Chemlab Practicals (Experiment 5-8) (FINALS)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Preparation of Formaldehyde
heat a copper in oxidizing (blue) flame
dip it into 1 ml methanol (CH₃OH) + water
stopper the test tube after dipping the wire
repeat process 10 times
2CH₃OH + O₂ ——> 2CH₂O + 2H₂O
Schiff’s Test
-test for presence of aldehyde
-differentiate aldehydes and ketones
-positive result= MAGENTA SOLUTION
-negative result= CLEAR SOLUTION
SCHIFF’S REAGENT= fuchsin decolorized by sulfur dioxide SO2)
1 ml Schiff’s solution + ½ prepared formaldehyde (HCHO)
—> MAGENTA SOLUTION1ml 1 ml Schiff’s solution + 5 drops benzaldehyde (C₆H₅CHO)
—> MAGENTA SOLUTION (very slow reaction)1 ml Schiff’s solution + 5 drops acetone (CH₃COCH₃)—> NEGATIVE
Resorcinol Test
-formaldehyde only (HCHO)
formaldehyde (HCHO) + .5% resorcinol solution + conc. H₂SO₄ (inclined test tube) ——> (TWO LAYERS) RED FLOCCULENT PRECIPITATE AT THE JUNCTION OF TWO LATERS
Tollen’s Test (Silver Mirror Test)
-gives positive result for all aldehydes and benzaldehyde (C₆H₅CHO)
-warmed in water bath
-positive result= SILVER MIRROR ON WALLS OF THE TEST TUBE
-negative result= CLEAR SOLUTION
TYPE OF REACTION:
Oxidation
TOLLEN’S REAGENT= Ammoniacal Solution of Silver Nitrate [(NH₃)₂Ag]
1 ml Ammoniacal Solution of Silver Nitrate (NH₃)₂Ag solution (Tollen’s Reagent) + 5 drops of formalin (37-40% of formaldehyde in water)
—> SILVER MIRROR ON WALLS OF THE TEST TUBE1 ml (NH₃)₂Ag solution (Tollen’s Reagent) + 5 drops benzaldehyde (C₆H₅CHO)
—> SILVER MIRROR ON WALLS OF THE TEST TUBE1 ml (NH₃)₂Ag solution (Tollen’s Reagent) + 5 drops acetone (CH₃COCH₃)—> NEGATIVE
EQUATIONS:
HCHO + 2(NH₃)₂Ag + 3 OH —→ HCOOH + 2Ag + 4NH₃ + 2H₂O
C₆H₅CHO+ 2(NH₃)₂Ag + 3 OH —→ C₆H₅COOH+ 2Ag + 4NH₃ + 2H₂O
CH₃COCH₃ + 2(NH₃)₂Ag + 3 OH —→ NEGATIVE
Formaldehyde on Protein Substances
-formaldehyde only
-When protein is immersed in formalin, it forms chemical cross-links between proteins
("fixing" them in place and preventing degradation)
that’s why formaldehyde is used for preservation
-positive result= proteins become insoluble in formalin due to the formation of cross-links between amino acids
Gelatin sheets 2 SET UPS
1ML FORMALIN + 1 ML WATER + GELATIN
=gelatin sheet hardened
=less soluble because of the formalin
2 ML WATER + GELATIN
=gelatin sheet softened
= more soluble in water
Fehling’s Test (exp 5)
-warmed in water bath
-positive result= BRICK RED PRECIPITATE
-negative result= REMAINED BLUE
TYPE OF REACTION:
Oxidation
FEHLING’S SOLUTION= Copper Sulfate (CuSO₄) + Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) + Rochelle’s Salt
1 ml Fehling’s Solution + 5 drops of formalin (37-40% of formaldehyde in water)
—> BRICK RED PRECIPITATE [CUPROUS OXIDE or COPPER (I) OXIDE] Cu₂O1 ml Fehling’s Solution + 5 drops benzaldehyde (C₆H₅CHO)
—> NEGATIVE1 ml Fehling’s Solution + 5 drops acetone (CH₃COCH₃)—> NEGATIVE
EQUATIONS:
HCHO + Cu(OH)₂ —→ HCOOH + Cu₂O (Cuprous Oxide or Copper (I) Oxide + H₂O
C₆H₅CHO+ Cu(OH)₂ —→ NEGATIVE
CH₃COCH₃ + Cu(OH)₂ —→ NEGATIVE
Auto Oxidation of Benzaldehyde
Benzaldehyde (C₆H₅CHO) is exposed to the atmosphere in a watch glass
-positive result= TURNED TO BENZOIC ACID (C₆H₅COOH)
EQUATION: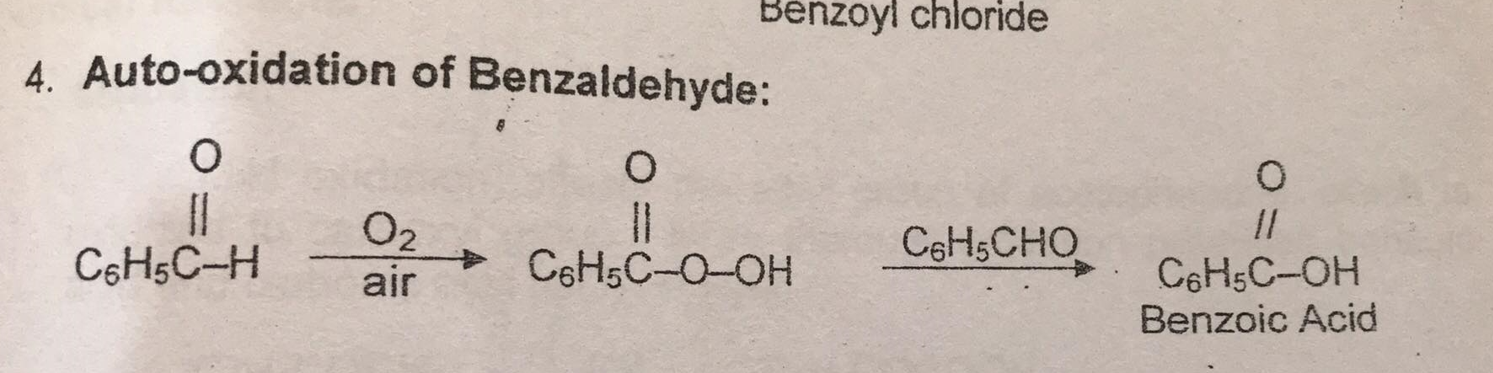
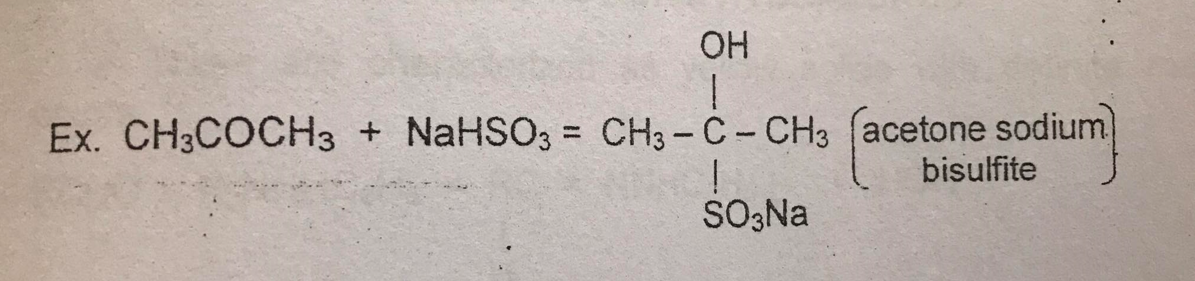
Addition of Sodium Bisulfite
TYPE OF REACTION:
Addition
-positive result= TURBIDITY/ CLOUDINESS (WHITE PRECIPITATE)
.5 ml of acetone (CH₃COCH₃) + (Sodium Bisulfite) NaHSO₃——> ACETONE SODIUM BISULFITE
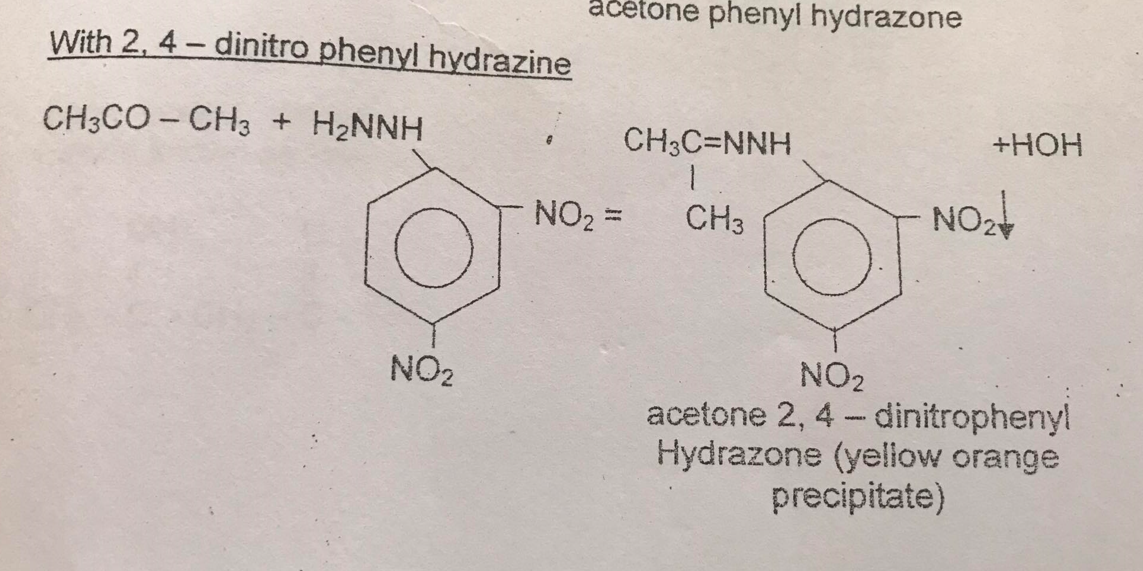
Formation of Phenylhydrazone (
TYPE OF REACTION:
Addition
-positive result= YELLOW ORANGE PRECIPITATE (YELLOW SOLIDS)
3 drops of acetone (CH₃COCH₃) + 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (C₆H₅NHNH₂)—-> ACETONE PHENYL HYDRAZONE

Iodoform Test
-test for compounds with methyl carbonyl group
(—CH₃CO—)
TYPE OF REACTION:
Haloform Reaction
-positive result= YELLOW PRECIPITATE (YELLOW SOLIDS)
3 drops of acetone (CH₃COCH₃) +8 drops of 10% Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) + Iodine Solution (I2)
—-> IODOFORM (CHI₃) yellow precipitateEQUATIONS:
CH₃COCH₃ + 4NaOH + 3I2 ——> CHI₃ + CH₃COONa + 3NaI + 3H2OCHI₃= Iodoform
CH₃COONa = Sodium Acetate
NaI = Sodium Iodide
Biuret’s Test
- general test for proteins
- test for peptide bonds (—CONH)
- rgts: CuSO₄ + NaOH
-positive result= ROSEPINK TO VIOLET COLORATION SOLUTION
1% Solution of Egg Albumin + Copper (II) Sulfate CuSO₄ + 10% Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
—-> ROSEPINK TO VIOLET COLORATION SOLUTION
Xanthoproteic Test
- general test for amino acids
- solution turns yellow due to the nitration of benzene ring in amino acids like tyrosine, tryptophan, phenylalanine
-rgts: HNO₃ + NH₄OH
-positive result= DARK YELLOW TO ORANGE PRECIPITATE(when neutralized with NH₄OH)
1% Solution of Egg Albumin + Conc. Nitric Acid HNO₃ + Conc. Ammonium Hydroxide NH₄OH
—-> DARK YELLOW TO ORANGE PRECIPITATE
Millon’s Test
- general test for the presence of phenolic/phenol group
- proteins containing tyrosine
-rgts: HgNO₃/[Hg (NO₃)₂
MILLON’S REAGENT= Dissolving Mercury (Hg) in Nitric Acid (HNO₃)
=mercuric (HgNO₃)and mercurous nitrates [Hg (NO₃)2]
-positive result= FLESH TO RED COLOR PRECIPITATE
1% Solution of Egg Albumin + Millon’s Reagent (HgNO₃/[Hg (NO₃)2])
—-> FLESH TO RED COLOR PRECIPITATE
Molisch’s Test (exp 6)
-general test for carbohydrates
-glyco-protein is present
- 2 ml egg albumin + Molisch Rgt + 2 drops conc. sulfuric acid (INCLINED/ AT THE SIDE OF TEST TUBE)
-rgts: Molisch Rgt + H2SO₄
MOLISCH REAGENT= Alpha napthol in alcohol
-positive result= VIOLET RING/PRECIPITATE AT THE JUNCTION OF TWO LAYERS
1% Solution of Egg Albumin + Molisch’s Reagent
—-> VIOLET RING/PRECIPITATE AT THE JUNCTION OF TWO LAYERS
Sulfur Test
-general test for cysteine, cystine, or methionine
-when heated with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), splits up the sulfur to form Sodium Sulfide (Na2S)
-2 ml egg albumin + 6 ml NaOH (BOIL)+ CH₃COOH (COVER WITH FILTER PAPER SOAKED IN LEAD ACETATE Pb(CH₃COO)2)
-positive result= BLACK PRECIPITATE (PbS [LEAD (II) SULFIDE]
2 ml egg albumin + 6 ml Sodium Hydroxide NaOH (BOIL)+ Acetic Acid CH₃COOH (COVER WITH FILTER PAPER SOAKED IN LEAD (II) ACETATE [Pb(CH₃COO)2]
—-> BLACK PRECIPITATE (PbS [LEAD (II) SULFIDE]
Effects of heat in proteins
-albumin is a simple protein
-coagulated by heat, soluble in water, and dilute in salt solution
2 drops of Egg Albumin + heated —→ Coagulates (turbid/cloudy)
Heller’s Ring Test
-commonly used to detect albumin in urine
-Nitric Acid (HNO₃) at lower portion of the test tube, with Protein (albumin) above
- egg albumin + conc. HNO₃
-rgts: concentrated HNO₃
-positive result=WHITE PRECIPITATE OF COAGULATED PROTEIN/RING AT JUNCTION OF TWO LAYERS
1 drop egg albumin + 1 drop conc. HNO₃ (DROPPED AT THE SIDE OF THE TEST TUBE)
—-> WHITE PRECIPITATE / RING AT JUNCTION OF TWO LAYERS
Heavy-Metal Salts
1 drop egg albumin + 3 drops Copper (II) Sulfate (CuSO₄)
—> BLUE PRECIPITATE1 drop egg albumin + 3 drops Lead (II) Acetate [Pb(CH₃COO)2]
—> WHITE PRECIPITATE (LEAD ALBUMINATE)1 drop egg albumin + 3 drops Silver Nitrate (AgNO3)
—> WHITE PRECIPITATE (SILVER ALBUMINATE)
Alkaloidal Reagents
3 drops egg albumin + 2 drops 5% Tannic Acid
—> LIGHT BROWN PRECIPITATE3 drops egg albumin + 2 drops 5% Potassium Ferrocyanide
—> PRUSSIAN BLUE PRECIPITATE3 drops egg albumin + 2 drops Concentrate Picric Acid
—> YELLOW PRECIPITATE
Molisch’s Test (exp 7)
-general test for carbohydrates
-sulfuric acid H2SO₄ acts as a dehydrating agent forming furfural derivatives
- 1 ml substance + Molisch Rgt (a-naphthol in alcohol) + 3 mL conc. sulfuric acid (INCLINED/ AT THE SIDE OF TEST TUBE)
-rgts: Molisch Rgt + H2SO₄
MOLISCH REAGENT= Alpha napthol in alcohol
-positive result= VIOLET RING/PRECIPITATE AT THE JUNCTION OF TWO LAYERS
1 mL of H2O + Molisch’s Reagent
—-> NEGATIVE1 mL of Glucose (Monosaccharide)+ Molisch’s Reagent
—-> VIOLET RING/PRECIPITATE AT THE JUNCTION OF TWO LAYERS1 mL of Sucrose (Disaccharide) + Molisch’s Reagent
—-> VIOLET RING/PRECIPITATE AT THE JUNCTION OF TWO LAYERS1 mL of Starch (Polysaccharide) + Molisch’s Reagent
—-> VIOLET RING/PRECIPITATE AT THE JUNCTION OF TWO LAYERS (slow reaction)
Phenylhydrazine Test (exp 7)
-general test for carbonyl group
-Osazone formation
-reducing sugars form osazone crystals
-presence of aldehyde and ketone group
-glucose, fructose, and mannose yield the same osazone crystals
-1 ml glucose + Phenyl hydrazine (C₆H₅NHNH2)—>
GLUCOSAZONE/ GLUCOSE PHENYLHYDRAZONE
rgts: Phenyl hydrazine (C₆H₅NHNH2)
-positive result= YELLOW- ORANGE PRECIPITATE/CRYSTALS
1 mL of Glucose (Monosaccharide)+ Phenyl hydrazine (C₆H₅NHNH2)
—-> YELLOW- ORANGE PRECIPITATE/CRYSTALS (GLUCOSAZONE/ GLUCOSE PHENYLHYDRAZONE)
Action of Alkali (Moore’s Test)
-test for reducing sugars
-when heated with an alkali NaOH, it turns yellow to orange to dark brown
-gives caramel odor
-liberation of aldehydes to form a resinous/viscous substance; caramel
- 5 mL substance + 25% NaOH
-rgts: 25% NaOH
-positive result= CARAMEL ODOR
5 mL 10% glucose solution + 25% NaOH
—-> CARAMEL ODOR5 mL sucrose (non reducing sugar)+ 25% NaOH
—-> NEGATIVE
Benedict’s Test
-test for reducing sugars
-monosaccharides and disaccharides (except sucrose) have free aldehyde and ketone group
-reduce alkaline materials and transformed into organic acid
-metals —> acid
TYPE OF REACTION:
Oxidation
BENEDICT’S REAGENT= Sodium Carbonate Na₂CO₃, Sodium Citrate, Copper (II) Sulfate CuSO₄
-positive result= RED PRECIPITATE (CU₂O)
CUPROUS OXIDE/COPPER (I) OXIDE
2 drops of Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) + Benedict’s solution —→ RED PRECIPITATE (CUPROUS OXIDE/ COPPER (I) OXIDE
2 drops of Lactose (C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁) + Benedict’s solution —→ RED PRECIPITATE (CUPROUS OXIDE/ COPPER (I) OXIDE
2 drops of Sucrose [non-reducing sugar] (C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁) + Benedict’s solution —→ NEGATIVE (REMAINED BLUE)
2 drops of Starch [non-reducing sugar] (C6H10O5)n + Benedict’s solution —→ NEGATIVE(REMAINED BLUE)
EQUATIONS:
C₆H₁₂O₆ + Cu(OH)₂ —→ gluconic acid (C6H12O7) + Cu₂O (Cuprous Oxide or Copper (I) Oxide + H₂O
C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁+ Cu(OH)₂ —→ lactonic acid (C12H22O12) + Cu₂O (Cuprous Oxide or Copper (I) Oxide + H₂O
C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁+ Cu(OH)₂ —→ NEGATIVE
C6H10O5+ Cu(OH)₂ —→ NEGATIVE
Hydrolysis of Sucrose
-in the presence of HCl Hydrochloric Acid, disaccharides and polysaccharides react with water to yield monosaccharides
-breaking down of Disaccharide into monosaccharide: for sucrose: FRUCTOSE AND GLUCOSE
5 mL Dilute sucrose C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁ + HCl (BOIL) then (COOLED)
-positive result= REACTS WITH BENEDICT’S TEST AND SELIWANOFF’S TEST
Benedict’s test (hyrolyzed sucrose)
-test if the hydrolyzed sucrose has broken down into monosaccharides: glucose and fructose
-its glycosidic bond has now broken down
-neutralized with NaOH
Hydrolyzed sucrose + NaOH (TO NEUTRALIZE) —>
Hydrolyzed sucrose + Benedict’s Solution—→ BRICK RED PRECIPITATE
Seliwanoff’s Test (hyrolyzed sucrose)
-test if the hydrolyzed sucrose has broken down into monosaccharides: glucose and fructose
-test for presence of FRUCTOSE
-neutralized with NaOH
SELIWANOFF’S REAGENT= Resorcinol + HCl
Hydrolyzed sucrose + NaOH (TO NEUTRALIZE) —>
Hydrolyzed sucrose + Seliwanoff’s Reagent—→ MAHOGANY RED PRECIPITATE
Hydrolysis of Starch
-in the presence of HCl Hydrochloric Acid, disaccharides and polysaccharides react with water to yield monosaccharides
-breaking down of polysaccharide into monosaccharide: GLUCOSE
20 mL starch solution + 1 mL conc. HCl
IODINE TEST=
continuously drop hydroyzed starch solution on I₂ (Iodine solution) until it gives no color
soluble starch—> blue
amylodextrin —> purple
erythrodextrin—> red
achrodextrin —> no color
ACHROMATIC POINT=gives no color
maltose—> no color
glucose —>no color
FULLY HYDROLYZED
Benedict’s test (hyrolyzed starch)
-test if the hydrolyzed sucrose has broken down into monosaccharides: glucose and fructose
-its glycosidic bond has now broken down
-neutralized with NaOH
TYPE OF REACTION:
Oxidation
BENEDICT’S REAGENT= Sodium Carbonate Na₂CO₃, Sodium Citrate, Copper (II) Sulfate CuSO₄
Hydrolyzed starch + NaOH (TO NEUTRALIZE) —>
Hydrolyzed starch + Benedict’s Solution—→ BRICK RED PRECIPITATE
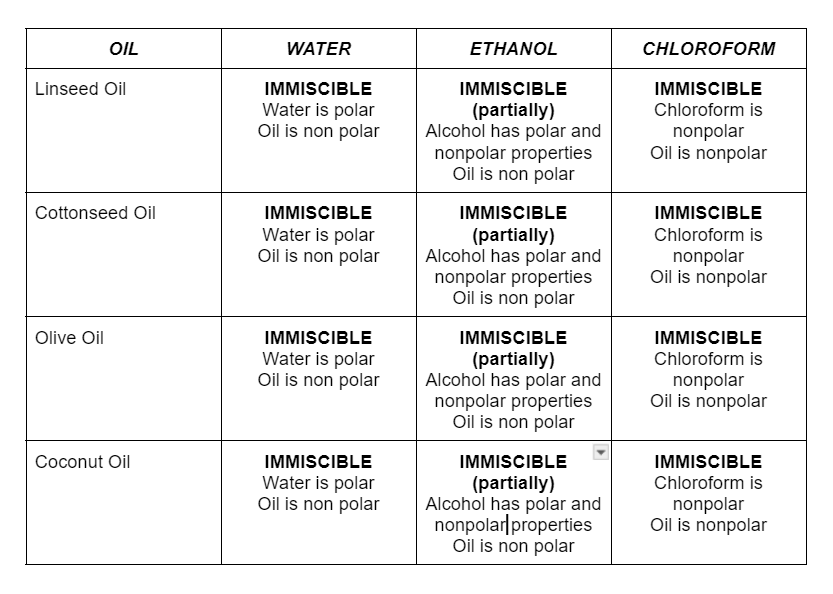
Miscibility
Acrolein Test
- when heated with Potassium Hydrogen Sulfate (KHSO₄) dehydrating agent— undergo hydrolysis'
- dehydration then gives an irritating odor
- the compounds formed are fatty acids and acrolein (unsaturated Aldehyde 2-propenal)
- dehydrating the glycerol part
rgts: KHSO₄/ dehydrating agent
TYPE OF REACTION:
Elimination (??)
- positive result: IRRITATING/PUNGENT ODOR
3 drops coconut oil + .2 g of KHSO₄ —→ MILD ODOR, COOKING OIL
3 drops CH2OHCHOHCH2OH+ .2 g of KHSO₄ —→ IRRITATING ODOR
EQUATIONS:
CH2OHCHOHCH2OH+ KHSO₄ —→ CH2CHCHO + K2SO₄ + H2O
- CH2CHCHO= Acrolein (2-Propenal)
- K2SO₄ = Potassium Sulfate
Unsaturation (huble’s test)
-the more iodine is being absorbed by the substance, the more unsaturated it is
-the more iodine is being decolorized, the lighter the oil, the more unsaturation
-unsaturated compounds absorb iodine because of halogenation
-unsaturated compounds are either double or triple bonded
TYPE OF REACTION:
Halogenation
LEVEL OF UNSATURATION
Linseed Oil + I2 solution —→ light brown oil
Cottonseed Oil + I2 solution —→ light brown oil
Olive Oil + I2 solution —→ dark brown oil
Coconut Oil + I2 solution —→ dark brown oil
Saponification
-basic hydrolysis
-Fat is heated with NaOH— glycerol and metallic salt form
TYPE OF REACTION:
Basic Hydrolysis
Coconut Oil is heated with NaOH— glycerol and metallic salt form
15 mL Coconut Oil +25 mL 10% NaOH solution—-. thick solution
- heat the remaining mixture and stir
- reaction is complete if result has thickened