Ch.5 Supply Decisions and Factors of Production
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Supply
The ability and willingness to sell (produce) specific quantities of a good at alternative prices in a given time period.
Factors of Production
Resource inputs used to produce goods and services (Land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship).
Production Function
Technological relationship expressing the maximum quantity of a good attainable from different combinations of factor inputs.
Efficiency
Achieving the maximum output attainable from given inputs.
Marginal Physical Product (MPP)
Change in total output associated with one additional unit of input.
Law of Diminishing Returns
Diminishing MPP; additional units of resources (inputs) are less valuable to the firm.
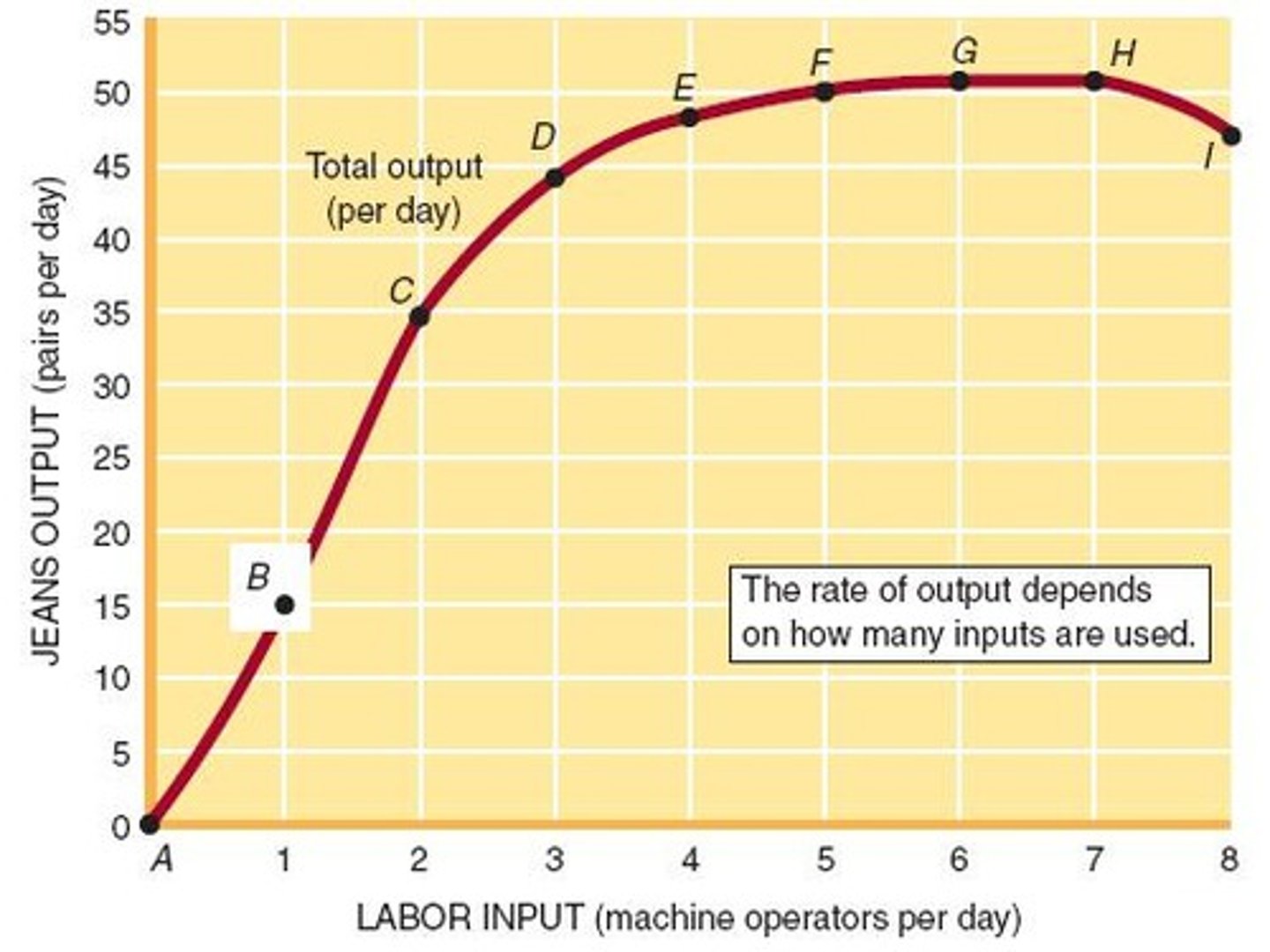
Negative MPP
MPP may become negative if too much labor is added to a fixed level of capital and land.
Cost of Production
Production function tells us how much a firm could produce but not how much it will want to produce.
Total Profit
Total profit = total revenue - total cost.
Total Revenue
Total revenue = price x quantity; price of a product multiplied by the quantity sold in a given time period.
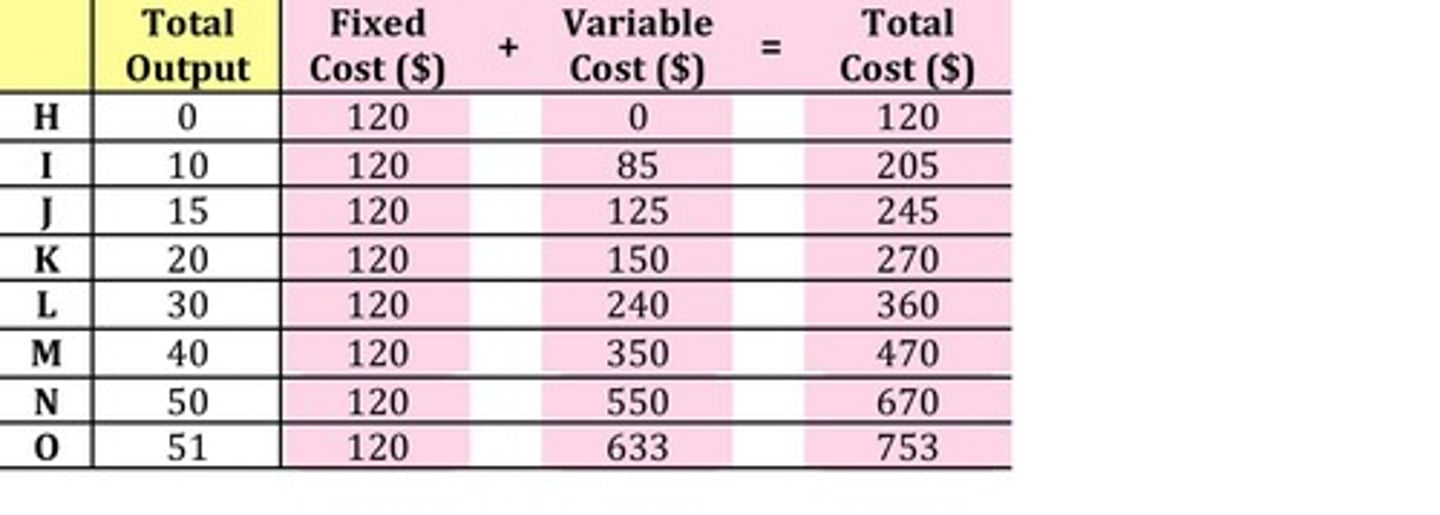
Total Cost
Total cost = market value of all resources used to produce a good or service.
Fixed Costs
Costs of production that do NOT change with the rate of output.
Variable Costs
Costs of production that change when the rate of output is altered.
Average Total Cost (ATC)
Total cost divided by the quantity produced in a given time period.
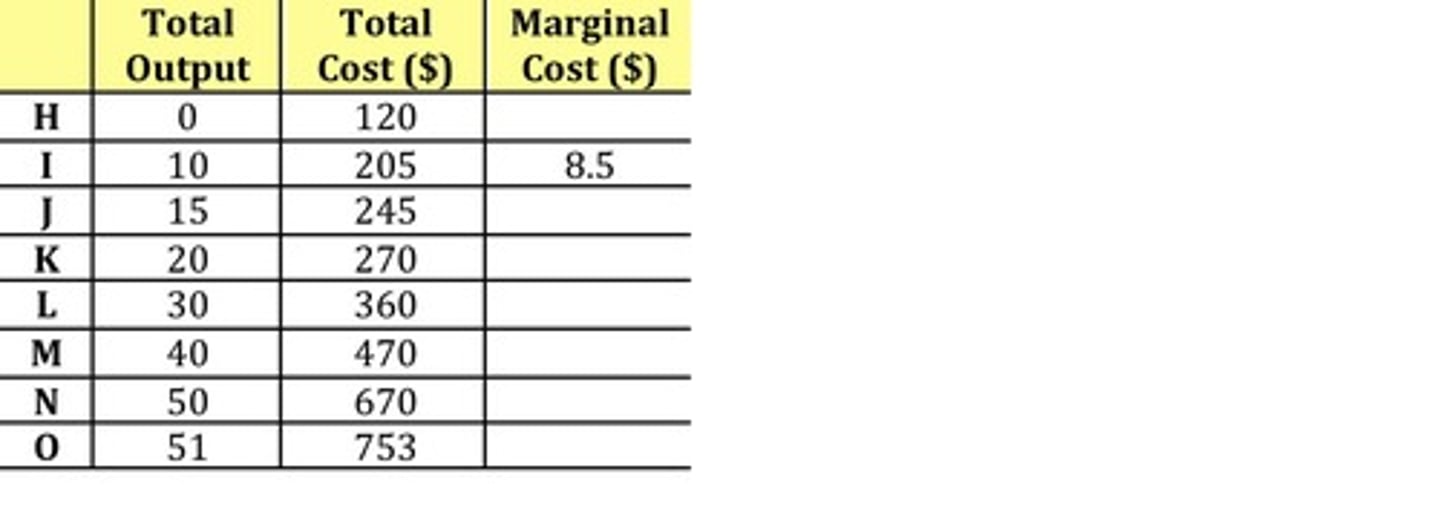
Marginal Cost (MC)
The change in total cost when one more unit of output is produced.

Economic Profit
In economic terms, profit is the difference between total revenue and total economic costs.
Total Cost Formula
Total Cost = Fixed Cost + Variable Cost.
Average Total Cost Formula
Average Total Cost = Total Cost / Total Output.
Marginal Cost Formula
Marginal Cost (MC) = change in total cost / change in total output.
Example of Total Profit Calculation
Total profit = $100 - $30 = $70.
Impact of Fixed Costs
Fixed costs cannot be avoided in the short-run.
Impact of Variable Costs
Any short-run change in total costs is a result of change in variable costs.
Production Inefficiency
Producing any less than the maximum output means production is inefficient.
Decline of MPP
As more labor is hired, each unit of labor has less capital and land to work with, causing MPP to decline.