Unit 4 - Periodic Table
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Dmitri Mendeleev
Organized elements by increasing atomic mass Predicted properties of undiscovered elements Some discrepancies
Henry Mosely
Organized elements by increasing atomic number
Periodic Table
Shows all known elements in the universe and organizes them by chemical properties
Key to the Periodic Table
Elements are organized on the table according to their atomic number
Atomic Number
Refers to how many protons an atom of that element has
Bohr Model of Hydrogen Atom
A model that describes the structure of a hydrogen atom
Wave Model
A model that describes the behavior of electrons as waves
Atomic Mass
Refers to the 'weight' of the atom
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the outer energy level of an atom
Rows
Called 'Periods'
Columns
Called 'Groups' or 'Families'
Properties of Metals
Good conductors of heat and electricity
Properties of Non-Metals
Poor conductors of heat and electricity
Sulfur
A non-metal element
Properties of Metalloids
Have properties of both metals and non-metals
Silicon
A metalloid element
Group 1: Alkali Metals
Have 1 valence electron
Group 2: Alkaline Earth Metals
Have 2 valence electrons
Groups 3 - 12: Transition Metals
Have 1-2 valence electrons
Lanthanide Series
Shiny reactive metals
Actinide Series
Radioactive and unstable
Group 17: Halogens
Have 7 valence electrons
Group 18: Noble Gases
Have 8 valence electrons (except He which has 2)
Periodic Law
When elements are arranged in increasing atomic number, elements with similar properties appear
at regular intervals.
Atomic Radius
size of atom
Ionization Energy
Energy Required to remove an electron from a neutral atom
Electronegativity
The tendency of an atom for a shared pair of electrons
Electron Affinity
The amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom
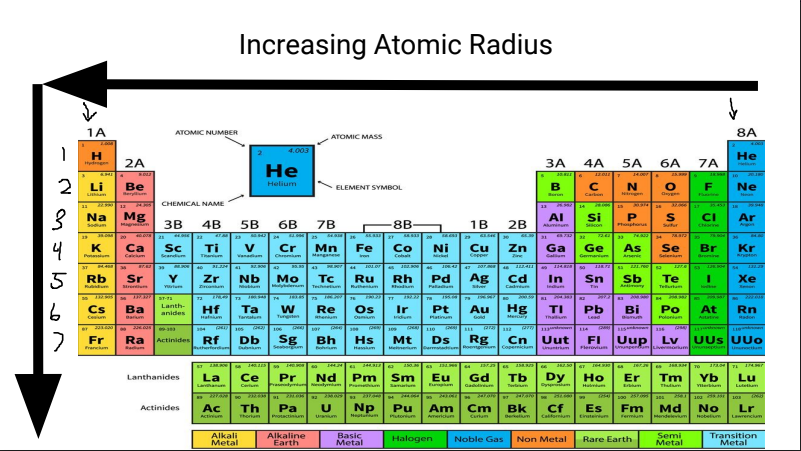
What is this?
Increasing Atomic Radius
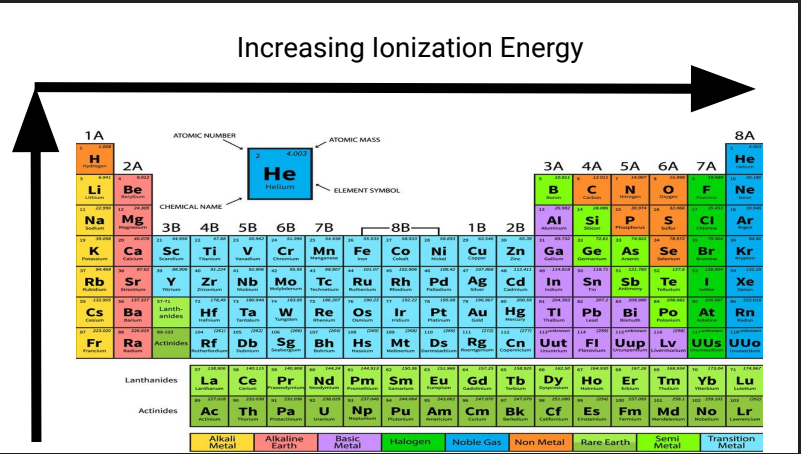
What is this?
Increasing Ionization Energy
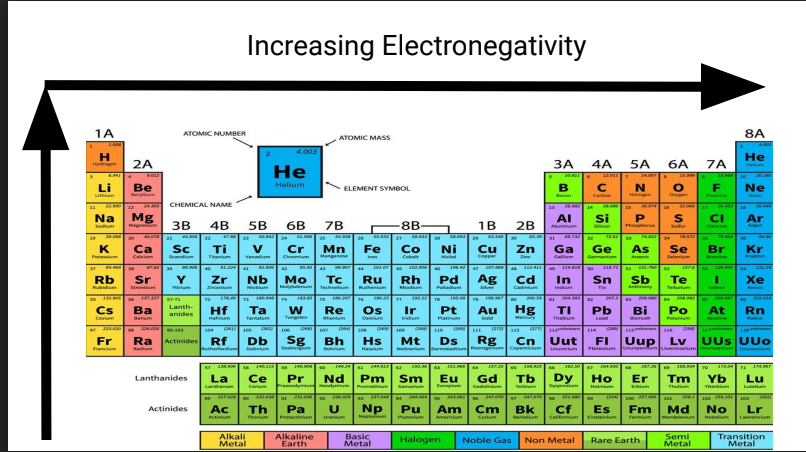
What is this?
Increasing Electronegativity
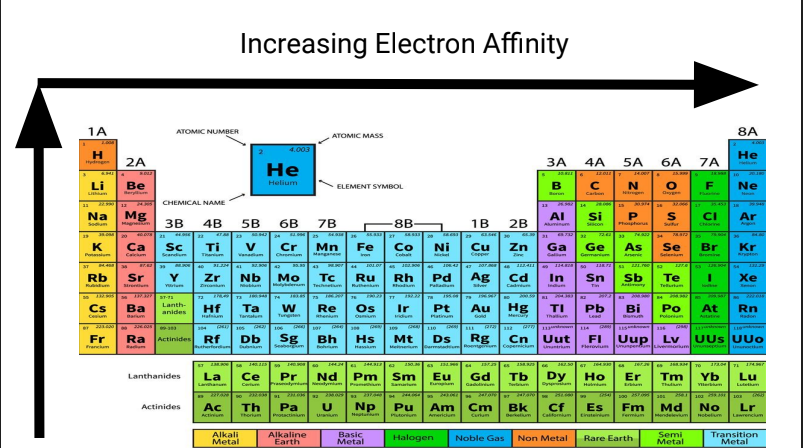
What is this
Increasing Electron Affinity
Ionic Radius
More Electrons, the larger it is.
n^-1 is larger than N
N is larger than N²