REG The Facts: Anatomy Chapter 1 Freshie-
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Gross Anatomy & Subdivisions: Regional Anatomy and example?
To look at one particular area of the body and know everything in that area. Example: If you're looking at the shoulder you need to know the nerves, joints, bones, everything
Gross Anatomy & Subdivisions: Systemic Anatomy and Example
going system by system, cellular design, the tissue, the bones, the nerves, the muscles
Gross Anatomy & Subdivisions: Surface Anatomy and example
Don't look internally but you have to know what is under there, like knowing where to take a pulse and stuff; know what is underneath that surface. Dont wanna hit a nerve or something. Knowing something from its external features.
Gross Anatomy & Subdivisions: Microscopic Anatomy and example
Need a microscope for, down to the cellular and tissue level of anatomy. Example: Study of single body cells and internal structures.
Specialized Branches of Anatomy: Developmental Anatomy
to trace ur structural changes in your body from when u were a fetus to now a grown person
Specialized Branches of Anatomy: Pathological Anatomy
looking at structural changes in the body that are causing diseases. Example: Have to go back and review what the bone looks like normally so that you know the difference
Specialized Branches of Anatomy: radiographic anatomy
Looking at the structure of the body diagnostically, like through X-rays
Specialized Branches of Anatomy:Molecular Anatomy
studying the structure of DNA, into the design of DNA through the disease individuals or regular individuals.
Physiology: Function
focuses on Cellular or Molecular Level:
Basic Life Processes:
certain processes that distinguish organisms (living things) from non-living things
Metabolism:
the sum of all the chemical processes that occur in the human body there are 2 phases
Movement
includes motion of the whole body, individual organs single cells, and even tiny structures inside cells
Responsiveness
Responding to all the changes that happen to us during the day, for example: the nervous system.
Reproduction
Continue the species, formation of new cells for tissue growth, repair or replacement of the productions of a new individual Like having an injury, having a cut, repairing damage is also reproduction
Growth
increase in body size that results from an increase in the size of existing cells
Differentiation
Development of a cell from an unspecialized to a specialized state.??
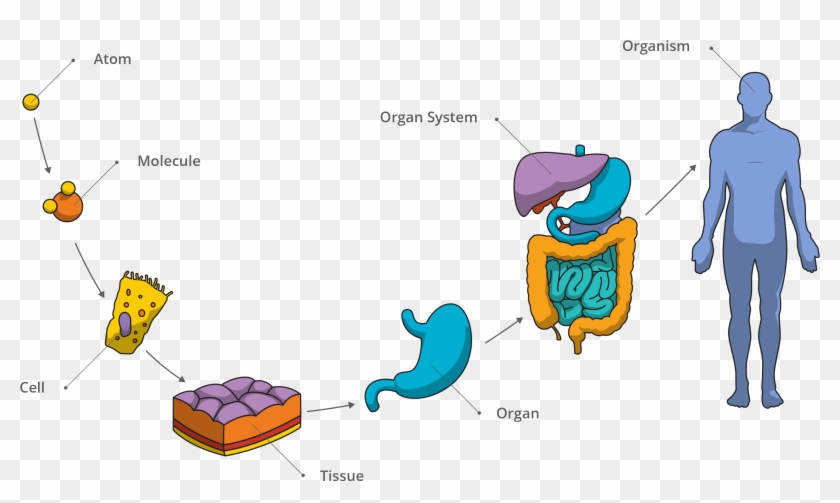
Structiral Organization of Life
Homeostasis
A dynamic state of equilibrium
-A state in which the body’s internal environment stays within certain physiological limits
If Homeostasis is disturbed (for too long), ill-health (state of disease) can occur •What can disturb Homeostasis? External? Internal?
External Factors: heat; cold; lack of oxygen. Internal Factors: stress, high BP; tumors; unpleasant thoughts
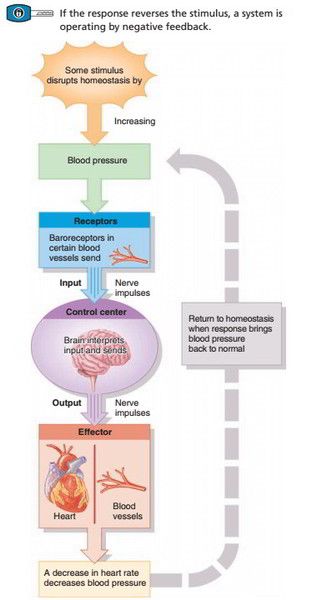
Homeostasis: Controlled by a Feedback system
Medical Imaging: Radiology – and what can they diagnose
X-Rays; they can diagnose Bone Fractures, Dental Cavities, Foreign Objects, Cancer.
Certain Patient Aspects Must be Considered when it comes to Radiology
Patient Considerations- X-Rays
•Sensitivity
– Allergies = Contrast Dyes
•Pregnancy
- Can harm the developing fetus
•Nursing- mothers may be asked to store enough milk for 48 hrs.
•Age- Intensity of the X-Rays
•Cancer Medications- act as Radio sensitizers- amplifying the effects of X-rays
MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging
•Not Appropriate for Patients With:
•Pacemakers
•Drug Pump- medications
•Artificial Joints
•IUD- made of plastic or copper (Metal)
Computerized Tomography – CT Scan
Computerized Axial Tomography –CAT Scan
•Focused X-ray beams-Caution with pregnancy
•3-D Computerized Image
Ultrasound
US- High Frequency Waves