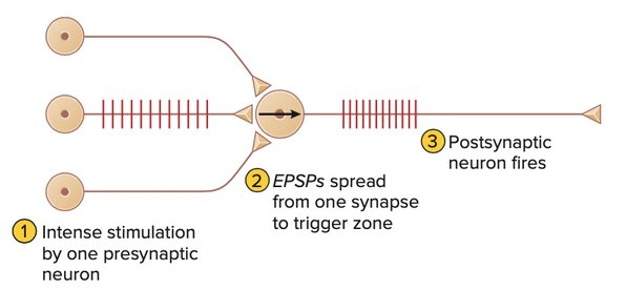
what is temporal summation
additive effect produced by many epsp generated at the same synapse by a series of high frequency ap on the presynaptic neuron. One neuron fires repeatedly.
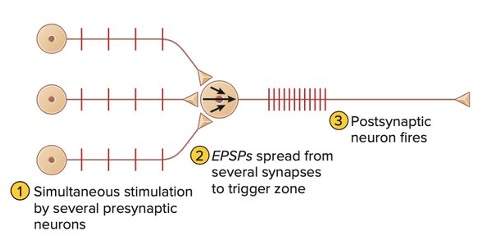
spatial summation
additive effect produced by many EPSPs that have been generated at many diff synapases on the same post synaptic neuron at the same time. many neurons fire at the same time to produce EPSPs in the post synaptic neuron.
IPSPs produce ___ thru spatial and temporal summation
larger hyperpolarizations
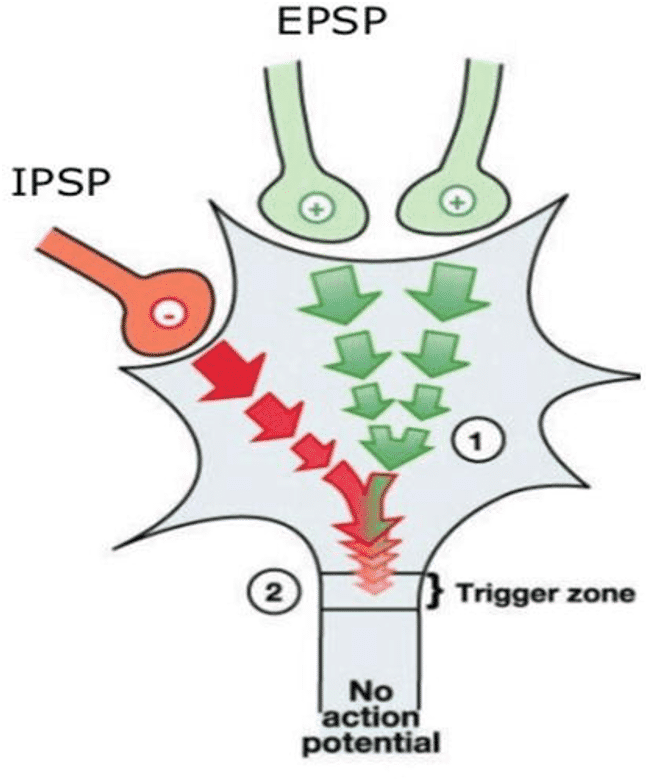
what is happening (2 steps)
both IPSPs and EPSPs decay as they move towards axon hillock
IPSPs and EPSPs summed at axon hillock and since threshold is not met at hillock, no ap generated
After being released, the neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft, binds to receptors on the post-synaptic membrane and produces a response in the post-synaptic neuron. Depending on the type of neurotransmitter, this response may be excitatory, leading to 1.____ of the 2._____ in the form of 3.____.
If the 4.____ is strong enough, it may fire an 5. _____.
depolarization,
membrane
EPSPs
depolarization
action potential
On the other hand, the neurotransmitter could produce an 1.___ response leading to 2. _____ of the 3.____________ in the form of 4.____. This makes it 5._____ to generate an action potential.
inhibitory
hyperpolarization
post-synaptic membrane
IPSPs
harder