MOLBIO LAB - Nucleic Acid Extraction
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Nucleic Acid Extraction
First step of any amplification experiment, no matter what kind of amplification method is used to detect a specific pathogen.
Nucleic Acid Extraction
Considered as a pre-analytical step in an amplification method.
1. Lysis
2. Precipitation
3. Binding
4. Washing
5. Elution
Principles of Nucleic Acid Extraction (5)
Lysis
Identify Principle:
- Nucleic acids are released and nucleases are denatured
Precipitation
Identify Principle:
- Brings the nucleic acid out of the solution
Binding
Identify Principle:
- Nucleic acids to a membrane surface such as silicates.
- This binding is facilitated by the chaotropic salt conditions and high ionic strength of the lysis/binding
buffer.
Washing
Identify Principle:
- Removal of unbound substances (e.g. proteins, cell debris, and PCR inhibitors) by several washing steps.
Elution
Identify Principle:
- Purified nucleic acid from the membrane (the solution will now contain a purified nucleic acid)
Cell lysis
In the extraction method, there is the initial release of cellular material by breaking the cell and nuclear membrane called as ?
Density gradient and Centrifugation strategies
- Discovered by Meselson and Stahl in 1959
- Demonstrates the semiconservative replication of DNA
- In alkaline lysis procedure, only 1-50kb of plasmid DNA are allowed since if too large, it will form large aggregates
Cesium Chloride/Ethidium Bromide Density Gradient Centrifugation
- Used in the 1950s for DNA extraction
- PP: Uses the difference in density between cesium ion and water and intercalation of ethidium bromide which shows good results for separation of various DNase and the procurement of high-yield DNA.
- Requires an expensive ultracentrifuge and considerable time, difficult to perform, ethidium bromide is harmful
Nucleated cells in suspension
- Examples of this sample are blood and BM specimens
- These specimens should be PRE-TREATED
- WBCs extracted, then blood/BM specimens are then mixed with isotonic saline, then overlaid with Ficoll
Ficoll
- Highly branched sucrose polymer; does not penetrate biological membranes
- Where WBCs will settle
- Washed by at least 2 rounds of resuspension and centrifugation saline
Less dense plasma components ; PMNs and RBCs
Using Ficoll, what can be found BELOW? How about ABOVE?
Tissue samples
- This sample can be fresh or frozen
- Should be dissociated first before DNA isolation
Xylene ; ethanol
Fixed embedded tissue should be deparaffinized by soaking in ______ which is 3 isomers of dimethyl benzene.
Afterwards it is rehydrated in decreasing concentration of _______
Microrganisms
- These samples have tough cell walls, so they are digested by lysozyme or zymolase
- Alternatively, grinding or vigorously mixing with glass beads can be performed
- Can also be treated with detergent and strong base
Phenol and chloroform
In Organic Isolation Methods, this is in a biphasic emulsion
Fungi
In Organic Isolation Methods, these have small amounts of DNA
RNase
In Organic Isolation Methods, these are added to avoid RNA contamination
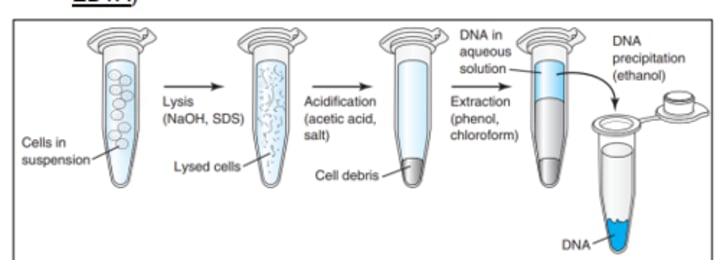
Organic Isolation Methods
- Phenol and chloroform are added
- The upper phase contains DNA and is collected and precipitated using ethanol or isopropanol in a high concentration of salt
- DNA pellet is dissolved in rehydration buffer
- Less volatile, precipitates DNA at room temperature, lesser volume is added for precipitation
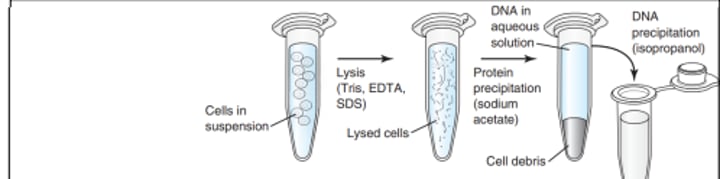
Inorganic Isolation Methods
- Salting Out
- Initially cant provide clean DNA, so additional treatment needed ; meaning DNA yield and purity are variable
- Use low pH and high salt, then add Isopropanol to precipitate DNA in a pellet
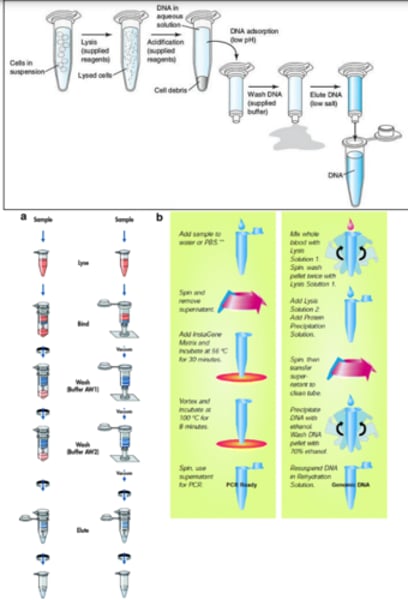
Solid-Phase Isolation
-Introduced by McCormick et al. in 1989
-Involves insoluble siliceous core particle which functions similar to
phenol, and the addition of Cell lysate
- Safer and cross-contamination is reduced.
- Suitable for PCR and southern blot analysis
Diatomaceous earth
What is a source of Silica particles?
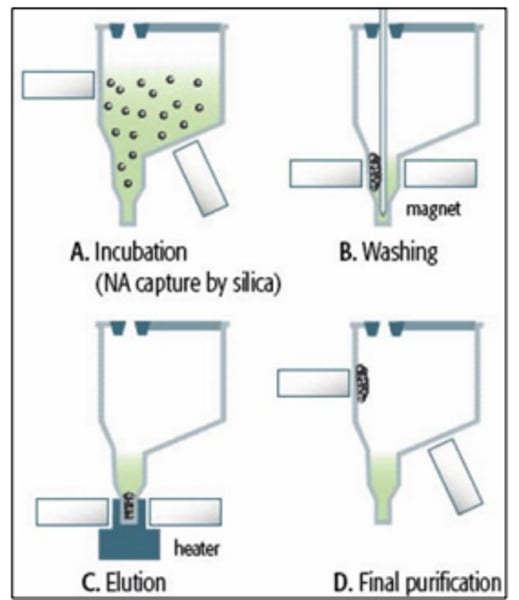
Magnetic Bead Method
- Modification of solid-phase extraction or isolation.
- No need for centrifugation, etc
- Commonly used in automated extraction methods
- Uses beads with negative charge which binds proteins and cellular debris
Anion Exchange Methods
- Solid-phase anion-exchange chromatography
- This is based on the interaction between negatively-charged phosphates of the nucleic acid and positively charged surface molecules of the substrate
-DNA yield purity and its biological activity is equal to at least two rounds of purification in the cesium chloride (CsCl) gradients, but in much lesser time
- Isolated DNA: size can be up to 150 kb
Filter Paper-Based Methods
- Store dried biological specimen and isolate
- Uses filter paper that can kill microorganisms and inhibit non-microbial degradation of DNA.
- Adequate for banking of DNA in dried blood spot: At least 19 months at ambient temperature
Crude Lysis
- For large amount of samples
- Isolation of DNA from limited amounts and challenging samples
-Involves simple lysis
Fixed tissue
In Crude Lysis, what sample should be in thin sections?
Paraffin-embedded specimen
In Crude Lysis, what sample should be dewaxed with xylene and rehydrated before nucleic acid isolation?
Simple screening methods
In Crude Lysis, what method uses cells lysed with detergents?
PCR
In Crude Lysis, what method uses Tris buffer and Proteinase K?
Proteinase K
This substance digests proteins lysing the cells and inactivate other enzymes.
Chelex / Cation-chelating resin
A Crude lysis substance that is only used in forensic applciations
Centrifugation ; Isolate total DNA
The 2 Methods in Isolation of DNA
Diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC)
converts primary and secondary amines to carbamic acid esters
Diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC)
- Is added to water and buffers, except for Tris buffers
- Converts primary and secondary amines to carbamic acid esters
Vanandyl-ribonucleoside complexes
- Binds active sites of RNase enzymes
Macaloid clays
- Absorbs RNase proteins
RNA (80-90%)
- Consists of 2 components, large and small, which are visualized by agarose gel electrophoresis
mRNA (2.5-5%)
- Has a faint background underlying the ribosomal RNA
Reticulocytes
In extraction of Total RNA:
- Extracted using osmosis or centrifugation
Tissue
In extraction of Total RNA:
- Kept frozen in liquid nitrogen or immersed in buffer
buffer
The ________ in the tissue inactivates intracellular RNases which is true for pancreas which contains large amounts of innate
RNases.
Bacterial and fungal RNA
In extraction of Total RNA:
- Used as chemical lysis or grinding in liquid nitrogen
Viral RNA
In extraction of Total RNA:
- Isolated directly from serum or other cell-free fluids (through spin-columns or beads)
Cell lysis
In extraction of Total RNA:
- Involves detergent or phenol in the presence of high salt
(0.2-0.5 M NaCl) or RNase inhibitors (Guanidine thiocyanate or 2-mercaptoehanol)
25:24:1
In extraction of Total RNA, Acid phenol:Chloroform:Isoamyl alcohol should be in what ratio
Chloroform
- Enhances extraction of nucleic acid by denaturing proteins and promoting phase separation
Isoamyl alcohol
- Prevents foaming
(pH 4-5)
Organic phase should be acidic, which is what range of pH?
DNase
- Added at the lysis step to produce an RNase-free DNase
Organic Extraction of Total RNA
- RNA precipitated by addition of 2 volumes of ethanol or 1 volume of isopropanol.
- Glycogen or Yeast transfer RNA can be added as a carrier
- RNA is then precipitated and washed in 70% ethanol and resuspended in RNase-free buffer or water.
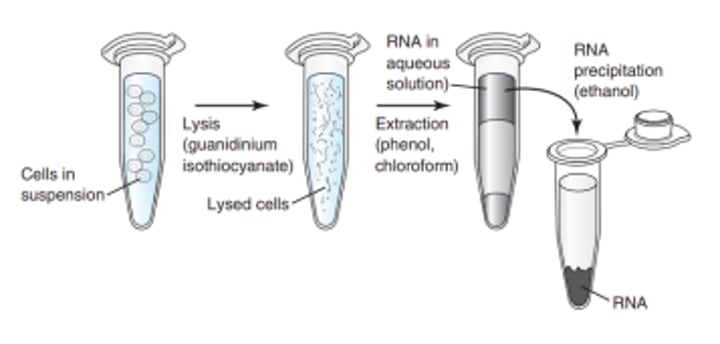
2 volumes ; 1 volume
What is the volume of ethanol if it is used in Organic Extraction of total RNA? How about isopropanol?
Solid-Phase Separation
- Uses a lysate to the column in high chaotropic buffer
-Strong denaturing buffer conditions must be adjusted before application of the lysate to the column.
-1,000,000 eukaryotic cells or 10-50 mg of tissue = yields about 10 μg of RNA
Isolatiom of Poly 4 (messenger) RNA
- Uses oligomers of thymine or uracil
- 1 μg of total RNA = yields 30-40 ng of mRNA
- Secondary structure competes with binding, mRNA with short polyA tails- does not bind efficiently
Manual Methods
-Commercial kits (commercially available)
-Requires cost, time, demands, and labor intensity
Advantage: Uses non-corrosive agents
-Limitations:
-Reproducibility (since it is manual)
-Use of Ethanol
-High complexity test (according to CLIA’88)
Automated
-Easily divided by workload capacity
-Each laboratory can select an appropriate instrument based on
throughput
-Fast TAT
-Avoids pipetting errors (since machine is used)
-Constant reproducibility
-Diminishes cross-contamination (involved reduced handling steps)
-QC monitoring (since it is an automated instrument)
Limitations:
-Economic aspect- an expensive instrument and extraction reagents including disposables are needed
-Troubleshooting
Economic aspect- an expensive instrument and extraction reagents including disposables are needed
Troubleshooting
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
● When performing nucleic acid extraction, proper PPE must be worn inside the laboratory.
→ Gloves (2 layers)
→ Eyegoggles
→ N95 respirator
→ Disposable lab gown (solid front)
● Biosafety Cabinet (Class II BSC)
● Centrifuge
● Vortex
● Mini-Centrifuge
● Additional Equipments
● Safety Information
Equipments:
Biosafety Cabinet (Class II BSC)
→ Placed in the nucleic acid extraction area or sample preparation
area.
→ Before using it, the MT should check for its function, and decontaminate the BSC.
Centrifuge
→ Speed should be capable of 10,000 x g.
→ Must have a removable rotor placed inside the BSC
→ Must have a sealing biocontainment lid/cover inside.
→ It should push materials through the filter.
Vortex
→ Thoroughly mix samples and reagent
→ Variables peed, used inside the BSC
Mini-Centrifuge
→ Quickly spin MCTS (remove droplets from the lid)
→ Used inside BSC
Additional Equipments
Timer
Pipettes
Tuberackforthesamples
MicrocentrifugeTuberack Biohazardwastecontainers(forsolidandliquidwaste) Papertowels
Cold block
Safety Information
→ PPE must be worn at all times.
→ Buffer NVL contains chaotropes- may form highly reactive compounds with bleach
→ Sample containers should only be opened inside the BSC to avoid contamination
Preparation of Extraction Reagents
● When opening a new kit for RNA extraction, the buffer and the carrier RNA should be prepared.
Buffer Preparation
● Prepare RB1, RBW, and RNW
● Supplied as a concentrate.
● Add appropriate amount of ethanol (96-100% concentration)
● Mark the cap of the bottle with the date that it was added with ethanol
and the initials of the one who added the ethanol to the buffer.
The alcohol that should be used is not denatured ethanol but absolute ethanol (96-100%).
● Check Buffer NVL- contains chaotropes which can form highly reactive compounds when combined with bleach
Carrier RNA Preparation
● Prepare 1 μg/μL solution- by adding 370 μL of nuclease free water (rehydrated)
→ The carrier RNA is a lyophilized reagent found in the kit.
● Aliquot into sterile 1.5 mL MCTs, and stored at -20°C.
● Rehydrated RNA should be kept cold during use.
● Carrier RNA is added to improve the binding capacity of the mini-spin column when viral nucleic acids included in the sample are low copy, and it also protects the target nucleic acids from the chance of degradation due to RNase or residual RNase activity.
15-25C ; ethanol ; 56C
Before Starting:
1. Equilibrate samples to room temperature (______).
2. Check that buffer RB1, RBW, and RNW have has ________
added.
3. Check buffer NVL for precipitate, warm the bottle at _____ until
it is clear and the crystals are gone.
4. Thoroughly clean the BSC
True
True or False: When working inside the BSC, proper workflow should be followed (from
clean area→ dirty area).
Genolution NX-48S
AUTOMATED RNA EXTRACTION:
What equipment uses Magnetic Bead Method?
Lysis
AUTOMATED RNA EXTRACTION:
The nucleic acid binds to the magnetic beads.
Washing
AUTOMATED RNA EXTRACTION:
Wash the bead with the washing buffer
Elution
AUTOMATED RNA EXTRACTION:
The nucleic acid is released from the magnetic beads, and the
magnetic beads are removed by a magnet.