Hypo/Hypernatremia
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
isotonic, hypotonic, hypertonic
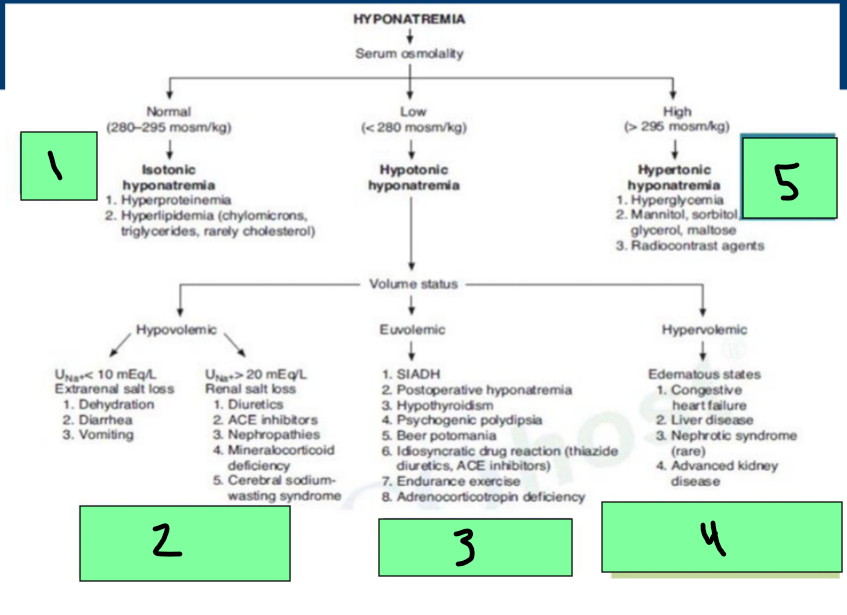
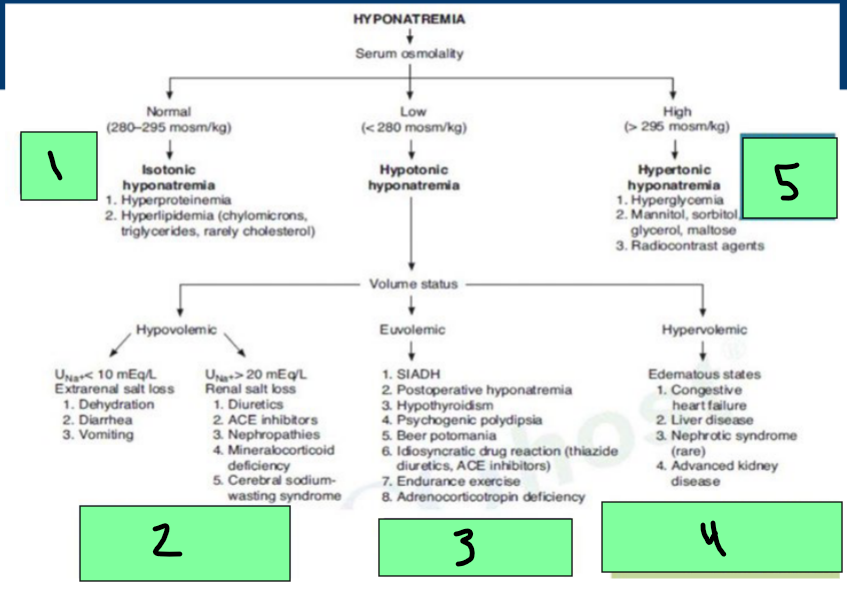
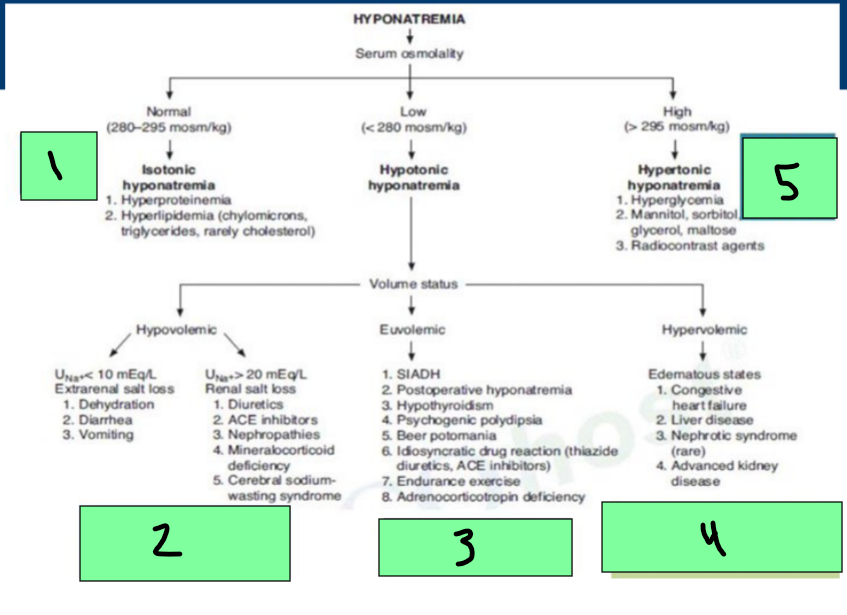
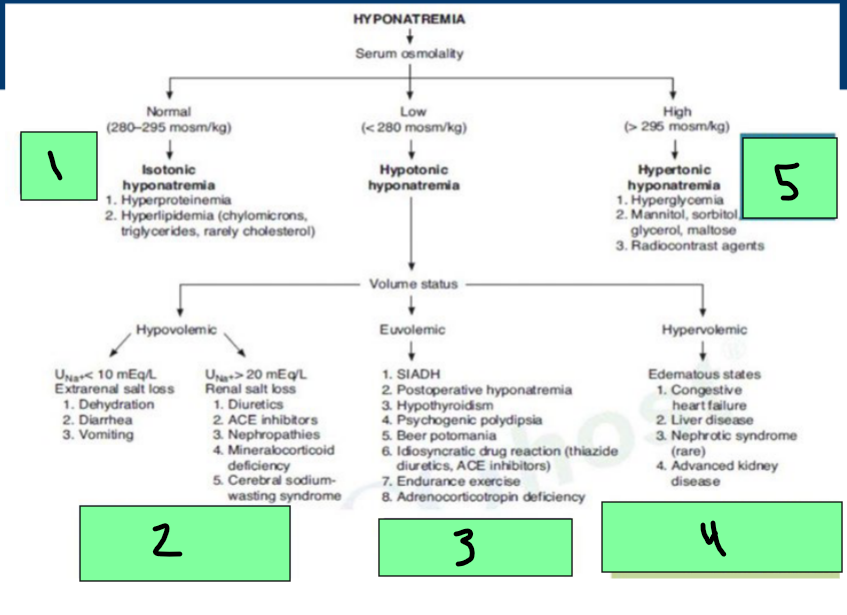
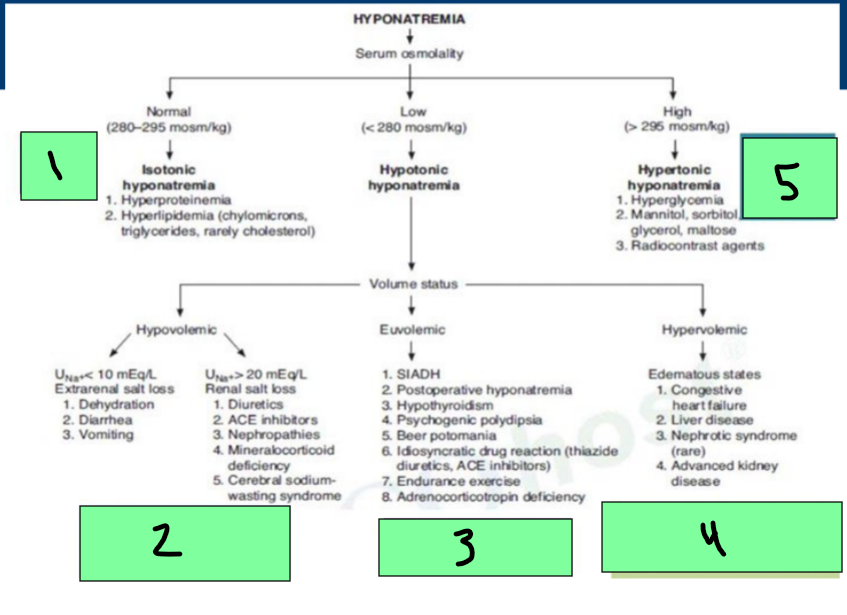
Hyponatremia
Normal Serum Osmo = _________ hyponatremia
Hyperproteinemia, Hyperlipidemia
Low Serum Osmo = ___________ Hyponatremia
Can be hypovolemic (dehydration/diuretics), euvolemic (SIADH), Hypervolemic (Edema states)
High serum Osmo = ____________ hyponatremia
hyperglycemia, radiocontrast agents
sodium, water, dehydration, diuretic, cerebral
Hypotonic Hyponatremia → Hypovolemic State
_______ depletion >>> _____ depletion
Etiologies
Renal and Extrarenal Sodium Losses
___________
__________ induced
Vomiting
Diarrhea
___________ salt wasting
Mineralocorticoid deficiency
Treatment: 0.9% and 3% NaCl
0.9% NaCl
How do you treat hypovolemic hypotonic hyponatremia with the following presentations?
Non-symptomatic
Chronic conditions
Ongoing Na losses present
3% NaCl
How do you treat hypovolemic hypotonic hyponatremia with the following presentations?
Severe, symptomatic patients
Pts high risk for experiencing symptoms
fatal, myelinolysis, 2-3
Rapid Na correction is _____
Central pontine ______________
Monitor rate of Na correction Q_-_ hours
Target symptom resolution
50, 2, 0.5, 1-2
Sodium Rate of Correction
Acute
__% of calculated dose over 12 hours
MAX _ mEq/L/hr (up to 8-12 mEq/L/day
Chronic
MAX _._ mEq/L/hr (up to 8-12 mEq/L/day)
Seizures/Coma
_-_ mL/kg/hr over 2-3 hours (RESERVED)
remove, restriction, Loop, AVP, Demeclocycline
Euvolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia Treatment
Etiology: SIADH
_______ cause
Fluid _________-
____ diuretics
___ antagonists
________________ - for chronic management only
steroids, hydrocortisone
Euvolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia Treatment
Etiology: Adrenal Insufficiency
_________ (mineralcorticoid)
Fludrocortisone
_____________
Thyroid replacement
Euvolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia Treatment
Etiology: Hypothyroidism
________ _____________
Vasopressin Antagonist
MoA: Promotes water excretion (without the loss of electrolytes)
Pushes H+ ions out and oxygen follows
conivaptan, tolvaptan
Vasopressin antagonist agents
2nd, 1st, CYP3A4, hypovolemic, 3A4
Vasopressin Antagonist Info
___ line to fluid restriction
___ line when fluid restriction NOT an option
Agents: Conivaptan, Tolvaptan
Both are ______ inhibitors
Contraindications
___________ hyponatremia
Use with strong CYP___ inhibitors
Anuria
orthostatic, kalemia, reactions
Vasopressin Antagonist → Conivaptan ADRs
__________ hypotension
Hypo________
Injection site ____________
dizziness, thirst, xerostomia, polyuria
Vasopressin Antagonist → Tolvaptan ADR
Fatigue
___________
Increased _______
Nausea
___________
diarrhea
___________
water, sodium, heart, liver, kidney
Hypervolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia
______ excess >>> ________ excess
Etiologies
______ failure
_______ failure (cirrhosis)
________ injury
diuretics, water restriction
How would you treat hypervolemic hypotonic hyponatremia?
Treat Cause
1
Replace water and sodium (crystalloids, 3% NaCl)
2
Restrict water, vasopressin antagonist
3
remove/restrict water, diuretics, restrict sodium
4
treat glucose, remove cause
5
0.9% NaCl
How do you treat hypovolemic hypernatremia with shock?
D5W
How do you treat hypovolemic hypernatremia without shock?
DDAVP (desmopressin)
How do you treat isovolemic hypernatremia that has a central cause?
Thiazide
How do you treat isovolemic hypernatremia that has a nephrogenic cause?
Stop the cause, diuretics
How do you treat hypervolemic hypernatremia?
half, 24-48, 0.5
D5W Clinical Pearls (hypernatremia)
Correct ____ of the deficit over first 24 hours, remaining over next __-__ hours
MAX Na correction _._ mEq/L/hr